Abstract
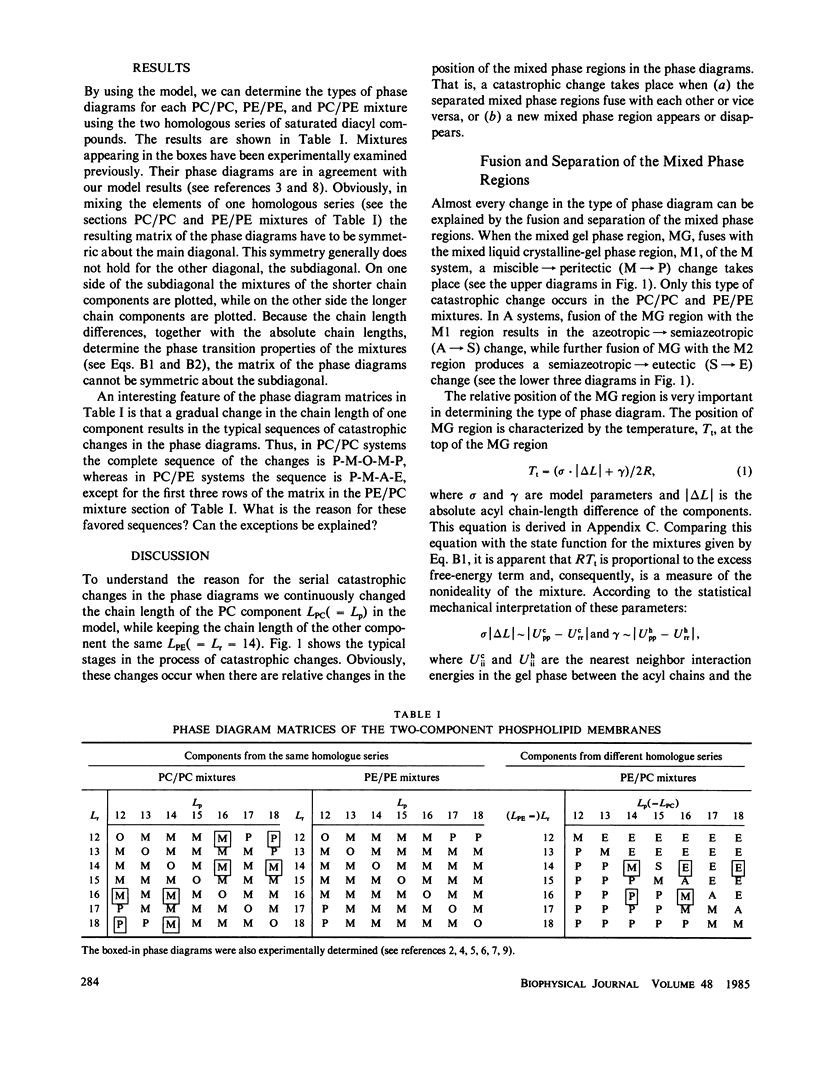
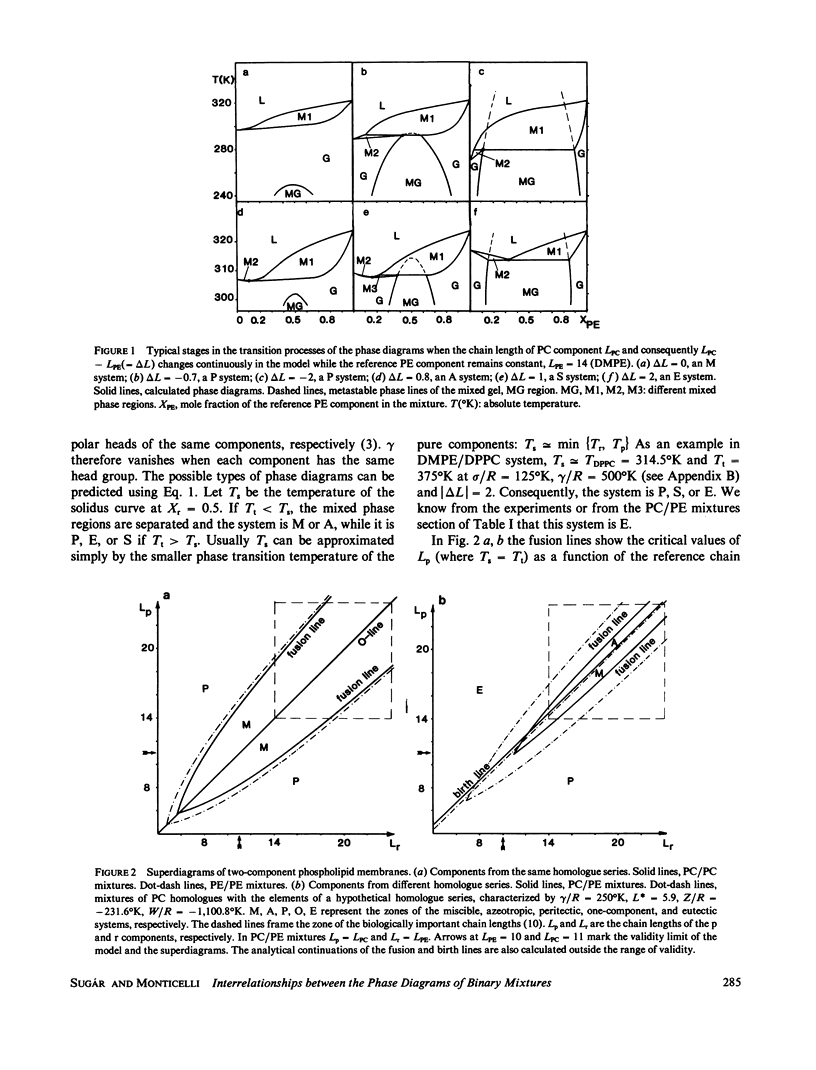
Basic relationships between the phase diagrams, previously considered independent of each other, are described. Phase diagrams of two-component phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylcholine (PC/PC), phosphatidylethanolamine/phosphatidylethanolamine (PE/PE), and PC/PE lipid membranes are systematically investigated by means of the Landau theory. While gradually changing the chain length of one of the components, a characteristic peritectic-miscible-azeotropic-semiazeotropic-eutectic (P-M-A-S-E) series of the phase diagram was found in the PC/PE system and a peritectic-miscible-one-component-miscible-peritectic (P-M-O-M-P) series was found in the PC/PC and PE/PE systems. These serial catastrophic changes in the phase diagrams could be explained by the fusion and birth of the mixed phase regions in the phase diagram. Finally when we constructed the superdiagrams, we obtained all of the possible series of the phase diagrams in a wide class of the two-component mixtures. Moreover, one can predict the type of the phase diagram when the components r and p contain equal-length saturated hydrocarbon chains. Depending on the relationships between the chain lengths (L, Lp) and that on the phase transition temperatures of the pure components (Tr, Tp), the system is: miscible (M), if 0 < Tr(L) - Tp(L) < 5 degrees C and L -Lp > 0, azeotropic (A), if 0 < T,(L) - Tp(L) < 5 degrees C and L -Lp < 0, peritectic (P), if T,(L) - Tp(L) > 40 degrees C and L -Lp - 0, eutectic (E), if Tr(L) - Tp(L) >40 degrees C and L - Lp <0,while it is M or P if 5 degrees C< Tr(L) - Tp(L) <40 degrees C and L - Lp>-0,and E,S,or Aif 5 degrees C < Tr(L) - Tp(L) < 40 degrees C and L,-Lp < 0.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blume A., Ackermann T. A calorimetric study of the lipid phase transitions in aqueous dispersions of phosphorylcholine--phosphorylethanolamine mixtures. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 1;43(1):71–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Urbina J. Biomembrane phase transitions. Studies of lipid-water systems using differential scanning calorimetry. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2512–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G. Lipid phase transitions and phase diagrams. II. Mictures involving lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 14;472(3-4):285–344. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Sturtevant J. M. Investigation of phase transitions of lipids and lipid mixtures by sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton G. M., Fasulo J. M., Robins S. J. Separation of phospholipids and individual molecular species of phospholipids by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jan;23(1):190–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugár I. P., Monticelli G. Landau theory of two-component phospholipid bilayers. I. Phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylethanolamine mixtures. Biophys Chem. 1983 Nov;18(4):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(83)80041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. A., Nagle J. F. Dilatometric study of binary mixtures of phosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4244–4249. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijck P. W., Kaper A. J., Oonk H. A., de Gier J. Miscibility properties of binary phosphatidylcholine mixtures. A calorimetric study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 3;470(1):58–69. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


