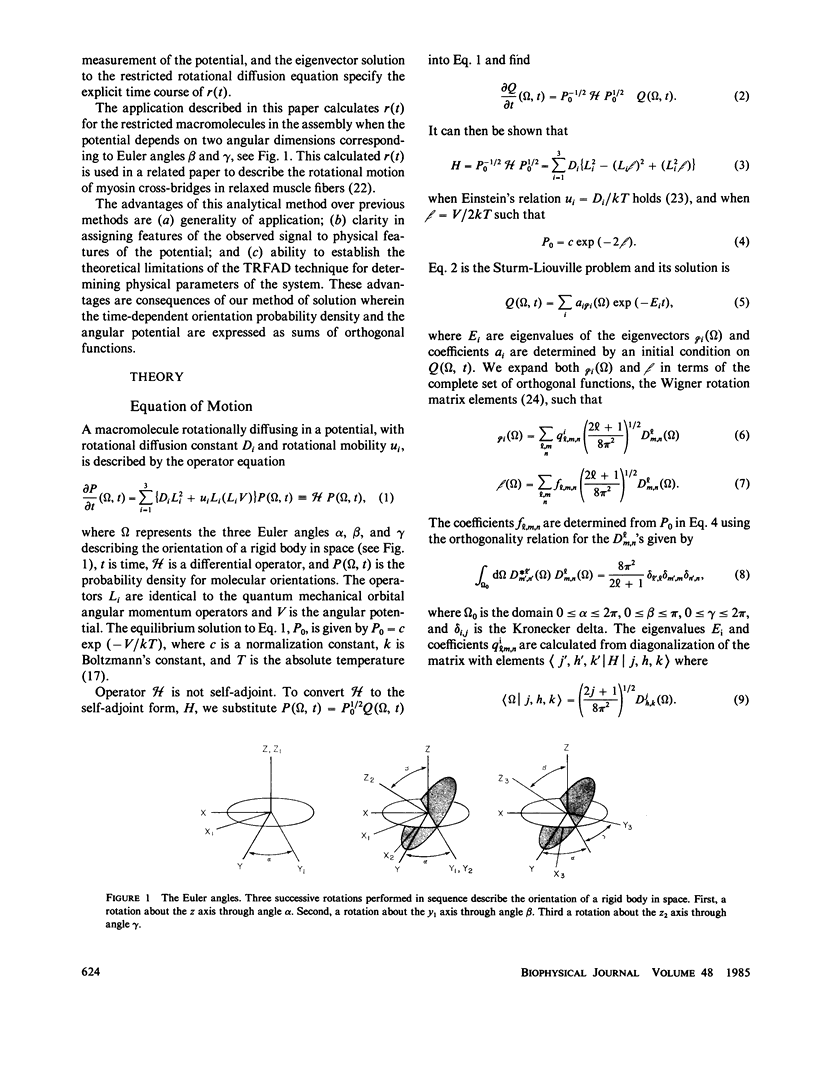
Abstract
We calculate the time dependence of the polarized fluorescence signal from fluorescent-labeled elements of a biological assembly that are rotationally diffusing in an arbitrary three-dimensional angular potential. We have formulated this calculation using the model-independent description of the angular potential wherein the angular potential is described by an expansion in a complete set of orthonormal functions with the expansion coefficients (or order parameters) determined by time-independent methods (Burghardt, T. P., 1984, Biopolymers, 23:2382-2406). We have applied the calculation to fluorescent-labeled myosin cross-bridges in relaxed muscle fibers. In a related paper we describe the experimental observation of the myosin cross-bridges rotationally diffusing in an angular potential (Burghardt, T. P., and N. L. Thompson, 1985, Biochemistry, 24:3731-3735).
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod D. Carbocyanine dye orientation in red cell membrane studied by microscopic fluorescence polarization. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):557–573. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85271-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badea M. G., Brand L. Time-resolved fluorescence measurements. Methods Enzymol. 1979;61:378–425. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)61019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borejdo J., Assulin O., Ando T., Putnam S. Cross-bridge orientation in skeletal muscle measured by linear dichroism of an extrinsic chromophore. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):391–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borejdo J., Putnam S. Polarization of fluorescence from single skinned glycerinated rabbit psoas fibers in rigor and relaxation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 11;459(3):578–595. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt T. P., Ando T., Borejdo J. Evidence for cross-bridge order in contraction of glycerinated skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7515–7519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt T. P. Model-independent fluorescence polarization for measuring order in a biological assembly. Biopolymers. 1984 Nov;23(11 Pt 2):2383–2406. doi: 10.1002/bip.360231118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt T. P., Thompson N. L. Effect of planar dielectric interfaces on fluorescence emission and detection. Evanescent excitation with high-aperture collection. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):729–737. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84071-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt T. P., Thompson N. L. Model-independent electron spin resonance for measuring order of immobile components in a biological assembly. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):401–409. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83796-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt T. P., Thompson N. L. Motion of myosin cross-bridges in skeletal muscle fibers studied by time-resolved fluorescence anisotropy decay. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3731–3735. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P. Determination of lipid order parameters and rotational correlation times from fluorescence depolarization experiments. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80564-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Structural order of lipids and proteins in membranes: evaluation of fluorescence anisotropy data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawato S., Kinosita K., Jr, Ikegami A. Effect of cholesterol on the molecular motion in the hydrocarbon region of lecithin bilayers studied by nanosecond fluorescence techniques. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):5026–5031. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Kawato S., Ikegami A. A theory of fluorescence polarization decay in membranes. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):289–305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85550-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipari G., Szabo A. Effect of librational motion on fluorescence depolarization and nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation in macromolecules and membranes. Biophys J. 1980 Jun;30(3):489–506. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85109-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson R. A., Cheung P. Muscle crossbridges: absence of direct effect of calcium on movement away from the thick filaments. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):190–192. doi: 10.1126/science.194.4261.190-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson R. A., Morales M. F., Botts J. Segmental flexibility of the S-1 moiety of myosin. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2250–2255. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson R. A., Wilson M. G. Three-dimensional disorder of dipolar probes in a helical array. Application to muscle cross-bridges. Biophys J. 1982 Aug;39(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84511-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson R., Cheung P. H. Intrinsic segmental flexibility of the S-1 moiety of myosin using single-headed myosin. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2139–2148. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales M. F. Calculation of the polarized fluorescence from a labeled muscle fiber. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):145–149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Cooke R. Orientation of spin-labeled myosin heads in glycerinated muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1980 Dec;32(3):891–906. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85024-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., McConnell H. M., Burhardt T. P. Order in supported phospholipid monolayers detected by the dichroism of fluorescence excited with polarized evanescent illumination. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):739–747. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84072-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torgerson P. M. Tryptophan emission from myosin subfragment 1: acrylamide and nucleotide effect monitored by decay-associated spectra. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 19;23(13):3002–3007. doi: 10.1021/bi00308a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. G., Mendelson R. A. A comparison of order and orientation of crossbridges in rigor and relaxed muscle fibres using fluorescence polarization. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Dec;4(6):671–693. doi: 10.1007/BF00712160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yguerabide J., Epstein H. F., Stryer L. Segmental flexibility in an antibody molecule. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):573–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


