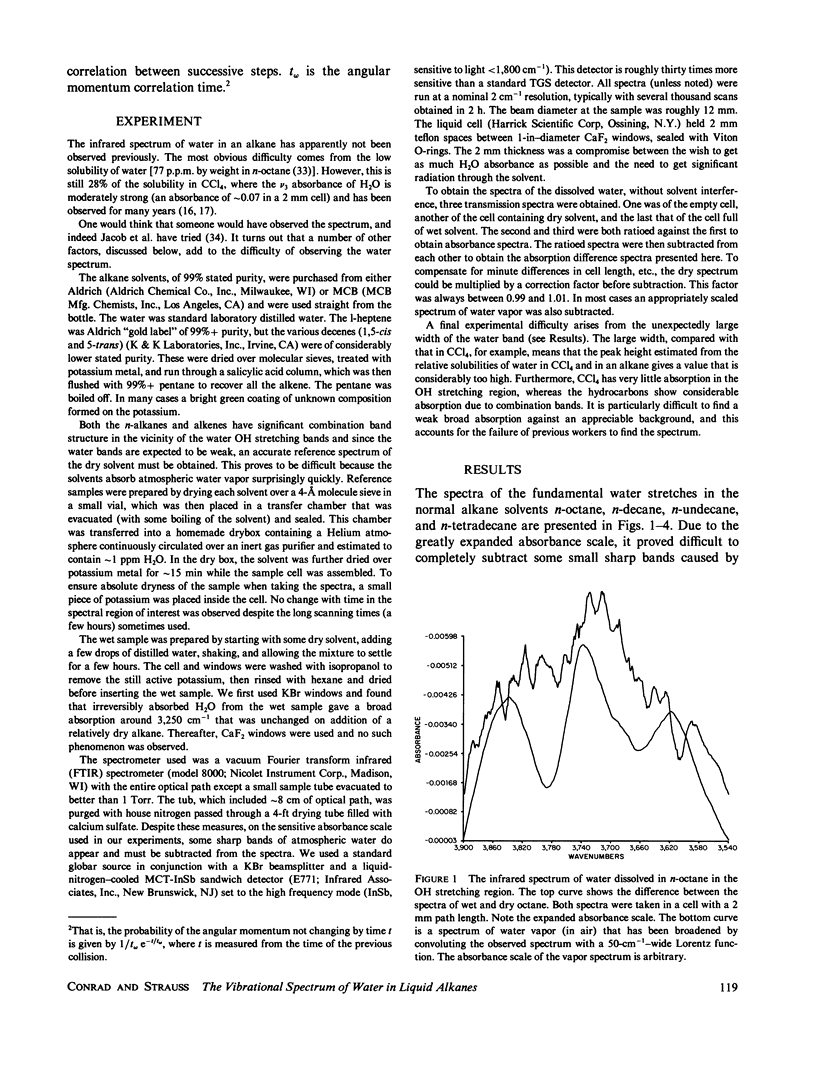
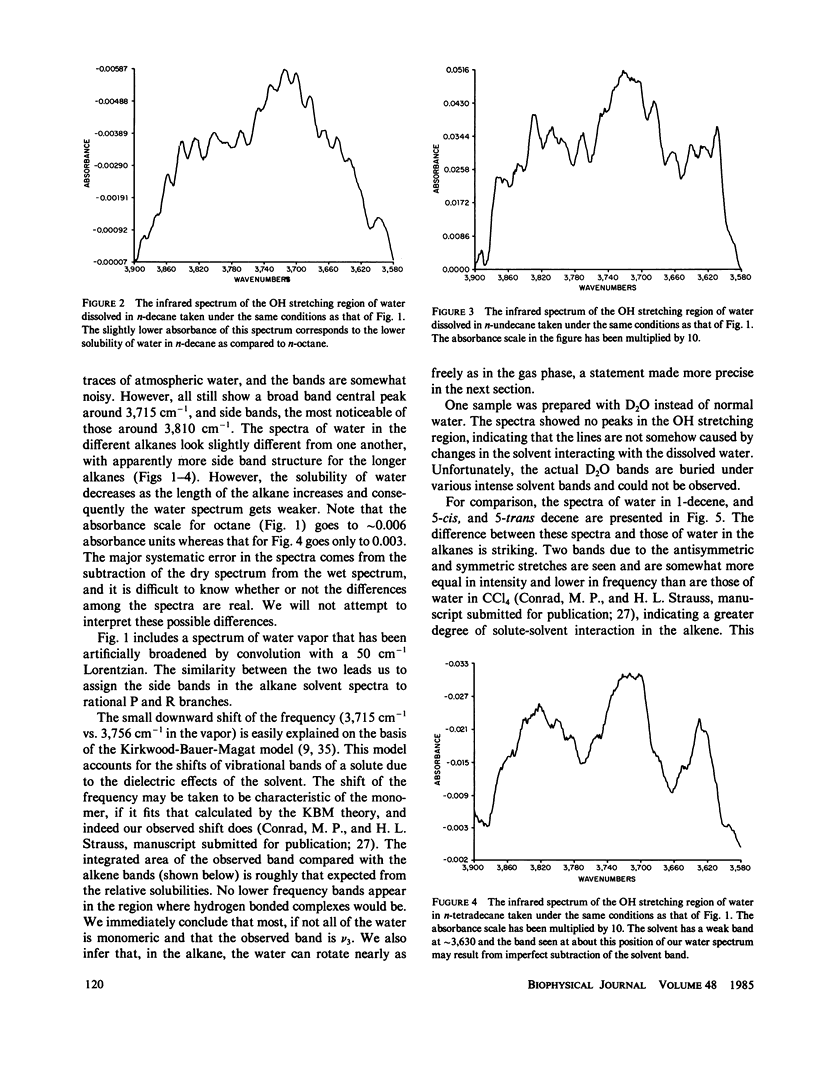
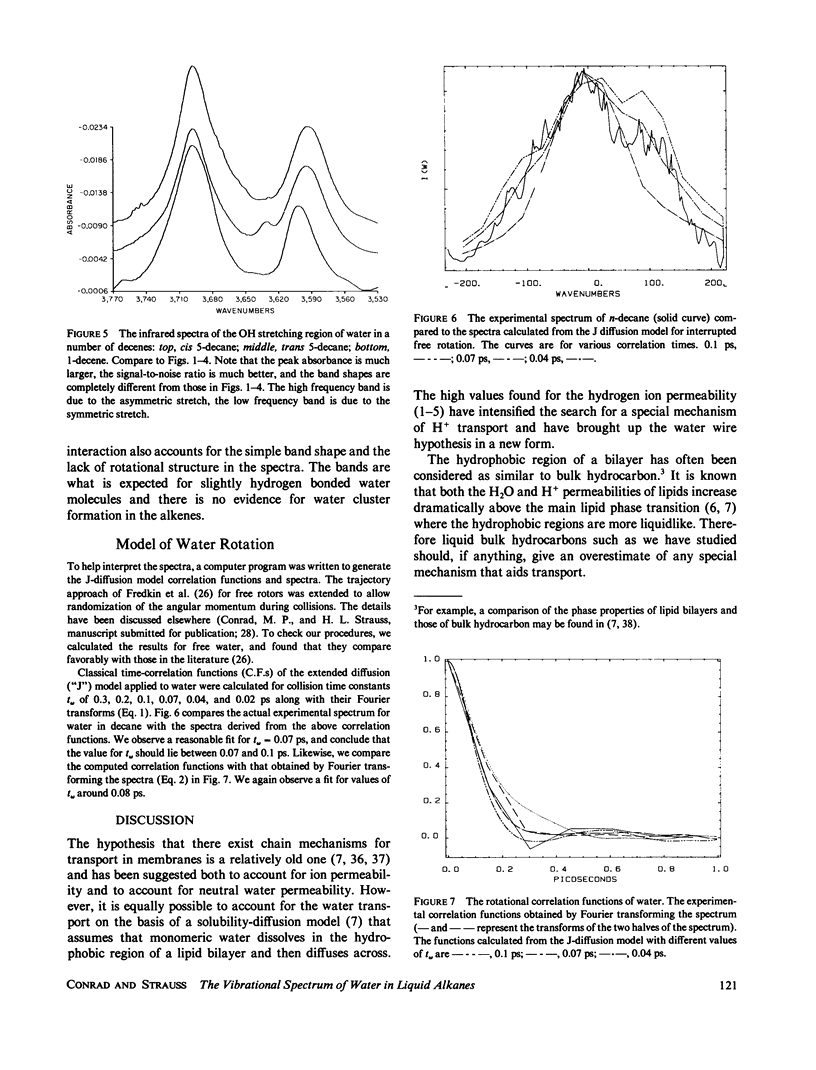
Abstract
The water wire hypothesis of hydrogen-ion transport in lipid bilayers has prompted a search for water aggregates in bulk hydrocarbons. The asymmetric stretching vibration of the water dissolved in n-decane and in a number of other alkanes and alkenes has been observed. The water band in the alkanes is very wide and fits to the results of a J-diffusion calculation for the water rotation. This implies that the water is freely rotating between collisions with the solvent and certainly not hydrogen bonded to anything. The existence of water aggregates is thus most unlikely. In contrast, water in an alkene is hydrogen bonded to the solvent molecules (although not to other water molecules) and shows an entirely different spectrum.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cafiso D. S., Hubbell W. L. Electrogenic H+/OH- movement across phospholipid vesicles measured by spin-labeled hydrophobic ions. Biophys J. 1983 Oct;44(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84276-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Nichols J. W. Proton-hydroxide permeability of liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):165–168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elamrani K., Blume A. Effect of the lipid phase transition on the kinetics of H+/OH- diffusion across phosphatidic acid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 5;727(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fettiplace R., Haydon D. A. Water permeability of lipid membranes. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):510–550. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A., MacDonald R. C. The organization of n-alkanes in lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 24;597(3):445–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Deamer D. W. Net proton-hydroxyl permeability of large unilamellar liposomes measured by an acid-base titration technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2038–2042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Hill M. W., Bangham A. D., Deamer D. W. Measurement of net proton-hydroxyl permeability of large unilamellar liposomes with the fluorescent pH probe, 9-aminoacridine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 13;596(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90126-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol M., Thomas P., Grignon C. Proton permeability of liposomes from natural phospholipid mixtures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 22;684(2):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


