Abstract
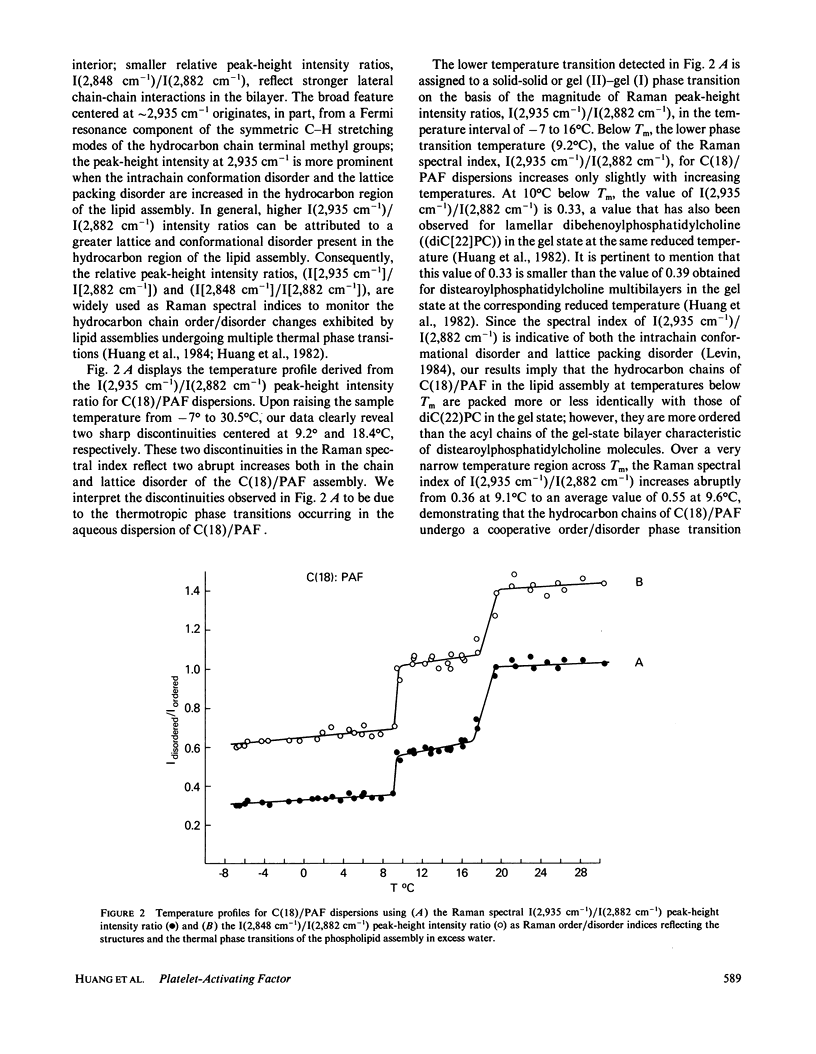
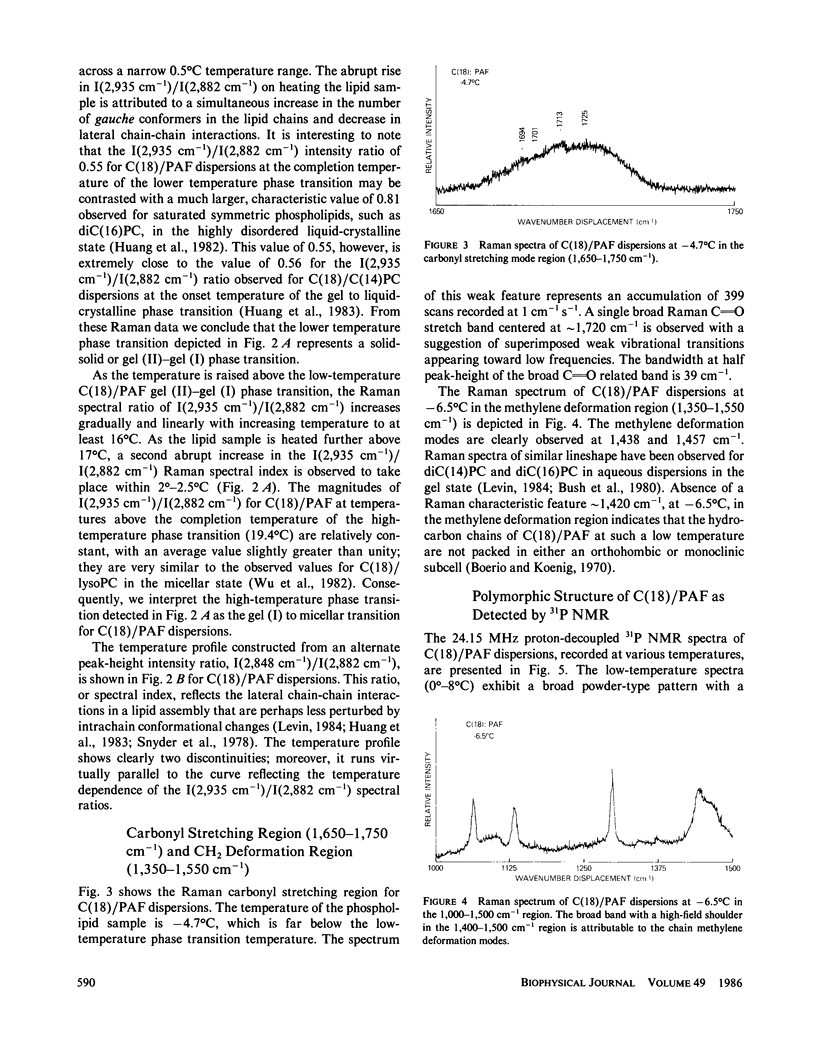
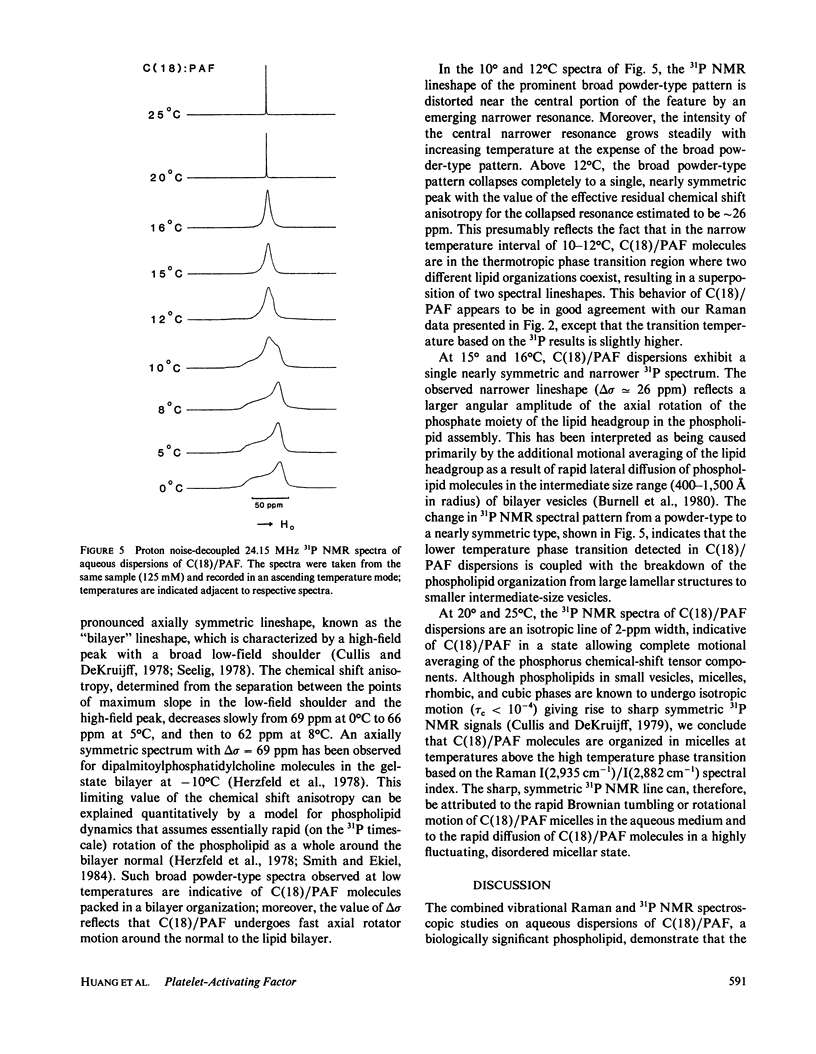
Vibrational Raman and 31P NMR spectroscopic experiments have been performed as a function of temperature on aqueous dispersions of 1-0-octadecyl-2-acetoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, a chemically synthesized platelet-activating factor. In the temperature range of -7 to 30 degrees C, the C(18)/PAF-H2O system is shown, upon heating, to undergo two thermal phase transitions centered at 9.2 degrees and 18.4 degrees C. The low temperature transition, attributed to the interdigitated lamellar gel (II)----gel (I) phase transition, is characterized by the breakdown of large lamellar organizations into small, but aggregated, bilayer vesicles. The high-temperature transition corresponds to the interdigitated lamellar gel (I)----micellar transition. The molecular ordering and packing structure of C(18)/PAF in the two lamellar phases and phase transition regions are described. It appears that the interdigitated lamellar gel (I) phase is unique for C(18)/PAF dispersions when compared with the behavior of other chemically closely related phospholipids in excess water.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnell E. E., Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Effects of tumbling and lateral diffusion on phosphatidylcholine model membrane 31P-NMR lineshapes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 2;603(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush S. F., Adams R. G., Levin I. W. Structural reorganizations in lipid bilayer systems: effect of hydration and sterol addition on Raman spectra of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine multilayers. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 16;19(19):4429–4436. doi: 10.1021/bi00560a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büldt G., Gally H. U., Seelig J., Zaccai G. Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. I. Head group conformation. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):673–691. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. The polymorphic phase behaviour of phosphatidylethanolamines of natural and synthetic origin. A 31P NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 19;513(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Pascher I., Pearson R. H., Sundell S. Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 16;650(1):21–51. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzfeld J., Griffin R. G., Haberkorn R. A. Phosphorus-31 chemical-shift tensors in barium diethyl phosphate and urea-phosphoric acid: model compounds for phospholipid head-group studies. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2711–2718. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Mason J. T., Levin I. W. Raman spectroscopic study of saturated mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine multilamellar dispersions. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2775–2780. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Mason J. T., Huang C. Acyl chain interdigitation in saturated mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine bilayer dispersions. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5570–5577. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Stewart T. P., Yeagle P. L. Temperature-dependent morphological and phase behavior of sphingomyelin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 18;601(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Lee C. S., Cheah M. J., Shen T. Y. Specific receptor sites for 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor) on rabbit platelet and guinea pig smooth muscle membranes. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4756–4763. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance and the head group structure of phospholipids in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 31;515(2):105–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Seelig A. Lipid conformation in model membranes and biological membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Feb;13(1):19–61. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer A. M., Kohler S. J. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectra characteristic of hexagonal and isotropic phospholipid phases generated from phosphatidylethanolamine in the bilayer phase. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6831–6834. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W., Huang C., Conley T. G., Martin R. B., Levin I. W. Lamellar--micellar transition of 1-stearoyllysophosphatidylcholine assemblies in excess water. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5957–5961. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L., Hutton W. C., Huang C. H., Martin R. B. Headgroup conformation and lipid--cholesterol association in phosphatidylcholine vesicles: a 31P(1H) nuclear Overhauser effect study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3477–3481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


