Abstract
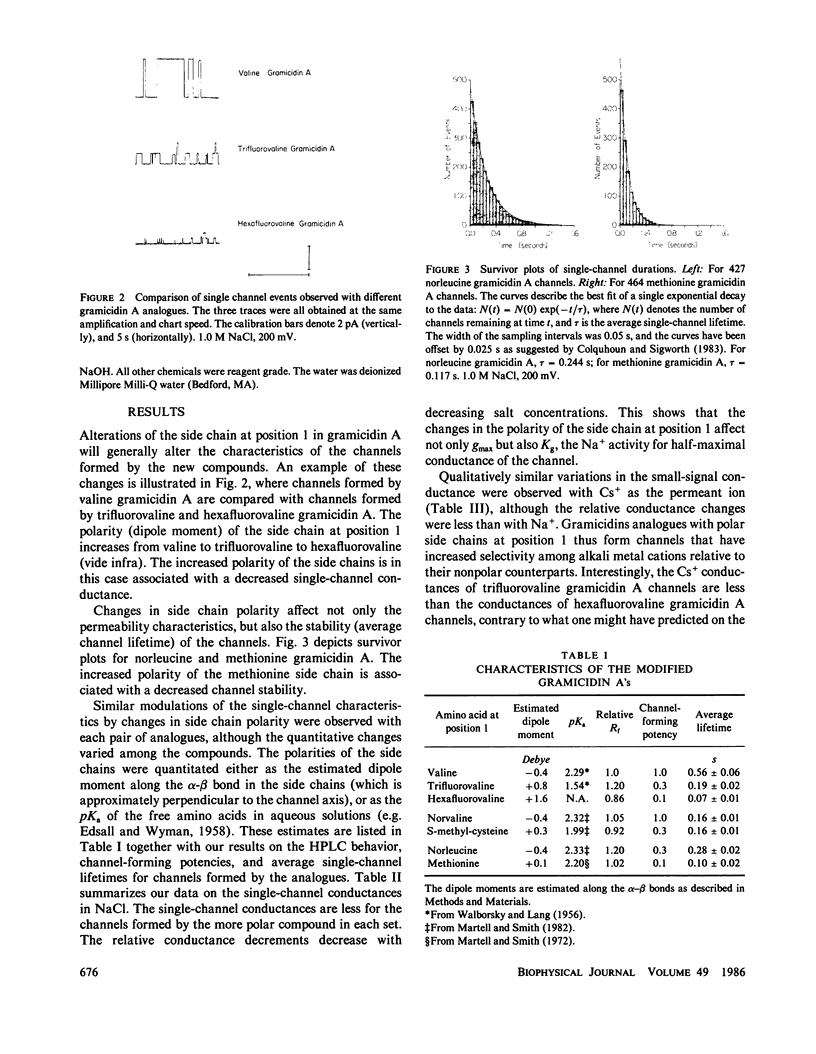
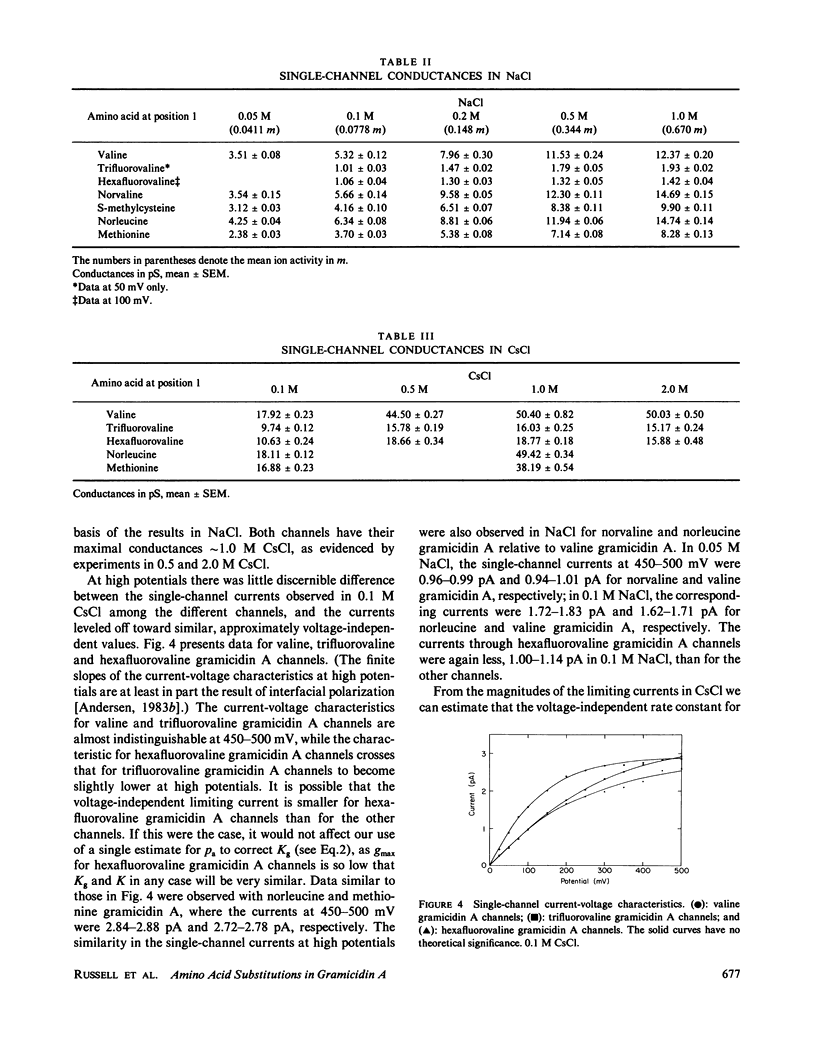
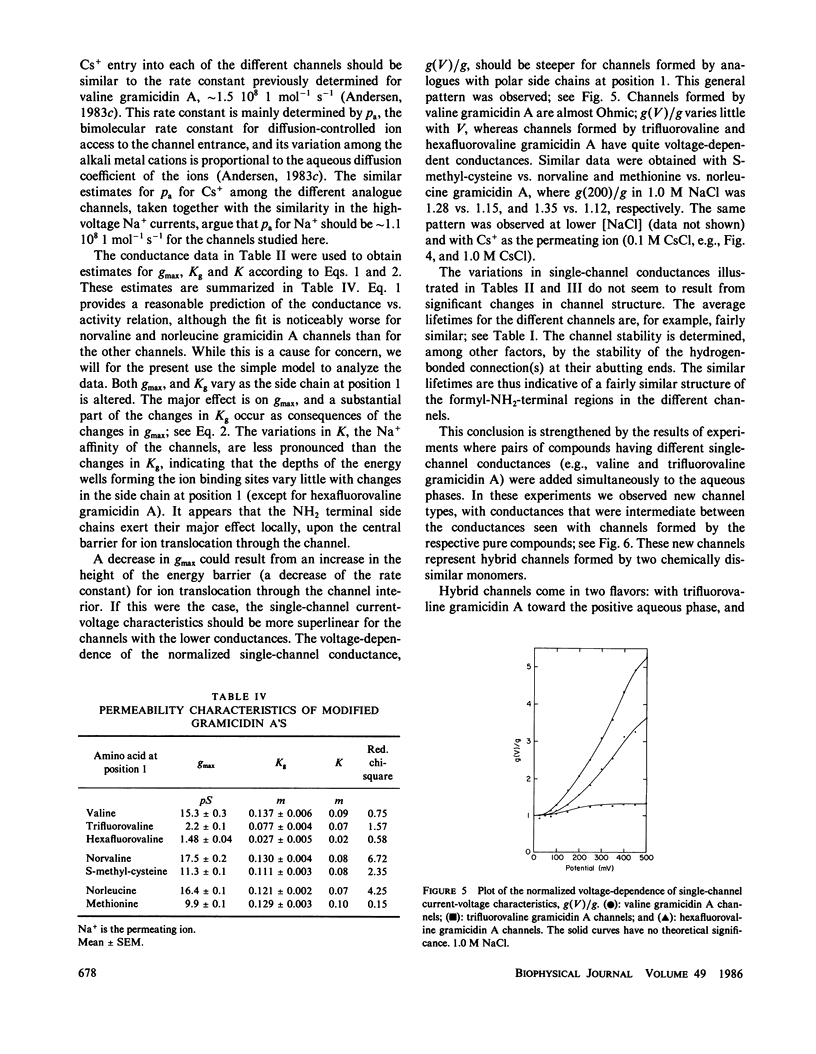
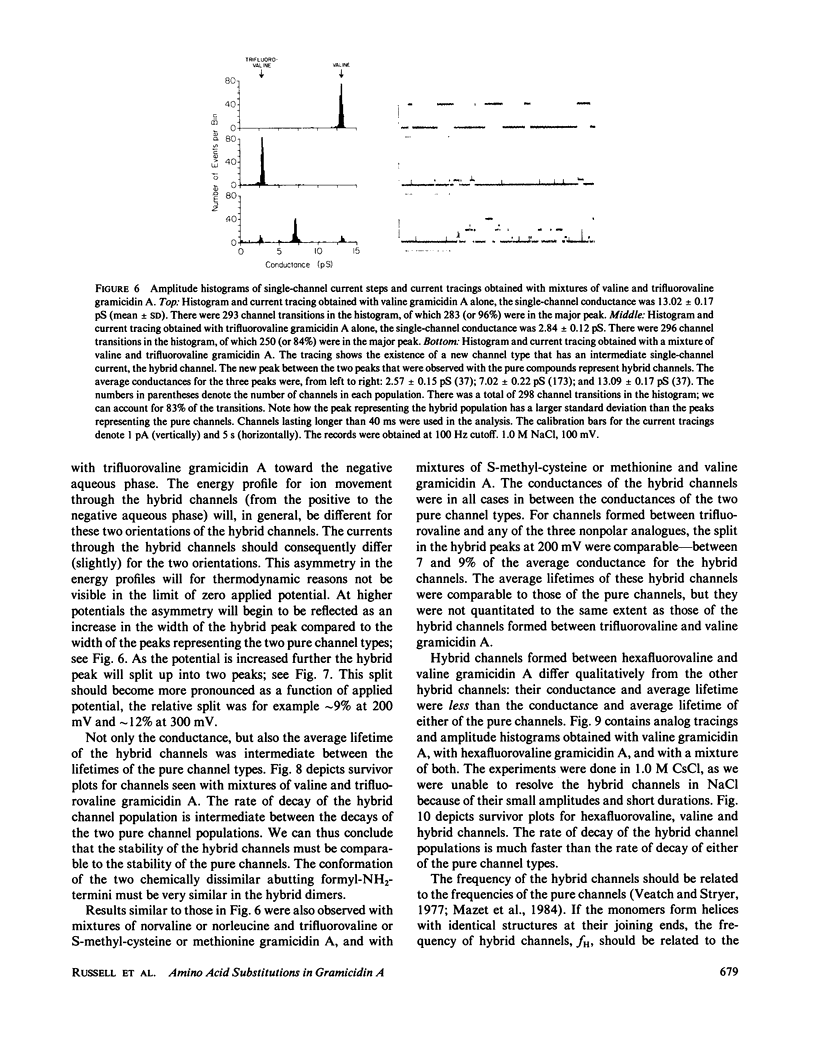
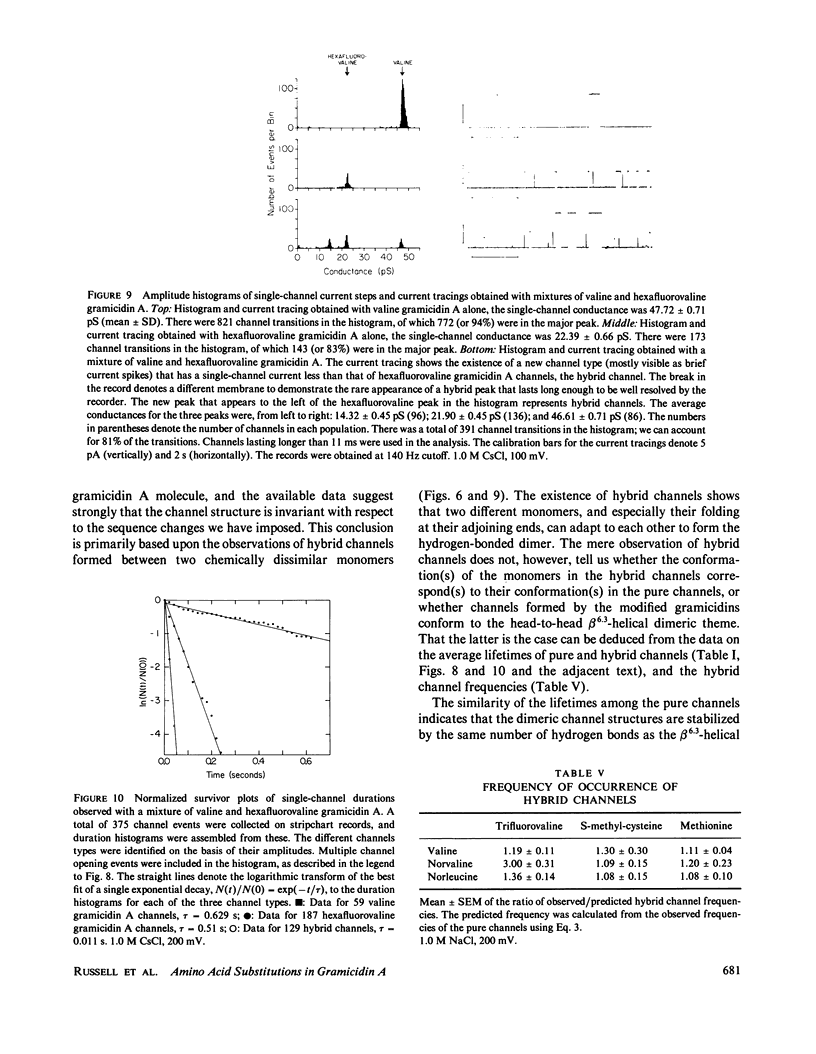
The modulation of gramicidin A single-channel characteristics by the amino acid side chains was investigated using gramicidin A analogues in which the NH2 terminal valine was chemically replaced by other amino acids. The replacements were chosen such that pairs of analogues would have essentially isosteric side chains of different polarities at position 1 (valine vs. trifluorovaline or hexafluorovaline; norvaline vs. S-methyl-cysteine; and norleucine vs. methionine). Even though the side chains are not in direct contact with the permeating ions, the single-channel conductances for Na+ and Cs+ are markedly affected by the changes in the physico-chemical characteristics of the side chains. The maximum single-channel conductance for Na+ is decreased by as much as 10-fold in channels formed by analogues with polar side chains at position 1 compared with their counterparts with nonpolar side chains, while the Na+ affinity is fairly insensitive to these changes. The relative conductance changes seen with Cs+ were less than those seen with Na+; the ion selectivity of the channels with polar side chains at position 1 was increased. Hybrid channels could form between compounds with a polar side chain at position 1 and either valine gramicidin A or their counterparts with a nonpolar side chain at position 1. The structure of channels formed by the modified gramicidins is thus essentially identical to the structure of channels formed by valine gramicidin A. The polarity of the side chain at position 1 is an important determinant of the permeability characteristics of the gramicidin A channel. We discuss the importance of having structural information when interpreting the functional consequences of site-directed amino acid modifications.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. Interfacial polarization effects on single-channel current measurements. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):135–146. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84415-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. Single-channel measurements at very high potentials. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):119–133. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84414-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. Studies on the diffusion-controlled association step. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):147–165. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84416-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apell H. J., Bamberg E., Alpes H., Läuger P. Formation of ion channels by a negatively charged analog of gramicidin A. J Membr Biol. 1977 Feb 24;31(1-2):171–188. doi: 10.1007/BF01869403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Apell H. J., Alpes H., Gross E., Morell J. L., Harbaugh J. F., Janko K., Läuger P. Ion channels formed by chemical analogs of gramicidin A. Fed Proc. 1978 Oct;37(12):2633–2638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Apell H. J., Alpes H. Structure of the gramicidin A channel: discrimination between the piL,D and the beta helix by electrical measurements with lipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2402–2406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Janko K. The action of a carbonsuboxide dimerized gramicidin A on lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 17;465(3):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Noda K., Gross E., Läuger P. Single-channel parameters of gramicidin A,B, and C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90348-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boni L. T., Connolly A. J., Kleinfeld A. M. Transmembrane distribution of gramicidin by tryptophan energy transfer. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):122–123. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83619-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., McLaughlin S. G., McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. The dielectric constant of phospholipid bilayers and the permeability of membranes to ions. Science. 1979 Dec 7;206(4423):1196–1198. doi: 10.1126/science.228394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENMAN G. Cation selective glass electrodes and their mode of operation. Biophys J. 1962 Mar;2(2 Pt 2):259–323. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86959-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Horn R. Ionic selectivity revisited: the role of kinetic and equilibrium processes in ion permeation through channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;76(3):197–225. doi: 10.1007/BF01870364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchebest C., Pullman A. The effect of the amino-acid side chains on the energy profiles for ion transport in the gramicidin A channel. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Feb;2(5):859–870. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10507605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Andersen O. S. The gramicidin A channel: a review of its permeability characteristics with special reference to the single-file aspect of transport. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 30;59(3):155–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01875422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman P. The carbon-fluorine bond in compounds of biological interest. Science. 1969 Jun 6;164(3884):1123–1130. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3884.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz F., Spach G., Trudelle Y. Single channels of 9, 11, 13, 15-destryptophyl-phenylalanyl-gramicidin A. Biophys J. 1982 Oct;40(1):87–89. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84462-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. C. Electrostatic modeling of ion pores. Energy barriers and electric field profiles. Biophys J. 1982 Aug;39(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84503-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Electrostatic calculations for an ion channel. I. Energy and potential profiles and interactions between ions. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85485-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Electrostatic calculations for an ion channel. II. Kinetic behavior of the gramicidin A channel. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):221–248. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85486-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Ion transport through pores: a rate-theory analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):423–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazet J. L., Andersen O. S., Koeppe R. E., 2nd Single-channel studies on linear gramicidins with altered amino acid sequences. A comparison of phenylalanine, tryptophane, and tyrosine substitutions at positions 1 and 11. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):263–276. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84153-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. S., Veatch W. R., Stryer L. Transmembrane channel activity of gramicidin A analogs: effects of modification and deletion of the amino-terminal residue. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):733–738. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARGES R., WITKOP B. GRAMICIDIN A. V. THE STRUCTURE OF VALINE- AND ISOLEUCINE-GRAMICIDIN A. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 May 5;87:2011–2020. doi: 10.1021/ja01087a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioiri T., Ninomiya K., Yamada S. Diphenylphosphoryl azide. A new convenient reagent for a modified Curtus reaction and for the peptide synthesis. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Aug 23;94(17):6203–6205. doi: 10.1021/ja00772a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo G., Urry D. W. N-acetyl gramicidin: single-channel properties and implications for channel structure. Science. 1979 Jan 5;203(4375):55–57. doi: 10.1126/science.83000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban B. W., Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion movements in gramicidin pores. An example of single-file transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 4;602(2):331–354. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban B. W., Hladky S. B. Ion transport in the simplest single file pore. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):410–429. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Goodall M. C., Glickson J. D., Mayers D. F. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: characteristics of head-to-head dimerized (L,D) helices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1907–1911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. Protein conformation in biomembranes: optical rotation and absorption of membrane suspensions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):115–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Trapane T. L., Prasad K. U. Is the gramicidin a transmembrane channel single-stranded or double-stranded helix? A simple unequivocal determination. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1064–1067. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4615.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Walker J. T., Trapane T. L. Ion interactions in (1-13C)D-Val8 and D-Leu14 analogs of gramicidin A, the helix sense of the channel and location of ion binding sites. J Membr Biol. 1982;69(3):225–231. doi: 10.1007/BF01870401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Fossel E. T., Blout E. R. The conformation of gramicidin A. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5249–5256. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W., Stryer L. The dimeric nature of the gramicidin A transmembrane channel: conductance and fluorescence energy transfer studies of hybrid channels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein S., Wallace B. A., Blout E. R., Morrow J. S., Veatch W. Conformation of gramicidin A channel in phospholipid vesicles: a 13C and 19F nuclear magnetic resonance study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4230–4234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein S., Wallace B. A., Morrow J. S., Veatch W. R. Conformation of the gramicidin A transmembrane channel: A 13C nuclear magnetic resonance study of 13C-enriched gramicidin in phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. B., Koeppe R. E., 2nd Semisynthesis of linear gramicidins using diphenyl phosphorazidate (DPPA). Int J Pept Protein Res. 1985 Sep;26(3):305–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1985.tb03209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S. I., Ikota N., Shioiri T., Tachibana S. Letter: Diphenyl phosphorazidate (DPPA) and diethyl phosphorocyanidate (DEPC). Two new reagents for solid-phase peptide synthesis and their application to the synthesis of porcine motilin. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Nov 26;97(24):7174–7175. doi: 10.1021/ja00857a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


