Abstract
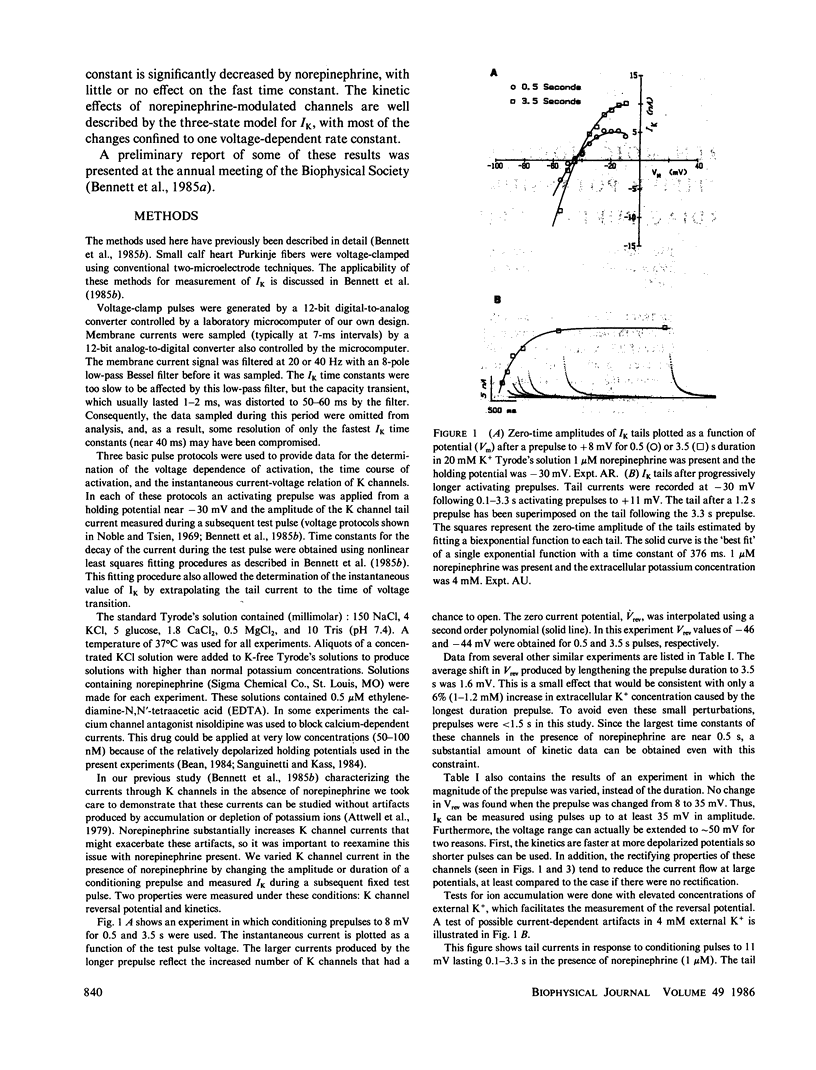
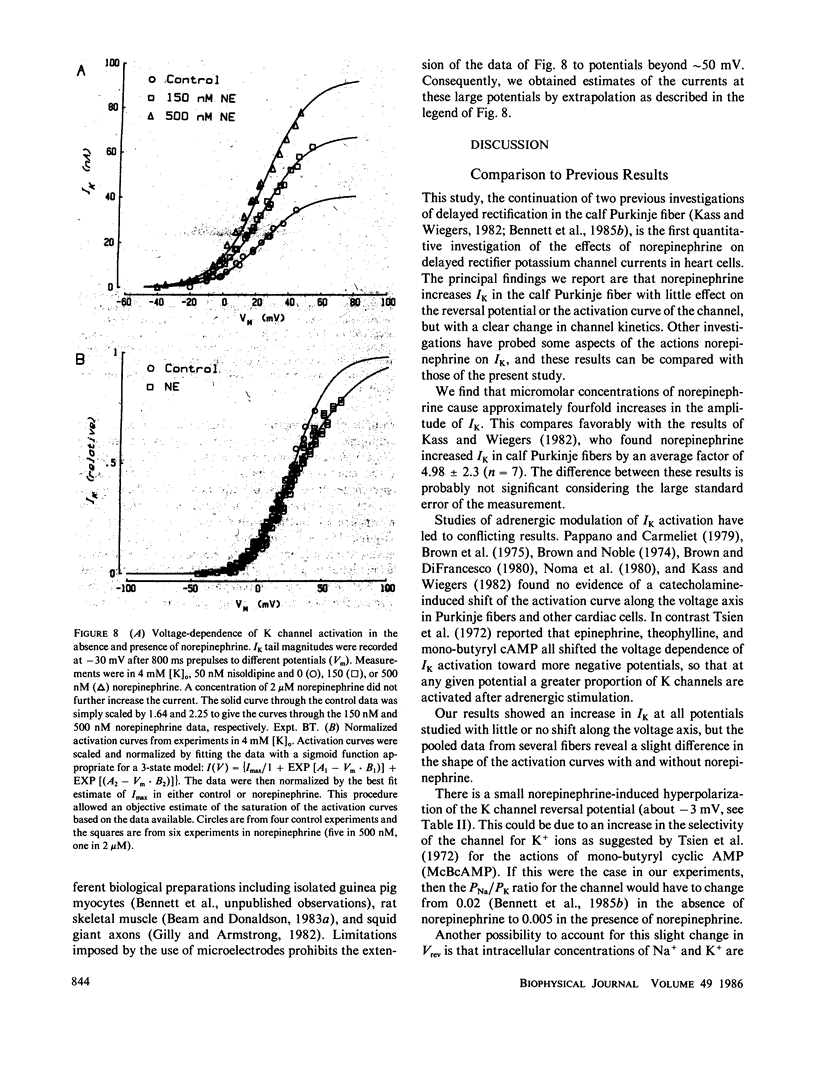
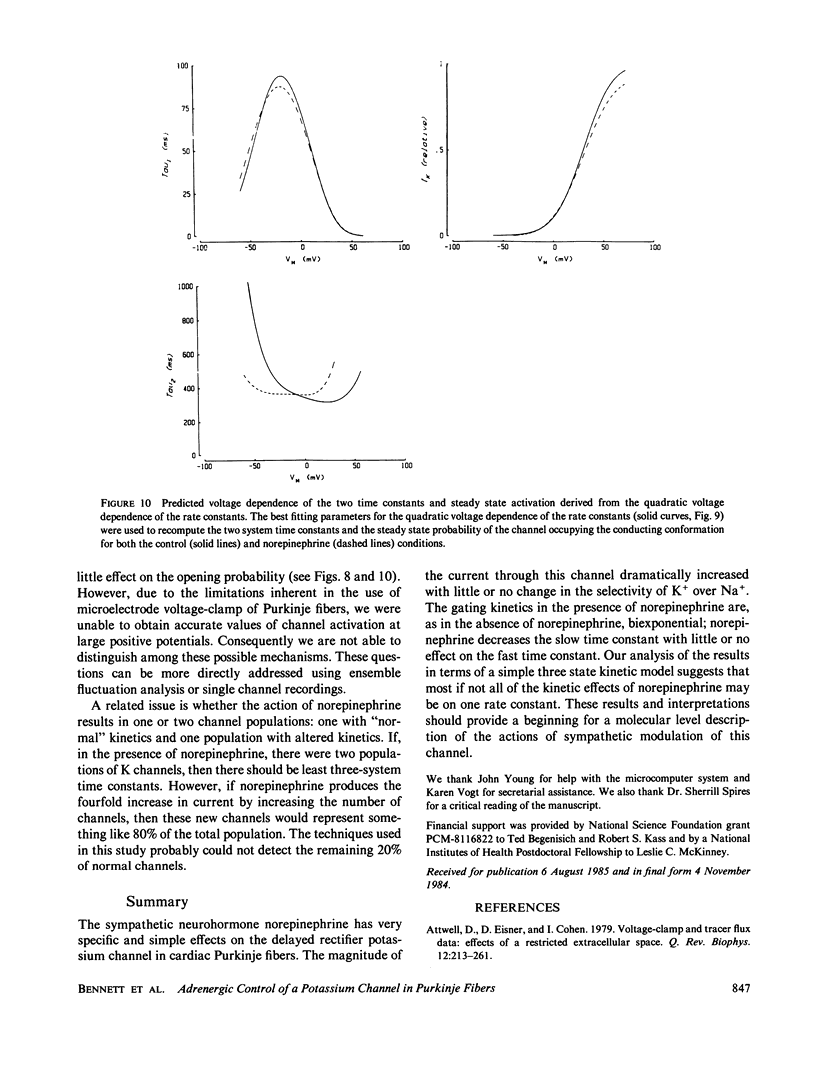
We have investigated the modulation of the delayed rectifier potassium channel in calf cardiac Purkinje fibers by the neurohormone norepinephrine. We find that 0.5 microM norepinephrine increases this K channel current by a factor of 2.7. A maximal increase of about four was found for concentrations of 1 microM and above. Norepinephrine produced a small (less than 5 mV) and variable shift of the K channel reversal potential toward more negative values. The kinetics of the potassium channel are well described by a two-exponential process, both in the absence and presence of norepinephrine. However, norepinephrine substantially decreases the slower time constant with no significant effect on the fast time constant. Potassium channel activation curves in the presence of norepinephrine are very similar to control curves except at large positive potentials. A simple sequential three-state model for this channel can reproduce these data both with and without norepinephrine. The logarithms of the rate constants derived from this model are quadratic functions of voltage, suggesting the involvement of electric field-induced dipoles in the gating of this channel. Most of the kinetic effects of norepinephrine appear to be on a single rate constant.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attwell D., Eisner D., Cohen I. Voltage clamp and tracer flux data: effects of a restricted extra-cellular space. Q Rev Biophys. 1979 Aug;12(3):213–261. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Donaldson P. L. A quantitative study of potassium channel kinetics in rat skeletal muscle from 1 to 37 degrees C. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Apr;81(4):485–512. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.4.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Nitrendipine block of cardiac calcium channels: high-affinity binding to the inactivated state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6388–6392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Beta-adrenergic modulation of calcium channels in frog ventricular heart cells. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):371–375. doi: 10.1038/307371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler G. W., Reuter H. Reconstruction of the action potential of ventricular myocardial fibres. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):177–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett P. B., McKinney L. C., Kass R. S., Begenisich T. Delayed rectification in the calf cardiac Purkinje fiber. Evidence for multiple state kinetics. Biophys J. 1985 Oct;48(4):553–567. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83813-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. F., McNaughton P. A., Noble D., Noble S. J. Adrenergic control of cardian pacemaker currents. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):527–537. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. F., Noble S. J. Proceedings: Effects of adrenaline on membrane currents underlying pacemaker activity in frog atrial muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):51P–53P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H., Difrancesco D. Voltage-clamp investigations of membrane currents underlying pace-maker activity in rabbit sino-atrial node. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:331–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F., Osterrieder W., Trautwein W. Injection of catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase into isolated cardiac myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Jul;398(2):147–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00581064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Vereecke J. Adrenaline and the plateau phase of the cardiac action potential. Importance of Ca++, Na+ and K+ conductance. Pflugers Arch. 1969;313(4):300–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00593955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Flatman J. A. The effect of catecholamines on Na-K transport and membrane potential in rat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):383–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Noble D. A model of cardiac electrical activity incorporating ionic pumps and concentration changes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jan 10;307(1133):353–398. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1985.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C. Beta-adrenoceptor agonists increase membrane K+ conductance in cardiac Purkinje fibres. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):691–693. doi: 10.1038/306691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilly W. F., Armstrong C. M. Divalent cations and the activation kinetics of potassium channels in squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jun;79(6):965–996. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Wiegers S. E. The ionic basis of concentration-related effects of noradrenaline on the action potential of calf cardiac purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:541–558. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. E., Noble D., Tsien R. W. Reconstruction of the electrical activity of cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;251(1):1–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. F., Trautwein W. The potassium current underlying delayed rectification in cat ventricular muscle. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:217–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D. The surprising heart: a review of recent progress in cardiac electrophysiology. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:1–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D., Tsien R. W. Outward membrane currents activated in the plateau range of potentials in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):205–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A., Kotake H., Irisawa H. Slow inward current and its role mediating the chronotropic effect of epinephrine in the rabbit sinoatrial node. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Oct;388(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00582621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappano A. J., Carmeliet E. E. Epinephrine and the pacemaking mechanism at plateau potentials in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Oct;382(1):17–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00585899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quadbeck J., Reiter M. Cardiac action potential and inotropic effect of noradrenaline and calcium. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;286(4):337–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00506649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):569–574. doi: 10.1038/301569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Kass R. S. Voltage-dependent block of calcium channel current in the calf cardiac Purkinje fiber by dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists. Circ Res. 1984 Sep;55(3):336–348. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.3.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. Interactions between intrinsic membrane protein and electric field. An approach to studying nerve excitability. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85490-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Cyclic AMP and contractile activity in heart. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:363–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Giles W., Greengard P. Cyclic AMP mediates the effects of adrenaline on cardiac purkinje fibres. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 6;240(101):181–183. doi: 10.1038/newbio240181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


