Abstract
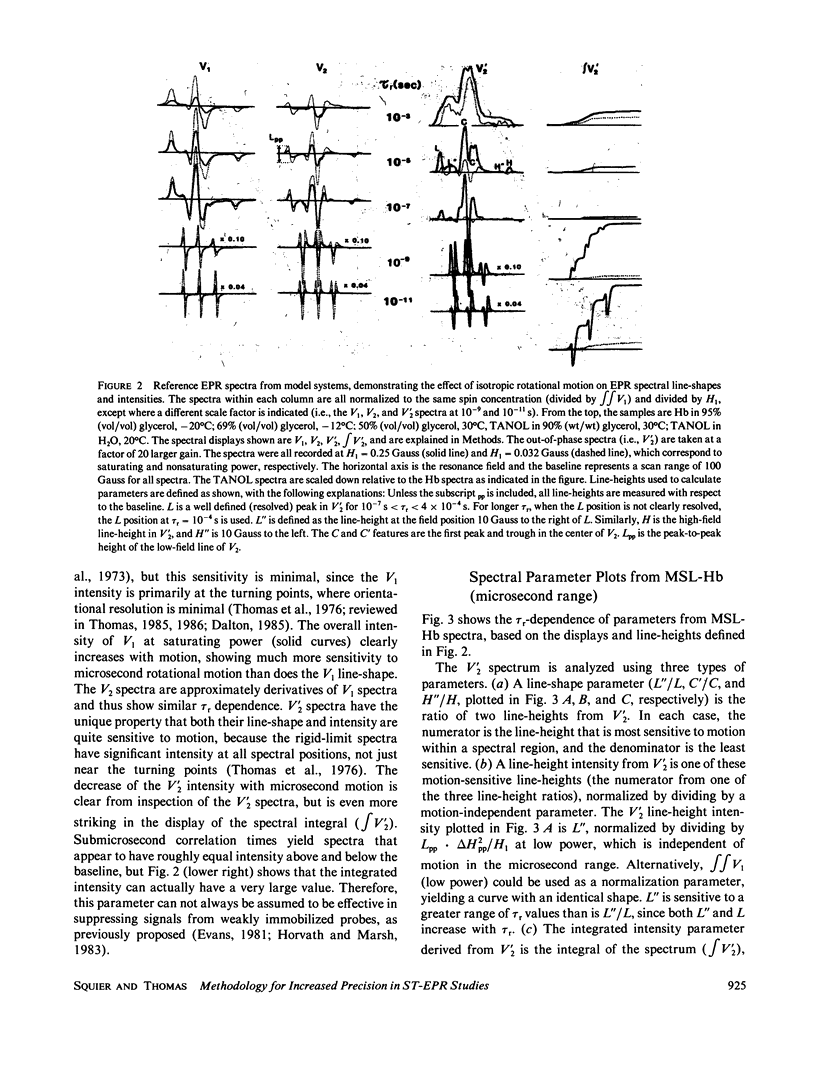
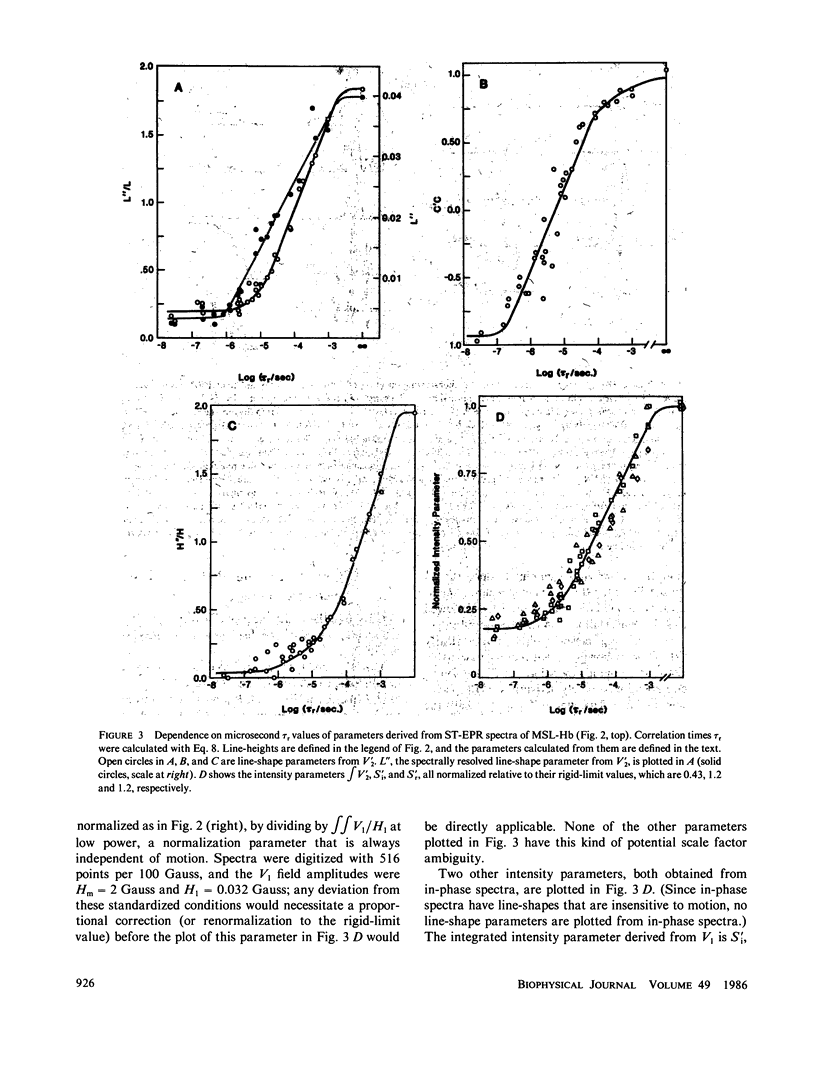
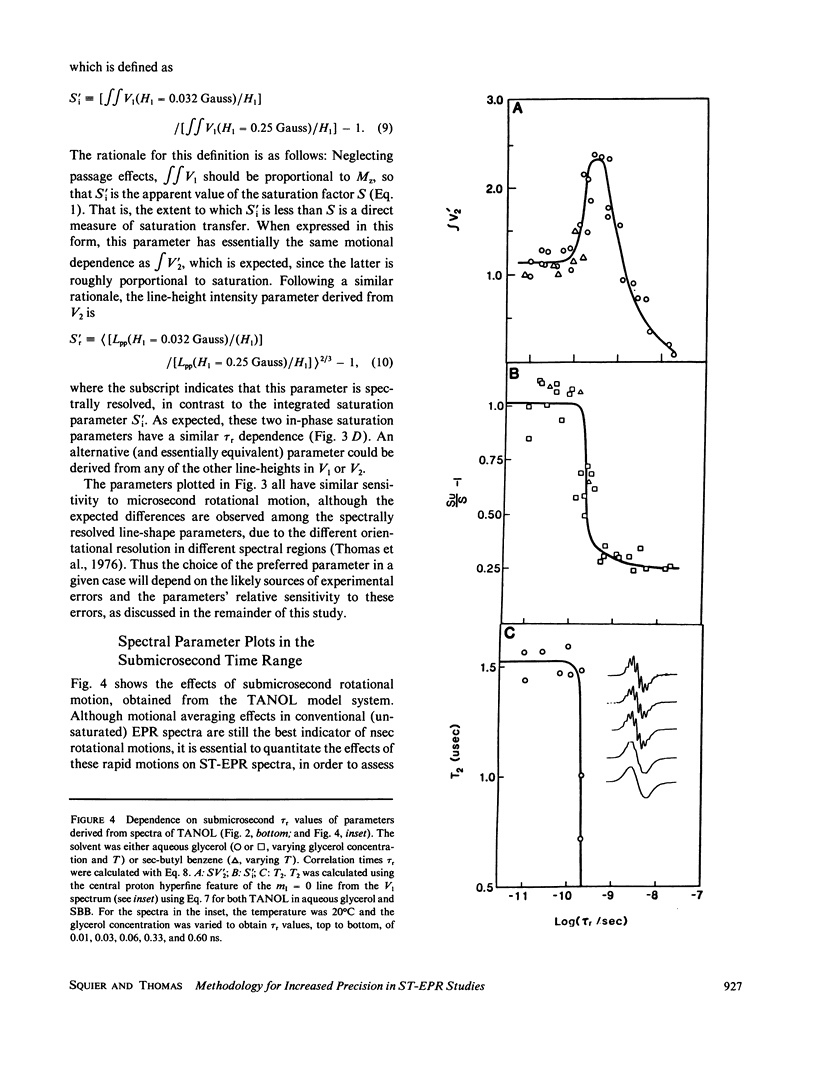
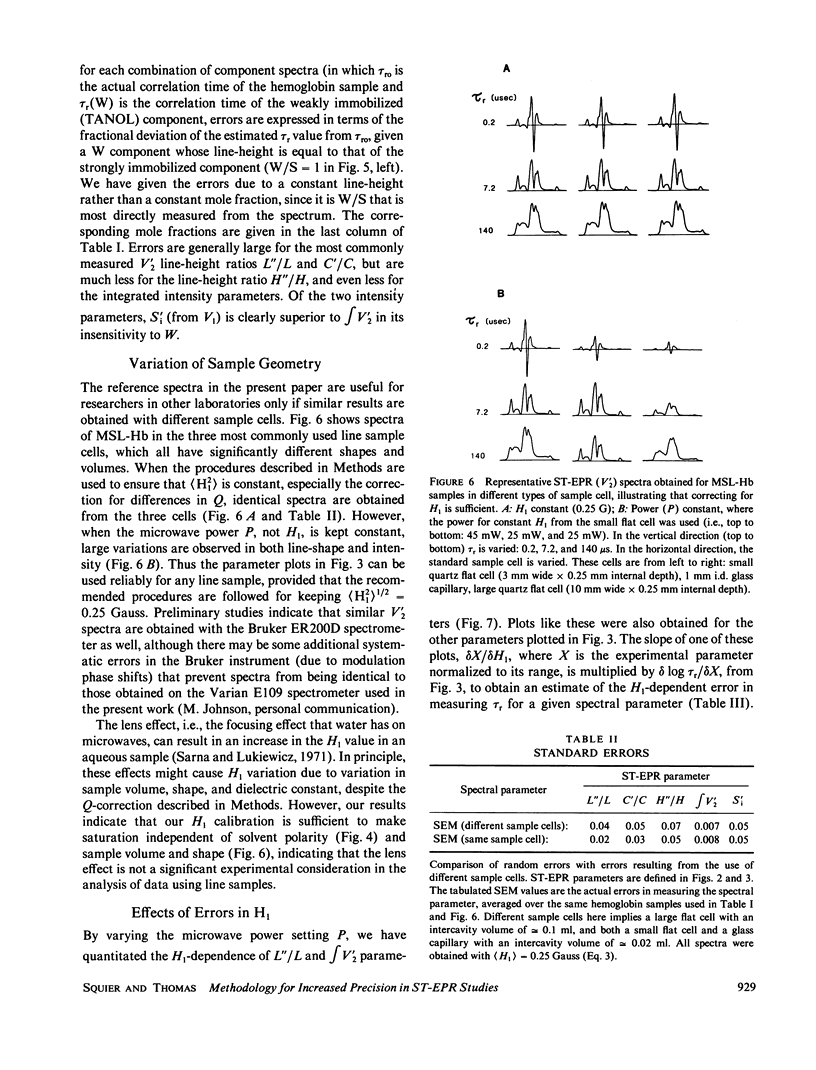
Microsecond rotational motions of nitroxide spin labels are measured primarily with saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance (ST-EPR). In the present study we have used model system experiments to quantitatively evaluate different ST-EPR spectral parameters, both in-phase and out-of-phase, with an emphasis on techniques for suppressing the interference from weakly immobilized probes. Analyses of both systematic and random errors show that maximum sensitivity to small changes in correlation time and minimum ambiguity of interpretation are best achieved by combining measurements of both spectral line-shape, i.e., the ratio of line-heights, and spectral intensity, i.e., the absolute amplitude of either a position within a spectrum or a spectral integral. Errors in the measurement of correlation times for the two types of parameters tend to be complementary. Integrated intensity parameters are particularly useful in measuring microsecond probe motions in the presence of weakly immobilized components. We confirm that integrated intensity parameters are sometimes effective in rejecting signals from weakly immobilized probes, but the effectiveness of this rejection is more limited than previously supposed and depends on the type of parameter being measured. We describe procedures for evaluating and minimizing errors due to weakly immobilized probes, emphasizing the advantages of a new kind of intensity parameter obtained from integrated in-phase spectra. We provide detailed descriptions of experimental procedures, along with calibration plots of the most useful spectral parameters vs. rotational correlation time, which should make it possible for workers in other laboratories, using different instruments and sample geometries, to reproduce spectra quantitatively and to make accurate correlation time measurements.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENESCH R., MACDUFF G., BENESCH R. E. DETERMINATION OF OXYGEN EQUILIBRIA WITH A VERSATILE NEW TONOMETER. Anal Biochem. 1965 Apr;11:81–87. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow D. J., Squier T. C., Thomas D. D. Temperature dependence of rotational dynamics of protein and lipid in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):194–202. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmelle M., Butler K. W., Smith I. C. Saturation transfer electron spin resonance spectroscopy as a probe of anisotropic motion in model membrane systems. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):698–704. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eads T. M., Thomas D. D., Austin R. H. Microsecond rotational motions of eosin-labeled myosin measured by time-resolved anisotropy of absorption and phosphorescence. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):55–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. S., Eriksson L. E., Ehrenberg A. EPR relaxation of slowly moving flavin radicals: "anomalous" saturation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 29;222(3):688–692. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. S., Thomas D. D. New EPR methods for the study of very slow motion: application to spin-labeled hemoglobin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Dec 31;222:680–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb15295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. E., Hyde J. S. 35-GHz (Q-band) saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance studies of rotational diffusion. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2875–2880. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. E., Lee L., Fung L. W. Models for slow anisotropic rotational diffusion in saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance at 9 and 35 GHz. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4459–4467. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith A., Bulfield G., Snipes W. Spin-labeled Neurospora mitochondria. Biophys J. 1970 Jul;10(7):618–629. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86324-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusumi A., Subczynski W. K., Hyde J. S. Oxygen transport parameter in membranes as deduced by saturation recovery measurements of spin-lattice relaxation times of spin labels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1854–1858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. Molecular motion in phospholipid bilayers in the gel phase: long axis rotation. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1632–1637. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi S., Boeyens J. C., McConnell H. M. Spin-labeled hemoglobin crystals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):809–813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna T., Lukiewicz S. The double role of water in quantitative electron spin resonance (ESR) determinations on samples of biological materials. Folia Histochem Cytochem (Krakow) 1971;9(2):203–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel J. C. The effects of actin on the electron spin resonance of spin-labeled myosin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Aug;157(2):588–596. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90678-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Thomas D. D. Applications of new saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance methodology to the rotational dynamics of the Ca-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biophys J. 1986 Apr;49(4):937–942. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83721-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subczynski W. K., Hyde J. S. Diffusion of oxygen in water and hydrocarbons using an electron spin resonance spin-label technique. Biophys J. 1984 Apr;45(4):743–748. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84217-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Seidel J. C., Gergely J., Hyde J. S. The quantitative measurement of rotational motion of the subfragment-1 region of myosin by saturation transfer epr spectroscopy. J Supramol Struct. 1975;3(4):376–390. doi: 10.1002/jss.400030410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


