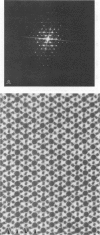
Abstract
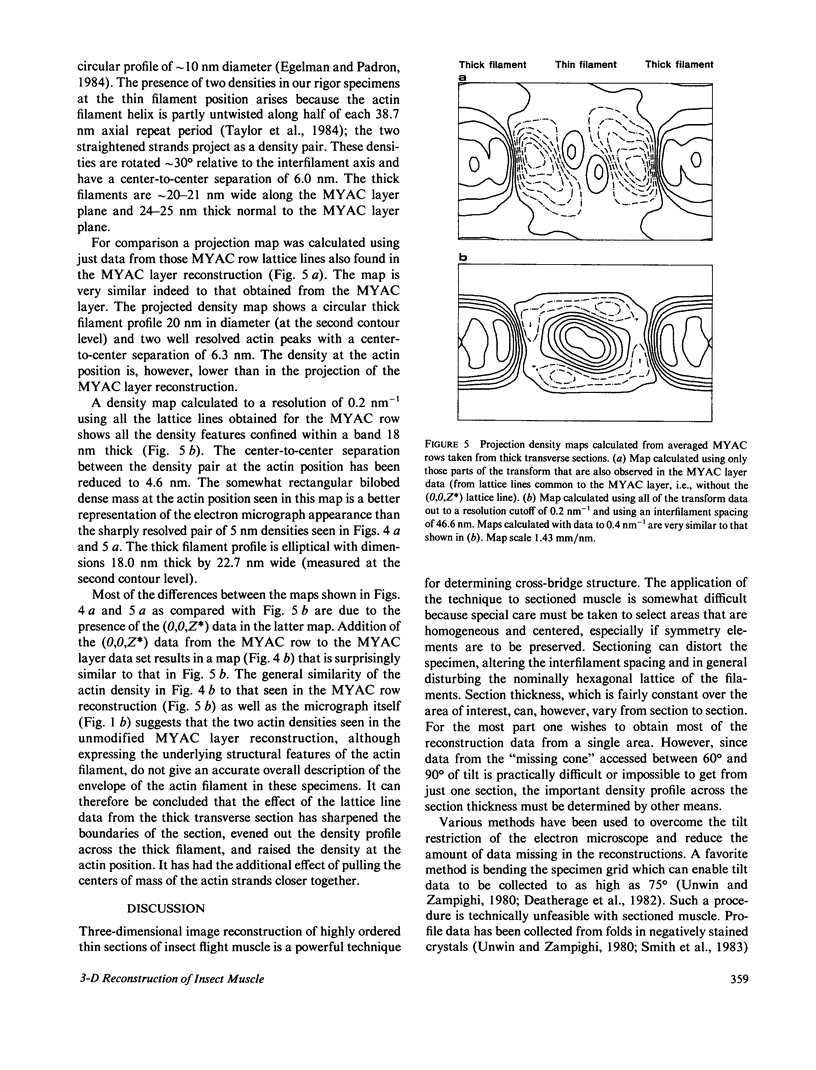
Three-dimensional reconstruction using electron micrographs of thin sections is a powerful technique for determining cross-bridge structure. Tilt restrictions in the electron microscope prevent data collection beyond tilt angles of 60 degrees, giving rise to a "missing cone" of transform data. We show here how much of this data can be obtained using micrographs of thick transverse sections, and the effect this data has on reconstructed images of the insect flight muscle MYAC layer. As a byproduct, the analysis showed that section thinning resulting from prolonged electron irradiation had occurred in the thin longitudinal section used for the previously published MYAC layer reconstruction (Taylor et al., 1984). Comparison of projection density maps calculated from the thin longitudinal section reconstruction and the thick section data show that the data within the missing cone that is not accessible by tilting sharpens the boundaries of the components, flattens the density profile across the thick filament, and enlarges the molecular envelope of the thin filament. We conclude that the reconstructed images of the MYAC layer provide a picture of the structural principles underlying the system but that transform data within the missing cone are necessary to describe accurately the envelopes and profiles of these structural elements.
Full text
PDF

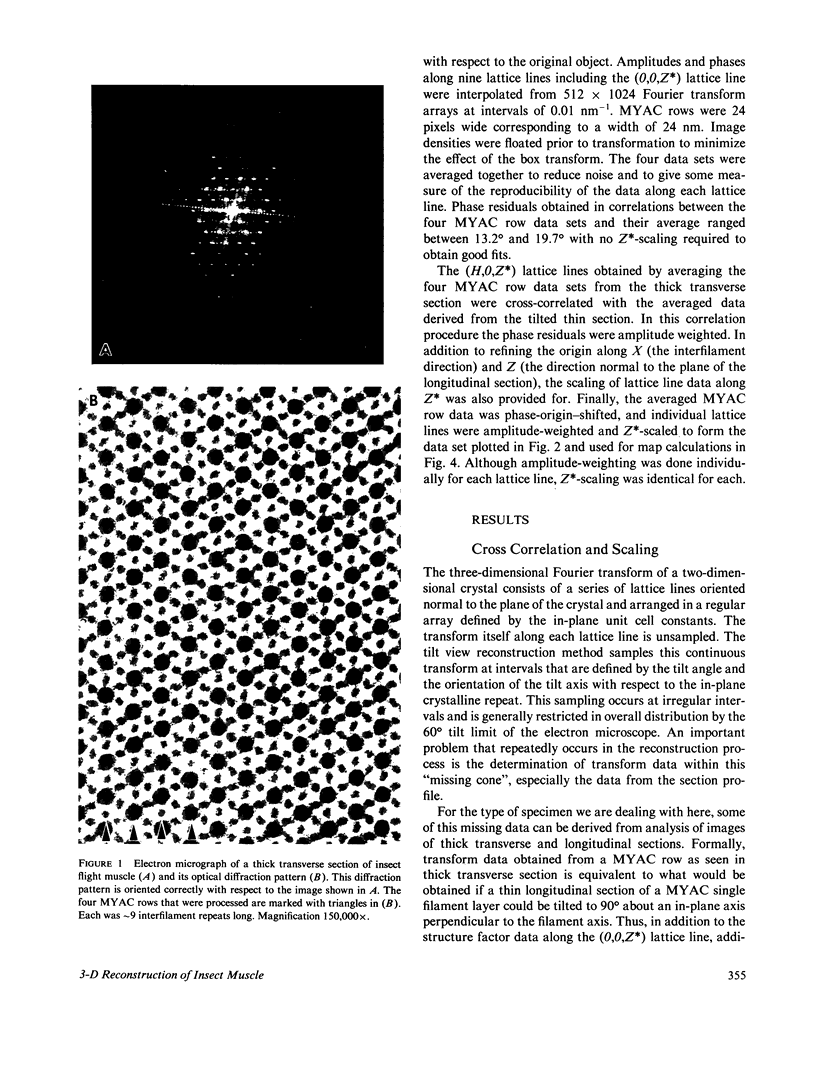
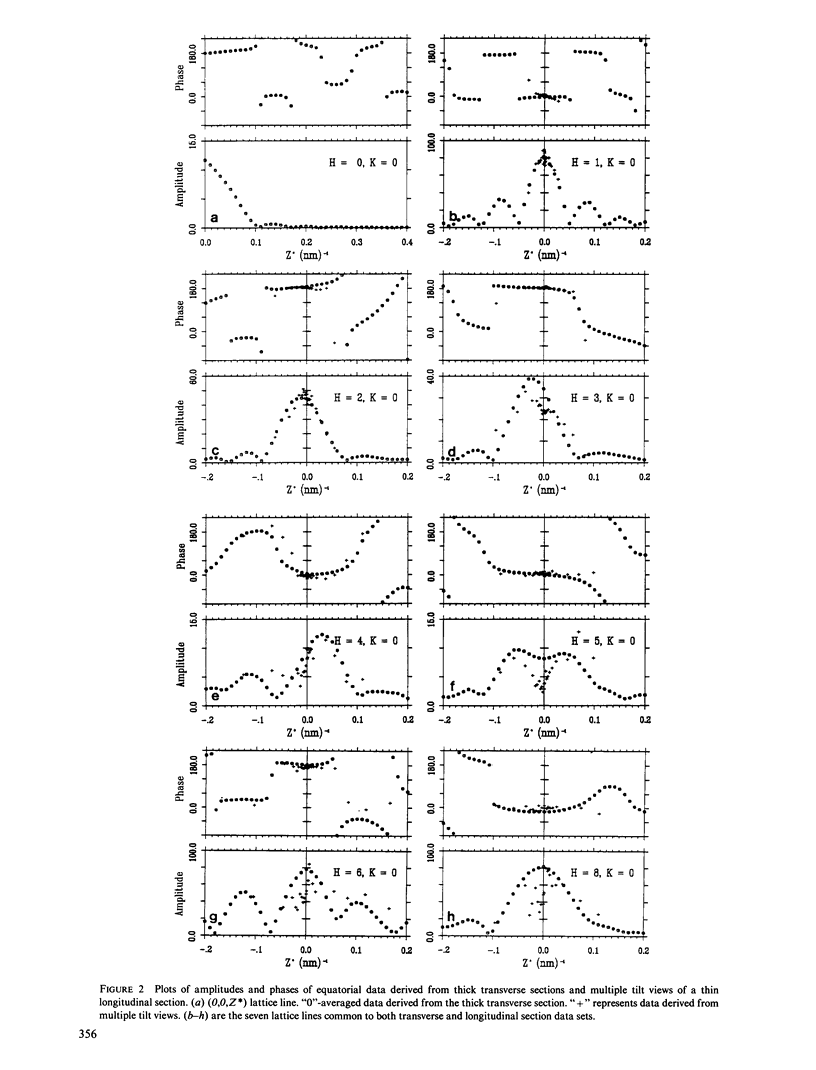

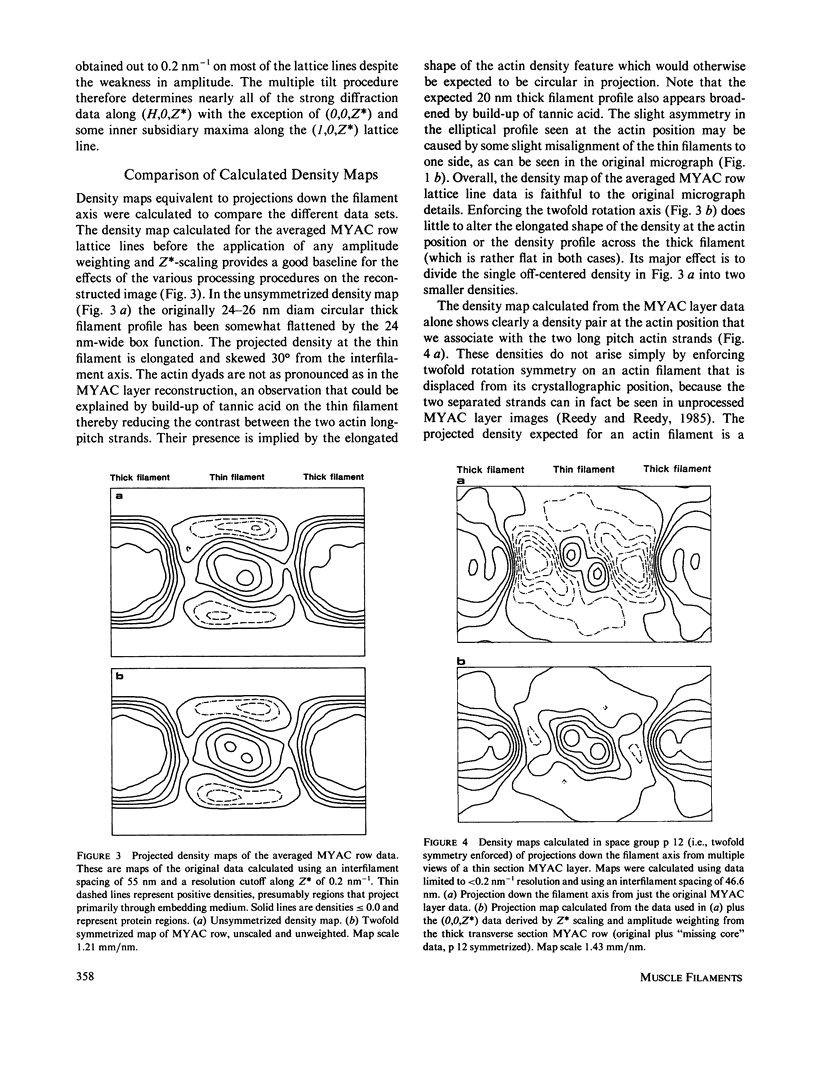



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett P. M. Decrease in section thickness on exposure to the electron beam; the use of tilted sections in estimating the amount of shrinkage. J Cell Sci. 1974 Aug;15(3):693–701. doi: 10.1242/jcs.15.3.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Yu L. C., Podolsky R. J. X-ray diffraction evidence for cross-bridge formation in relaxed muscle fibers at various ionic strengths. Biophys J. 1984 Sep;46(3):299–306. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84026-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Luther P. K. Three-dimensional reconstruction from a single oblique section of fish muscle M-band. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):569–570. doi: 10.1038/307569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deatherage J. F., Taylor K. A., Amos L. A. Three-dimensional arrangement of the cell wall protein of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 15;167(4):823–848. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goody R. S., Holmes K. C., Mannherz H. G., Leigh J. B., Rosenbaum G. Cross-bridge conformation as revealed by x-ray diffraction studies on insect flight muscles with ATP analogues. Biophys J. 1975 Jul;15(7):687–705. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85848-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of purple membrane obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):28–32. doi: 10.1038/257028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E. Structure of the myosin crossbridge lattice in insect flight muscle. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):123–154. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Simmons R. M., Faruqi A. R., Kress M., Bordas J., Koch M. H. Changes in the X-ray reflections from contracting muscle during rapid mechanical transients and their structural implications. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 15;169(2):469–506. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell S. J., Knight P. J., Harrington W. F. Fraction of myosin heads bound to thin filaments in rigor fibrils from insect flight and vertebrate muscles. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):664–666. doi: 10.1038/293664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luther P. K., Crowther R. A. Three-dimensional reconstruction from tilted sections of fish muscle M-band. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):566–568. doi: 10.1038/307566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Huxley H. E., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of F-actin, thin filaments and decorated thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):279–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedy M. C., Reedy M. K., Goody R. S. Co-ordinated electron microscopy and X-ray studies of glycerinated insect flight muscle. II. Electron microscopy and image reconstruction of muscle fibres fixed in rigor, in ATP and in AMPPNP. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Feb;4(1):55–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00711958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedy M. K., Goody R. S., Hofmann W., Rosenbaum G. Co-ordinated electron microscopy and X-ray studies of glycerinated insect flight muscle. I. X-ray diffraction monitoring during preparation for electron microscopy of muscle fibres fixed in rigor, in ATP and in AMPPNP. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Feb;4(1):25–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00711957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedy M. K., Holmes K. C., Tregear R. T. Induced changes in orientation of the cross-bridges of glycerinated insect flight muscle. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1276–1280. doi: 10.1038/2071276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedy M. K. Ultrastructure of insect flight muscle. I. Screw sense and structural grouping in the rigor cross-bridge lattice. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):155–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Fowler W. E., Pollard T. D., Aebi U. Structure of the actin molecule determined from electron micrographs of crystalline actin sheets with a tentative alignment of the molecule in the actin filament. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):641–660. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Amos L. A. A new model for the geometry of the binding of myosin crossbridges to muscle thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):297–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Reedy M. C., Córdova L., Reedy M. K. Three-dimensional reconstruction of rigor insect flight muscle from tilted thin sections. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):285–291. doi: 10.1038/310285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Cooke R., Barnett V. A. Orientation and rotational mobility of spin-labelled myosin heads in insect flight muscle in rigor. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Jun;4(3):367–378. doi: 10.1007/BF00712002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Cooke R. Orientation of spin-labeled myosin heads in glycerinated muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1980 Dec;32(3):891–906. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85024-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima C., Wakabayashi T. Three-dimensional image analysis of the complex of thin filaments and myosin molecules from skeletal muscle. V. Assignment of actin in the actin-tropomyosin-myosin subfragment-1 complex. J Biochem. 1985 Jan;97(1):245–263. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of membrane-bound ribosomes obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):118–122. doi: 10.1038/269118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Zampighi G. Structure of the junction between communicating cells. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):545–549. doi: 10.1038/283545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vibert P., Craig R. Electron microscopy and image analysis of myosin filaments from scallop striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):303–320. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vibert P., Craig R. Three-dimensional reconstruction of thin filaments decorated with a Ca2+-regulated myosin. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 15;157(2):299–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi T., Huxley H. E., Amos L. A., Klug A. Three-dimensional image reconstruction of actin-tropomyosin complex and actin-tropomyosin-troponin T-troponin I complex. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 25;93(4):477–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90241-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida T. Angles of nucleotides bound to cross-bridges in glycerinated muscle fiber at various concentrations of epsilon-ATP, epsilon-ADP and epsilon-AMPPNP detected by polarized fluorescence. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 15;146(4):539–560. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]