Abstract
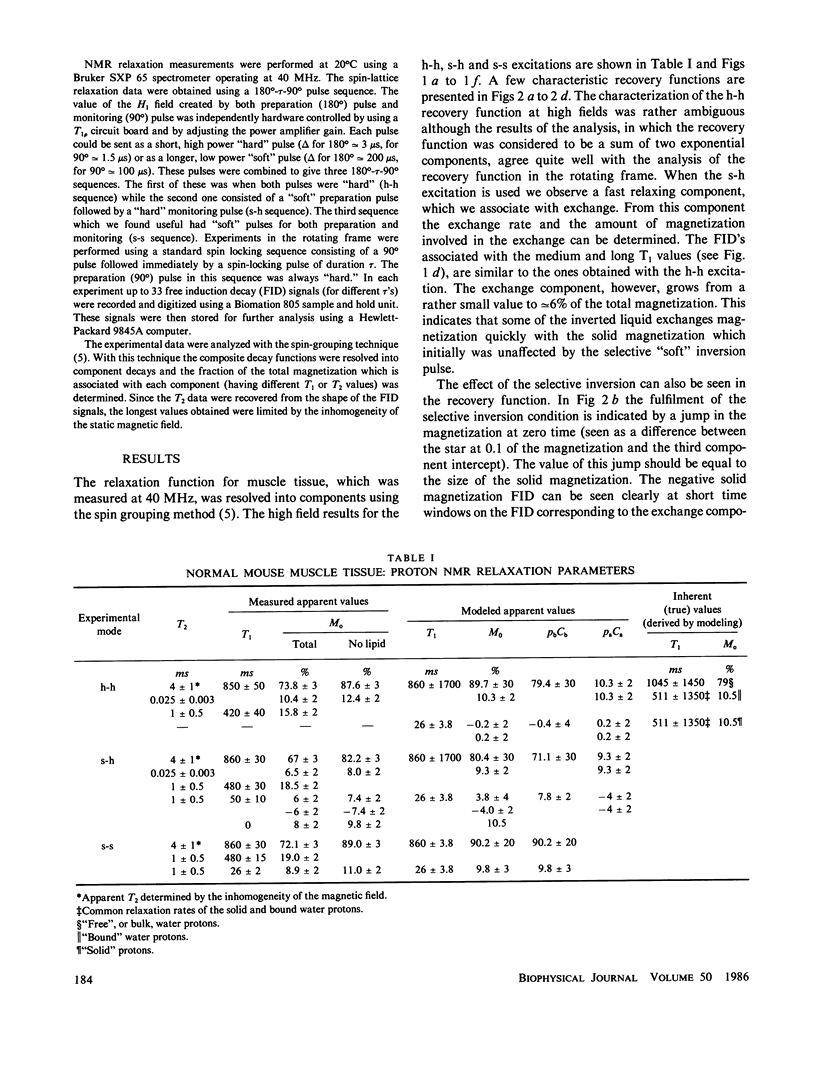
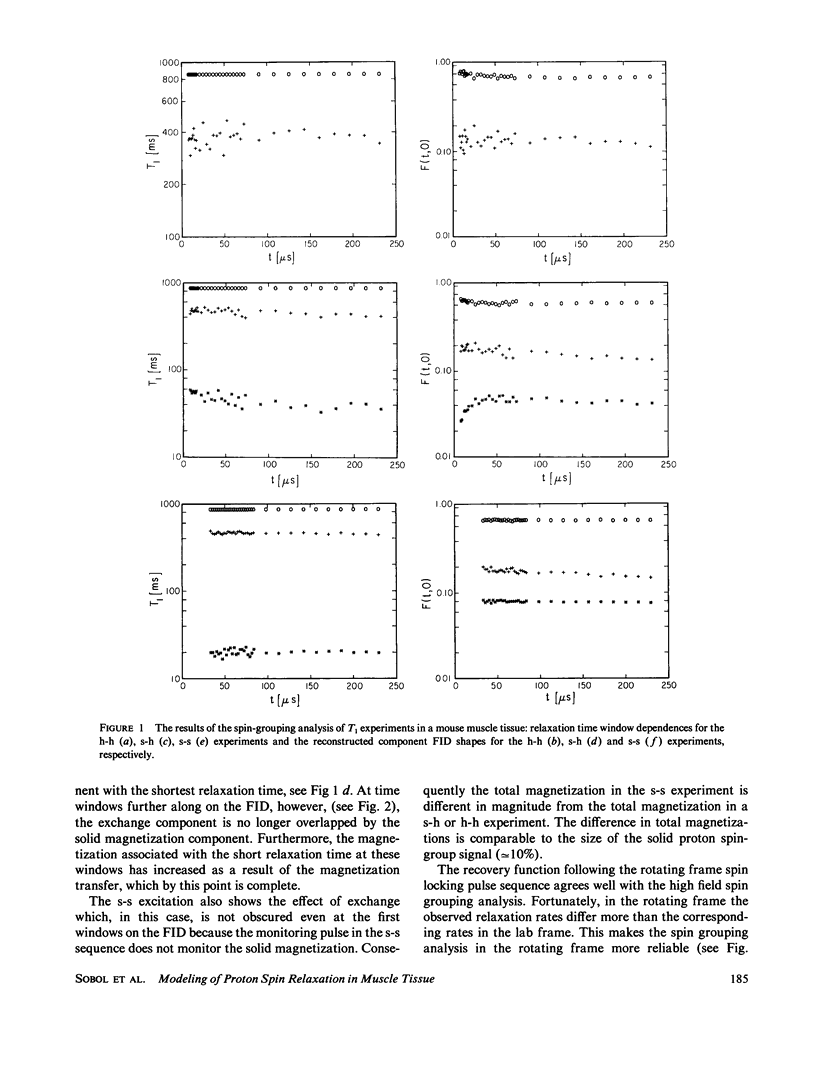
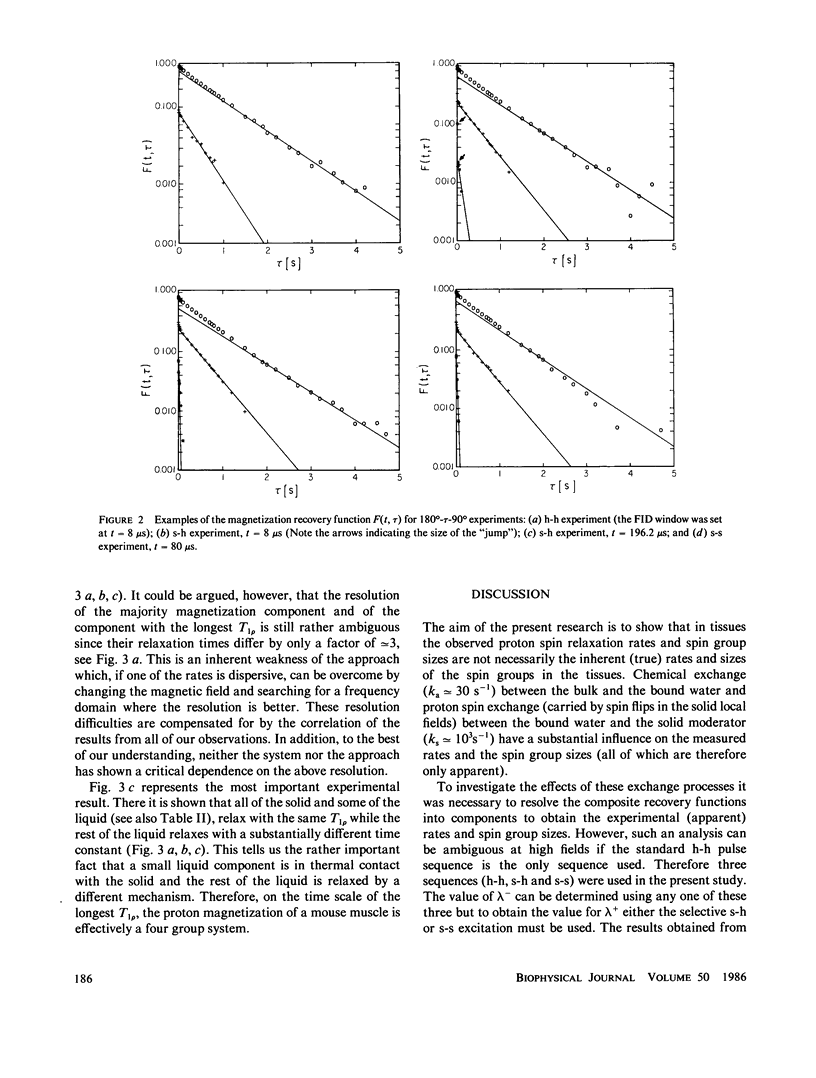
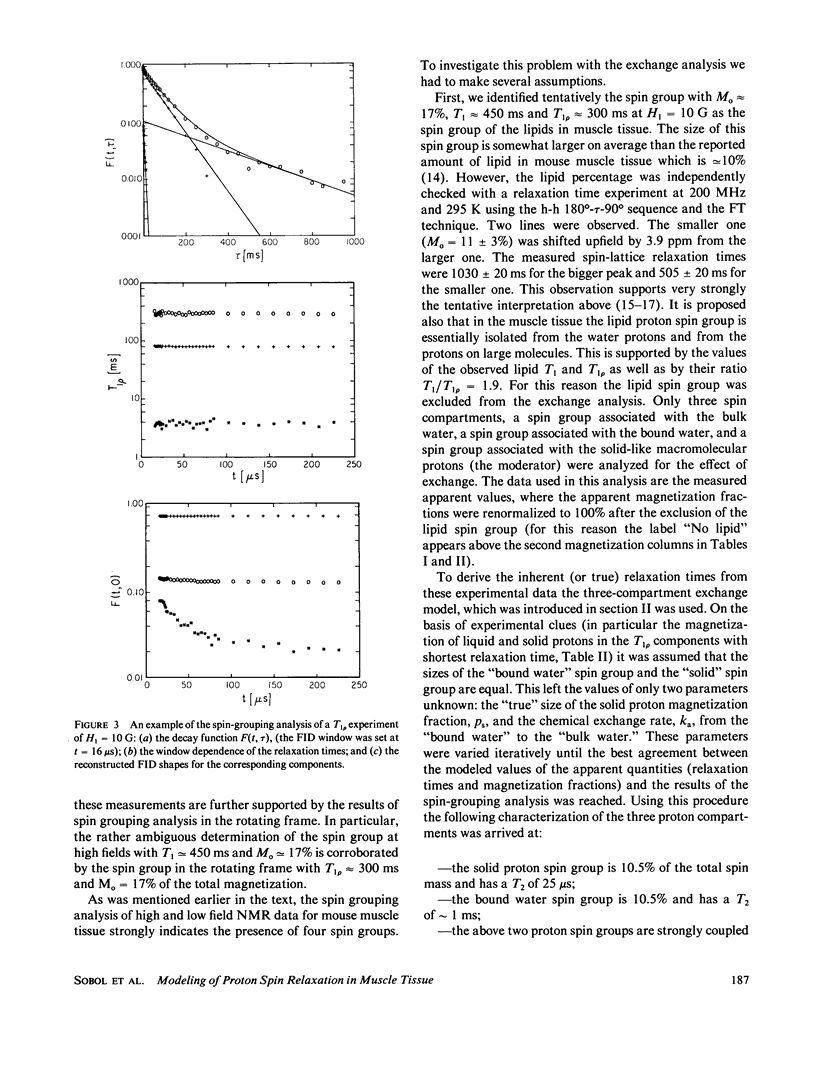
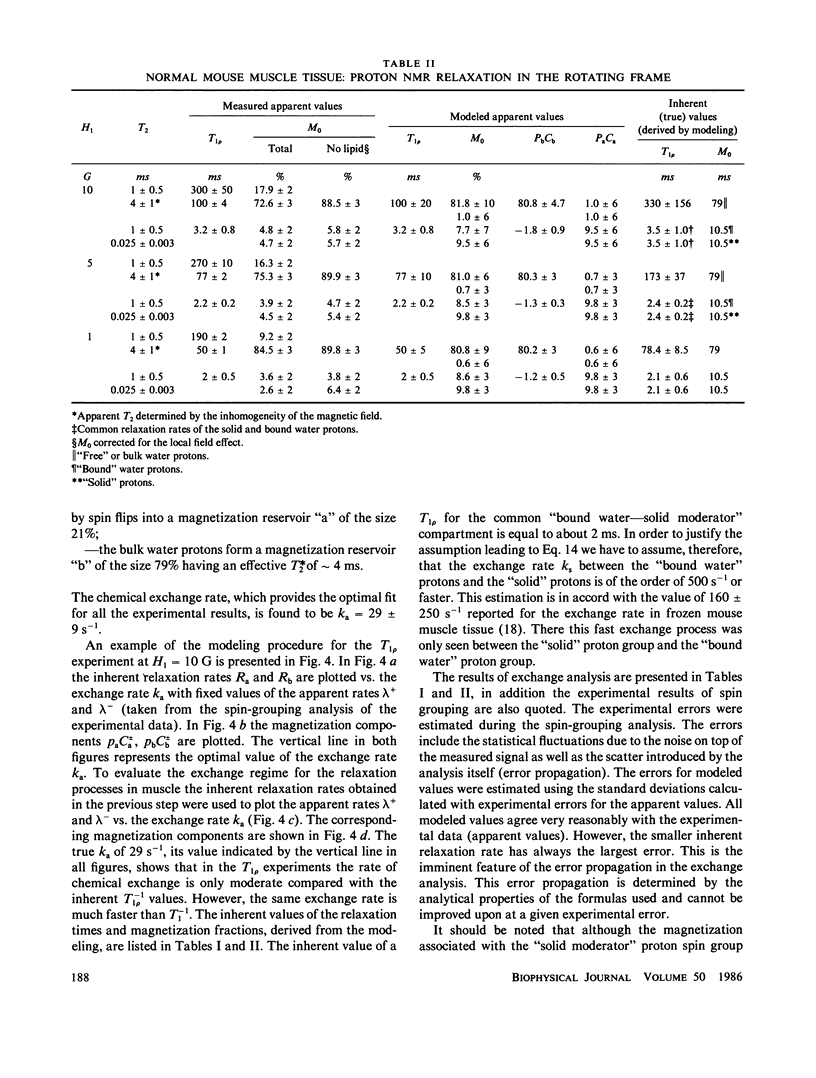
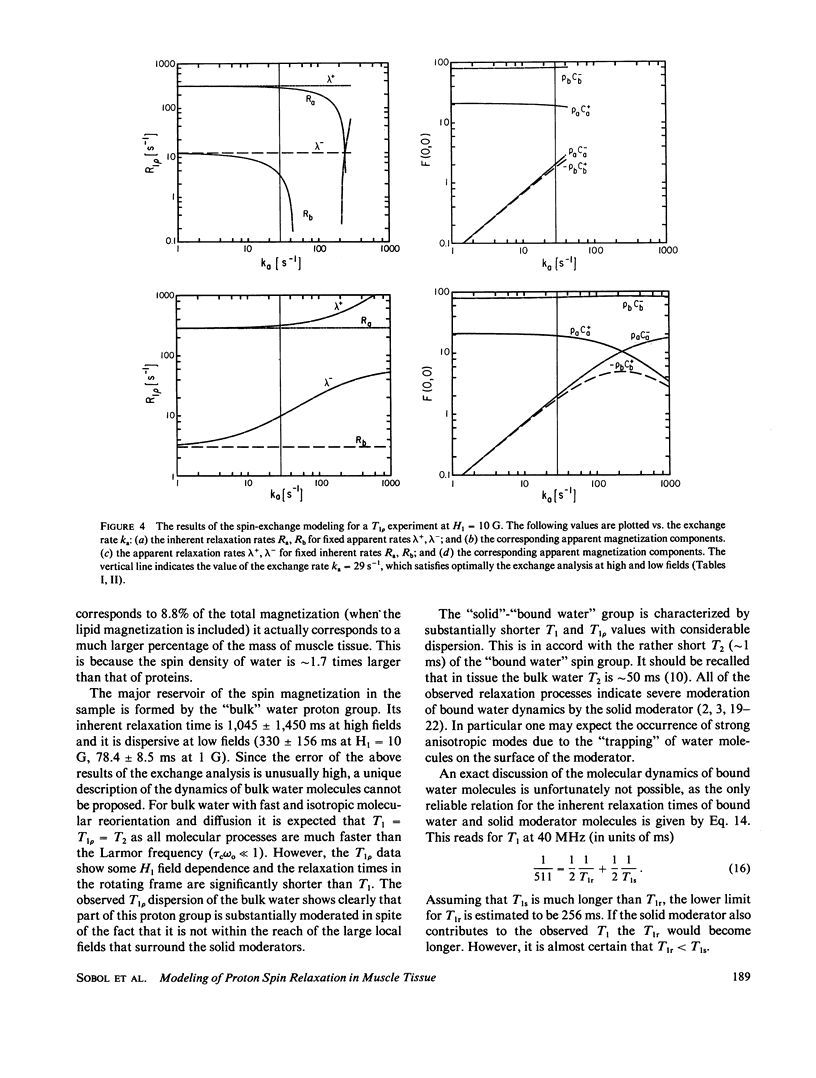
NMR spin relaxation experiments performed on healthy mouse muscle tissue at 40 MHz and 293 K are reported. The spin-lattice relaxation experiments were performed using different combinations of selective and nonselective radio frequency pulses. Relaxation experiments in the rotating frame at H1 = 10, 5 and 1 G are also reported. The experimental results were analyzed using the spin-grouping method, which yields the sizes of the resolved magnetization components as well as their T2's and T1's (or T1p's) for the nonexponential relaxation functions. These results were analyzed further for the exchange between different spin groups. It has been found that to explain all of these experimental data it was necessary to use a four-compartment model of the muscle tissue that consists of a lipid spin group, a "solid-like" spin group (mainly proteins), a "bulk water" spin group and a "bound water" spin group. The chemical exchange rate between "bulk" and "bound" water was found to be 29 +/- 9s-1 at room temperature. The exchange rate between the bound water and the solid moderator was estimated to be approximately 500 s-1.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker C. J., Vriend J. Multi-exponential water proton spin-lattice relaxation in biological tissues and its implications for quantitative NMR imaging. Phys Med Biol. 1984 May;29(5):509–518. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/29/5/003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar K. L., den Hollander J. A., Stromski M. E., Ogino T., Shulman R. G., Petroff O. A., Prichard J. W. High-resolution 1H nuclear magnetic resonance study of cerebral hypoxia in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4945–4948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A., Foster T. H., Argersinger R. E., Pfeifer L. M. A review of normal tissue hydrogen NMR relaxation times and relaxation mechanisms from 1-100 MHz: dependence on tissue type, NMR frequency, temperature, species, excision, and age. Med Phys. 1984 Jul-Aug;11(4):425–448. doi: 10.1118/1.595535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diegel J. G., Pintar M. M. Origin of the nonexponentiality of the water proton spin relaxations in tissues. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):855–860. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85861-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escanye J. M., Canet D., Robert J. Frequency dependence of water proton longitudinal nuclear magnetic relaxation times in mouse tissues at 20 degrees C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 17;721(3):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. D., Homer L. D. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation measurements in frog muscle. Biophys J. 1974 Dec;14(12):907–921. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85958-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. M., McGaughy T. W. Study of spin-lattice and spin-spin relaxation times of 1H, 2H, and 17O in muscular water. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):293–303. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85177-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. M. Proton and deuteron relaxation of muscle water over wide ranges of resonance frequencies. Biophys J. 1977 May;18(2):235–239. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85610-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Chang D. C., Nichols B. L., Woessner D. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation times of water protons in skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1974 Aug;14(8):583–606. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85937-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S. H., Bryant R. G., Hallenga K., Jacob G. S. Magnetic cross-relaxation among protons in protein solutions. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4348–4358. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer K. J. The dynamics of water in heterogeneous systems. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Mar 29;278(959):59–87. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1977.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


