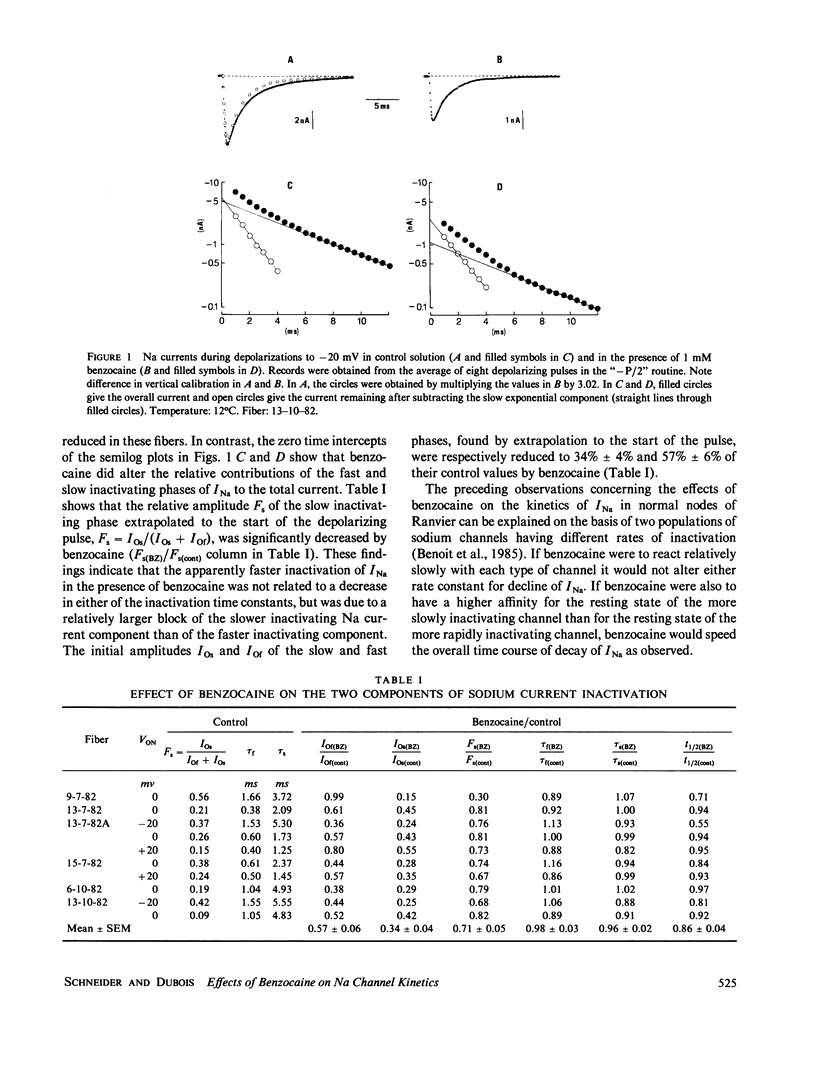
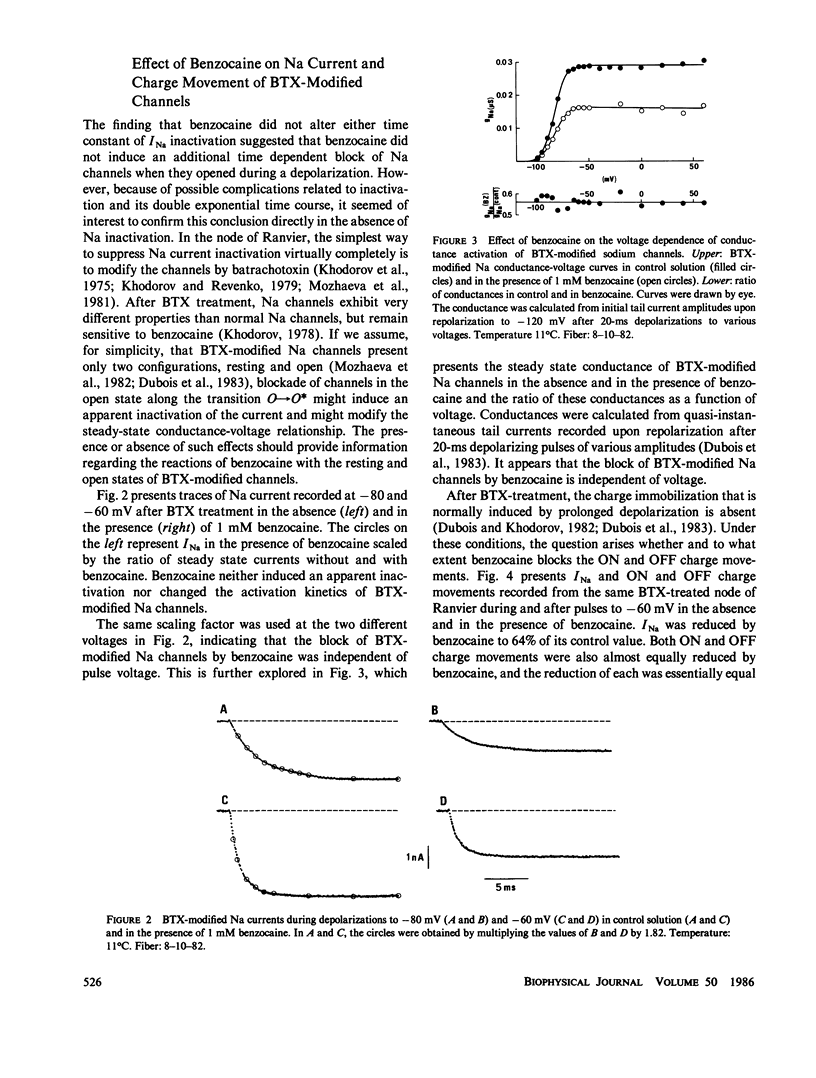
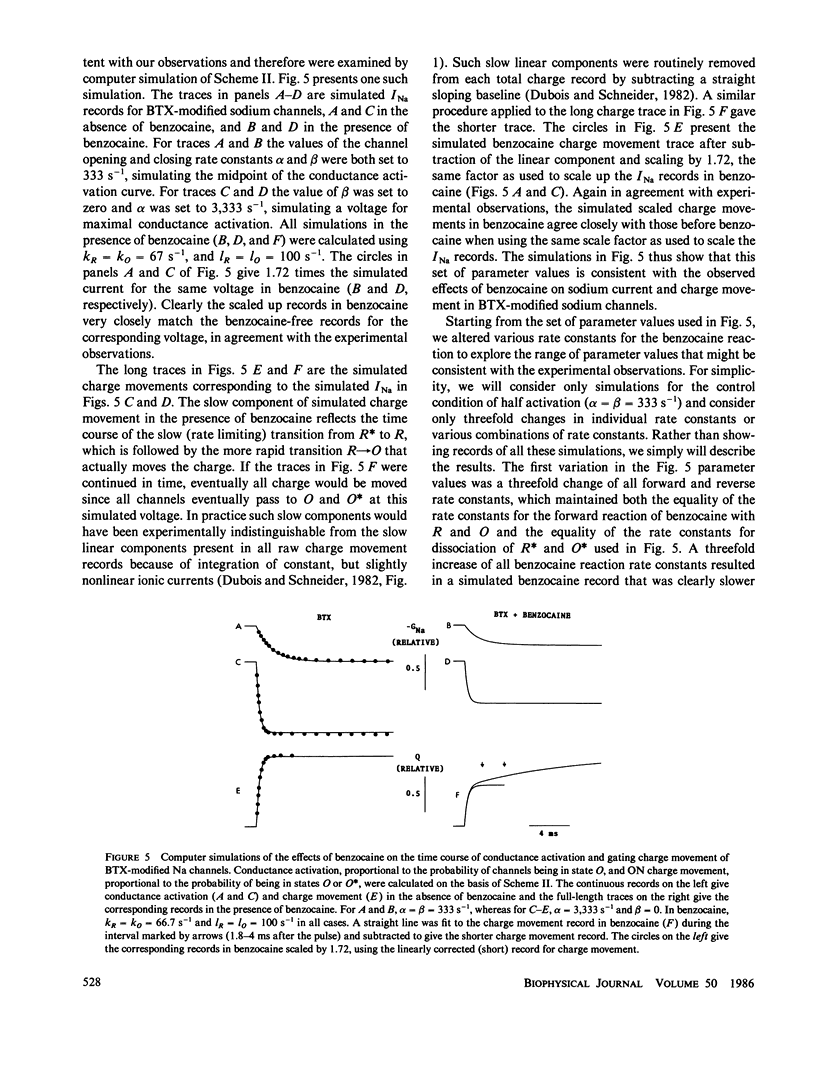
Abstract
The effects of benzocaine (0.5-1 mM) on normal Na currents, and on Na current and gating charge movement (Q) of batrachotoxin (BTX)-modified Na channels were analyzed in voltage-clamped frog node of Ranvier. Without BTX treatment the decay of Na current during pulses to between -40 and 0 mV could be decomposed into two exponential components both in the absence and in the presence of benzocaine. Benzocaine did not significantly alter the inactivation time constant of either component, but reduced both their amplitudes. The amplitude of the slow inactivating component was more decreased by benzocaine than the amplitude of the fast one, leading to an apparently faster decline of the overall Na current. After removal of Na inactivation and charge movement immobilization by BTX, benzocaine decreased the amplitude of INa with no change in time course. INa, QON, and QOFF were all reduced by the same factor. The results suggest that the rate of reaction of benzocaine with its receptor is slow compared to the rates of channel activation and inactivation. The differential effects of benzocaine on the two components of Na current inactivation in normal channels can be explained assuming two types of channel with different rates of inactivation and different affinities for the drug.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arhem P., Frankenhaeuser B. Local anesthetics: effects on permeability properties of nodal membrane in myelinated nerve fibres from xenopus. Potential clamp experiments. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 May;91(1):11–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoit E., Corbier A., Dubois J. M. Evidence for two transient sodium currents in the frog node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Almers W. Interactions between quaternary lidocaine, the sodium channel gates, and tetrodotoxin. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):39–55. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85201-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y. Inactivation of sodium channels: second order kinetics in myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):573–596. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Khodorov B. I. Batrachotoxin protects sodium channels from the blocking action of oenanthotoxin. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):55–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00584968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Schneider M. F., Khodorov B. I. Voltage dependence of intramembrane charge movement and conductance activation of batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels in frog node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jun;81(6):829–844. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.6.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Schneider M. F. Kinetics of intramembrane charge movement and conductance activation of batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels in frog node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Sep;86(3):381–394. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Schneider M. F. Kinetics of intramembrane charge movement and sodium current in frog node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Apr;79(4):571–602. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.4.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Local anesthetics: hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):497–515. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodorov B. I., Peganov E. M., Revenko S. V., Shishkova L. D. Sodium currents in voltage clamped nerve fiber of frog under the combined action of batrachotoxin and procaine. Brain Res. 1975 Feb 14;84(3):541–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90771-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodorov B. I., Revenko S. V. Further analysis of the mechanisms of action of batrachotoxin on the membrane of myelinated nerve. Neuroscience. 1979;4(9):1315–1330. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodorov B. I. Sodium inactivation and drug-induced immobilization of the gating charge in nerve membrane. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1981;37(2):49–89. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumcke B., Schwarz W., Stämpfli R. Block of Na channels in the membrane of myelinated nerve by benzocaine. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Jun;390(3):230–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00658267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumcke B., Schwarz W., Stämpfli R. Modification of sodium inactivation in myelinated nerve by Anemonia toxin II and iodate. Analysis of current fluctuations and current relaxations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 4;600(2):456–466. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumcke B., Stämpfli R. Sodium currents and sodium-current fluctuations in rat myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:163–184. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonner W. Relations between the inactivation of sodium channels and the immobilization of gating charge in frog myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:573–603. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonner W., Rojas E., Stämpfli R. Asymmetrical displacement currents in the membrane of frog myelinated nerve: early time course and effects of membrane potential. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Jun 21;375(1):75–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00584151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs G., Bromm B., Schwarz J. R. A three-state model for inactivation of sodium permeability. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 20;645(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtmayer J., Ulbricht W. Interaction of lidocaine and benzocaine in blocking sodium channels. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Aug;387(1):47–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00580843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Covariance of nonstationary sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. Biophys J. 1981 Apr;34(1):111–133. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84840-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strichartz G. R. The inhibition of sodium currents in myelinated nerve by quaternary derivatives of lidocaine. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jul;62(1):37–57. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


