Abstract
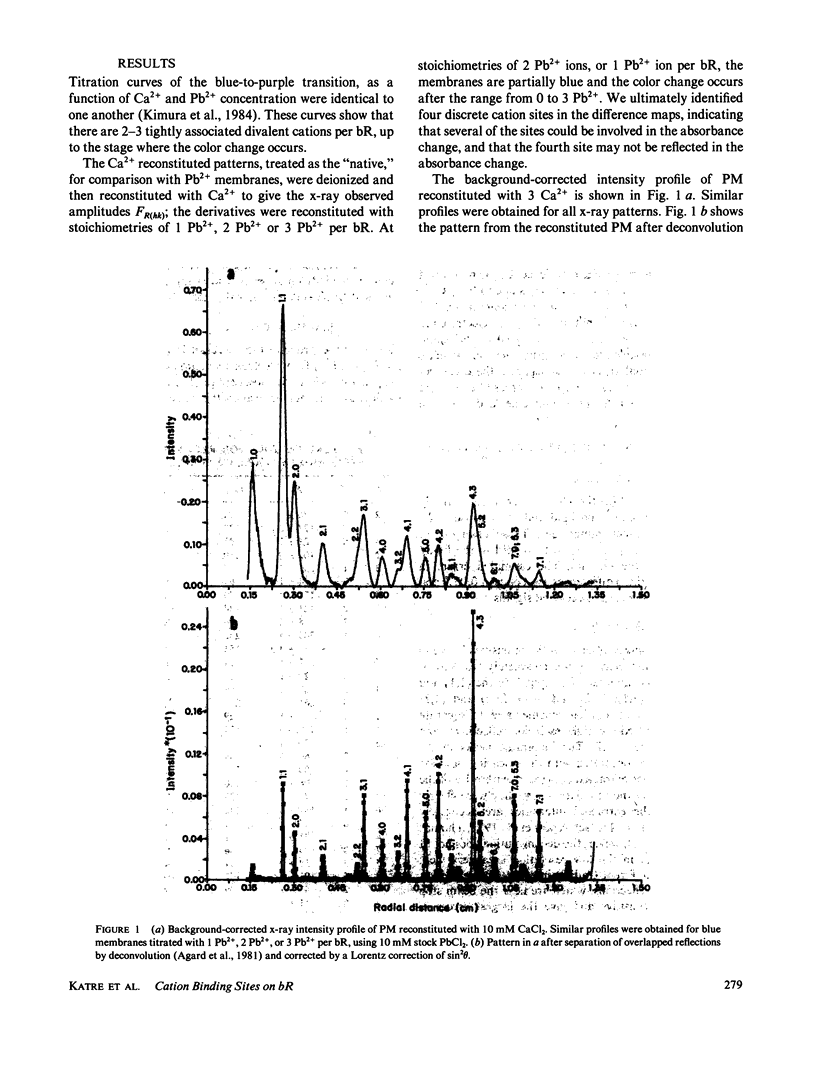
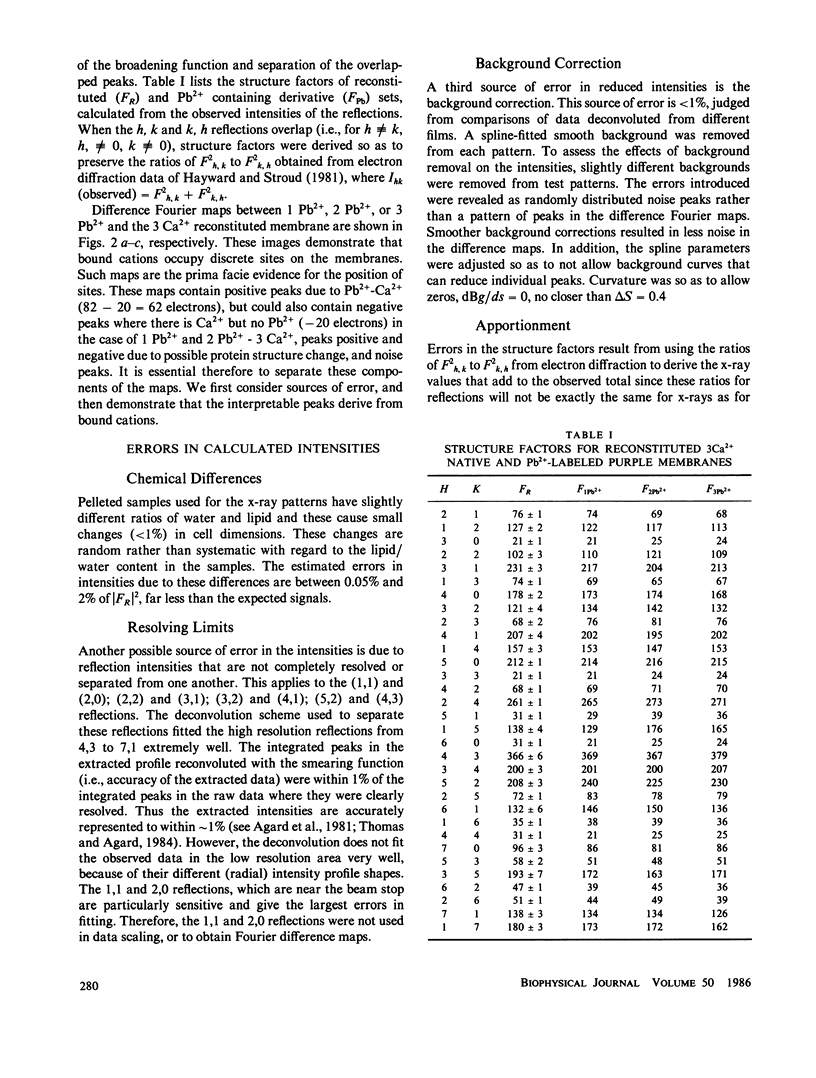
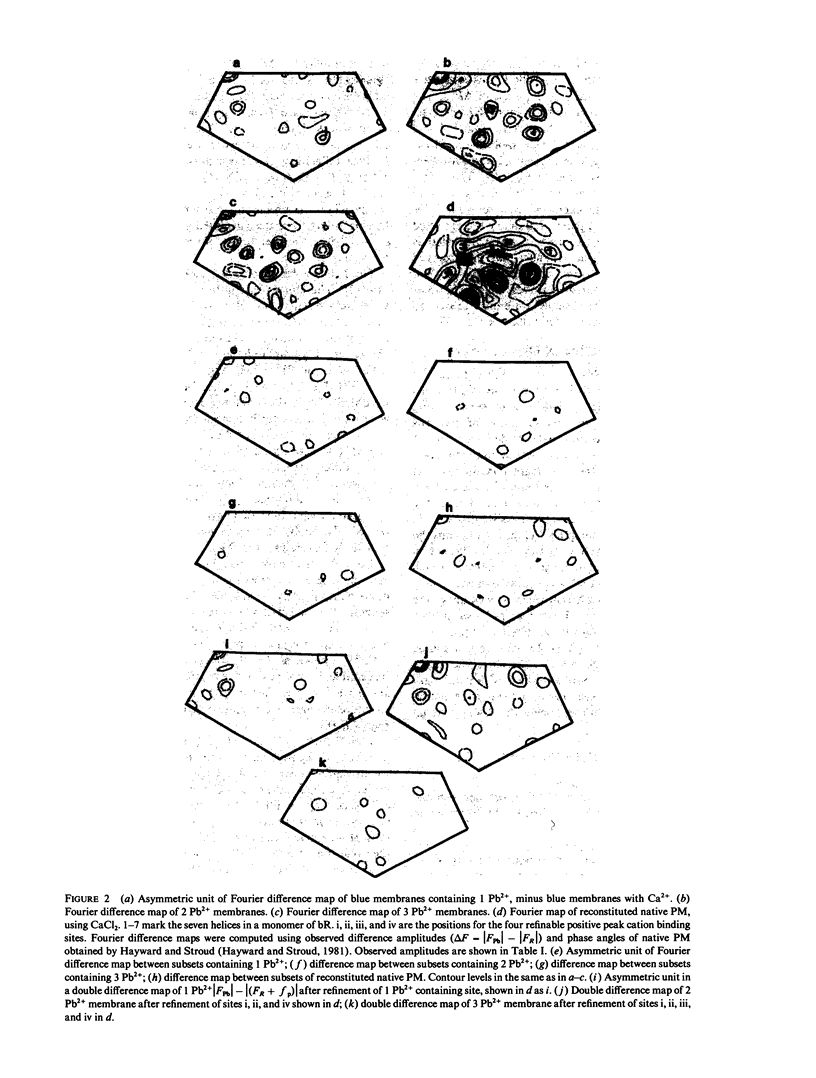
Divalent cations are involved in the function of bacteriorhodopsin (bR) as a light-driven proton pump. If cations are removed from purple membranes they become blue. Divalent cations such as Ca2+ or Pb2+ or trivalent ions, can be stoichiometrically titrated back on to these deionized membranes. The color transitions as a function of ion concentration for Ca2+ or Pb2+ are precisely comparable and indicate that approximately three stoichiometric equivalents of cations are required to effect the color transition (Kimura et al., 1984). We found four main partially occupied binding sites for cations at a stoichiometric ratio of 3 Pb2+/bR. We localized the binding sites for Pb2+ using x-ray diffraction of membranes reconstituted with 1, 2, and 3 equivalents of Pb2+ per bR. The site of highest affinity is located on helix 7. At 2 Pb2+/bR, sites on helix 6 and between helix 2 and 3 are occupied. At 3 Pb2+/bR a fourth site above helix 3 is occupied.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agard D. A., Steinberg R. A., Stroud R. M. Quantitative analysis of electrophoretograms: a mathematical approach to super-resolution. Anal Biochem. 1981 Mar 1;111(2):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90562-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley H., Huang K. S., Radhakrishnan R., Ross A. H., Takagaki Y., Khorana H. G. Site of attachment of retinal in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2225–2229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Chen J. G., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. Cation binding by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):396–400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis P., Corcoran T. C., El-Sayed M. A. Importance of bound divalent cations to the tyrosine deprotonation during the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3662–3664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg B., Berezin Y. Surface potential on purple membranes and its sidedness studied by a resonance Raman dye probe. Biophys J. 1984 Apr;45(4):663–670. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84208-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Henderson R., McLachlan A. D., Wallace B. A. Path of the polypeptide in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2023–2027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Zaccai G. Bacteriorhodopsin is an inside-out protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward S. B., Stroud R. M. Projected structure of purple membrane determined to 3.7 A resolution by low temperature electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):491–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katre N. V., Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M., Hayward S. B. Location of an extrinsic label in the primary and tertiary structure of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84013-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katre N. V., Wolber P. K., Stoeckenius W., Stroud R. M. Attachment site(s) of retinal in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4068–4072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y., Ikegami A., Stoeckenius W. Salt and pH-dependent changes of the purple membrane absorption spectrum. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 Nov;40(5):641–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb05353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathies R., Stryer L. Retinal has a highly dipolar vertically excited singlet state: implications for vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2169–2173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowery P. C., Lozier R. H., Chae Q., Tseng Y. W., Taylor M., Stoeckenius W. Effect of acid pH on the absorption spectra and photoreactions of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4100–4107. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M. J., Klymkowsky M. W., Agard D. A., Stroud R. M. Structural studies of a membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):635–659. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr, Agard D. A. Quantitative analysis of nucleic acids, proteins, and viruses by Raman band deconvolution. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):763–768. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84074-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji K., Rosenheck K. The low pH species of bacteriorhodopsin. Structure and proton pump activity. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Henderson R. Location of the carboxyl terminus of bacteriorhodopsin in purple membrane. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):233–239. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84513-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


