Abstract
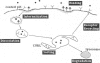
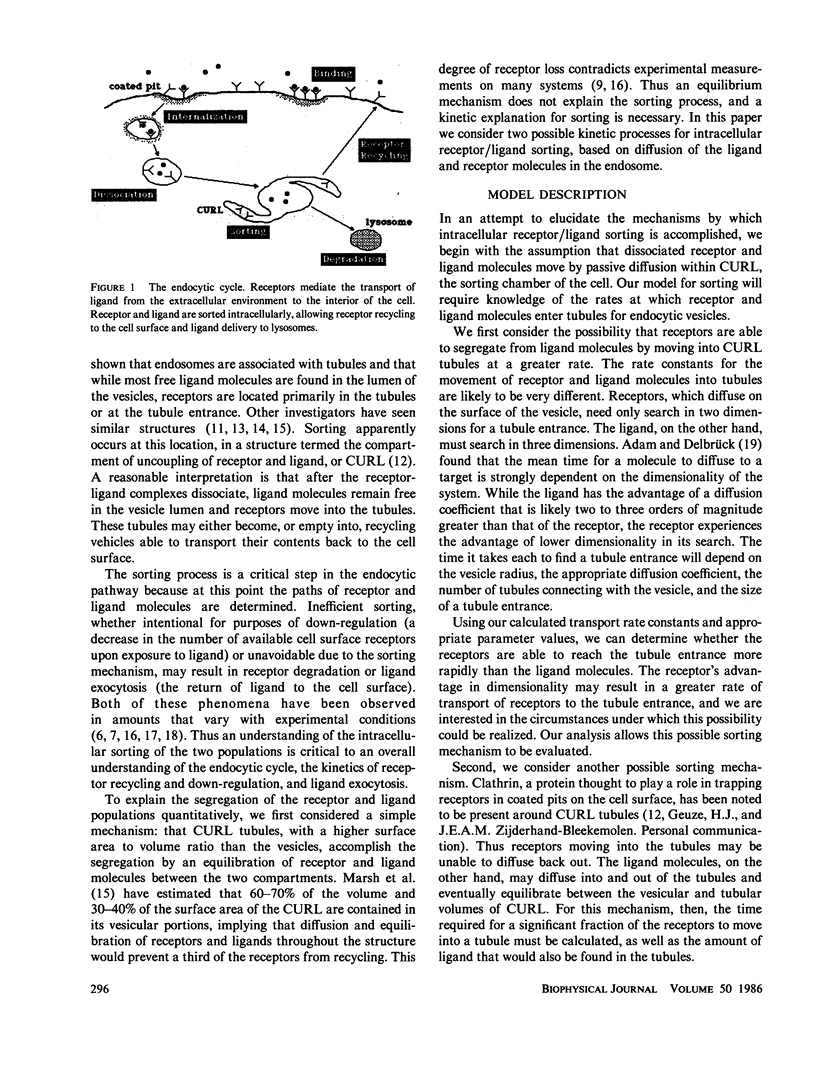
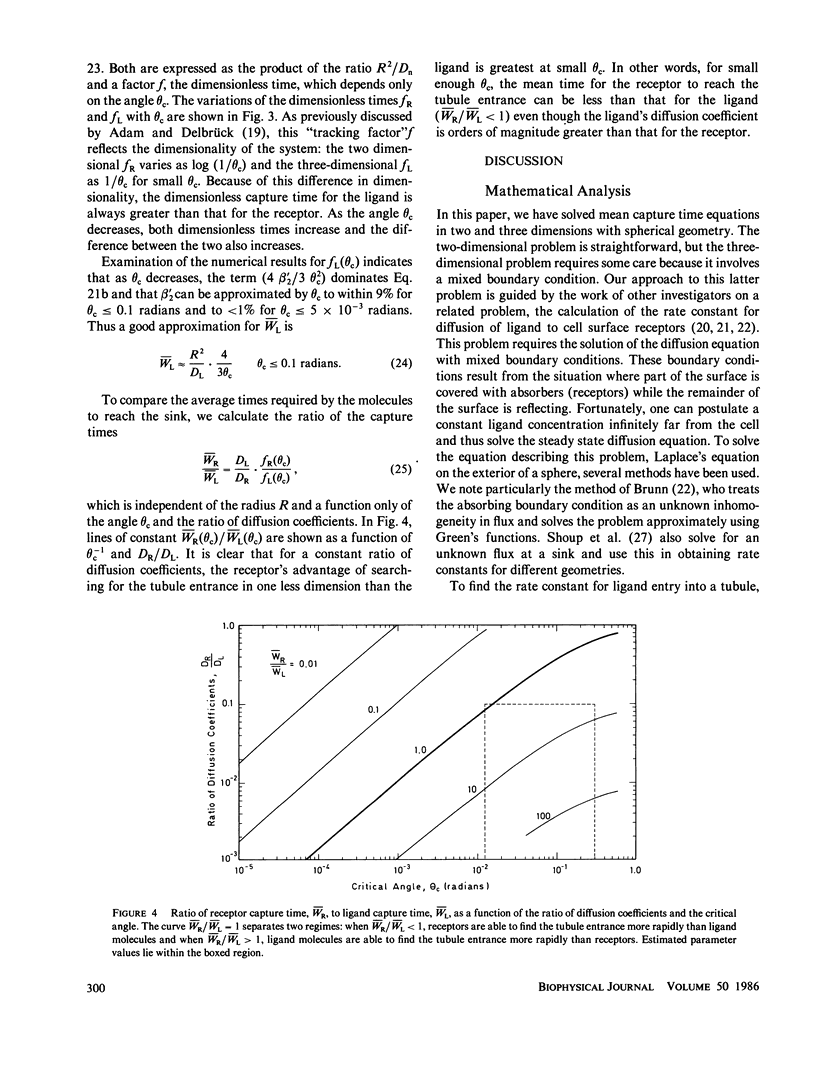
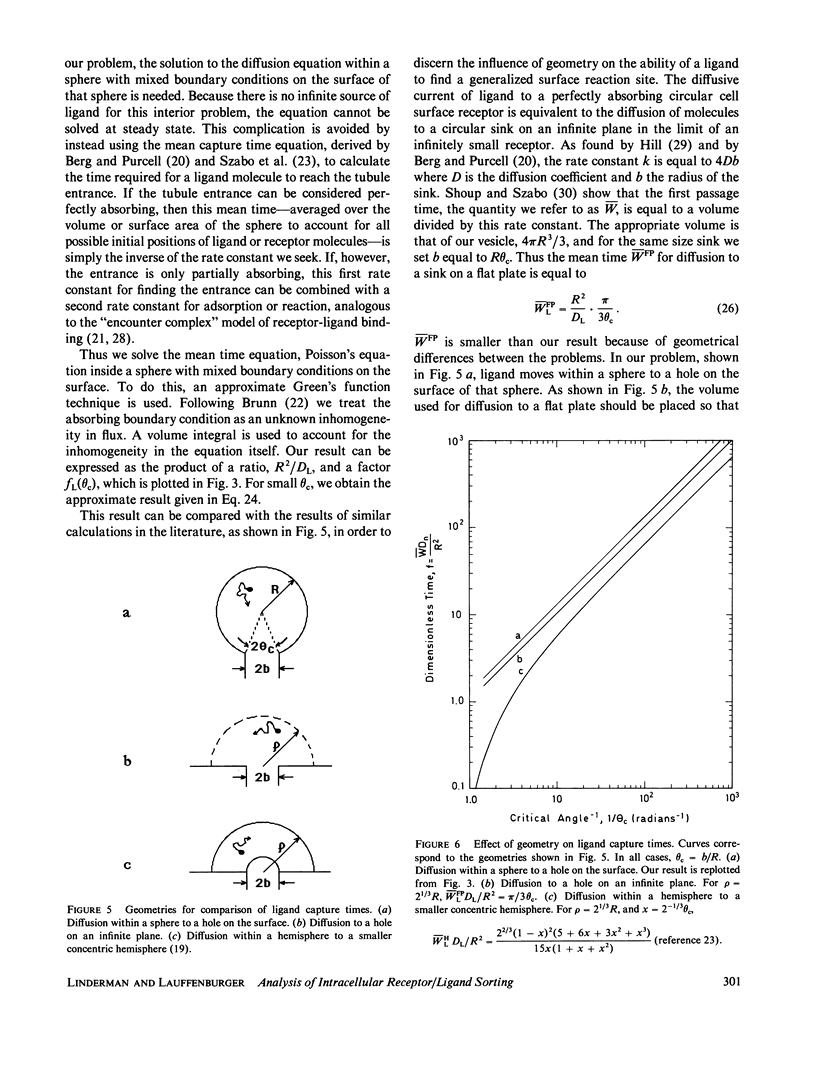
Cell surface receptors bind extracellular ligand molecules and transport those ligands into the cell by a process termed receptor-mediated endocytosis. Receptor and ligand molecules are sorted from one another after endocytosis, apparently within a structure consisting of intracellular vesicles and connected thin tubules. The experimental observation is that most free (unbound) ligand molecules are found in the lumen of the vesicles and receptors are located primarily within the tubules. Because equilibrium and geometric considerations do not explain this segregation, a kinetic scheme involving the passive diffusion of molecules from a vesicle into a tubule is investigated. Two possible sorting mechanisms are considered: first, that receptors are able to move into tubules more rapidly than ligand molecules due to an advantage in dimensionality and, second, that receptors diffusing into tubules are trapped there while ligands are not. Mean diffusion times for receptor and ligand movement into a tubule are calculated by solving Poisson's equation in two and three dimensions, respectively, on the surface of and within a sphere. Using estimated parameter values, we found that only the second scheme is able to account for the experimentally observed sorting. An estimate is obtained for the length of time a tubule and vesicle must be connected in order to remove a significant number of receptors into a tubule. The fraction of free ligand that is "mis-sorted" with the recycling receptor population and thus exocytosed is also determined.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Brown M. S., Beisiegel U., Goldstein J. L. Surface distribution and recycling of the low density lipoprotein receptor as visualized with antireceptor antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):523–531. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Purcell E. M. Physics of chemoreception. Biophys J. 1977 Nov;20(2):193–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85544-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield V. A., Prager S. Diffusion-controlled reactions on spherical surfaces. Application to bacteriophage tail fiber attachment. Biophys J. 1979 Sep;27(3):447–453. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85228-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Directed lipid flow in cell membranes. Nature. 1976 Mar 4;260(5546):21–23. doi: 10.1038/260021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L. Recycling receptors: the round-trip itinerary of migrant membrane proteins. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):663–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunn P. O. Absorption by bacterial cells: interaction between receptor sites and the effect of fluid motion. J Biomech Eng. 1981 Feb;103(1):32–37. doi: 10.1115/1.3138242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daukas G., Lauffenburger D. A., Zigmond S. Reversible pinocytosis in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1642–1650. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C. The biophysics of ligand-receptor interactions. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 May;13(2):201–230. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Wiegel F. W. Effect of nonspecific forces and finite receptor number on rate constants of ligand--cell bound-receptor interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5569–5572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. A., Hubbard A. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of epidermal growth factor by hepatocytes in the perfused rat liver: ligand and receptor dynamics. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2148–2159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Slot J. W., Strous G. J., Lodish H. F., Schwartz A. L. Intracellular site of asialoglycoprotein receptor-ligand uncoupling: double-label immunoelectron microscopy during receptor-mediated endocytosis. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90518-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C., Levy M. A., Stahl P. Morphological analysis of ligand uptake and processing: the role of multivesicular endosomes and CURL in receptor-ligand processing. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;36(2):230–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L. Effect of rotation on the diffusion-controlled rate of ligand-protein association. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4918–4922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Griffiths G., Dean G. E., Mellman I., Helenius A. Three-dimensional structure of endosomes in BHK-21 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2899–2903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S. Kinetics of insulin receptor internalization and recycling in adipocytes. Shunting of receptors to a degradative pathway by inhibitors of recycling. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4136–4144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Plutner H. Internalization and degradation of macrophage Fc receptors bound to polyvalent immune complexes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1170–1177. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Plutner H., Ukkonen P. Internalization and rapid recycling of macrophage Fc receptors tagged with monovalent antireceptor antibody: possible role of a prelysosomal compartment. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1163–1169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka J. A., Weigel P. H. Recycling of the asialoglycoprotein receptor in isolated rat hepatocytes. Dissociation of internalized ligand from receptor occurs in two kinetically and thermally distinguishable compartments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10253–10262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER J. R. Passage of molecules through capillary wals. Physiol Rev. 1953 Jul;33(3):387–423. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1953.33.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Quantitative determination of the lateral diffusion coefficients of the hormone-receptor complexes of insulin and epidermal growth factor on the plasma membrane of cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5353–5357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. L., Fridovich S. E., Lodish H. F. Kinetics of internalization and recycling of the asialoglycoprotein receptor in a hepatoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4230–4237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoup D., Lipari G., Szabo A. Diffusion-controlled bimolecular reaction rates. The effect of rotational diffusion and orientation constraints. Biophys J. 1981 Dec;36(3):697–714. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84759-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoup D., Szabo A. Role of diffusion in ligand binding to macromolecules and cell-bound receptors. Biophys J. 1982 Oct;40(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84455-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons C. F., Jr, Schwartz A. L. Cellular pathways of galactose-terminal ligand movement in a cloned human hepatoma cell line. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):509–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Mellman I. S., Muller W. A., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis and the recycling of plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):1–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tietze C., Schlesinger P., Stahl P. Mannose-specific endocytosis receptor of alveolar macrophages: demonstration of two functionally distinct intracellular pools of receptor and their roles in receptor recycling. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):417–424. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend R. R., Wall D. A., Hubbard A. L., Lee Y. C. Rapid release of galactose-terminated ligands after endocytosis by hepatic parenchymal cells: evidence for a role of carbohydrate structure in the release of internalized ligand from receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):466–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tycko B., Keith C. H., Maxfield F. R. Rapid acidification of endocytic vesicles containing asialoglycoprotein in cells of a human hepatoma line. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1762–1776. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall D. A., Wilson G., Hubbard A. L. The galactose-specific recognition system of mammalian liver: the route of ligand internalization in rat hepatocytes. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):79–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro D. J., Maxfield F. R. Acidification of endocytic compartments and the intracellular pathways of ligands and receptors. J Cell Biochem. 1984;26(4):231–246. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240260404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]