Abstract
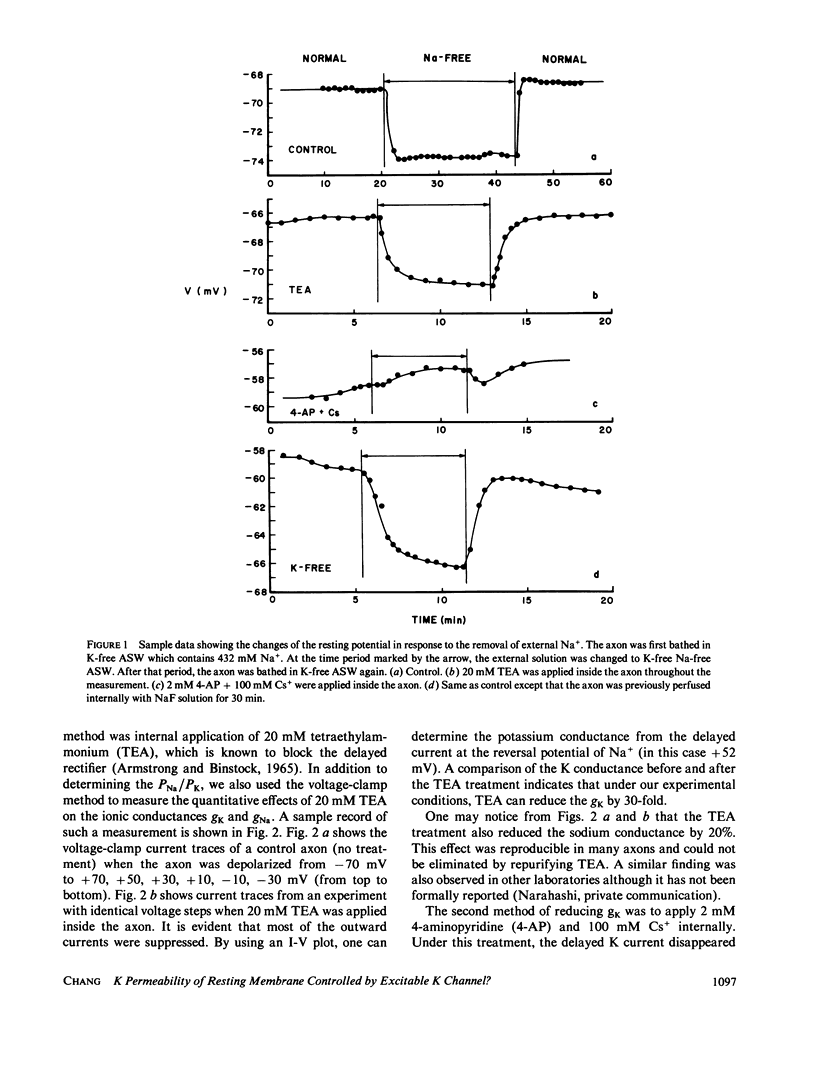
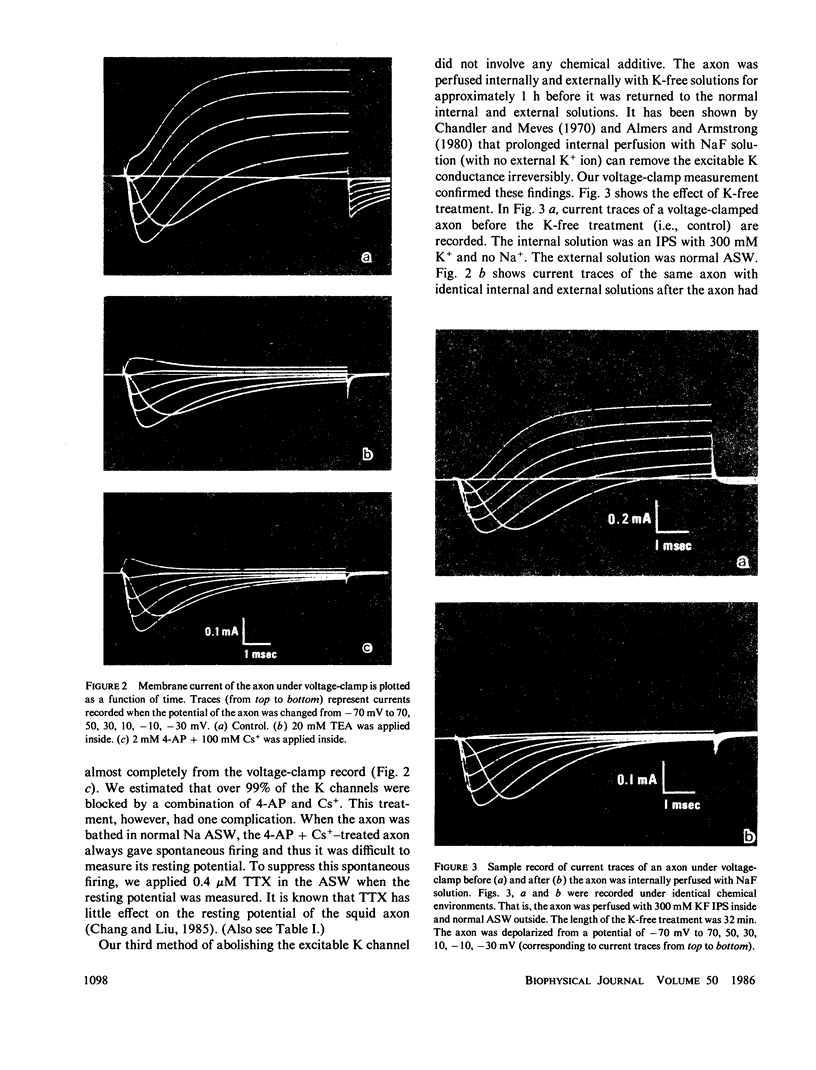
To test whether or not the potassium permeability of the resting membrane is controlled by the excitable K channels (delayed rectifier), we examined changes in the Na and K permeability ratio, PNa/PK, of the squid axon before and after the excitable K channels were blocked. The blockage of the K channels was accomplished by three independent methods: internal application of tetraethylammonium, internal application of 4-aminopyridine plus Cs, and prolong internal perfusion of NaF solution. The permeability ratio was determined using two different methods: the conventional electrophysiological method and a new method based on the measurements of the hyperpolarizing effect of Na removal. We found that blocking the K channels did not cause a proportional decrease in the K permeability of the resting membrane, suggesting that the semipermeable property of the resting membrane is not determined by the excitable K channels.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG C. M., BINSTOCK L. ANOMALOUS RECTIFICATION IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON INJECTED WITH TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:859–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Armstrong C. M. Survival of K+ permeability and gating currents in squid axons perfused with K+-free media. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jan;75(1):61–78. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., MEVES H. THE EFFECT OF DILUTING THE INTERNAL SOLUTION ON THE ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF A PERFUSED GIANT AXON. J Physiol. 1964 Apr;170:541–560. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. The effects of changes in internal ionic concentrations on the electrical properties of perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:355–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Sodium and potassium currents in squid axons perfused with fluoride solutions. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):623–652. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C. Dependence of cellular potential on ionic concentrations. Data supporting a modification of the constant field equation. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84335-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C., Liu J. A comparative study of the effects of tetrodotoxin and the removal of external Na+ on the resting potential: evidence of separate pathways for the resting and excitable Na currents in squid axon. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1985 Dec;5(4):311–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00755398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C., Vyskocil F. The effects of the replacement of K+ by Tl+, Rb+, and NH+4 on the muscle membrane potential. Gen Physiol Biophys. 1984 Jun;3(3):259–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. R. Electrophysiological activity of tetrodotoxin on the resting membrane of the squid giant axon. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1971 Sep 1;40(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(71)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):473–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L. Ionic movements and electrical activity in giant nerve fibres. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):1–37. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T., Albuquerque E. X., Deguchi T. Effects of batrachotoxin on membrane potential and conductance of squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):54–70. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauvé R., Bedfer G., Roy G. Single Ca Dependent K Currents in HeLa Cancer Cells. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):66–68. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84111-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I., HAGIWAR A. S. Demonstration of two stable potential states in the squid giant axon under tetraethylammonium chloride. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Jul 20;40(6):859–885. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.6.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasaki I., Singer I., Takenaka T. Effects of internal and external ionic environment on excitability of squid giant axon. A macromolecular approach. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Jul;48(6):1095–1123. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.6.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


