Abstract
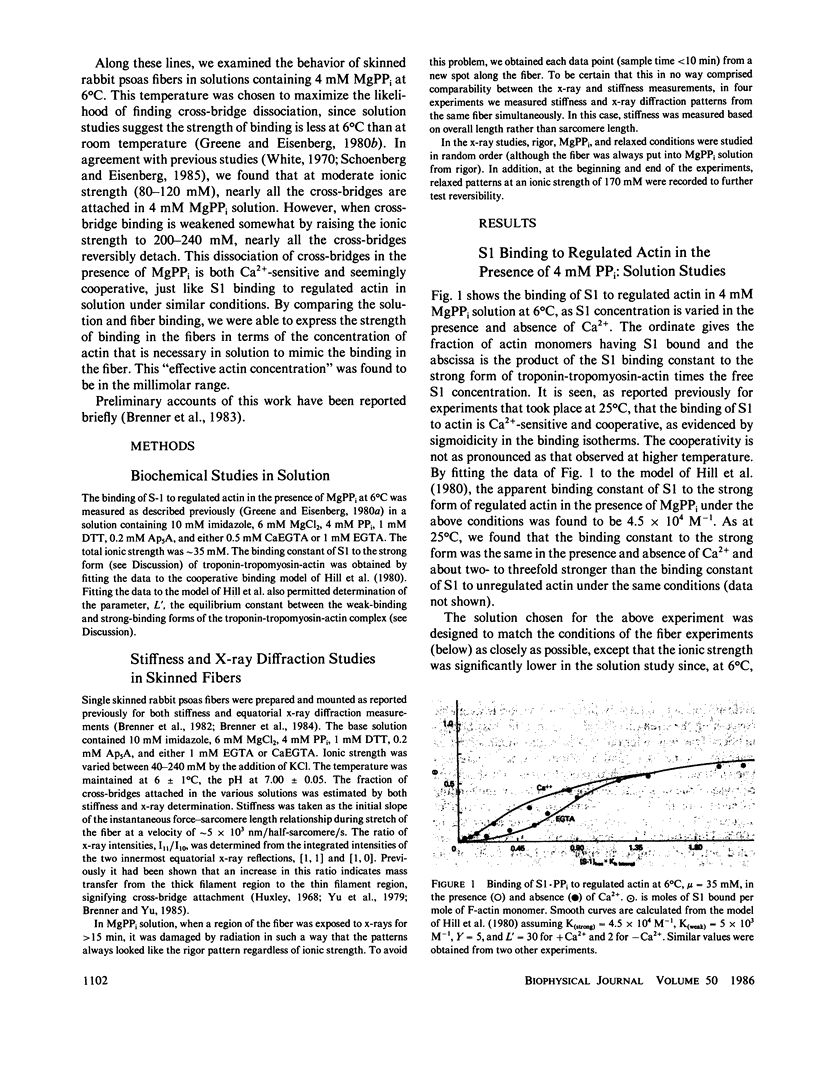
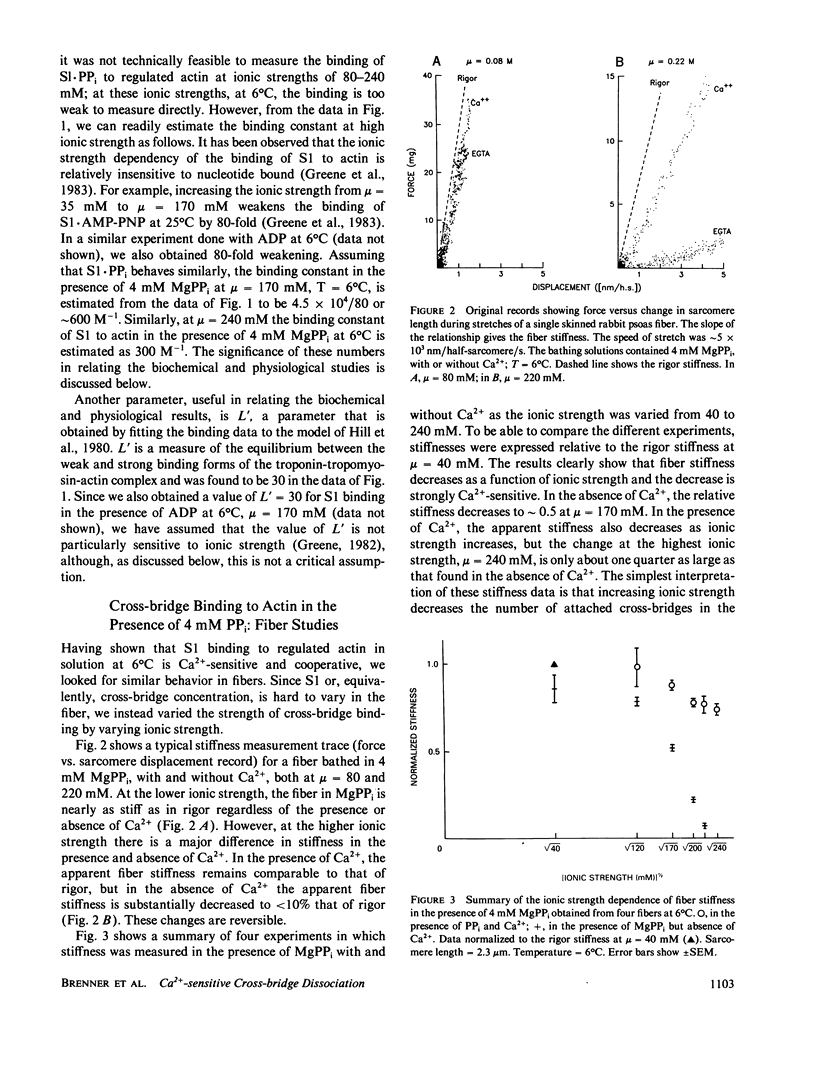
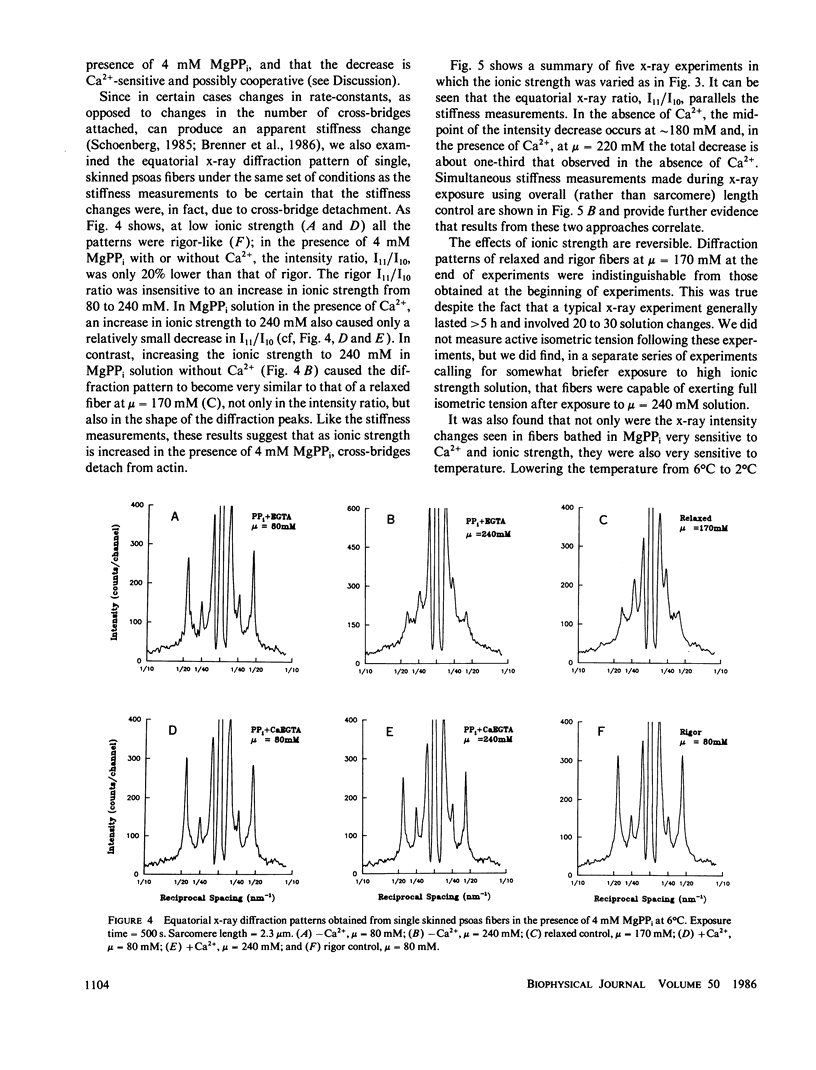
We find that at 6 degrees C in the presence of 4 mM MgPPi, at low or moderate ionic strength, skinned rabbit psoas fibers exhibit a stiffness and an equatorial x-ray diffraction pattern similar to that of rigor fibers. As the ionic strength is increased in the absence of Ca2+, both the stiffness and the equatorial x-ray diffraction pattern approach those of the relaxed state. This suggests that, as in solution, increasing ionic strength weakens the affinity of myosin cross-bridges for actin, which results in a decrease in the number of cross-bridges attached. The effect is Ca2+-sensitive. Assuming that stiffness is a measure of the number of cross-bridge heads attached, in the absence of Ca2+, the fraction of attached cross-bridge heads varies from approximately 75% to approximately 25% over an ionic strength range where ionic strength in solution weakens the binding constant for myosin subfragment-1 binding to unregulated actin by less than a factor of 3. Therefore, this phenomenon appears similar to the cooperative Ca2+-sensitive binding of S1 to regulated actin in solution (Greene, L. E., and E. Eisenberg, 1980, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 77:2616). By comparing the binding constants in solution and in the fiber under similar conditions, we find that the "effective actin concentration," that is, the concentration that gives the same fraction of S1 molecules bound to actin in solution as cross-bridge heads are bound to actin in a fiber, is in the millimolar range. An effective actin concentration in the millimolar range suggests that the strength of actin binding to cross-bridges in fibers may be several orders of magnitude weaker than the strength of ATP binding. Previously, it has been assumed that these two quantities were equal, as this gives the minimum energy loss when ATP dissociates the cross-bridge from actin (Morales, 1980, J. Supramol. Struct., 3:105:1975; Eisenberg, E.,Hill, T. L. and Y. Chen, 1980, Biophys. J., 29:195).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biosca J. A., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Binding of ADP and ATP analogs to cross-linked and non-cross-linked acto X S-1. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9793–9800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E., Schoenberg M. Stiffness of skinned rabbit psoas fibers in MgATP and MgPPi solution. Biophys J. 1986 Oct;50(4):685–691. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83509-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Schoenberg M., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Evidence for cross-bridge attachment in relaxed muscle at low ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7288–7291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Yu L. C. Equatorial x-ray diffraction from single skinned rabbit psoas fibers at various degrees of activation. Changes in intensities and lattice spacing. Biophys J. 1985 Nov;48(5):829–834. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83841-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Yu L. C., Podolsky R. J. X-ray diffraction evidence for cross-bridge formation in relaxed muscle fibers at various ionic strengths. Biophys J. 1984 Sep;46(3):299–306. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84026-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L., Chen Y. Cross-bridge model of muscle contraction. Quantitative analysis. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):195–227. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85126-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. The relation between stiffness and filament overlap in stimulated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:219–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goody R. S., Hofmann W., Mannherz G. H. The binding constant of ATP to myosin S1 fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):317–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E. Comparison of the binding of heavy meromyosin and myosin subfragment 1 in F-actin. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2120–2126. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Cooperative binding of myosin subfragment-1 to the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Dissociation of the actin.subfragment 1 complex by adenyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate, ADP, and PPi. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Formation of a ternary complex: actin, 5'-adenylyl imidodiphosphate, and the subfragments of myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):54–58. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Sellers J. R., Eisenberg E., Adelstein R. S. Binding of gizzard smooth muscle myosin subfragment 1 to actin in the presence and absence of adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):530–535. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. The effect of nucleotide on the binding of myosin subfragment 1 to regulated actin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13993–13999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Eisenberg E., Greene L. Theoretical model for the cooperative equilibrium binding of myosin subfragment 1 to the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3186–3190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann W., Goody R. S. The ternary complex formed between actin, myosin subfragment 1 and ATP (beta, gamma-NH). FEBS Lett. 1978 May 1;89(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80547-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. Structural difference between resting and rigor muscle; evidence from intensity changes in the lowangle equatorial x-ray diagram. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):507–520. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata S., Manuck B. A., Seidel J. C., Gergely J. Saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance study of the mobility of myosin heads in myofibrils under conditions of partial dissociation. Biophys J. 1986 Apr;49(4):821–828. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83711-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata S., Muramatsu K., Higuchi H. Disassembly from both ends of thick filaments in rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. An optical diffraction study. Biophys J. 1985 Mar;47(3):257–266. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83915-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. E. Effect of ethylene glycol and Ca2+ on the binding of Mg2+ x adenyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate to rabbit skeletal myofibrils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):728–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad M., Goody R. S. Kinetic and thermodynamic properties of the ternary complex between F-actin, myosin subfragment 1 and adenosine 5'-[beta, gamma-imido]triphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):547–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Rodger C. D., Tregear R. T. Changes in muscle crossbridges when beta, gamma-imido-ATP binds to myosin. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 14;104(1):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Cooke R. The inhibition of muscle contraction by adenosine 5' (beta, gamma-imido) triphosphate and by pyrophosphate. Biophys J. 1985 Jun;47(6):773–780. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83980-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M., Eisenberg E. Muscle cross-bridge kinetics in rigor and in the presence of ATP analogues. Biophys J. 1985 Dec;48(6):863–871. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83847-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M. Equilibrium muscle cross-bridge behavior. Theoretical considerations. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):467–475. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83802-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleep J., Glyn H. Inhibition of myofibrillar and actomyosin subfragment 1 adenosinetriphosphatase by adenosine 5'-diphosphate, pyrophosphate, and adenyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 11;25(5):1149–1154. doi: 10.1021/bi00353a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawada K., Kimura M. Stiffness of glycerinated rabbit psoas fibers in the rigor state. Filament-overlap relation. Biophys J. 1984 Mar;45(3):593–602. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84197-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. Rigor contraction and the effect of various phosphate compounds on glycerinated insect flight and vertebrate muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):583–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolcott R. G., Boyer P. D. Isotopic probes of catalytic steps of myosin adenosine triphosphatase. J Supramol Struct. 1975;3(2):154–161. doi: 10.1002/jss.400030208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. P., Hartt J. E., Podolsky R. J. Equatorial x-ray intensities and isometric force levels in frog sartorius muscle. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 25;132(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90495-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


