Abstract
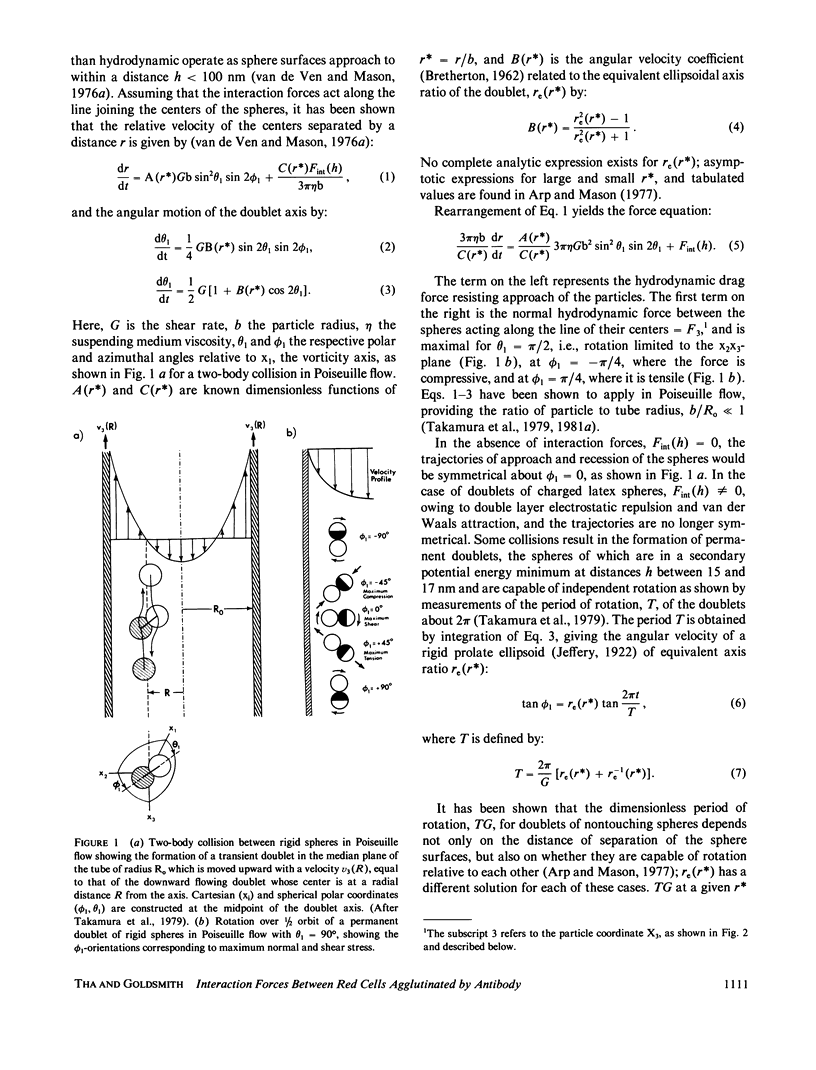
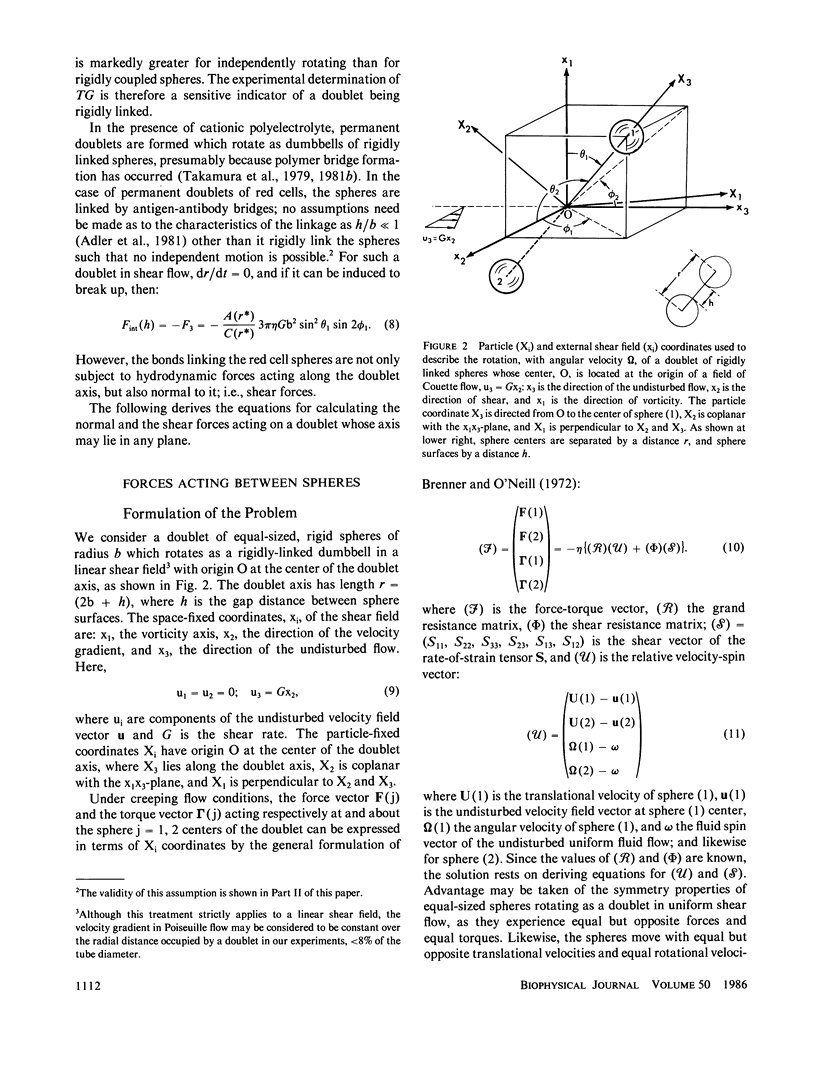
A general method of calculating forces, torques, and translational and rotational velocities of rigid, neutrally buoyant spheres suspended in viscous liquids undergoing a uniform shear flow has been given by Arp and Mason (1977). The method is based on the matrix formulation of hydrodynamic resistances in creeping flow by Brenner and O'Neill (1972). We describe the solution of the Brenner-O'Neill force-torque vector equation in terms of the particle and external flow field coordinates and derive expressions for the normal force acting along, and the shear force acting perpendicular to, the axis of the doublet of spheres, the latter explicitly given for the first time. The equations consist of a term comprising force and torque coefficients obtained from the matrices of the hydrodynamic resistances (functions of the distance h between sphere surfaces which have been computed), and terms comprising the orientation of the doublet axis relative to the coordinates of the external flow field and the shear stress (which can be experimentally determined). We have applied the theory to a system of doublets of sphered, hardened human red cells of group A or B antigenic type cross-linked by the corresponding antibody at a fixed interparticle distance. Working from studies of the breakup of doublets of red cells in an accelerating Poiseuille flow, given in the succeeding paper, we are able to compute the hydrodynamic force required to separate the two spheres. Previous work has shown that the theory can be applied to doublets in a variable shear, Poiseuille flow, provided the ratio of particle to tube diameter is small. In calculating the force-torque coefficients it was assumed that the cells are crosslinked by antibody with h = 20 nm.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science. 1978 May 12;200(4342):618–627. doi: 10.1126/science.347575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bongrand P., Capo C., Benoliel A. M., Depieds R. Evaluation of intercellular adhesion with a very simple technique. J Immunol Methods. 1979;28(1-2):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. E., Goodwin J. W., Seaman G. V. Interactions among erythrocytes under shear. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Feb;28(2):172–177. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.2.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum K., Evans E., Brooks D. E. Quantitation of surface affinities of red blood cells in dextran solutions and plasma. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3235–3239. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capo C., Garrouste F., Benoliel A. M., Bongrand P., Ryter A., Bell G. I. Concanavalin-A-mediated thymocyte agglutination: a model for a quantitative study of cell adhesion. J Cell Sci. 1982 Aug;56:21–48. doi: 10.1242/jcs.56.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Jan K. Ultrastructural basis of the mechanism of rouleaux formation. Microvasc Res. 1973 Mar;5(2):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(73)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Sung L. A., Kim S., Burke A. M., Usami S. Determination of aggregation force in rouleaux by fluid mechanical technique. Microvasc Res. 1977 May;13(3):327–333. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Sung L. A., Simchon S., Lee M. M., Jan K. M., Skalak R. Energy balance in red cell interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983;416:190–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb35189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis A. S. On the occurrence of specific adhesion between cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1970 Feb;23(1):253–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis A. S. The measurement of cell adhesiveness by an absolute method. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1969 Nov;22(3):305–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economidou J., Hughes-Jones N. C., Gardner B. Quantitative measurements concerning A and B antigen sites. Vox Sang. 1967 May;12(5):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1967.tb03362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Minimum energy analysis of membrane deformation applied to pipet aspiration and surface adhesion of red blood cells. Biophys J. 1980 May;30(2):265–284. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85093-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Parsegian V. A. Energetics of membrane deformation and adhesion in cell and vesicle aggregation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983;416:13–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb35176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Buxbaum K. Affinity of red blood cell membrane for particle surfaces measured by the extent of particle encapsulation. Biophys J. 1981 Apr;34(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84834-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Leung A. Adhesivity and rigidity of erythrocyte membrane in relation to wheat germ agglutinin binding. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1201–1208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein A., Munn E. A. Conformation of the free and antigen-bound IgM antibody molecules. Nature. 1969 Dec 27;224(5226):1307–1309. doi: 10.1038/2241307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerche D. The role of electrostatic and structural properties of the cell surface in the energetics of cell-cell and cell-surface interaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983;416:66–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb35179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Levine M., Sharp K. A., Brooks D. E. Theory of the electrokinetic behavior of human erythrocytes. Biophys J. 1983 May;42(2):127–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84378-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schönbein H., Volger E., Klose H. J. Microrheology and light transmission of blood. II. The photometric quantification of red cell aggregate formation and dispersion in flow. Pflugers Arch. 1972;333(2):140–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00586913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J., Absolom D. R. Zeta potentials, van der Waals forces and hemagglutination. Vox Sang. 1983 Mar;44(3):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb01883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


