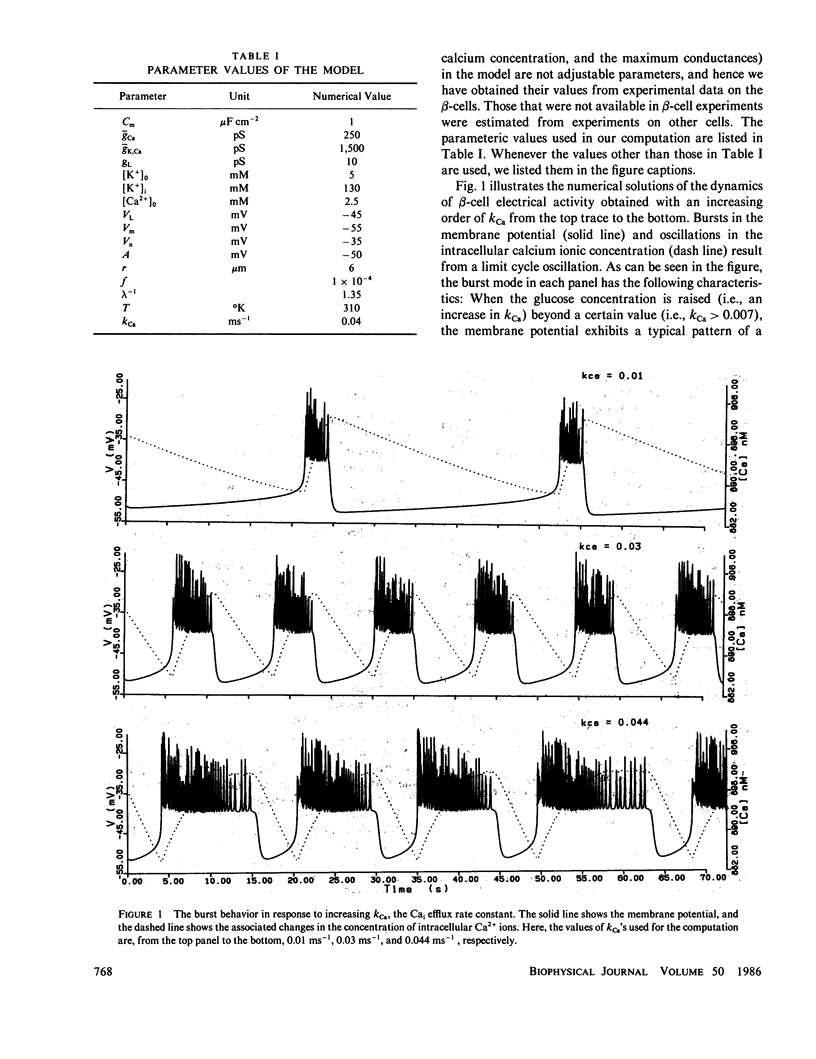
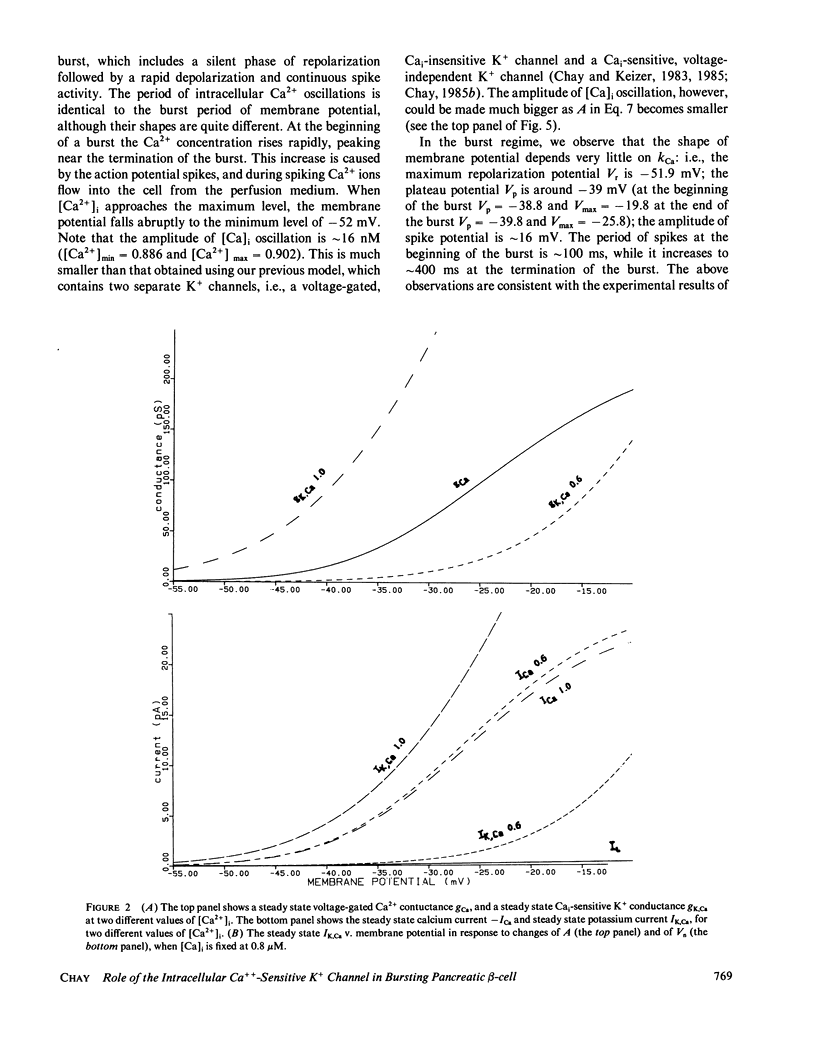
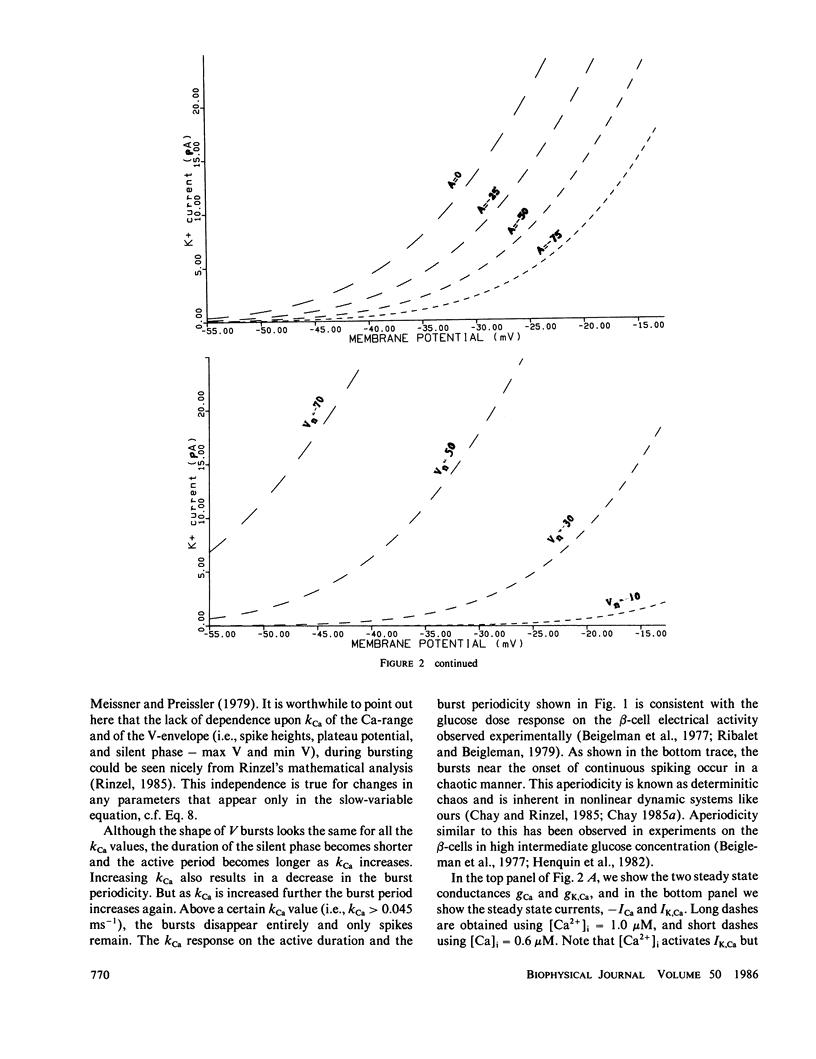
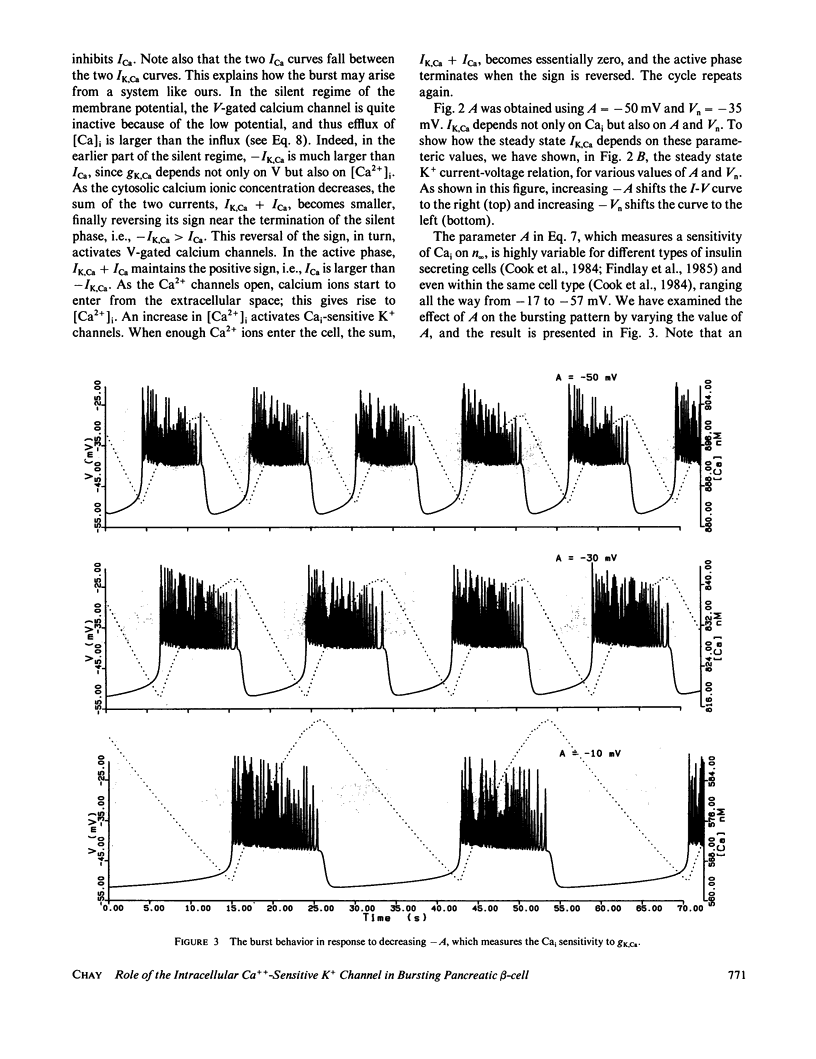
Abstract
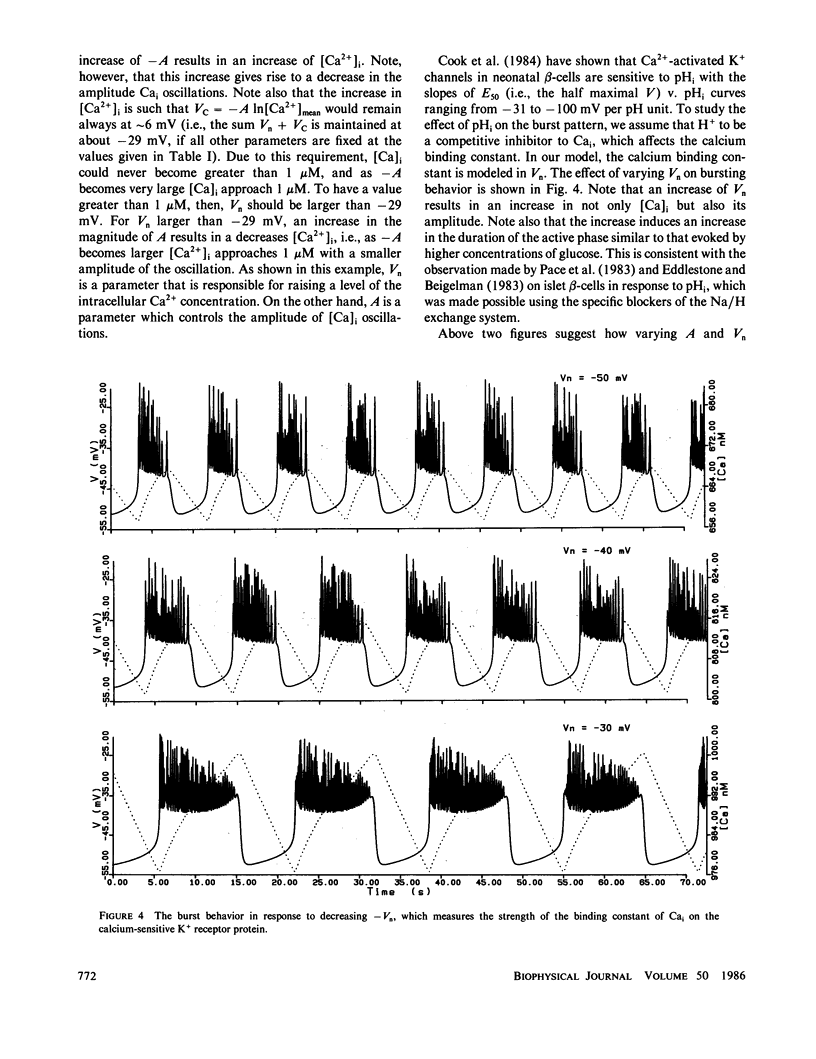
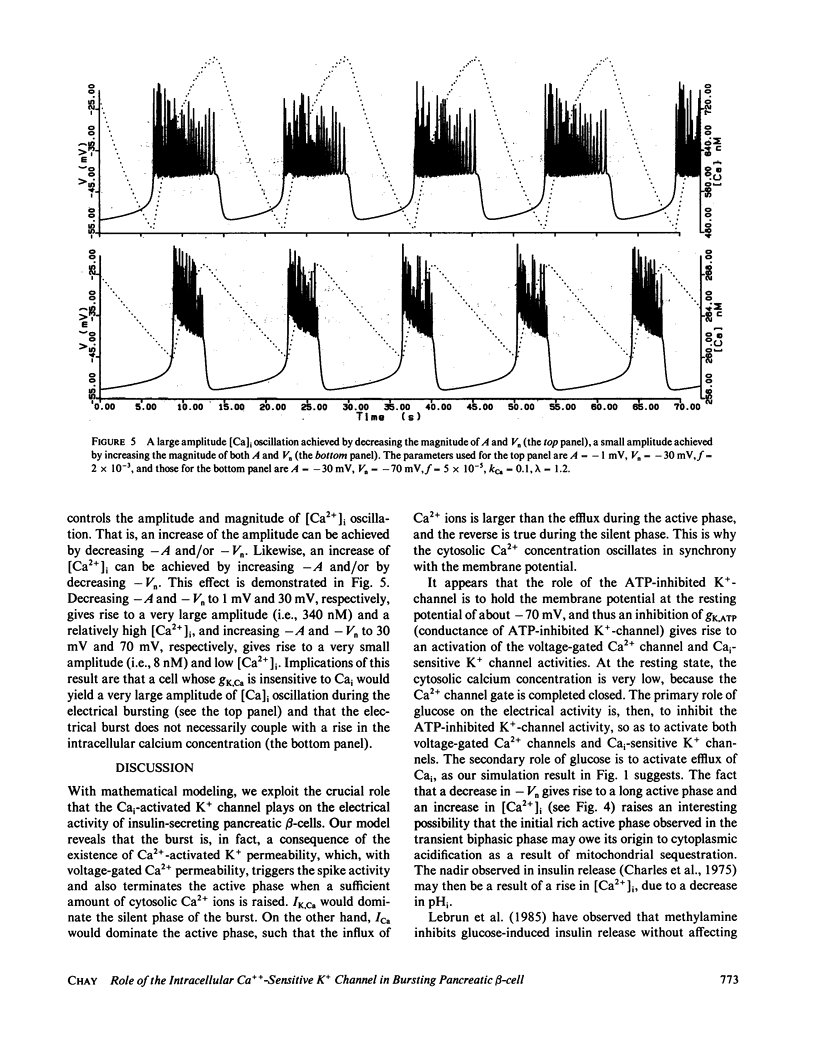
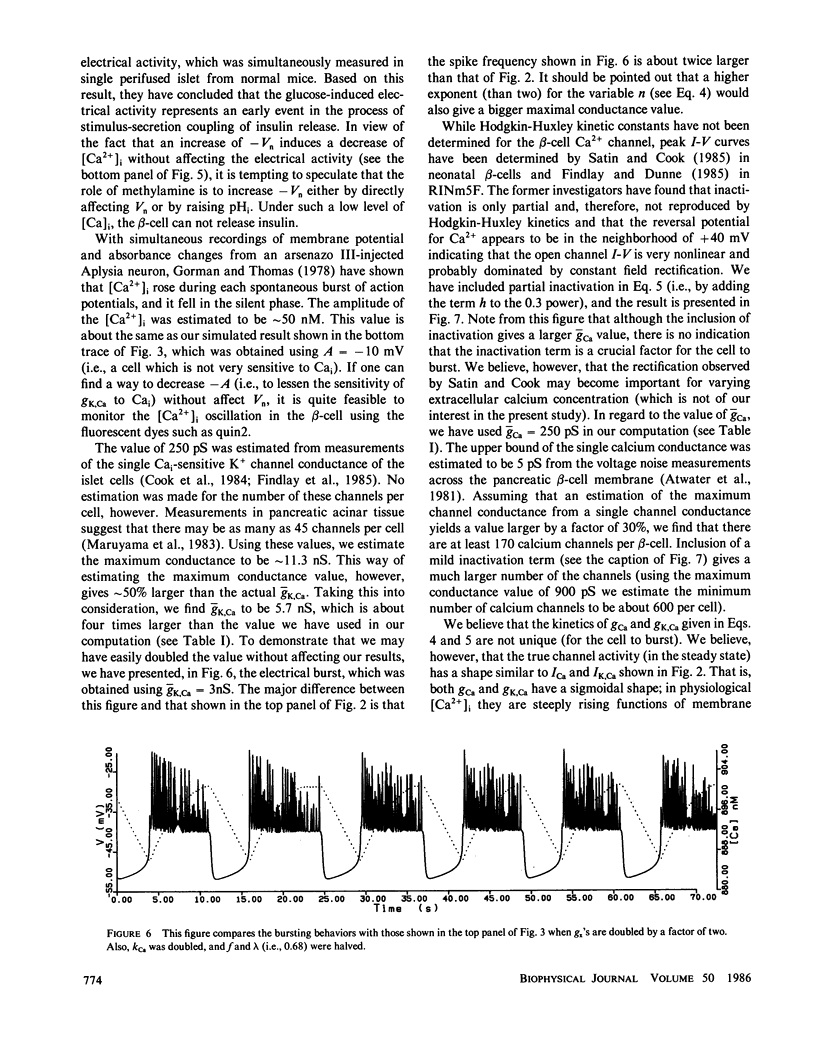
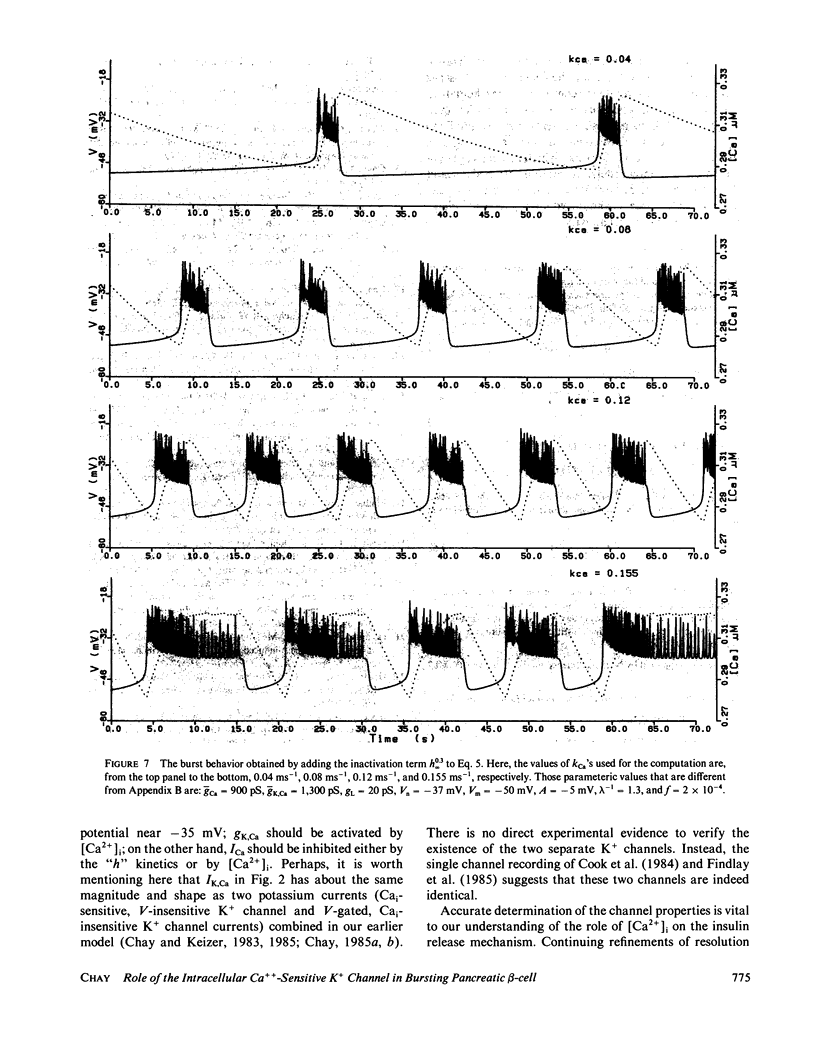
Based on the observation that the calcium-activated K+ channel in the pancreatic islet cells can also be activated by the membrane potential, we have formulated a mathematical model for the electrical activity in the pancreatic beta-cell. Our model contains two types of ionic channels, which are active above the subthreshold glucose concentration in the limit-cycle region: a Ca2+-activated, voltage-gated K+ channel and voltage-gated Ca2+ channel. Numerical simulation of the model generates bursts of electrical activity in response to a variation of kCa, the rate constant for sequestration of intracellular calcium ions. The period and duration of the bursts in response to kCa are in good agreement with experiment. The model predicts that a combined spike and burst pattern can be created using only single species of inward and outward currents, the inactivation kinetics (i.e., h) in the inward current is not a necessary condition for the generation of the pattern, and a given pattern or intensity of electrical activity may produce different levels of intracellular Ca2+ depending on the set of certain electrical parameters.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Eddlestone G. T., Rojas E. Voltage noise measurements across the pancreatic beta-cell membrane: calcium channel characteristics. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:195–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Potassium permeability activated by intracellular calcium ion concentration in the pancreatic beta-cell. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:575–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Scott A., Eddlestone G., Rojas E. The nature of the oscillatory behaviour in electrical activity from pancreatic beta-cell. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beigelman P. M., Ribalet B., Atwater I. Electric activity of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. II. Effects of glucose and arginine. J Physiol (Paris) 1977 Jul;73(2):201–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles M. A., Lawecki J., Pictet R., Grodsky G. M. Insulin secretion. Interrelationships of glucose, cyclic adenosine 3:5-monophosphate, and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6134–6140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R. Glucose response to bursting-spiking pancreatic beta-cells by a barrier kinetic model. Biol Cybern. 1985;52(5):339–349. doi: 10.1007/BF00355756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R., Keizer J. Minimal model for membrane oscillations in the pancreatic beta-cell. Biophys J. 1983 May;42(2):181–190. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84384-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R., Keizer J. Theory of the effect of extracellular potassium on oscillations in the pancreatic beta-cell. Biophys J. 1985 Nov;48(5):815–827. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83840-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chay T. R., Rinzel J. Bursting, beating, and chaos in an excitable membrane model. Biophys J. 1985 Mar;47(3):357–366. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83926-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Ikeuchi M., Fujimoto W. Y. Lowering of pHi inhibits Ca2+-activated K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):269–271. doi: 10.1038/311269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):255–264. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddlestone G. T., Beigelman P. M. Pancreatic beta-cell electrical activity: the role of anions and the control of pH. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):C188–C197. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.3.C188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. ATP-sensitive inward rectifier and voltage- and calcium-activated K+ channels in cultured pancreatic islet cells. J Membr Biol. 1985;88(2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01868430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. High-conductance K+ channel in pancreatic islet cells can be activated and inactivated by internal calcium. J Membr Biol. 1985;83(1-2):169–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01868748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J. Voltage-activated Ca2+ currents in insulin-secreting cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Changes in the intracellular concentration of free calcium ions in a pace-maker neurone, measured with the metallochromic indicator dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P., Schmeer W. Cyclic variations of glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic B cells. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jun;393(4):322–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00581418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun P., Atwater I., Rosario L. M., Herchuelz A., Malaisse W. J. Dissociation by methylamine of insulin release from glucose-induced electrical activity in isolated mouse islets of Langerhans. Metabolism. 1985 Dec;34(12):1122–1127. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Petersen O. H., Flanagan P., Pearson G. T. Quantification of Ca2+-activated K+ channels under hormonal control in pig pancreas acinar cells. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):228–232. doi: 10.1038/305228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Sakamoto Y. Electrical characteristics of pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):421–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Preissler M. Glucose-induced changes of the membrane potential of pancreatic B-cells: their significance for the regulation of insulin release. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;119:97–107. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9110-8_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Preissler M. Ionic mechanisms of the glucose-induced membrane potential changes in B-cells. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:91–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Schmelz H. Membrane potential of beta-cells in pancreatic islets. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(3):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00586918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Tarvin J. T., Smith J. S. Stimulus-secretion coupling in beta-cells: modulation by pH. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):E3–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.1.E3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Maruyama Y. Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):693–696. doi: 10.1038/307693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Beigelman P. M. Cyclic variation of K+ conductance in pancreatic beta-cells: Ca2+ and voltage dependence. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):C137–C146. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.237.3.C137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Abrahamsson H., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Dual effects of glucose on the cytosolic Ca2+ activity of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):196–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin L. S., Cook D. L. Voltage-gated Ca2+ current in pancreatic B-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Aug;404(4):385–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00585354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. M., Atwater I., Rojas E. A method for the simultaneous measurement of insulin release and B cell membrane potential in single mouse islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia. 1981 Nov;21(5):470–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00257788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Pozzan T. Correlation between cytosolic free Ca2+ and insulin release in an insulin-secreting cell line. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2262–2267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S., Lecar H., Adler M. Single calcium-dependent potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):313–317. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84522-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


