Abstract
A structural and dynamic model has been developed for the branch point formed when two DNA double helices exchange strands during genetic recombination. This model, which generalizes most previous structural models, maintains the twofold symmetry inherent in the covalent and hydrogen bonded structure, yet has three degrees of freedom about virtual bonds, constituting a simplified junction. Using this structural model, a three-step dynamic model for branch point migration has been developed: longitudinal diffusion about the virtual bonds to achieve a structure in which the helix axes are approximately parallel; opening of the base pairs; and rotary diffusion about the helix axis to effect a migratory event. The model, which includes the possible role of electrostatic interactions, solves problems inherent in previous treatments. We find that no significant electrostatic torques arise that promote branch point migration. The absence of a kinetic mechanism to circumvent thermodynamic barriers due to mispairing suggests that an energy source is used for those situations in living systems.
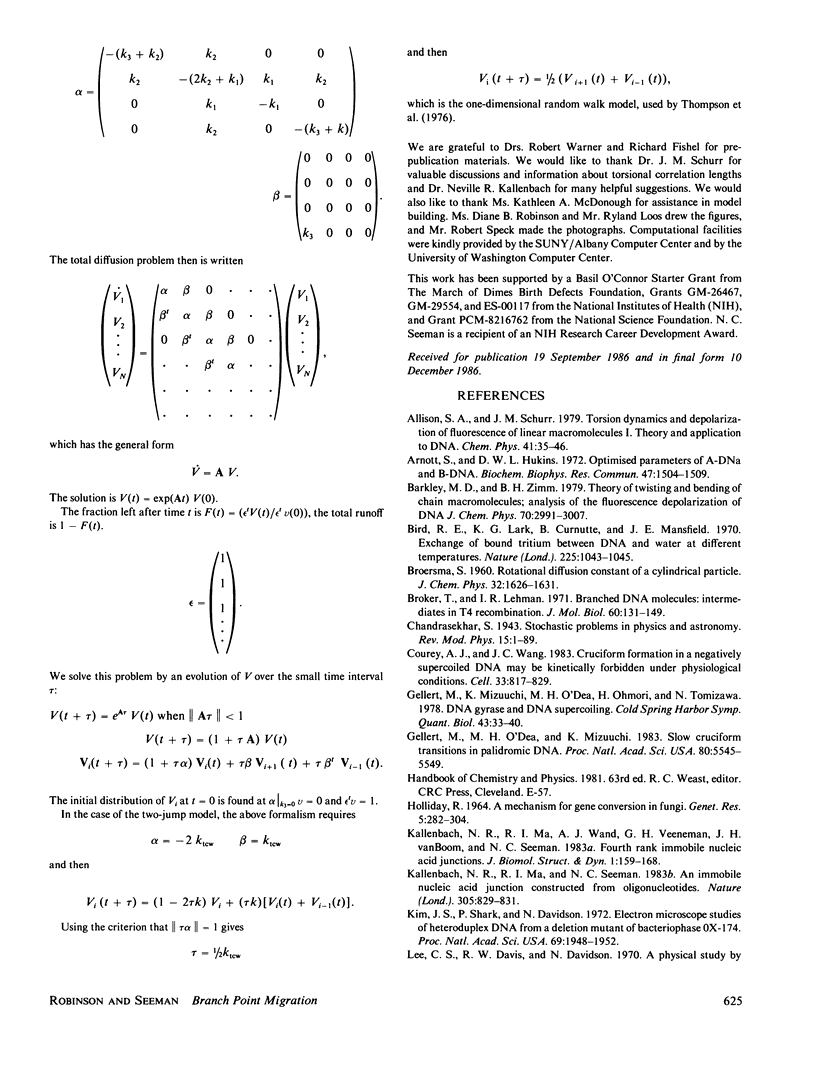
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird R. E., Lark K. G., Curnutte B., Maxfield J. E. Exchange of bound tritium between DNA and water at different temperatures. Nature. 1970 Mar 14;225(5237):1043–1045. doi: 10.1038/2251043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broker T. R., Lehman I. R. Branched DNA molecules: intermediates in T4 recombination. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90453-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Wang J. C. Cruciform formation in a negatively supercoiled DNA may be kinetically forbidden under physiological conditions. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Tomizawa J. DNA gyrase and DNA supercoiling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Mizuuchi K. Slow cruciform transitions in palindromic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5545–5549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallenbach N. R., Ma R. I., Wand A. J., Veeneman G. H., van Boom J. H., Seeman N. C. Fourth rank immobile nucleic acid junctions. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):159–168. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Sharp P. A., Davidson N. Electron microscope studies of heteroduplex DNA from a deletion mutant of bacteriophage phiX-174. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1948–1952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. S., Davis R. W., Davidson N. A physical study by electron microscopy of the terminally reptitious, circularly permuted DNA from the coliphage particles of Escherichia coli 15. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Hallam L. R. Thermodynamics of the ColE1 cruciform. Comparisons between probing and topological experiments using single topoisomers. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):179–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal C., Kallenbach N. R., Englander S. W. Base-pair opening and closing reactions in the double helix. A stopped-flow hydrogen exchange study in poly(rA).poly(rU). J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):391–411. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90443-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Weinstock G. M., Lehman I. R. Initiation of general recombination catalyzed in vitro by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2615–2619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin S. A model for the specific pairing of homologous double-stranded nucleic acid molecules during genetic recombination. Heredity (Edinb) 1977 Aug;39(1):15–25. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1977.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. Formation of hybrid DNA by rotary diffusion during genetic recombination. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):795–798. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C. Nucleic acid junctions and lattices. J Theor Biol. 1982 Nov 21;99(2):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N., Alberts B. Genetic recombination: the nature of a crossed strand-exchange between two homologous DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):789–793. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M. Molecular mechanism for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2483–2487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson B. J., Camien M. N., Warner R. C. Kinetics of branch migration in double-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2299–2303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner R. C., Fishel R. A., Wheeler F. C. Branch migration in recombination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):957–968. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H. Nick-free formation of reciprocal heteroduplexes: a simple solution to the topological problem. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3641–3645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Hsu M. T. Visualization of genetic recombination intermediates of human adenovirus type 2 DNA from infected HeLa cells. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):168–171. doi: 10.1038/287168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]