Abstract
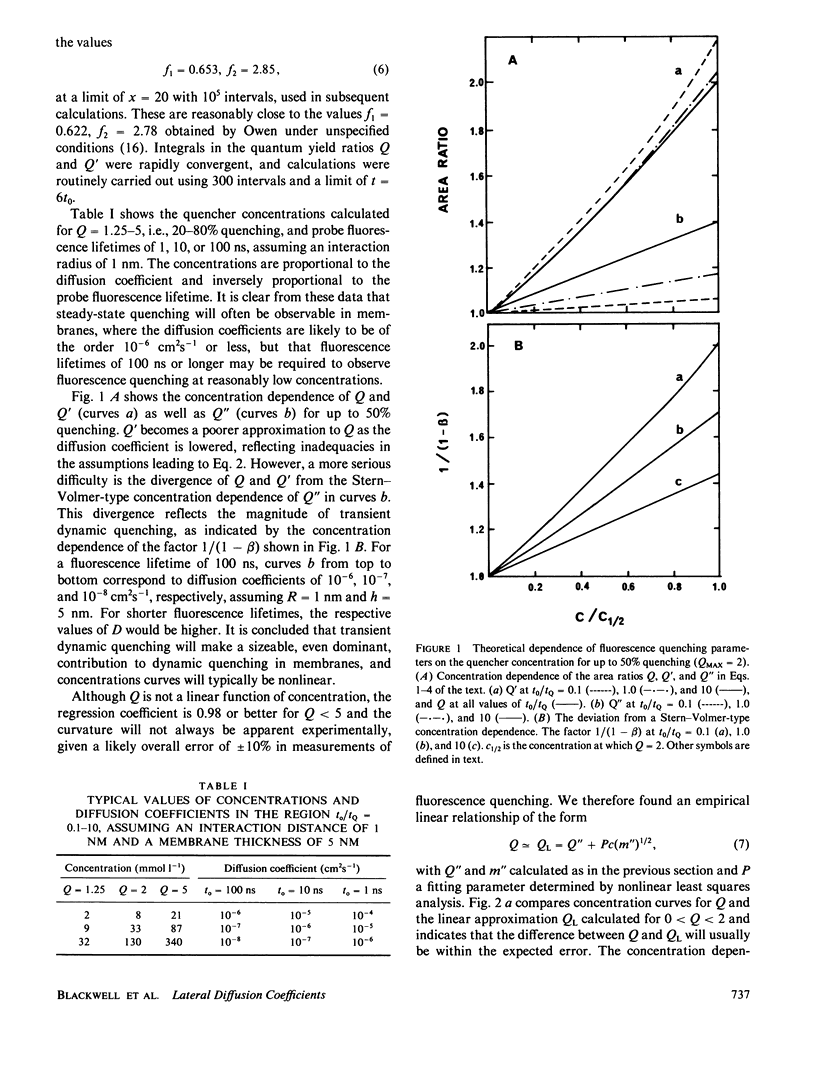
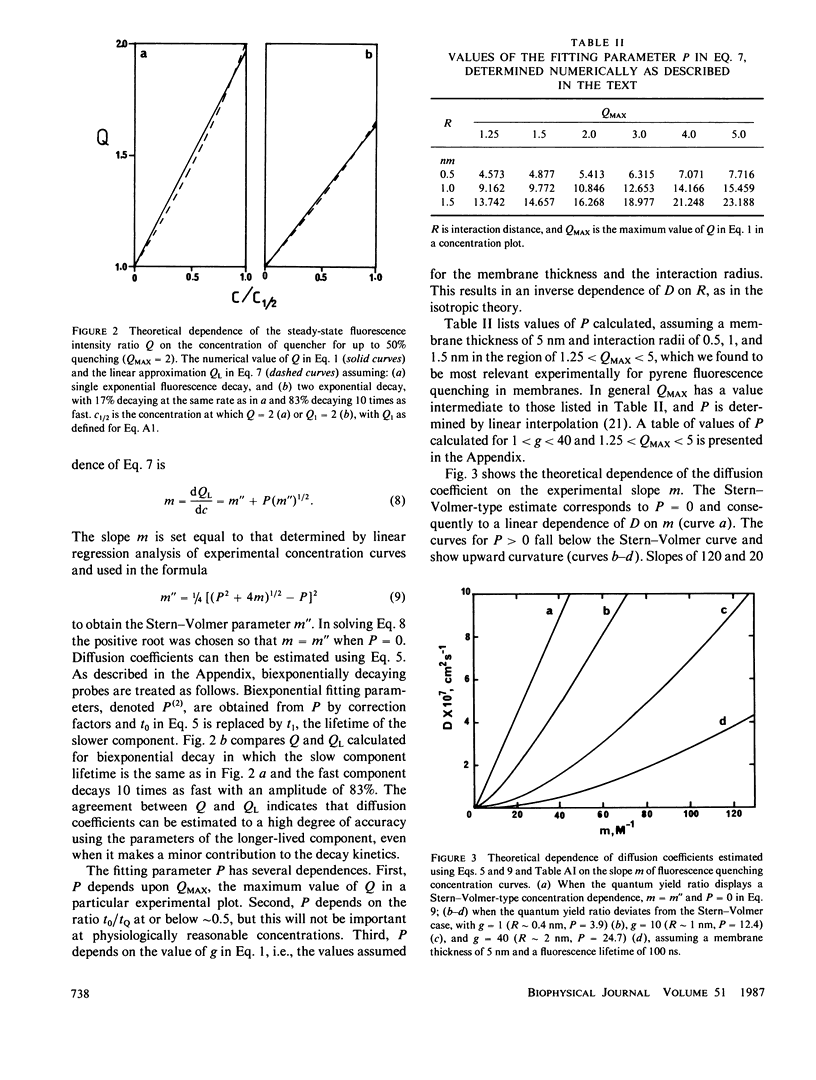
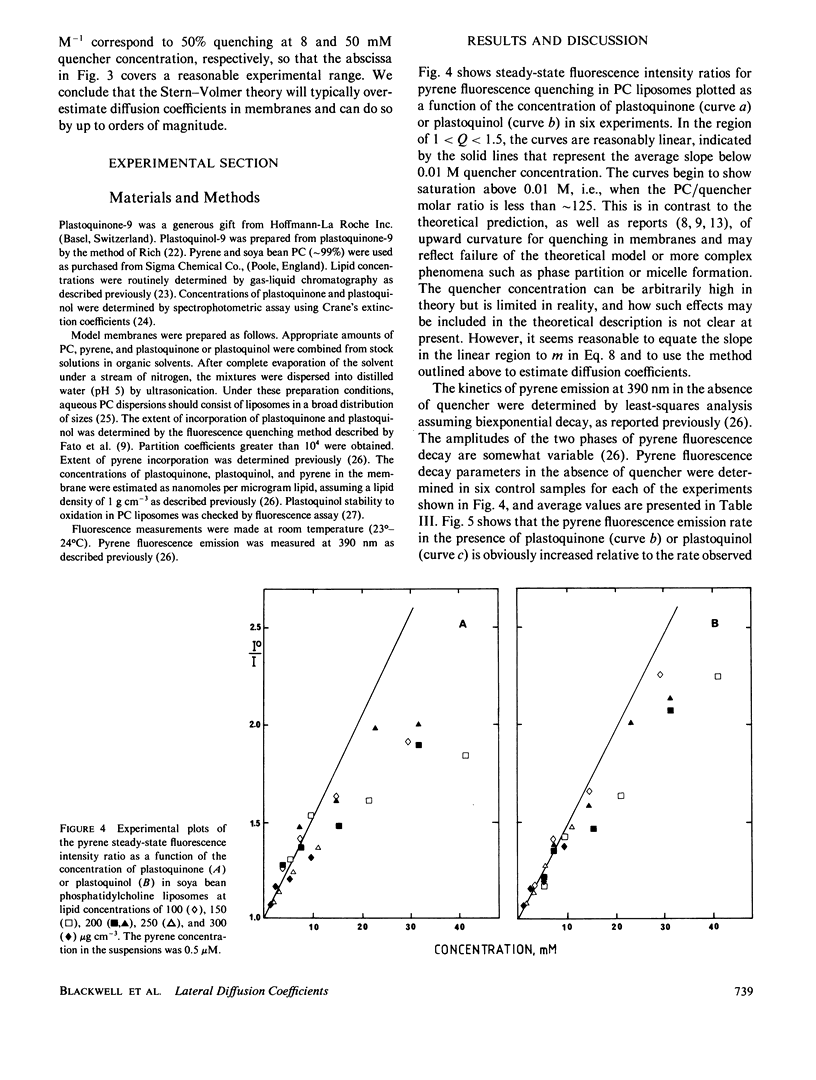
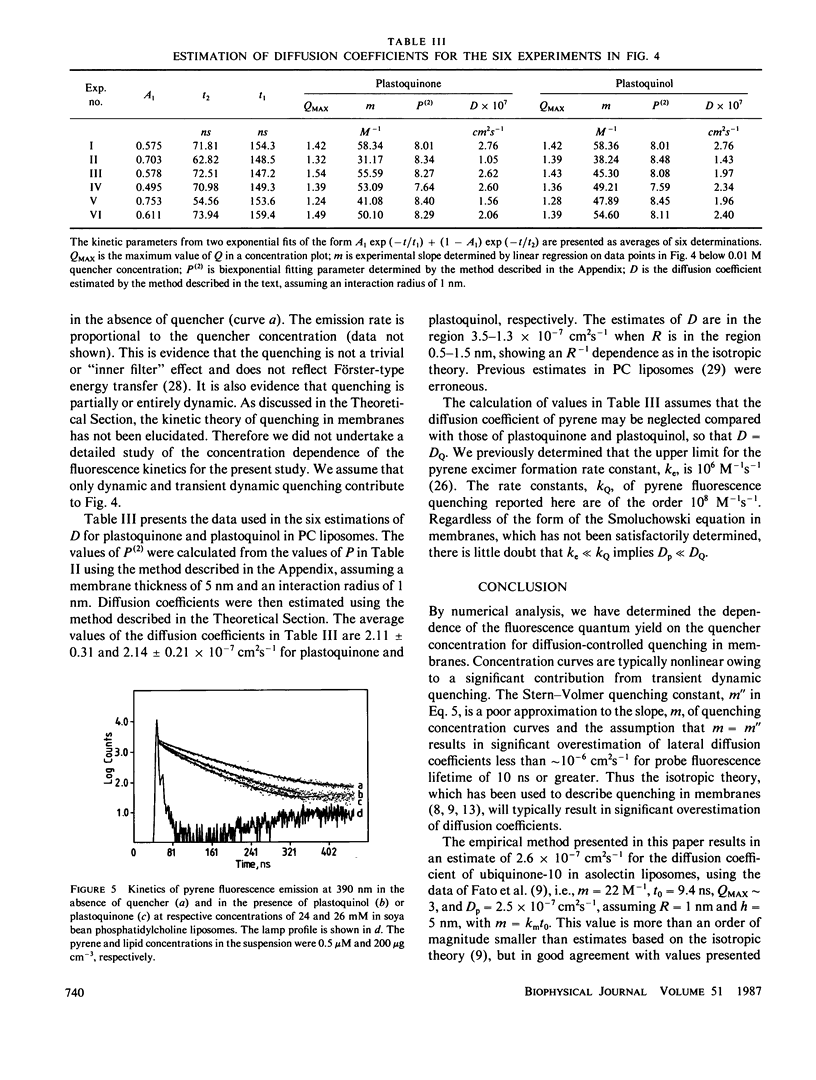
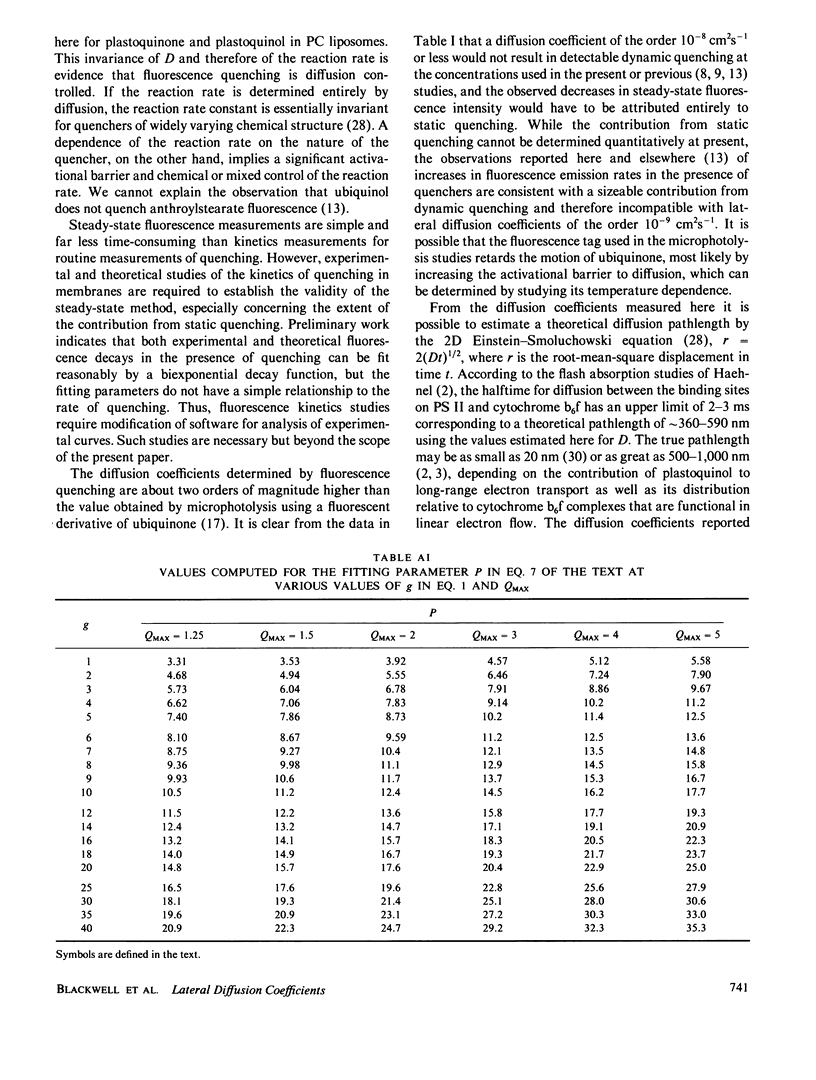
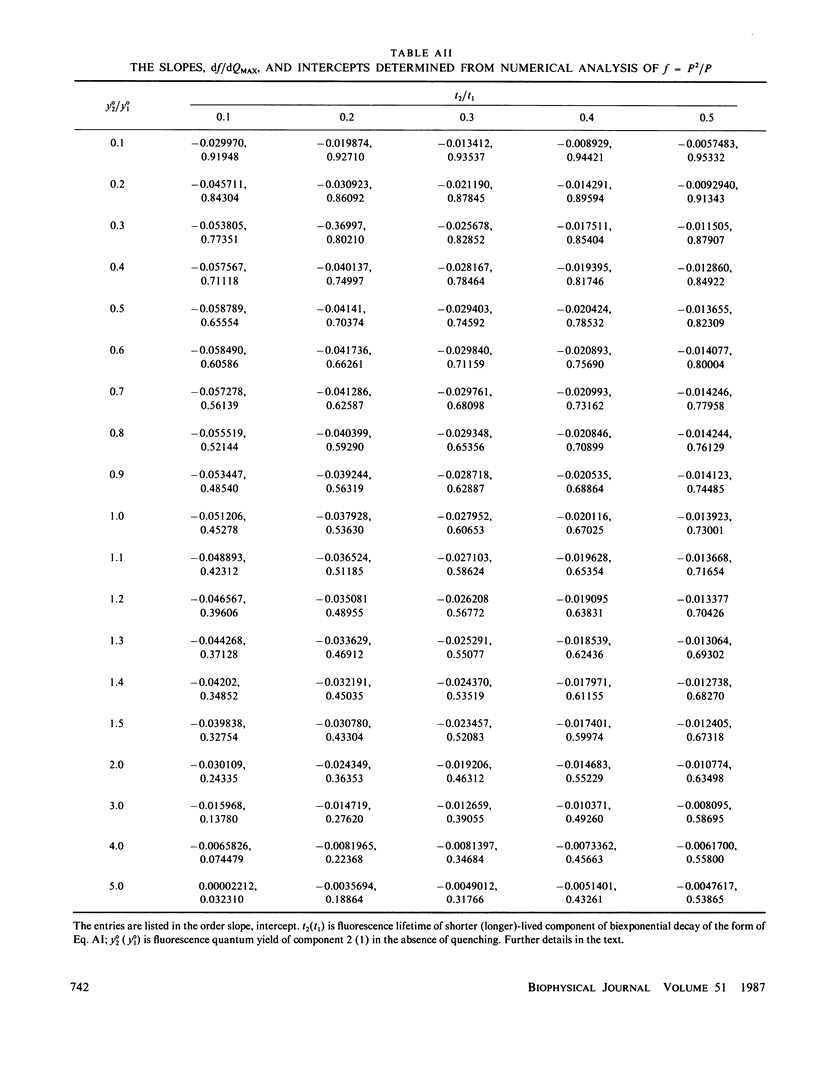
The Stern-Volmer theory, in which the quantum yield ratio (Io/I) depends linearly on the quencher concentration, will typically be inapplicable to fluorescence quenching in membranes. Numerical analysis shows that diffusion-controlled quenching results in a nonlinear concentration dependence for diffusion coefficients less than or of the order of 10(-6) cm2 s-1 and probe fluorescence lifetimes in the region of 10-100 ns. Lateral diffusion coefficients in membranes are typically overestimated an order of magnitude or more by the Stern-Volmer theory. An alternative empirical method is presented, which represents nonlinear concentration curves by a single parameter linear approximation determined by a least-squares analysis. The fitting parameter, P, depends on the interaction distance, the membrane thickness, the maximum extent of quenching and, in the case of biexponential probe fluorescence decay, the fluorescence kinetic parameters. P is presented in tabular form for a useful range of these parameters. The method is used to estimate diffusion coefficients for plastoquinone and plastoquinol from pyrene fluorescence quenching in soya bean phosphatidylcholine liposomes. It is found that the diffusion coefficients are nearly equal and in the region of 1.3-3.5 X 10(-7) cm2 s-1 for interaction radii of 1.5-0.5 nm, respectively.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell M. F., Gounaris K., Barber J. Evidence that pyrene excimer formation in membranes is not diffusion-controlled. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 26;858(2):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Erecinska M. 12-(9-Anthroyl)stearic acid, a fluorescent probe for the ubiquinone region of the mitochondrial membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):521–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane F. L. Isolation of Two Quinones with Coenzyme Q Activity from Alfalfa. Plant Physiol. 1959 Sep;34(5):546–551. doi: 10.1104/pp.34.5.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fato R., Battino M., Degli Esposti M., Parenti Castelli G., Lenaz G. Determination of partition and lateral diffusion coefficients of ubiquinones by fluorescence quenching of n-(9-anthroyloxy)stearic acids in phospholipid vesicles and mitochondrial membranes. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3378–3390. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fato R., Battino M., Parenti Castelli G., Lenaz G. Measurement of the lateral diffusion coefficients of ubiquinones in lipid vesicles by fluorescence quenching of 12-(9-anthroyl)stearate. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 7;179(2):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80526-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galla H. J., Sackmann E. Lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes: use of pyrene excimers as optical probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupte S., Wu E. S., Hoechli L., Hoechli M., Jacobson K., Sowers A. E., Hackenbrock C. R. Relationship between lateral diffusion, collision frequency, and electron transfer of mitochondrial inner membrane oxidation-reduction components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman G. C., Huang C. Structural studies on phophatidylcholine-cholesterol mixed vesicles. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 29;14(15):3363–3370. doi: 10.1021/bi00686a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Callis J. B. Pyrene. A probe of lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4000–4006. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


