Abstract
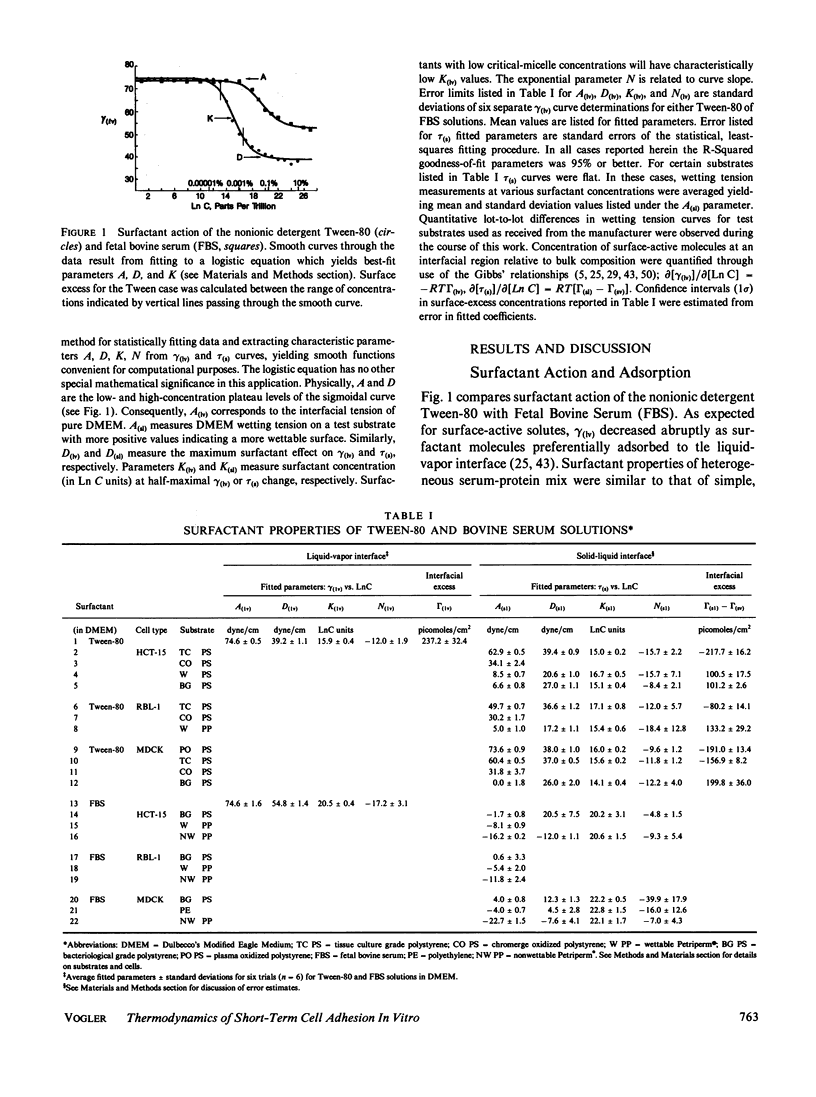
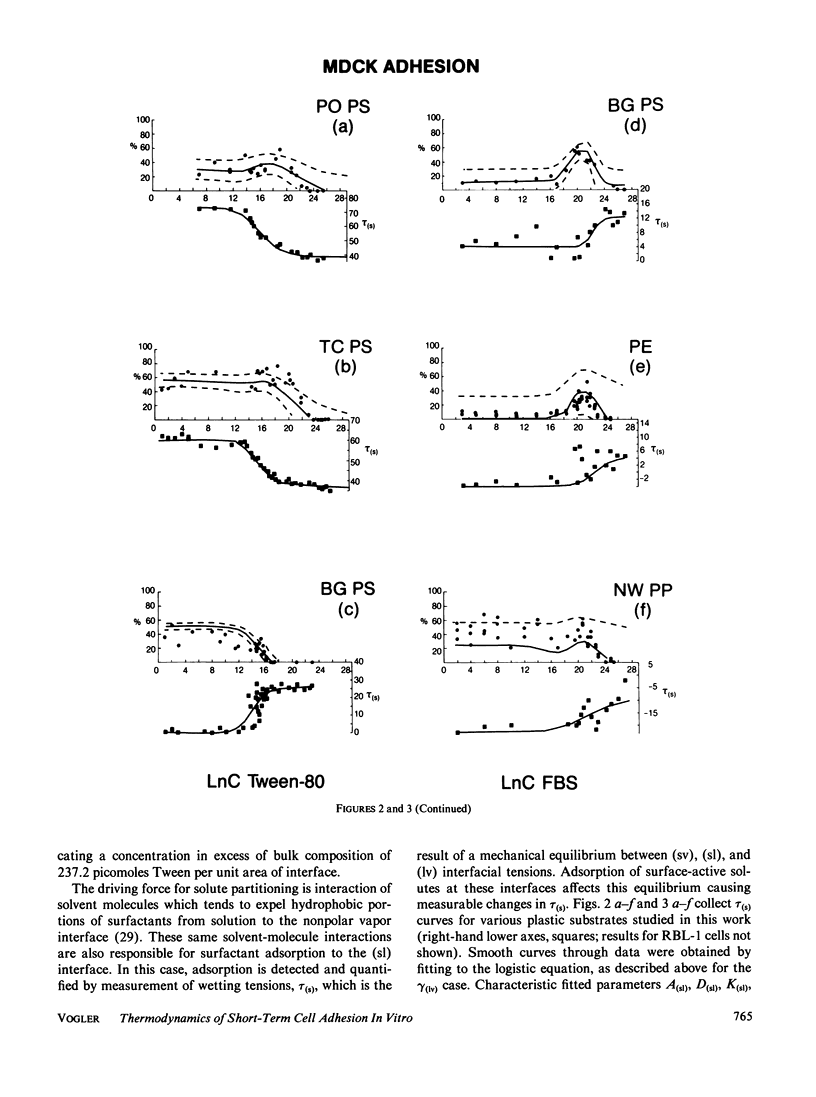
A thermodynamic theory of short-term (less than 2 hr) in vitro cell adhesion has been developed which allows calculation of reversible work of adhesion and estimation of a term proportional to cell-substrate contact area. The theory provides a means of determining a parameter related to membrane wetting tension for microscopic cells that does not require special manipulations which might desiccate or denature delicate cell membranes. Semiquantitative agreement between predicted and experimentally-measured cell adhesion obtained for three different cell types (MDCK, RBL-1, and HCT-15) in two different liquid phase compositions of surfactants (Tween-80 and fetal bovine serum) supports concepts and approximations utilized in development of theory. Cell-substrate contact areas were largest for wettable surfaces treated with ionizing corona or plasma discharges and smallest for hydrophobic materials for each cell type studied. Contact area for the continuous dog-kidney cell line MDCK was larger than that of either the leukemic blood cell RBL-1 or the anaplastic human colon cell HCT-15.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Absolom D. R., van Oss C. J., Genco R. J., Francis D. W., Neumann A. W. Surface thermodynamics of normal and pathological human granulocytes. Cell Biophys. 1980 Jun;2(2):113–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02795838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amstein C. F., Hartman P. A. Adaptation of plastic surfaces for tissue culture by glow discharge. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jul;2(1):46–54. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.1.46-54.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baier R. E. Adhesion in the biologic environment. Biomater Med Devices Artif Organs. 1984;12(3-4):133–159. doi: 10.3109/10731198409118830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baier R. E. The role of surface energy in thrombogenesis. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1972 Feb;48(2):257–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee D., Pentney R. J., Chackalaparampil I., Mukherjee B. B. Ability of oncogenically transformed cells to grow without anchorage correlates with phosphorylation of a group of cell surface membrane proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Oct;166(2):442–454. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedict R. W., Williams M. C. Bonding erythrocytes to plastic substrates by glow-discharge activation. Biomater Med Devices Artif Organs. 1979;7(4):477–493. doi: 10.3109/10731197909118963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger K., Sauvage L. R., Rao A. M., Wood S. J. Healing of arterial prostheses in man: its incompleteness. Ann Surg. 1972 Jan;175(1):118–127. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197201000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busscher H. J., Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., van Pelt A. W., de Jong H. P., Arends J. Measurement of the surface free energy of bacterial cell surfaces and its relevance for adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):980–983. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.980-983.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. C., Williams D. F. Effects of physical configuration and chemical structure of suture materials on bacterial adhesion. A possible link to wound infection. Am J Surg. 1984 Feb;147(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis A. S., Forrester J. V., McInnes C., Lawrie F. Adhesion of cells to polystyrene surfaces. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1500–1506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerson D. F. Cell surface energy, contact angles and phase partition. I. Lymphocytic cell lines in biphasic aqueous mixtures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 4;602(2):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90310-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F. Cellular adhesiveness and extracellular substrata. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;53:65–144. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gristina A. G., Oga M., Webb L. X., Hobgood C. D. Adherent bacterial colonization in the pathogenesis of osteomyelitis. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):990–993. doi: 10.1126/science.4001933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggli R., Baumgartner H. R. Platelet interactions with collagenous substrates in the presence of flowing blood. Suppl Thromb Haemost. 1978;63:289–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann A. W., Absolom D. R., van Oss C. J., Zingg W. Surface thermodynamics of leukocyte and platelet adhesion to polymer surfaces. Cell Biophys. 1979 Mar;1(1):79–92. doi: 10.1007/BF02785058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann A. W., Hope C. J., Ward C. A., Herbert M. A., Dunn G. W., Zingg W. The role of surface thermodynamics in thromboresistance of biomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res. 1975 Mar;9(2):127–142. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820090203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann A. W., Hum O. S., Francis D. W., Zingg W., van Oss C. J. Kinetic and thermodynamic aspects of platelet adhesion from suspension to various substrates. J Biomed Mater Res. 1980 Jul;14(4):499–509. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820140416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey W. S., Hertl W., Nowlan E. D., Binkowski N. J. Surface treatments and cell attachment. In Vitro. 1984 Oct;20(10):802–808. doi: 10.1007/BF02618296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt D. D., Bandyk D. F., Pequet A. J., Towne J. B. Bacterial adherence to vascular prostheses. A determinant of graft infectivity. J Vasc Surg. 1986 May;3(5):732–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürch S., Gerson D. F., McIver D. J. Determination of cell/medium interfacial tensions from contact angles in aqueous polymer systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 22;640(2):557–571. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90480-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz T. L., Noonan K. D., Hench L. L., Noonan N. E. Effect of fibronectin on the adhesion of an established cell line to a surface reactive biomaterial. J Biomed Mater Res. 1982 May;16(3):195–207. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820160303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney J. H., Moody M. R., Newman K. A., Schimpff S. C., Wade J. C., Costerton J. W., Reed W. P. Adherent microorganisms on lumenal surfaces of long-term intravenous catheters. Importance of Staphylococcus epidermidis in patients with cancer. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Oct;146(10):1949–1954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torney D. C., Dembo M., Bell G. I. Thermodynamics of cell adhesion. II. Freely mobile repellers. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):501–507. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83660-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voger E. A., Bussian R. W. Short-term cell-attachment rates: a surface-sensitive test of cell-substrate compatibility. J Biomed Mater Res. 1987 Oct;21(10):1197–1211. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820211004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vroman L. What factors determine thrombogenicity. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1972 Feb;48(2):302–310. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Harlos J. P. Some speculations on the rate of adhesion of cells to coverslips. J Theor Biol. 1972 Oct;37(1):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(72)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Valk P., van Pelt A. W., Busscher H. J., de Jong H. P., Wildevuur C. R., Arends J. Interaction of fibroblasts and polymer surfaces: relationship between surface free energy and fibroblast spreading. J Biomed Mater Res. 1983 Sep;17(5):807–817. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820170508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


