Abstract
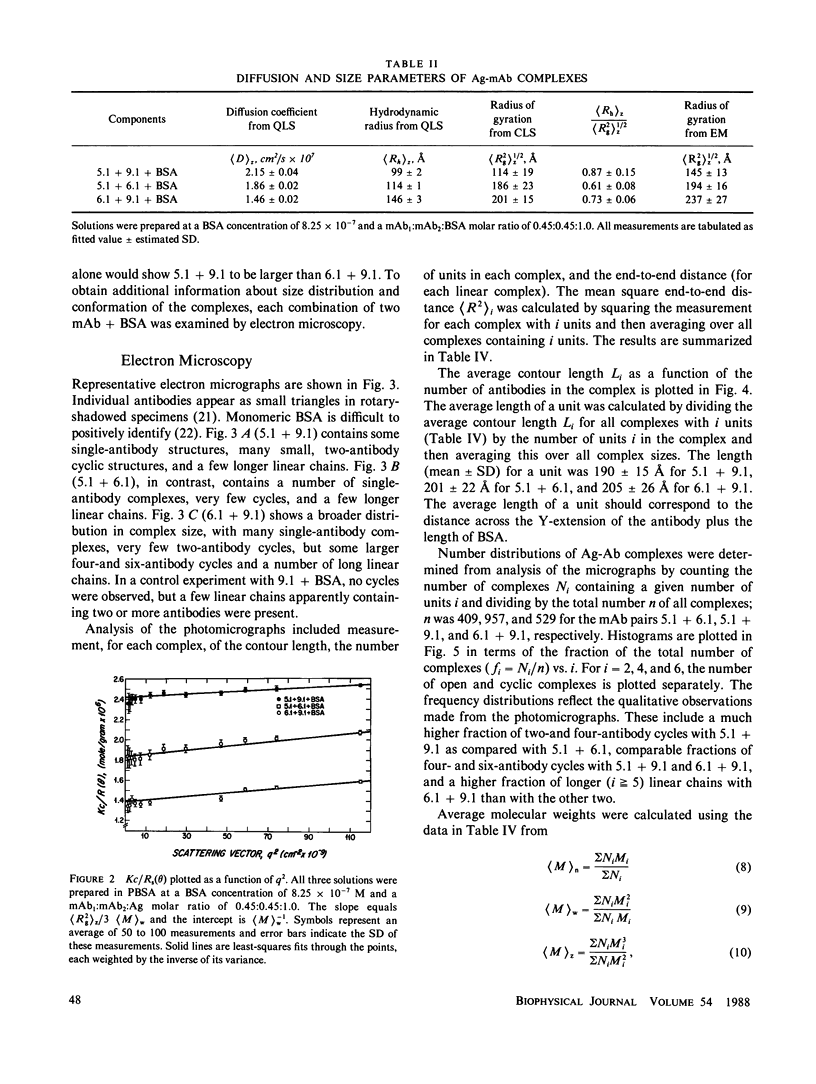
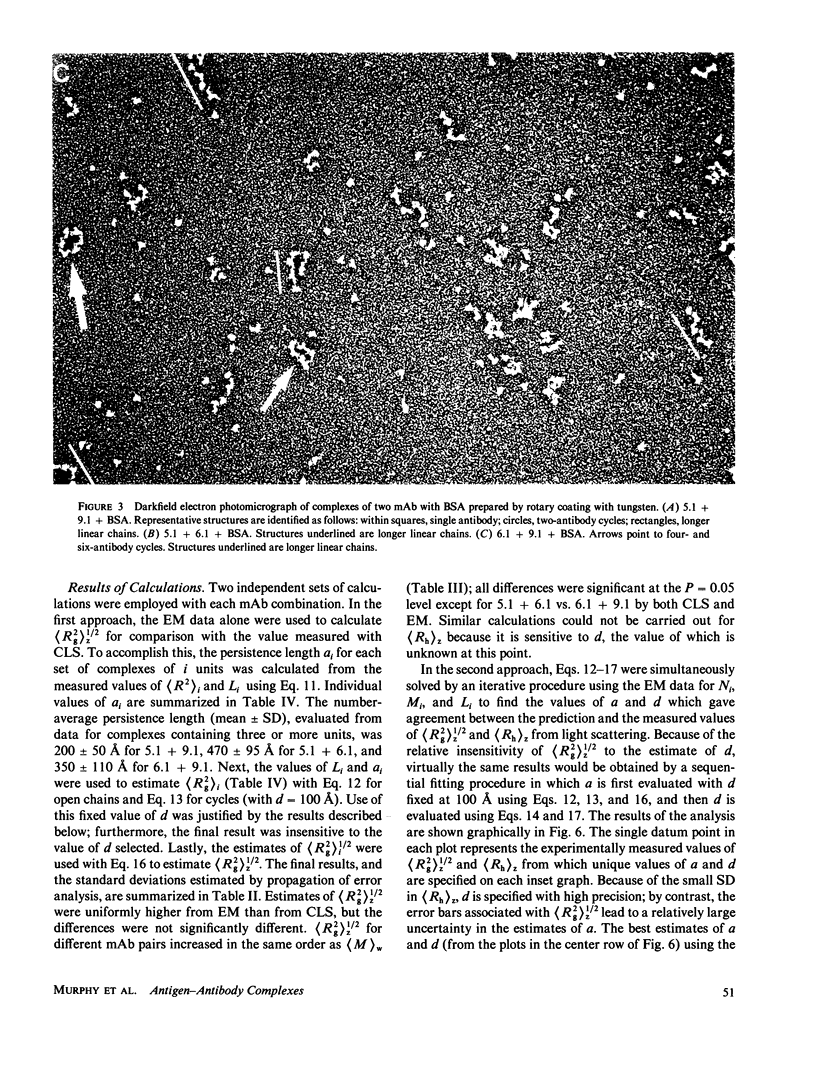
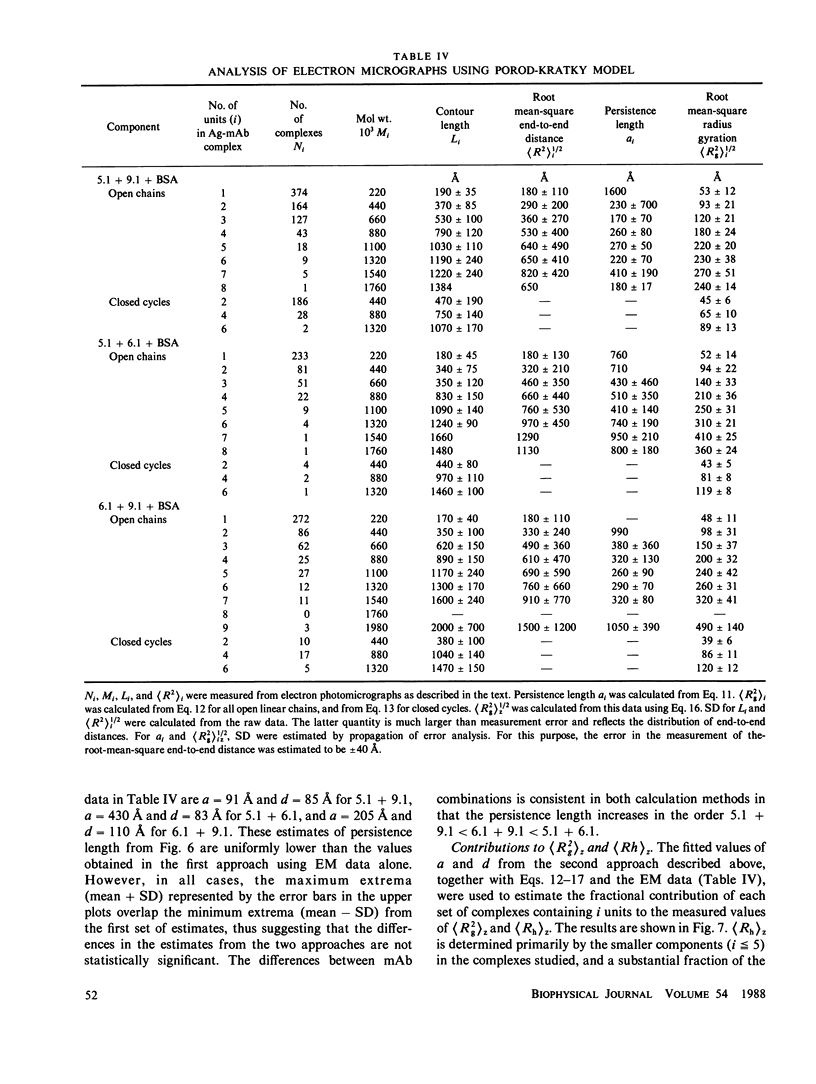
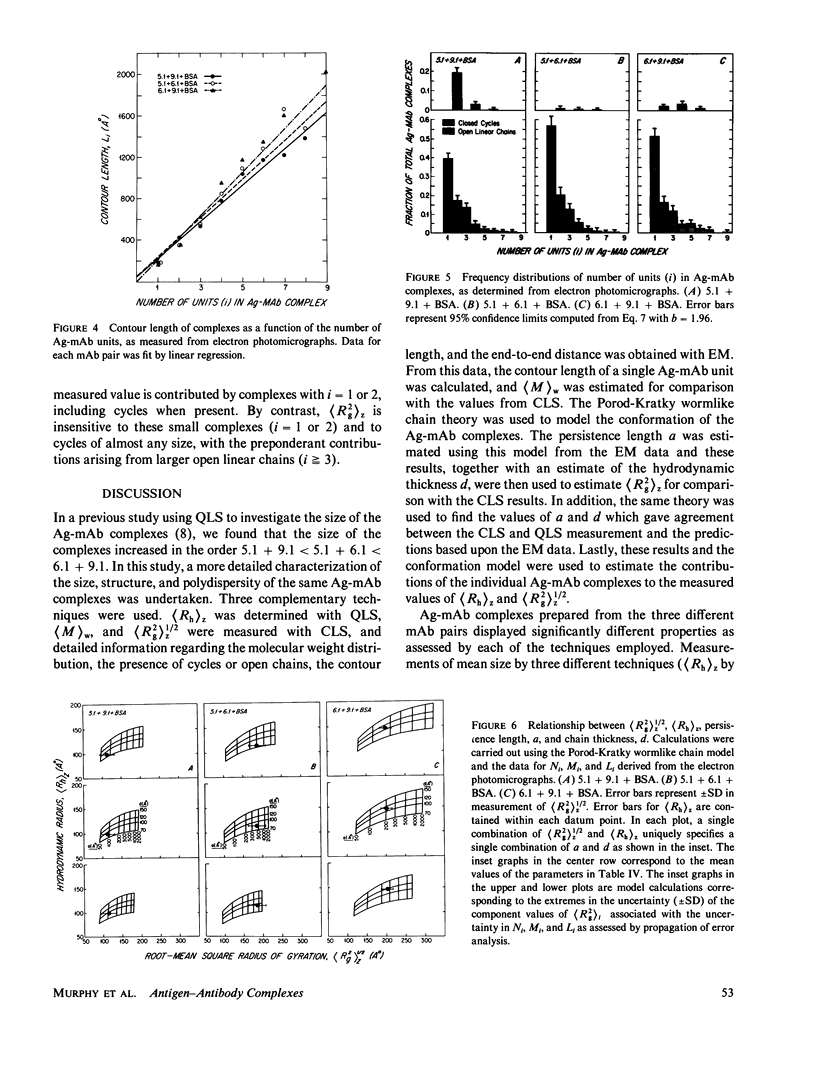
Size parameters of model antigen-antibody (Ag-Ab) complexes formed by the interaction of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and pairs of monoclonal anti-BSA antibodies (mAb) were evaluated by quasielastic light scattering, classical light scattering, and electron microscopy (EM). Mean values for the hydrodynamic radius, radius of gyration, and molecular weight were determined by light scattering. Detailed information regarding the molecular weight distribution and the presence of cycles or open chains was obtained with EM. Average molecular weights were calculated from the EM data, and the Porod-Kratky wormlike chain theory was used to model the conformational behavior of the Ag-mAb complexes. Ag-mAb complexes prepared from three different mAb pairs displayed significantly different properties as assessed by each of the techniques employed. Observations and size parameter calculations from EM photomicrographs were consistent with the results from light scattering. The differences observed between the mab pairs would not have been predicted by idealized thermodynamic models. These results suggest that the geometric constraints imposed by the individual epitope environment and/or the relative epitope location are important in determining the average size of complexes and the ratio of linear to cyclic complexes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer B. G., Krakauer H. Thermodynamics of antibody-antigen reactions. 2. The binding of bivalent synthetic random coil antigens to antibodies having different antigen precipitating properties. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):618–627. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Teller D. C., Mannik M. Molecular composition and sedimentation characteristics of soluble antigen-antibody complexes. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4063–4072. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan F. M., Grace S. A., Elson C. J. Preparation of covalent IgG complexes of defined size and their clearance from the circulation of mice. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jan 28;56(2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90406-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doekes G., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Binding and activation of the first complement component by soluble immune complexes: effect of complex size and composition. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Feb;19(2):99–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIDUSCHEK E. P., HOLTZER A. Application of light scattering to biological systems: deoxyribonucleic acid and the muscle proteins. Adv Biol Med Phys. 1958;6:431–551. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4832-3112-9.50014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvin N. J., Dixit V. M., O'Rourke K. M., Santoro S. A., Grant G. A., Frazier W. A. Mapping of epitopes for monoclonal antibodies against human platelet thrombospondin with electron microscopy and high sensitivity amino acid sequencing. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1434–1441. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Electron microscopy of the immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60476-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D., Eisenberg H. Photon correlation spectroscopy, total intensity light scattering with laser radiation, and hydrodynamic studies of a well fractionated DNA sample. Biopolymers. 1976 Jan;15(1):61–95. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., Knutson D. W., van der Lelij A., van Es L. A. Characteristics of soluble immune complexes prepared from oligovalent DNP conjugates and anti-DNP antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(3-4):263–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel G. A., Yarmush D. M., Colton C. K., Benjamin D. C., Yarmush M. L. Monoclonal antibodies to bovine serum albumin: affinity and specificity determinations. Mol Immunol. 1988 Jan;25(1):7–15. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mould A. P., Holmes D. F., Kadler K. E., Chapman J. A. Mica sandwich technique for preparing macromolecules for rotary shadowing. J Ultrastruct Res. 1985 Apr;91(1):66–76. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(85)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle W. R., Lin C., Corson R. L., Ehrlich P. H. Quantitative explanation for increased affinity shown by mixtures of monoclonal antibodies: importance of a circular complex. Mol Immunol. 1983 Apr;20(4):439–452. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller N. P., Christiansen G. Fc-mediated immune precipitation. III. Visualization by electron microscopy. Immunology. 1983 Mar;48(3):469–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr Serum albumin. Adv Protein Chem. 1985;37:161–245. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux K. H., Metzger D. W. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of idiotypes and allotypes on immunoglobulin molecules. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2548–2553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker V. N., Seegan G. W., Smith C. A., Ma S. K., Rodwell J. D., Schumaker M. F. The free energy of angular position of the Fab arms of IgG antibody. Mol Immunol. 1980 Mar;17(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Dower S. K., Titus J. A. The FcR-mediated endocytosis of model immune complexes by cells from the P338D1 mouse macrophage line. I. Internalization of small, nonaggregating oligomers of IgG. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):130–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayter E. M. An electron microscope study of the conformational change in bovine serum albumin at low pH. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayter H. S. High-resolution metal replication of macromolecules. Ultramicroscopy. 1976 Sep-Oct;1(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(76)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayter H., Loscalzo J., Bockenstedt P., Handin R. I. Native conformation of human von Willebrand protein. Analysis by electron microscopy and quasi-elastic light scattering. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8559–8563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steensgaard J., Jacobsen C., Lowe J., Ling N. R., Jefferis R. Theoretical and ultracentrifugal analysis of immune complex formation between monoclonal antibodies and human IgG. Immunology. 1982 Aug;46(4):751–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Green N. M. Electron microscopy of an antibody-hapten complex. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):615–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley N. G., Brown E. B., Skehel J. J. Electron microscopic evidence for the axial rotation and inter-domain flexibility of the Fab regions of immunoglobulin G. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 25;169(3):771–774. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarmush D. M., Morel G., Yarmush M. L. A new technique for mapping epitope specificities of monoclonal antibodies using quasi-elastic light scattering spectroscopy. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1987 Aug;14(5):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(87)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarmush D. M., Murphy R. M., Colton C. K., Fisch M., Yarmush M. L. Quasi-elastic light scattering of antigen-antibody complexes. Mol Immunol. 1988 Jan;25(1):17–32. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]