Abstract
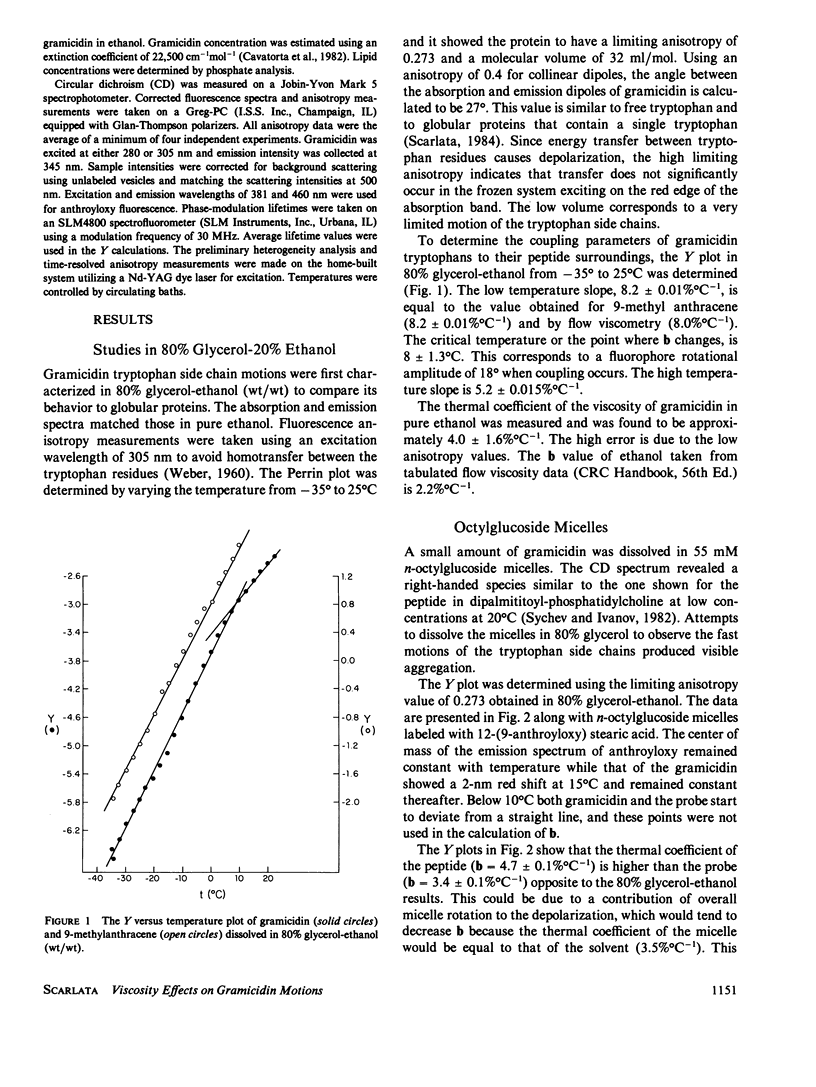
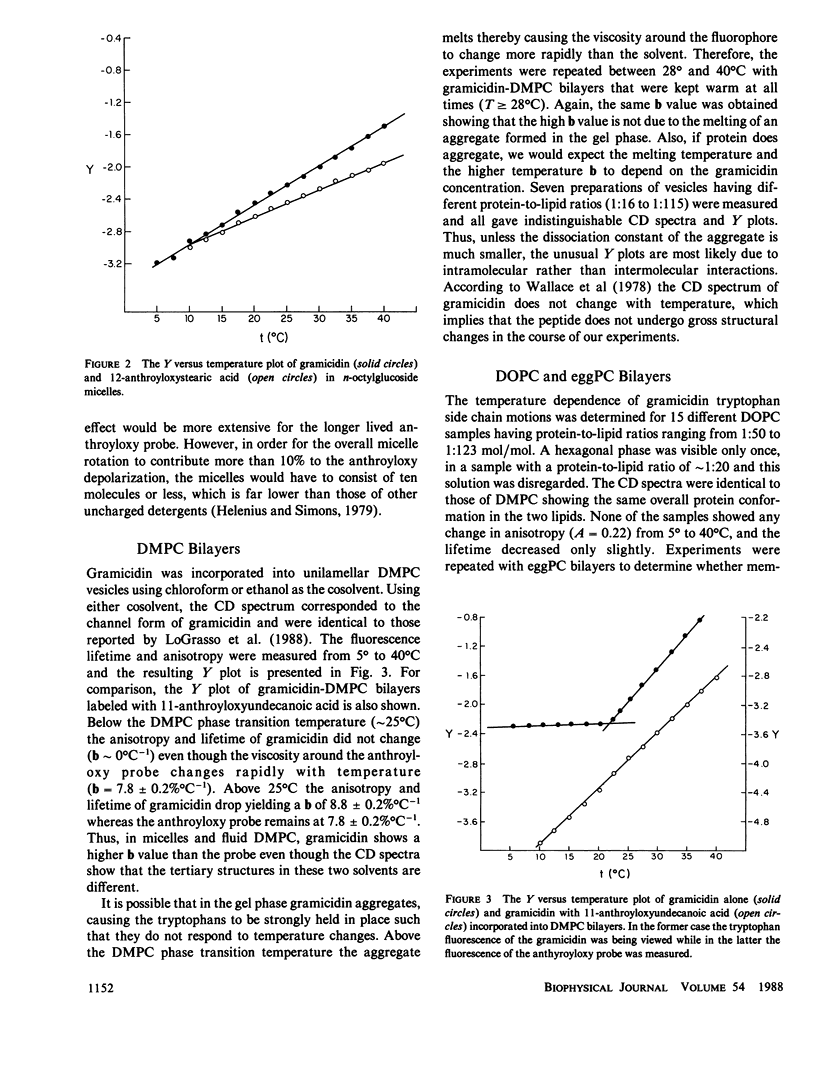
The rotational amplitude of gramicidin tryptophans was investigated as a function of temperature and viscosity in a variety of solvents using fluorescence spectroscopy. In 80% glycerol-ethanol, gramicidin behavior was similar to that of alpha helical globular proteins. In dioleoyl-phosphatidylcholine (DOPC) and egg-phosphatidylcholine bilayers, the rotational amplitude of the tryptophans remained constant from 5 degrees to 40 degrees C due to the large number of tryptophans participating in intermolecular aromatic ring stacking. In gel phase dimyristoyl-phosphatidylcholine (DMPC), the tryptophan rotations likewise do not respond to temperature and viscosity changes, presumably because of a combination of Trp 9 and 15 stacking and the high viscosity of the membrane. In fluid phase DMPC, stacking becomes disrupted as the temperature increases causing the change in tryptophan amplitude with temperature to be greater than allowed by the membrane. In n-octylglucoside micelles, ring interactions are also broken with heat. We conclude that membrane viscosity regulates both inter- and intramolecular gramicidin interactions but not in a straightforward manner.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S. Gramicidin channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:531–548. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aslanian D., Négrerie M., Chambert R. A Raman spectroscopic study on the interaction of an ion-channel protein with a phospholipid in a model membrane system (gramicidin A/L-alpha-lysophosphatidylcholine). Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohg A., Ristow H. DNA-supercoiling is affected in vitro by the peptide antibiotics tyrocidine and gramicidin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):587–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buster D. C., Hinton J. F., Millett F. S., Shungu D. C. 23Na-nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of gramicidin-induced ion transport through membranes under equilibrium conditions. Biophys J. 1988 Feb;53(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83076-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavatorta P., Spisni A., Casali E., Lindner L., Masotti L., Urry D. W. Intermolecular interactions of gramicidin A' transmembrane channels incorporated into lysophosphatidylcholine lipid systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 14;689(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Blumenthal T. An interaction between gramicidin and the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1045–1048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D., Hayon E., Busath D. Tryptophan photolysis is responsible for gramicidin-channel inactivation by ultraviolet light. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 25;861(1):62–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90371-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A., Timmermans J. W., Keur S., de Kruijff B. The tryptophans of gramicidin are essential for the lipid structure modulating effect of the peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 24;820(1):154–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A., de Kruijff B. Proposed Mechanism for H(II) Phase Induction by Gramicidin in Model Membranes and Its Relation to Channel Formation. Biophys J. 1988 Jan;53(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(88)83072-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langs D. A. Three-dimensional structure at 0.86 A of the uncomplexed form of the transmembrane ion channel peptide gramicidin A. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):188–191. doi: 10.1126/science.2455345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Barenholz Y., Thompson T. E. Fluorescence depolarization studies of phase transitions and fluidity in phospholipid bilayers. 1. Single component phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4521–4528. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Seelig J. Dynamic properties of gramicidin A in phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2357–2364. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masotti L., Cavatorta P., Sartor G., Casali E., Szabo A. G. Tryptophan interactions of gramicidin A' channels in lipids: a time-resolved fluorescence study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 17;862(2):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Barenholz Y. Fluidity parameters of lipid regions determined by fluorescence polarization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 15;515(4):367–394. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spisni A., Pasquali-Ronchetti I., Casali E., Lindner L., Cavatorta P., Masotti L., Urry D. W. Supramolecular organization of lysophosphatidylcholine-packaged Gramicidin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 13;732(1):58–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Fossel E. T., Blout E. R. The conformation of gramicidin A. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5249–5256. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G. Fluorescence-polarization spectrum and electronic-energy transfer in tyrosine, tryptophan and related compounds. Biochem J. 1960 May;75:335–345. doi: 10.1042/bj0750335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Ravikumar K. The gramicidin pore: crystal structure of a cesium complex. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):182–187. doi: 10.1126/science.2455344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. A., Veatch W. R., Blout E. R. Conformation of gramicidin A in phospholipid vesicles: circular dichroism studies of effects of ion binding, chemical modification, and lipid structure. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5754–5760. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


