Abstract
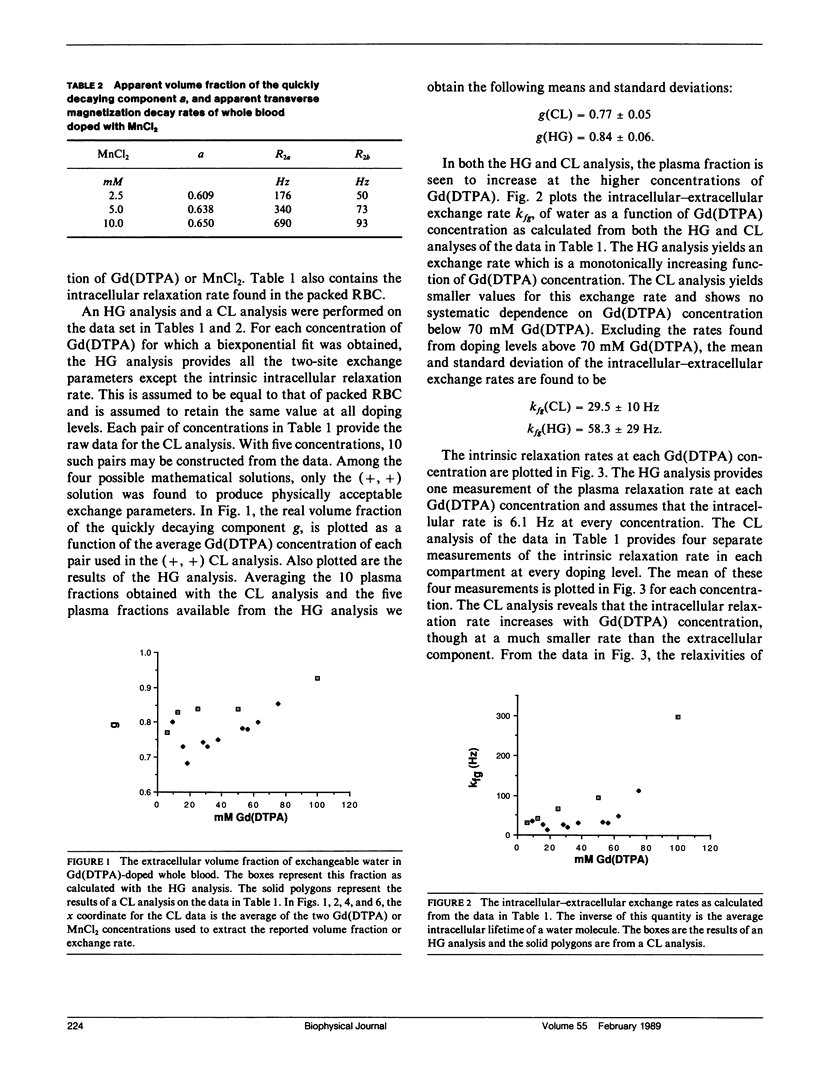
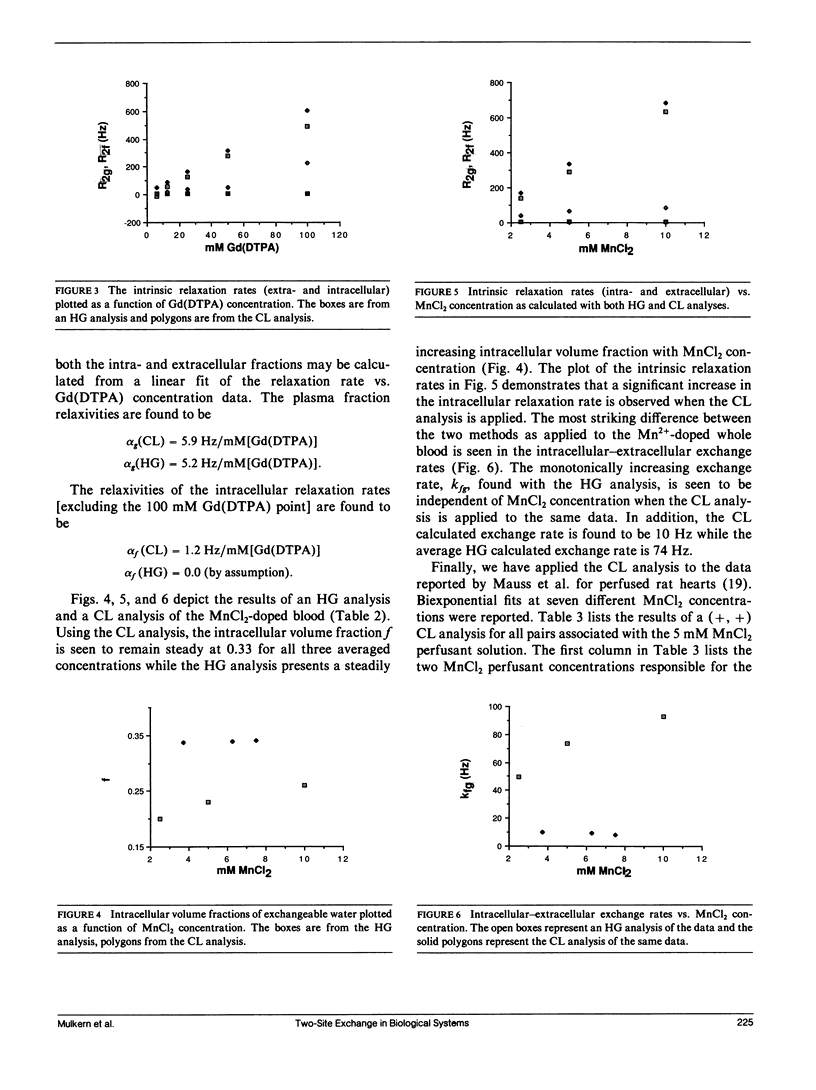
A new analysis is presented which links real volume fractions, relaxation rates, and intracompartmental exchange rates directly with apparent volume fractions and relaxation rates obtained from biexponential fits of transverse magnetization decay curves. The analysis differs from previous methods in that measurements from two paramagnetic doping levels are used to close the two-site exchange equations. Both the new method and one previously described by Herbst and Goldstein (HG) have been applied to paramagnetically doped whole-blood data sets. Significant differences in the calculated exchange parameters are found between the two methods. A small dependence of the intracellular relaxation rate on extracellular paramagnetic agent concentration, assumed nonexistent with the HG method, is inferred from the new analysis. The analysis was also applied to published data on perfused rat hearts, and we obtained a limited assessment of two-site exchange in this system.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrasko J., Frosén S. NMR study of rapid water diffusion across lipid bilayers in dipalmitoyl lecithin vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrasko J. Water diffusion permeability of human erythrocytes studied by a pulsed gradient NMR technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 23;428(2):304–311. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthwal R., Höhn-Berlage M., Gersonde K. In vitro proton T1 and T2 studies on rat liver: analysis of multiexponential relaxation processes. Magn Reson Med. 1986 Dec;3(6):863–875. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910030607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett H. F., Swartz H. M., Brown R. D., 3rd, Koenig S. H. Modification of relaxation of lipid protons by molecular oxygen and nitroxides. Invest Radiol. 1987 Jun;22(6):502–507. doi: 10.1097/00004424-198706000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindle K. M., Brown F. F., Campbell I. D., Grathwohl C., Kuchel P. W. Application of spin-echo nuclear magnetic resonance to whole-cell systems. Membrane transport. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):37–44. doi: 10.1042/bj1800037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein D. On the in vivo detection of intracellular water and sodium by nuclear magnetic resonance with shift reagents. Biophys J. 1988 Jul;54(1):191–192. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82945-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caines G. H., Morgan C. F., Long R. C., Jr, Goldstein J. H. Transverse relaxation of saline and plasma using Mn(II), HSA-EDTA-Mn, and HSA-EDTA-Gd: application to erythrocyte water exchange. Magn Reson Med. 1987 Sep;5(3):269–277. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910050308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. H., Brown J., Bydder G. M., Steiner R. E., Weinmann H. J., Speck U., Hall A. S., Young I. R. Gadolinium-DTPA as a contrast agent in MRI: initial clinical experience in 20 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984 Aug;143(2):215–224. doi: 10.2214/ajr.143.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon T., Outhred R. The temperature dependence of erythrocyte water diffusion permeability. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 17;511(3):408–418. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon T., Outhred R. Water diffusion permeability of erythrocytes using an NMR technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):354–361. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endre Z. H., Kuchel P. W., Chapman B. E. Cell volume dependence of 1H spin-echo NMR signals in human erythrocyte suspensions. The influence of in situ field gradients. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Mar 23;803(3):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry M. E., Eisenstadt M. Water exchange across red cell membranes: II. Measurements by nuclear magnetic resonance T1, T2, and T12 hybrid relaxation. The effects of osmolarity, cell volume, and medium. J Membr Biol. 1978 Sep 25;42(4):375–398. doi: 10.1007/BF01870357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry T. L. Mechanism of erythrocyte aggregation and sedimentation. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1572–1576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer R. E., Macey R. I. Perturbation of red cell volume: rectification of osmotic flow. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 6;196(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton G. D., Cameron I. L., Ord V. A. Frequency dependence of magnetic resonance spin-lattice relaxation of protons in biological materials. Radiology. 1984 Apr;151(1):135–138. doi: 10.1148/radiology.151.1.6322223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. M., Puon P. S. Nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation in muscle water. Biophys J. 1981 Jan;33(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84870-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getz D., Gibson J. F., Sheppard R. N., Micklem K. J., Pasternak C. A. Manganese as a calcium probe: electron paramagnetic resonance and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of intact cells. J Membr Biol. 1979 Nov 30;50(3-4):311–329. doi: 10.1007/BF01868895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis P., Koenig S. H. Transverse relaxation of solvent protons induced by magnetized spheres: application to ferritin, erythrocytes, and magnetite. Magn Reson Med. 1987 Oct;5(4):323–345. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910050404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst M. D., Goldstein J. H. Monitoring red blood cell aggregation with nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 14;805(1):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan K. M., Chien S. Influence of the ionic composition of fluid medium on red cell aggregation. J Gen Physiol. 1973 May;61(5):655–668. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.5.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan K. Red cell interactions in macromolecular suspension. Biorheology. 1979;16(3):137–148. doi: 10.3233/bir-1979-16302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneoke Y., Furuse M., Inao S., Saso K., Yoshida K., Motegi Y., Mizuno M., Izawa A. Spin-lattice relaxation times of bound water--its determination and implications for tissue discrimination. Magn Reson Imaging. 1987;5(6):415–420. doi: 10.1016/0730-725x(87)90375-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S. H., Spiller M., Brown R. D., 3rd, Wolf G. L. Relaxation of water protons in the intra- and extracellular regions of blood containing Gd(DTPA). Magn Reson Med. 1986 Oct;3(5):791–795. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910030514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILDVAN A. S., COHN M. MAGNETIC RESONANCE STUDIES OF THE INTERACTION OF THE MANGANOUS ION WITH BOVINE SERUM ALBUMIN. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:910–919. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauss Y., Grucker D., Fornasiero D., Chambron J. NMR compartmentalization of free water in the perfused rat heart. Magn Reson Med. 1985 Jun;2(3):187–194. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910020302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morariu V. V., Benga G. Evaluation of a nuclear magnetic resonance technique for the study of water exchange through erythrocyte membranes in normal and pathological subjects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 19;469(3):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morariu V. V., Pop V. I., Popescu O., Benga G. Effects of temperature and pH on the water exchange through erythrocyte membranes: nuclear magnetic resonance studies. J Membr Biol. 1981;62(1-2):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF01870194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naritomi H., Kanashiro M., Sasaki M., Kuribayashi Y., Sawada T. In vivo measurements of intra- and extracellular Na+ and water in the brain and muscle by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy with shift reagent. Biophys J. 1987 Oct;52(4):611–616. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83251-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naritomi H., Sasaki M., Kuribayashi Y., Sawada T., Kanashiro M. Validity of in vivo nuclear magnetic resonance methods in measurement of intracellular water and sodium. Biophys J. 1988 Jul;54(1):193–193. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82946-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outhred R. K., George E. P. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of hydrated systems using the frequency dependence of the relaxation processes. Biophys J. 1973 Feb;13(2):83–96. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)85971-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGANELLI C. V., SOLOMON A. K. The rate of exchange of tritiated water across the human red cell membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Nov 20;41(2):259–277. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peemoeller H., Pintar M. M. Nuclear magnetic resonance multiwindow analysis of proton local fields and magnetization distribution in natural and deuterated mouse muscle. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):339–355. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85181-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirkle J. L., Ashley D. L., Goldstein J. H. Pulse nuclear magnetic resonance measurements of water exchange across the erythrocyte membrane employing a low Mn concentration. Biophys J. 1979 Mar;25(3):389–406. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85311-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge V. M., Clanton J. A., Lukehart C. M., Partain C. L., James A. E., Jr Paramagnetic agents for contrast-enhanced NMR imaging: a review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983 Dec;141(6):1209–1215. doi: 10.2214/ajr.141.6.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandor T., Bleier A. R., Ruenzel P. W., Adams D. F., Jolesz F. A. Application of the maximum likelihood principle to separate exponential terms in T2 relaxation of nuclear magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Imaging. 1988;6(1):27–40. doi: 10.1016/0730-725x(88)90520-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shporer M., Civan M. M. NMR study of -17-O from H2-17-O in human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 14;385(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobol W. T., Cameron I. G., Inch W. R., Pintar M. M. Modeling of proton spin relaxation in muscle tissue using nuclear magnetic resonance spin grouping and exchange analysis. Biophys J. 1986 Jul;50(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83450-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobol W. T., Pintar M. M. NMR spectroscopy of heterogeneous solid-liquid mixtures. Spin grouping and exchange analysis of proton spin relaxation in a tissue. Magn Reson Med. 1987 Jun;4(6):537–554. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910040605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staemmler M., Gersonde K. Echo shape analysis and image size adjustment on the level of echoes: improvement of parameter-selective proton images. Magn Reson Med. 1986 Jun;3(3):418–424. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910030306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. E. Self diffusion of water in frog muscle. Biophys J. 1979 Oct;28(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85162-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villringer A., Rosen B. R., Belliveau J. W., Ackerman J. L., Lauffer R. B., Buxton R. B., Chao Y. S., Wedeen V. J., Brady T. J. Dynamic imaging with lanthanide chelates in normal brain: contrast due to magnetic susceptibility effects. Magn Reson Med. 1988 Feb;6(2):164–174. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910060205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEED R. I., ROTHSTEIN A. The uptake of divalent manganese ion by mature normal human red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Nov;44:301–314. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


