Abstract
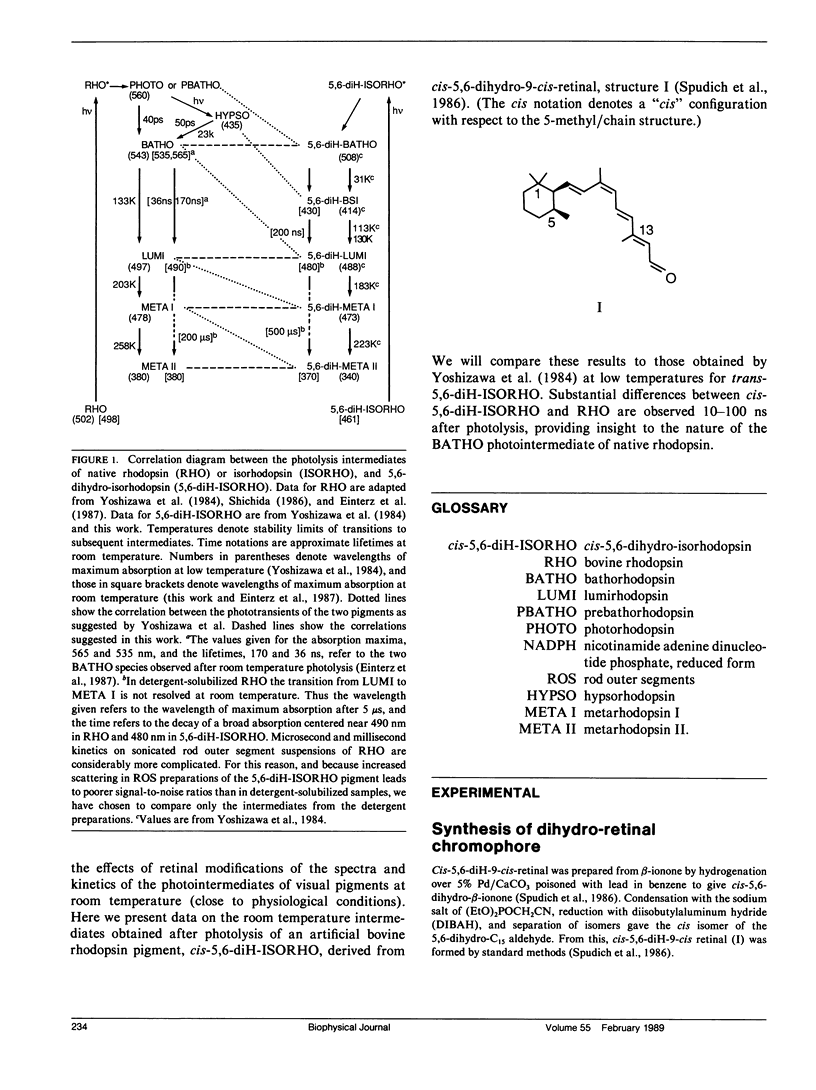
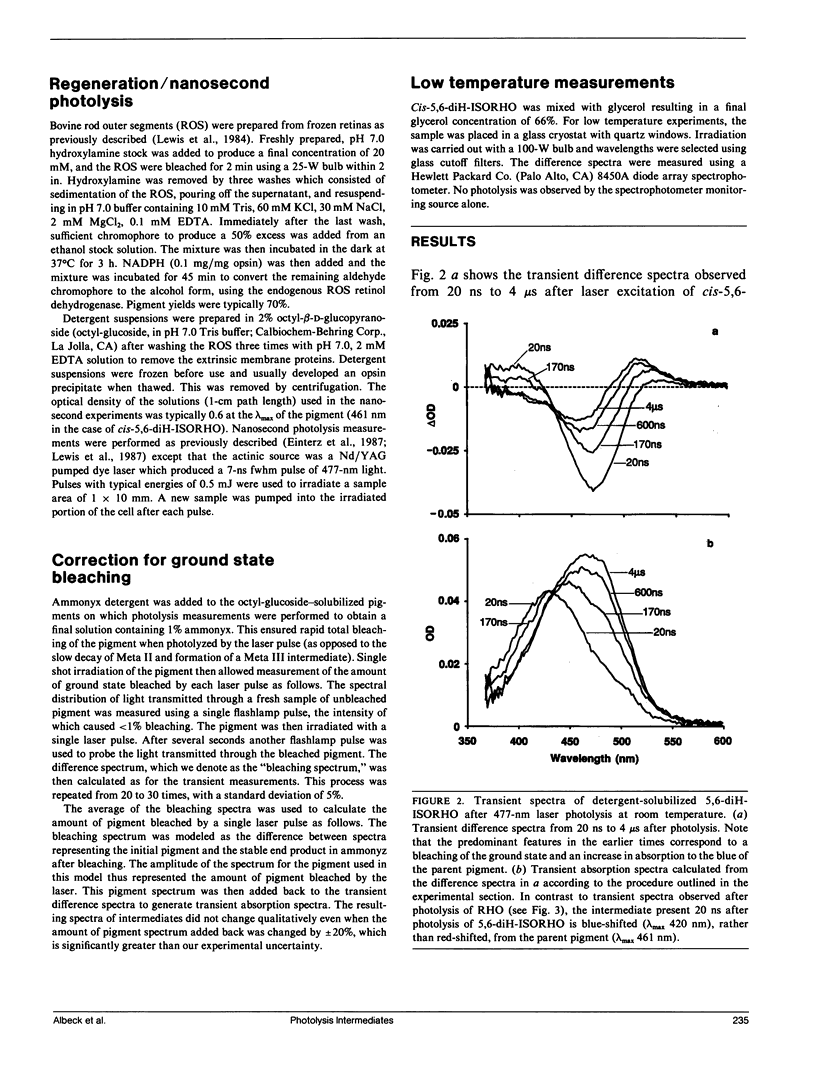
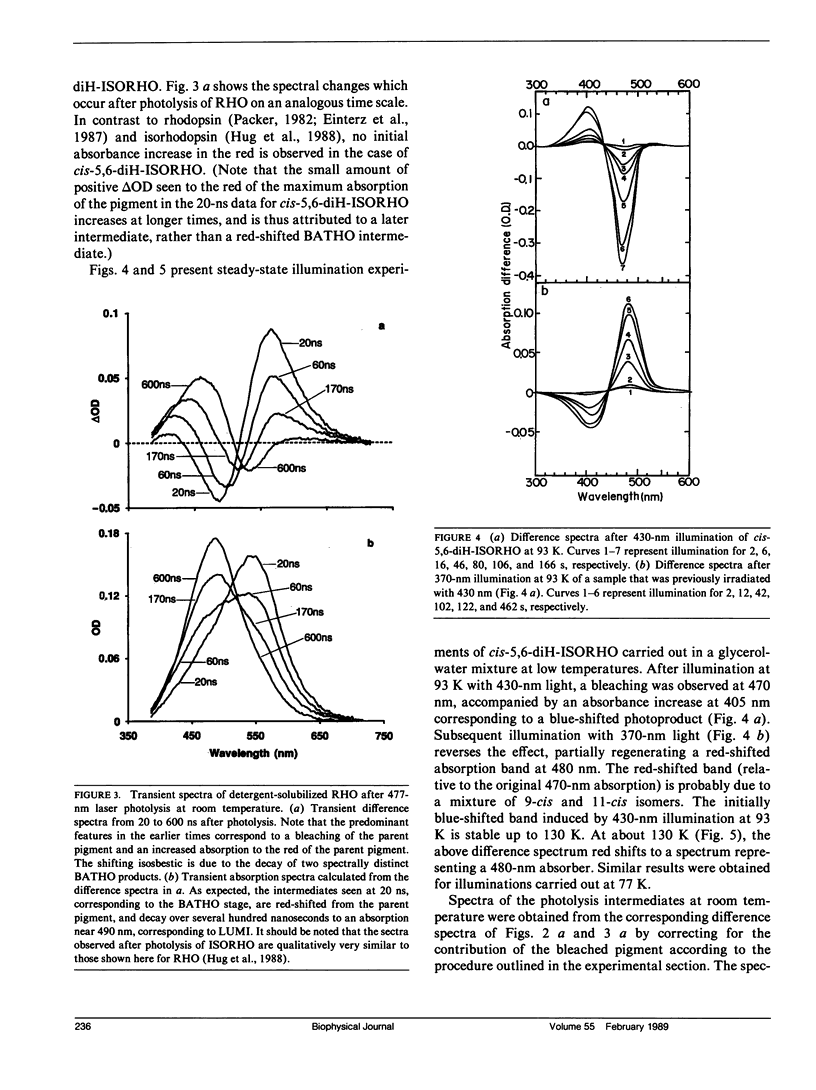
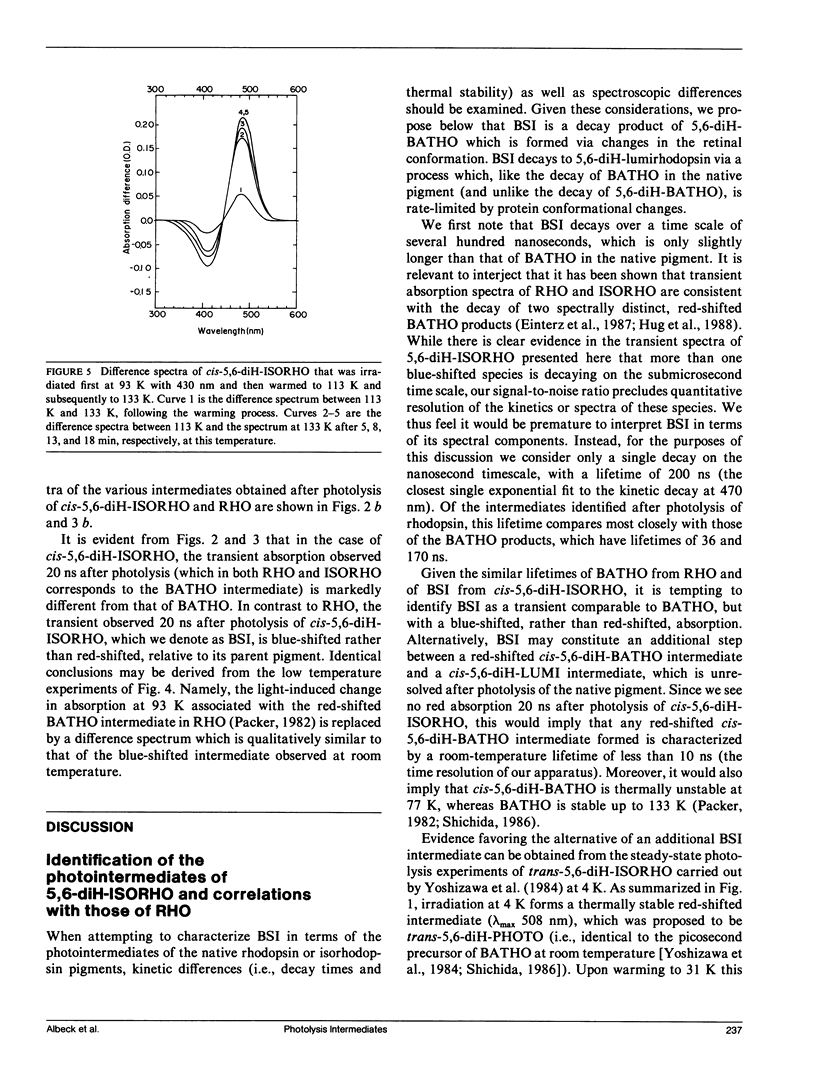
The photolysis intermediates of an artificial bovine rhodopsin pigment, cis-5,6-dihydro-isorhodopsin (cis-5,6,-diH-ISORHO, lambda max 461 nm), which contains a cis-5,6-dihydro-9-cis-retinal chromophore, are investigated by room temperature, nanosecond laser photolysis, and low temperature irradiation studies. The observations are discussed both in terms of low temperature experiments of Yoshizawa and co-workers on trans-5,6-diH-ISORHO (Yoshizawa, T., Y. Shichida, and S. Matuoka. 1984. Vision Res. 24: 1455-1463), and in relation to the photolysis intermediates of native bovine rhodopsin (RHO). It is suggested that in 5,6-diH-ISORHO, a primary bathorhodopsin intermediate analogous to the bathorhodopsin intermediate (BATHO) of the native pigment, rapidly converts to a blue-shifted intermediate (BSI, lambda max 430 nm) which is not observed after photolysis of native rhodopsin. The analogs from lumirhodopsin (LUMI) to meta-II rhodopsin (META-II) are generated subsequent to BSI, similar to their generation from BATHO in the native pigment. It is proposed that the retinal chromophore in the bathorhodopsin stage of 5,6-diH-ISORHO is relieved of strain induced by the primary cis to trans isomerization by undergoing a geometrical rearrangement of the retinal. Such a rearrangement, which leads to BSI, would not take place so rapidly in the native pigment due to ring-protein interactions. In the native pigment, the strain in BATHO would be relieved only on a longer time scale, via a process with a rate determined by protein relaxation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birge R. R., Einterz C. M., Knapp H. M., Murray L. P. The nature of the primary photochemical events in rhodopsin and isorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1988 Mar;53(3):367–385. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83114-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher F., Leblanc R. M. Energy storage in the primary photoreaction of bovine rhodopsin. A photoacoustic study. Photochem Photobiol. 1985 Apr;41(4):459–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1985.tb03512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. Energy uptake in the first step of visual excitation. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):531–533. doi: 10.1038/282531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einterz C. M., Lewis J. W., Kliger D. S. Spectral and kinetic evidence for the existence of two forms of bathorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3699–3703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyring G., Curry B., Broek A., Lugtenburg J., Mathies R. Assignment and interpretation of hydrogen out-of-plane vibrations in the resonance Raman spectra of rhodopsin and bathorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1982 Jan 19;21(2):384–393. doi: 10.1021/bi00531a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyring G., Curry B., Mathies R., Fransen R., Palings I., Lugtenburg J. Interpretation of the resonance Raman spectrum of bathorhodopsin based on visual pigment analogues. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2410–2418. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada Y., Shichida Y., Yoshizawa T., Ito M., Kodama A., Tsukida K. Studies on structure and function of rhodopsin by use of cyclopentatrienylidene 11-cis-locked-rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5826–5832. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Ebrey T., Callender R. H., Dinur U., Ottolenghi M. Photoisomerization, energy storage, and charge separation: a model for light energy transduction in visual pigments and bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2503–2507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard R., Kropf A. THE ACTION OF LIGHT ON RHODOPSIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Feb;44(2):130–139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.2.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. W., Miller J. L., Mendel-Hartvig J., Schaechter L. E., Kliger D. S., Dratz E. A. Sensitive light scattering probe of enzymatic processes in retinal rod photoreceptor membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):743–747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda A., Shichida Y., Yoshizawa T. Formation of 7-cis- and 13-cis-retinal pigments by irradiating squid rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1449–1453. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao B., Tsuda M., Ebrey T. G., Akita H., Balogh-Nair V., Nakanishi K. Flash photolysis and low temperature photochemistry of bovine rhodopsin with a fixed 11-ene. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):543–546. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84809-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto O., Tokunaga F., Yoshizawa T., Kamat V., Blatchly H. A., Balogh-Nair V., Nakanishi K. Photochemical reaction of 7,8-dihydrorhodopsin at low temperatures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 27;766(3):597–602. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(84)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palings I., Pardoen J. A., van den Berg E., Winkel C., Lugtenburg J., Mathies R. A. Assignment of fingerprint vibrations in the resonance Raman spectra of rhodopsin, isorhodopsin, and bathorhodopsin: implications for chromophore structure and environment. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2544–2556. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K., Applebury M. L., Rentzepis P. M. Primary photochemical event in vision: proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3119–3123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick G. A., Cooper T. M., Holloway R. A., Murray L. P., Birge R. R. Energy storage in the primary photochemical events of rhodopsin and isorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2556–2562. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shichida Y., Kropf A., Yoshizawa T. Photochemical reactions of 13-demethyl visual pigment analogues at low temperatures. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1962–1968. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., McCain D. A., Nakanishi K., Okabe M., Shimizu N., Rodman H., Honig B., Bogomolni R. A. Chromophore/protein interaction in bacterial sensory rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):479–483. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83657-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa T., Shichida Y., Matuoka S. Primary intermediates of rhodopsin studied by low temperature spectrophotometry and laser photolysis. Bathorhodopsin, hypsorhodopsin and photorhodopsin. Vision Res. 1984;24(11):1455–1463. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(84)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


