Abstract
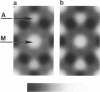
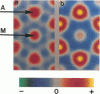
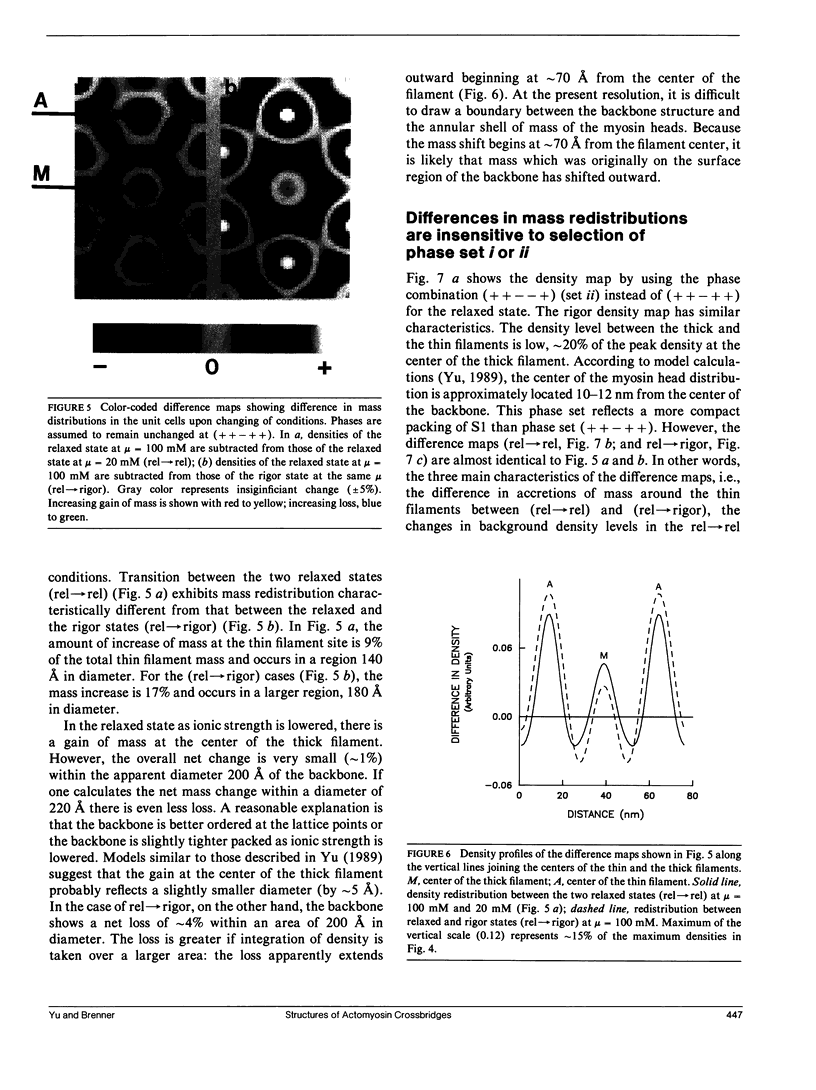
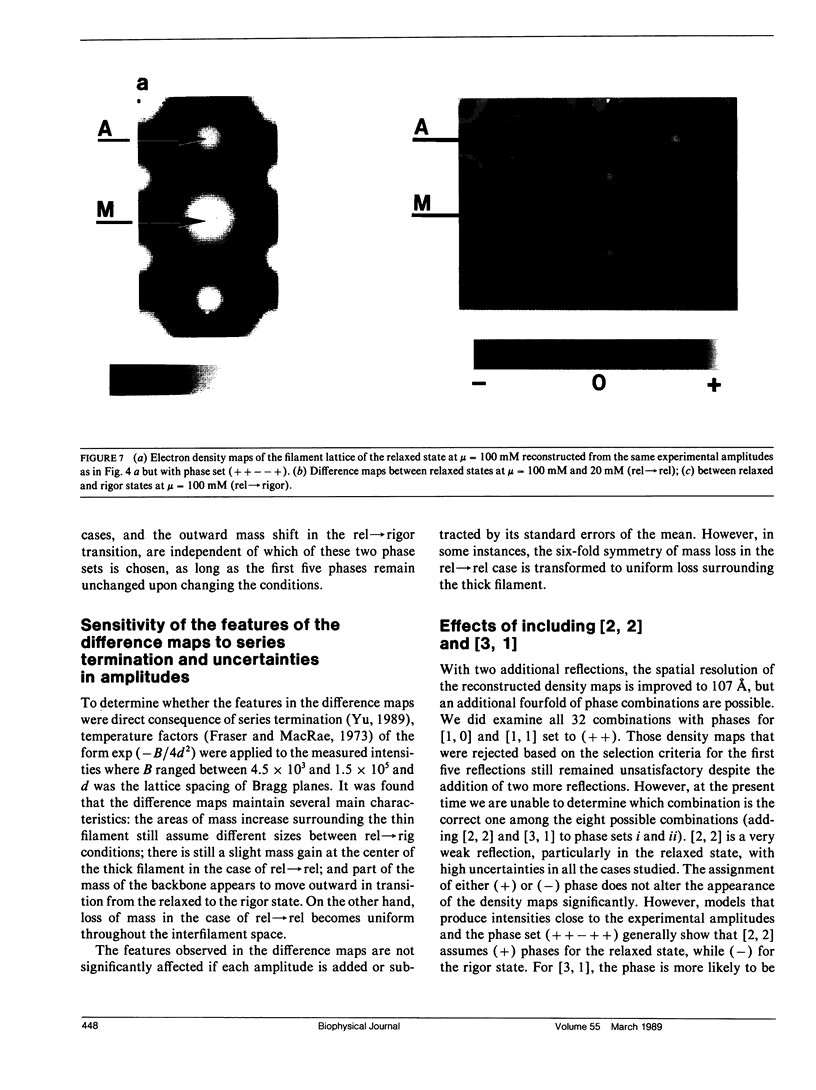
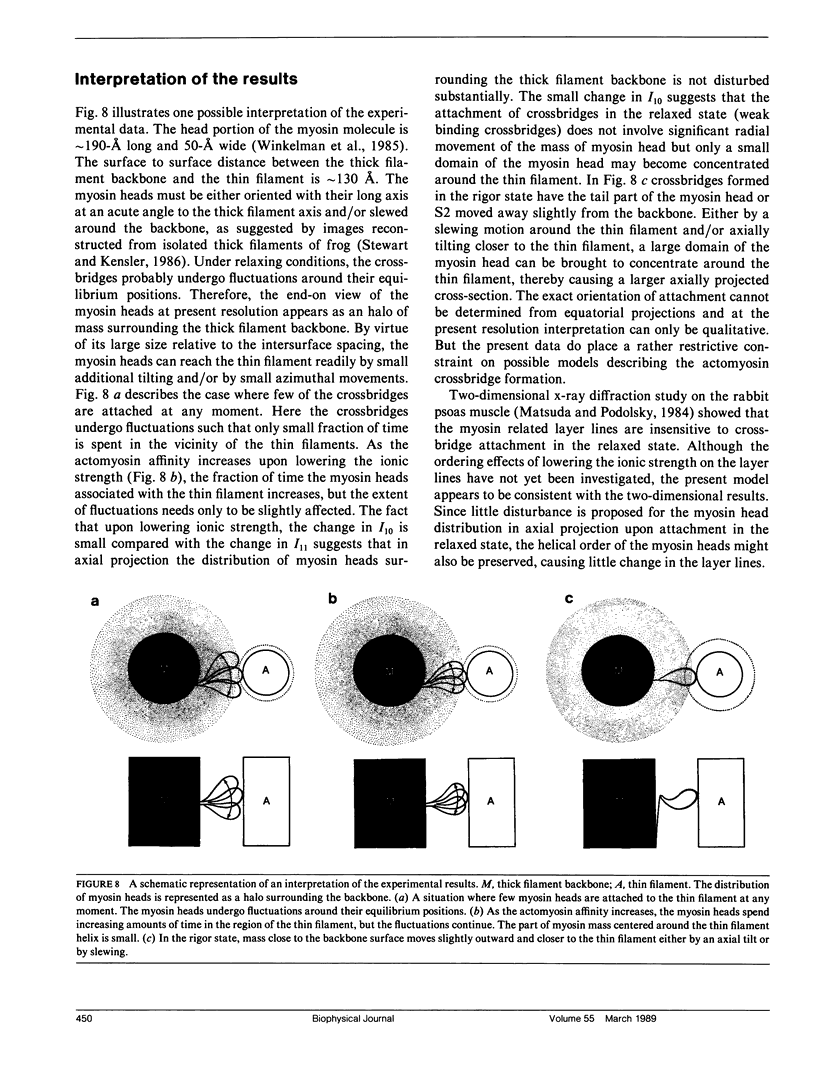
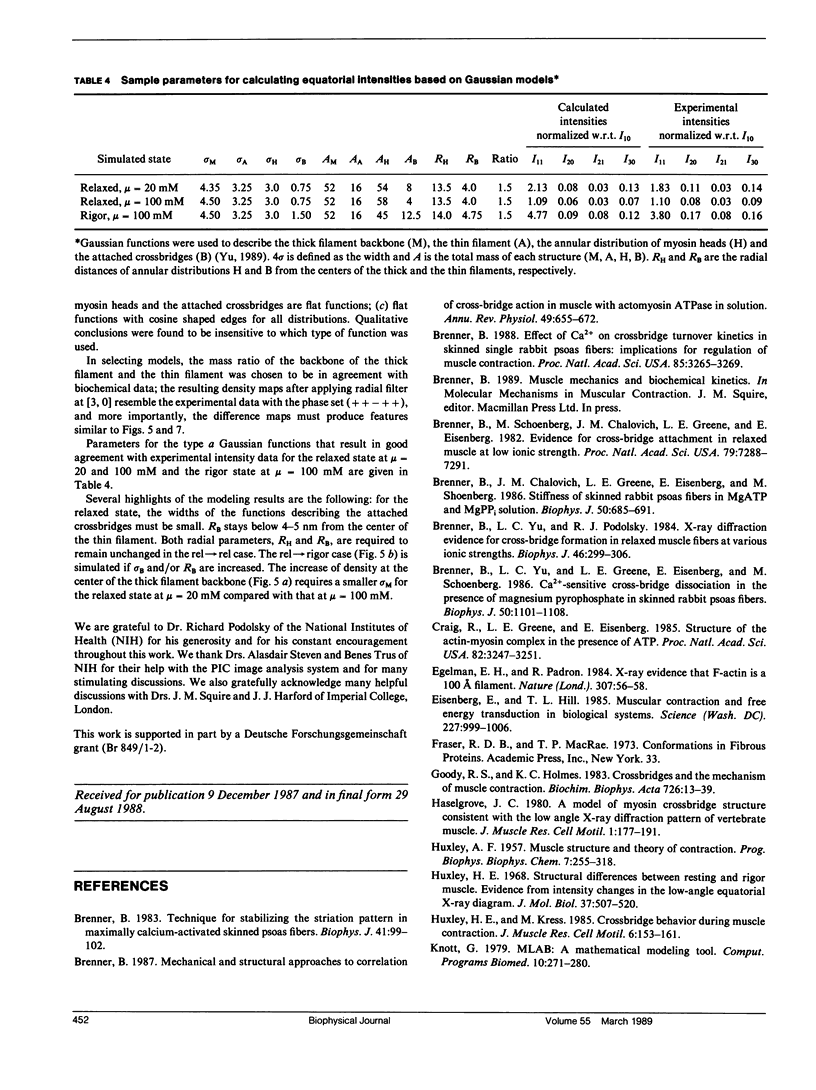
It was shown previously that a significant fraction of the myosin crossbridges is attached to actin in the skinned rabbit psoas fibers under relaxed conditions at low ionic strength and low temperature (Brenner, B., M. Schoenberg, J. M. Chalovich, L. E. Greene, and E. Eisenberg. 1982. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 79:7288-7291; Brenner, B., L. C. Lu, and R. J. Podolsky. 1984. Biophys. J. 46:299-306). In the present work, the structure of the attached crossbridges in the relaxed state between ionic strengths of 20 and 100 mM, as compared with that in the rigor state, is further examined by equatorial x-ray diffraction. Mass distributions projected along the fiber axis are reconstructed based on the first five equatorial reflections such that the spatial resolution is 128 A. The fraction of crossbridges attached under relaxed conditions are estimated to be in the range of 30% (at 100 mM ionic strength) and 60% (at 20 mM). The reconstructed density maps suggest that in the relaxed state, upon attachment the part of the crossbridge that centers around the thin filament is small, and the attachment does not significantly alter the center of mass of the myosin head distribution around the thick filament backbone. In contrast, accretion of mass in the rigor state occurs in a wider region surrounding the thin filament. In this case, mass in the surface region of the thick filament backbone is shifted slightly outward, probably by approximately 10 A. A schematic model for interpreting the present data is presented.
Full text
PDF


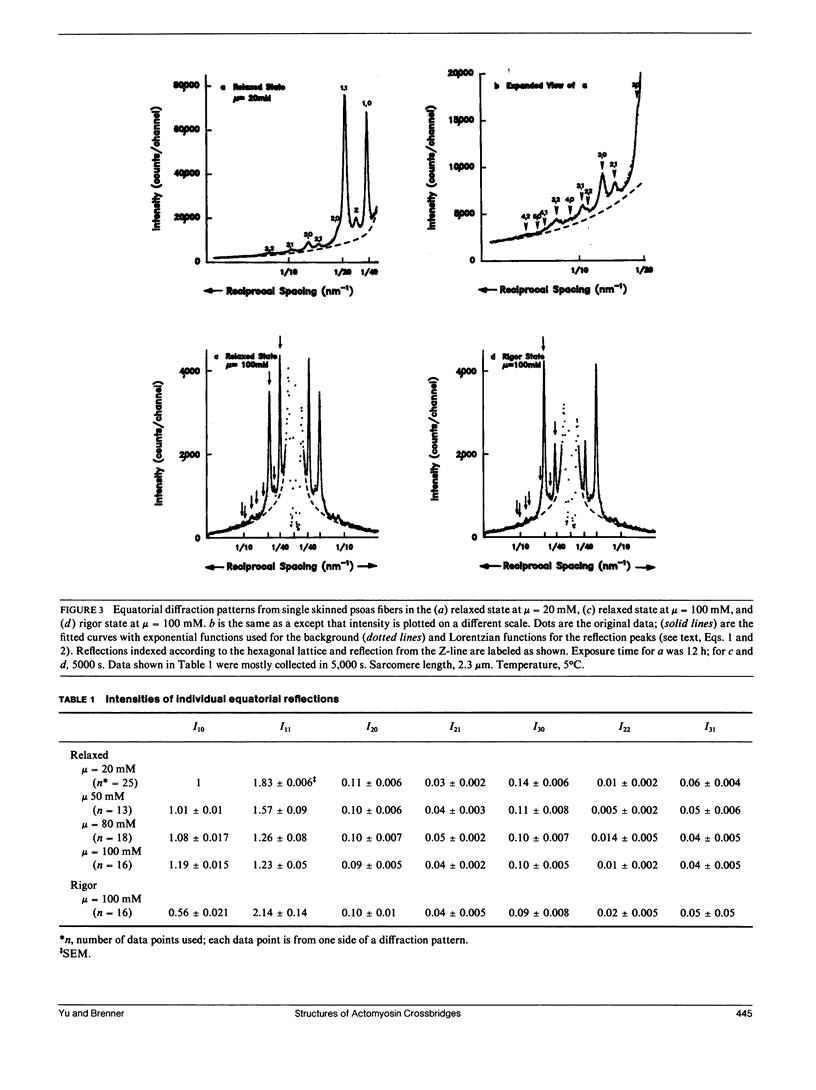




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner B., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E., Schoenberg M. Stiffness of skinned rabbit psoas fibers in MgATP and MgPPi solution. Biophys J. 1986 Oct;50(4):685–691. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83509-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Effect of Ca2+ on cross-bridge turnover kinetics in skinned single rabbit psoas fibers: implications for regulation of muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Mechanical and structural approaches to correlation of cross-bridge action in muscle with actomyosin ATPase in solution. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:655–672. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Schoenberg M., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Evidence for cross-bridge attachment in relaxed muscle at low ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7288–7291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Technique for stabilizing the striation pattern in maximally calcium-activated skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Biophys J. 1983 Jan;41(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84411-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Yu L. C., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E., Schoenberg M. Ca2+-sensitive cross-bridge dissociation in the presence of magnesium pyrophosphate in skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1101–1108. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83554-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Yu L. C., Podolsky R. J. X-ray diffraction evidence for cross-bridge formation in relaxed muscle fibers at various ionic strengths. Biophys J. 1984 Sep;46(3):299–306. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84026-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Structure of the actin-myosin complex in the presence of ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3247–3251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L. Muscle contraction and free energy transduction in biological systems. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):999–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.3156404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goody R. S., Holmes K. C. Cross-bridges and the mechanism of muscle contraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 15;726(1):13–39. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrove J. C. A model of myosin crossbridge structure consistent with the low-angle x-ray diffraction pattern of vertebrate muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1980 Jun;1(2):177–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00711798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Kress M. Crossbridge behaviour during muscle contraction. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Apr;6(2):153–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00713057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. Structural difference between resting and rigor muscle; evidence from intensity changes in the lowangle equatorial x-ray diagram. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):507–520. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott G. D. Mlab--a mathematical modeling tool. Comput Programs Biomed. 1979 Dec;10(3):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(79)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Podolsky R. J. X-ray evidence for two structural states of the actomyosin cross-bridge in muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2364–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky R. J., Arata T. Force generating mechanisms in striated muscle. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;226:319–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen F. R., Lowy J. Small-angle X-ray scattering from myosin heads in relaxed and rigor frog skeletal muscles. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):146–152. doi: 10.1038/303146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M. Characterization of the myosin adenosine triphosphate (M.ATP) crossbridge in rabbit and frog skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1988 Jul;54(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82938-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Kensler R. W. Arrangement of myosin heads in relaxed thick filaments from frog skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):831–851. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P. D., Giniger E. Calcium-sensitive binding of heavy meromyosin to regulated actin in the presence of ATP. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12647–12650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmann D. A., Mekeel H., Rayment I. Packing analysis of crystalline myosin subfragment-1. Implications for the size and shape of the myosin head. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 20;181(4):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S. G., Kress M., Huxley H. E. X-ray diffraction studies of the structural state of crossbridges in skinned frog sartorius muscle at low ionic strength. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1987 Feb;8(1):39–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01767263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. C. Analysis of equatorial x-ray diffraction patterns from skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1989 Mar;55(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82837-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. C., Brenner B. High-resolution equatorial x-ray diffraction from single skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):133–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83623-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. C., Steven A. C., Naylor G. R., Gamble R. C., Podolsky R. J. Distribution of mass in relaxed frog skeletal muscle and its redistribution upon activation. Biophys J. 1985 Mar;47(3):311–321. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83921-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]