Abstract
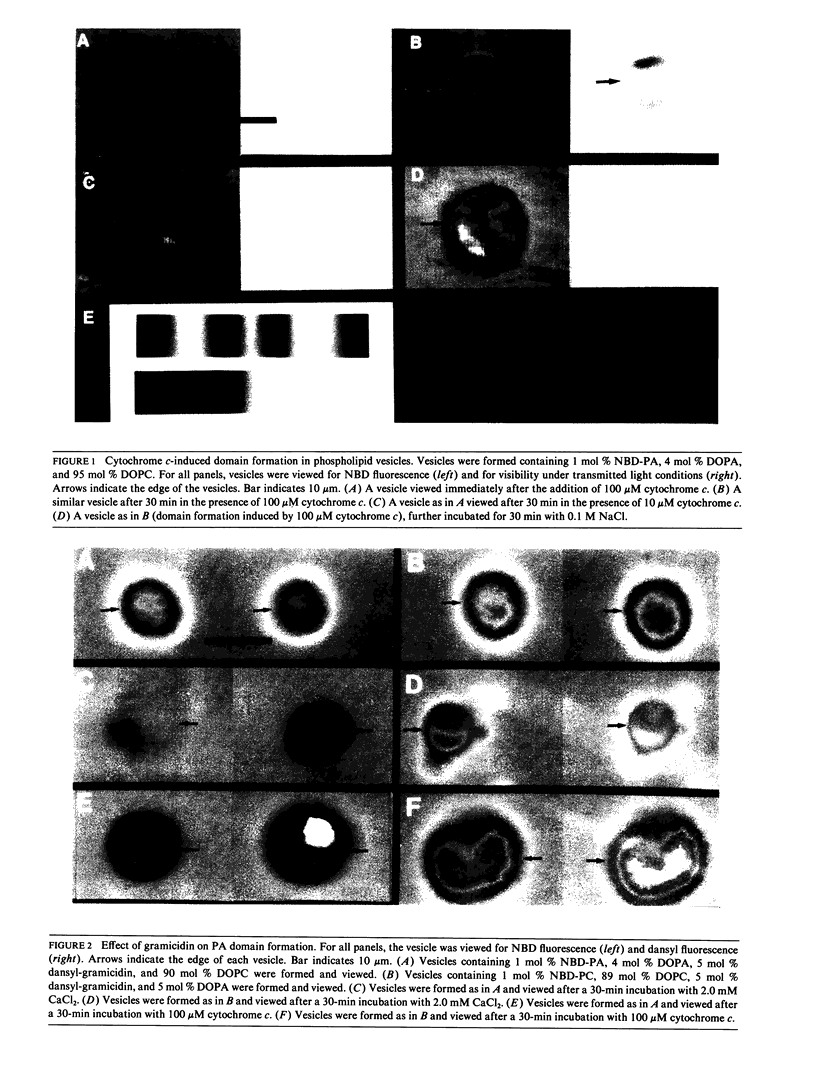
Using large (5-10 microns) vesicles formed in the presence of phospholipids fluorescently labeled on the acyl chain and visualized using a fluorescence microscope, charge-coupled-device camera, and digital image processor, we examined the effects of membrane proteins on phospholipid domain formation. In vesicles composed of phosphatidic acid and phosphatidylcholine, incubation with cytochrome c induced the reorganization of phospholipids into large phosphatidic acid-enriched domains with the exclusion of phosphatidylcholine. Cytochrome c binding was demonstrated to be highest in the phosphatidic acid-enriched domain of the vesicle using the absorbance of the heme moiety for visualization. Both binding of cytochrome c and phospholipid reorganization were blocked by pretreatment of the vesicles with 0.1 M NaCl. The pore forming peptide gramicidin was examined for the effects of an integral protein on domain formation. Initially, gramicidin distributed randomly within the vesicle and showed no phospholipid specificity. Phosphatidic acid domain formation in the presence of 2.0 mM CaCl2 or 100 microM cytochrome c was not affected by the presence of 5 mol % gramicidin within the vesicles. In both cases, gramicidin was preferentially excluded from the phosphatidic acid-enriched domain and became associated with phosphatidylcholine-enriched areas of the vesicle. Thus, cytochrome c caused a major reorganization of both the phospholipids and the proteins in the bilayer.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bearer E. L., Friend D. S. Modifications of anionic-lipid domains preceding membrane fusion in guinea pig sperm. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):604–615. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birrell G. B., Griffith O. H. Cytochrome c induced lateral phase separation in a diphosphatidylglycerol-steroid spin-label model membrane. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2925–2929. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffrey M., Feigenson G. W. Influence of metal ions on the phase properties of phosphatidic acid in combination with natural and synthetic phosphatidylcholines: an X-ray diffraction study using synchrotron radiation. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):323–331. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darszon A., Vandenberg C. A., Schönfeld M., Ellisman M. H., Spitzer N. C., Montal M. Reassembly of protein-lipid complexes into large bilayer vesicles: perspectives for membrane reconstitution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):239–243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaux P. F., Hoatson G. L., Favre E., Fellmann P., Farren B., MacKay A. L., Bloom M. Interaction of cytochrome c with mixed dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine-dimyristoylphosphatidylserine bilayers: a deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3804–3812. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaux P. F., Seigneuret M. Specificity of lipid-protein interactions as determined by spectroscopic techniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 12;822(1):63–125. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigenson G. W. Polypeptide clearing in model membranes: an analysis of the partition of gramicidin a' between cadmium ion induced gel and liquid-crystalline phases in vesicles of phosphatidic acid and phosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 21;22(13):3106–3112. doi: 10.1021/bi00282a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Cohn N., Glaser M. Fluidity of LM cell membranes with modified lipid compositions as determined with 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):1042–1049. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupte S., Wu E. S., Hoechli L., Hoechli M., Jacobson K., Sowers A. E., Hackenbrock C. R. Relationship between lateral diffusion, collision frequency, and electron transfer of mitochondrial inner membrane oxidation-reduction components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görrissen H., Marsh D., Rietveld A., de Kruijff B. Apocytochrome c binding to negatively charged lipid dispersions studied by spin-label electron spin resonance. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):2904–2910. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverstick D. M., Glaser M. Visualization of Ca2+-induced phospholipid domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4475–4479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D. Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of Ca2+-induced phase separations in phosphatidylserine-containing lipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 2;21(5):1055–1061. doi: 10.1021/bi00534a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P. C., Griffith O. H. The lipid-protein interface in biological membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;348:391–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb21315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J., Kleinfeld A. M., Hoover R. L., Dawidowicz E. A., McIntyre D. E., Salzman E. A., Klausner R. D. Lipid domains in membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;401:61–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A., de Kruijff B. The influence of proteins and peptides on the phase properties of lipids. Chem Phys Lipids. 1986 Jun-Jul;40(2-4):259–284. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(86)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London E., Feigenson G. W. Fluorescence quenching in model membranes. 2. Determination of local lipid environment of the calcium adenosinetriphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1939–1948. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannella C. A., Ribeiro A. J., Frank J. Cytochrome c binds to lipid domains in arrays of mitochondrial outer membrane channels. Biophys J. 1987 Feb;51(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83327-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustonen P., Virtanen J. A., Somerharju P. J., Kinnunen P. K. Binding of cytochrome c to liposomes as revealed by the quenching of fluorescence from pyrene-labeled phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 2;26(11):2991–2997. doi: 10.1021/bi00385a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C., Pangborn W., Nir S., Papahadjopoulos D. Specificity of Ca2+ and Mg2+ binding to phosphatidylserine vesicles and resultant phase changes of bilayer membrane structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 19;506(2):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Pagano R. E. Kinetics of soluble lipid monomer diffusion between vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2783–2789. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield E., Gilmore R., Glaser M., Gutowsky H. S., Hshung J. C., Kang S. Y., King T. E., Meadows M., Rice D. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of the effects of proteins and polypeptides on hydrocarbon chain order in model membrane systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4657–4660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Op den Kamp J. A. Lipid asymmetry in membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:47–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Vail W. J., Newton C., Nir S., Jacobson K., Poste G., Lazo R. Studies on membrane fusion. III. The role of calcium-induced phase changes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 17;465(3):579–598. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessin J. E., Glaser M. Budding of Rous sarcoma virus and vesicular stomatitis virus from localized lipid regions in the plasma membrane of chicken embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9044–9050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A., Newton C., Pangborn W., Papahadjopoulos D. Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: evidence for an intermembrane Ca2+-phospholipid complex, synergism with Mg2+, and inhibition by spectrin. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 6;18(5):780–790. doi: 10.1021/bi00572a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld A., Jordi W., de Kruijff B. Studies on the lipid dependency and mechanism of the translocation of the mitochondrial precursor protein apocytochrome c across model membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3846–3856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. Lipid-protein interaction in reconstituted cytochrome c oxidase/phospholipid membranes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Dec;359(12):1747–1756. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.1747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D., Hanahan D. J. Identification of domains of phosphatidylcholine in human erythrocyte plasma membranes. Differential action of acidic and basic phospholipases A2 from Agkistrodon halys blomhoffii. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2908–2911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Oldfield E. Dynamic structure of membranes by deuterium NMR. Science. 1984 Jul 20;225(4659):280–288. doi: 10.1126/science.6740310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson T. E., Tillack T. W. Organization of glycosphingolipids in bilayers and plasma membranes of mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:361–386. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W. R., Blout E. R. Preparation and properties of O-dansyltyrosine gramicidin C. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):3026–3030. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veatch W., Stryer L. The dimeric nature of the gramicidin A transmembrane channel: conductance and fluorescence energy transfer studies of hybrid channels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B., Cullis P. R. Cytochrome c specifically induces non-bilayer structures in cardiolipin-containing model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 18;602(3):477–490. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90327-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]