Abstract
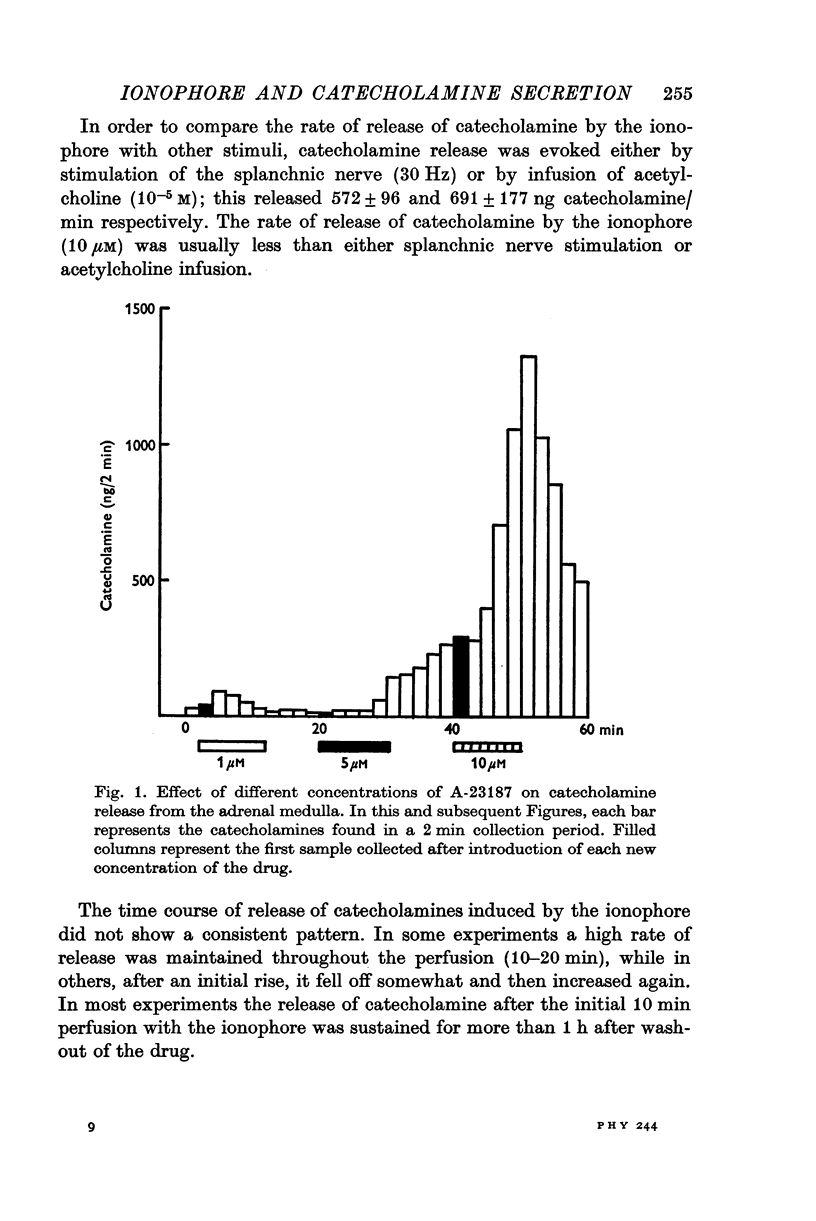
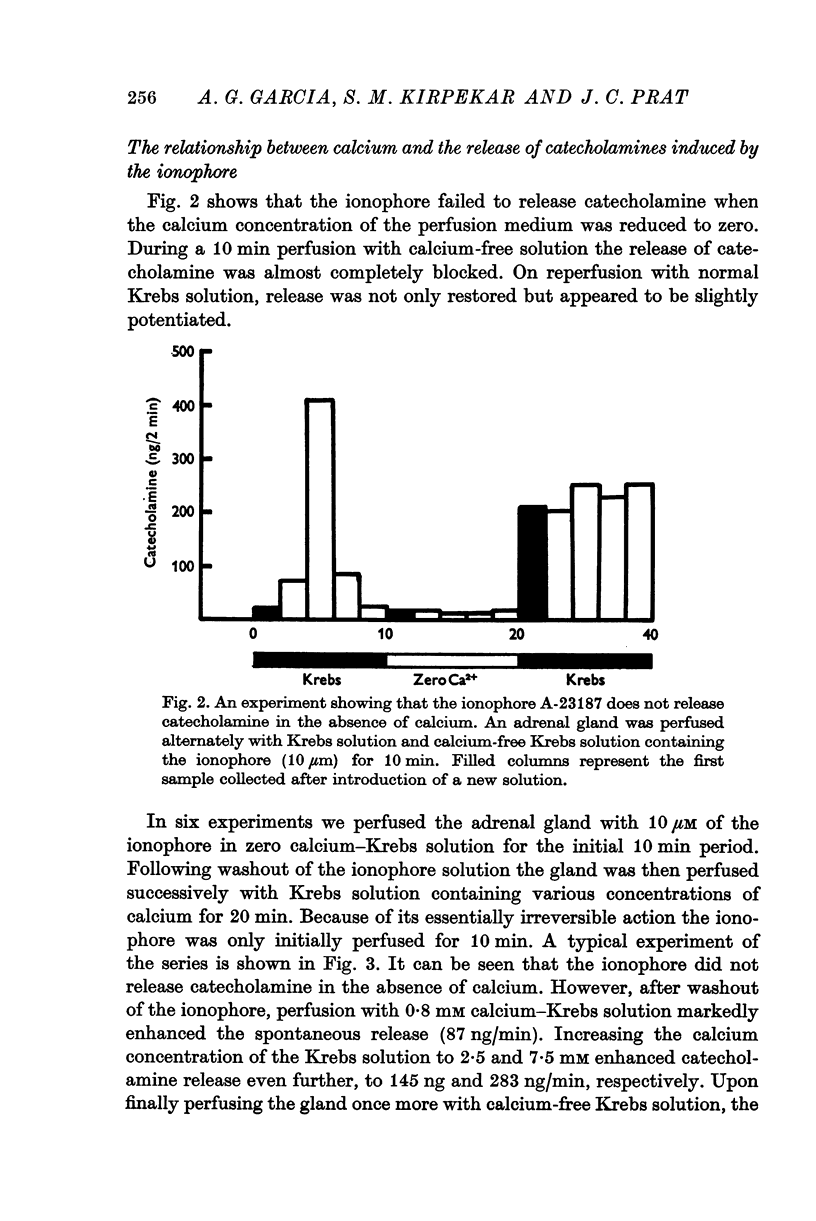
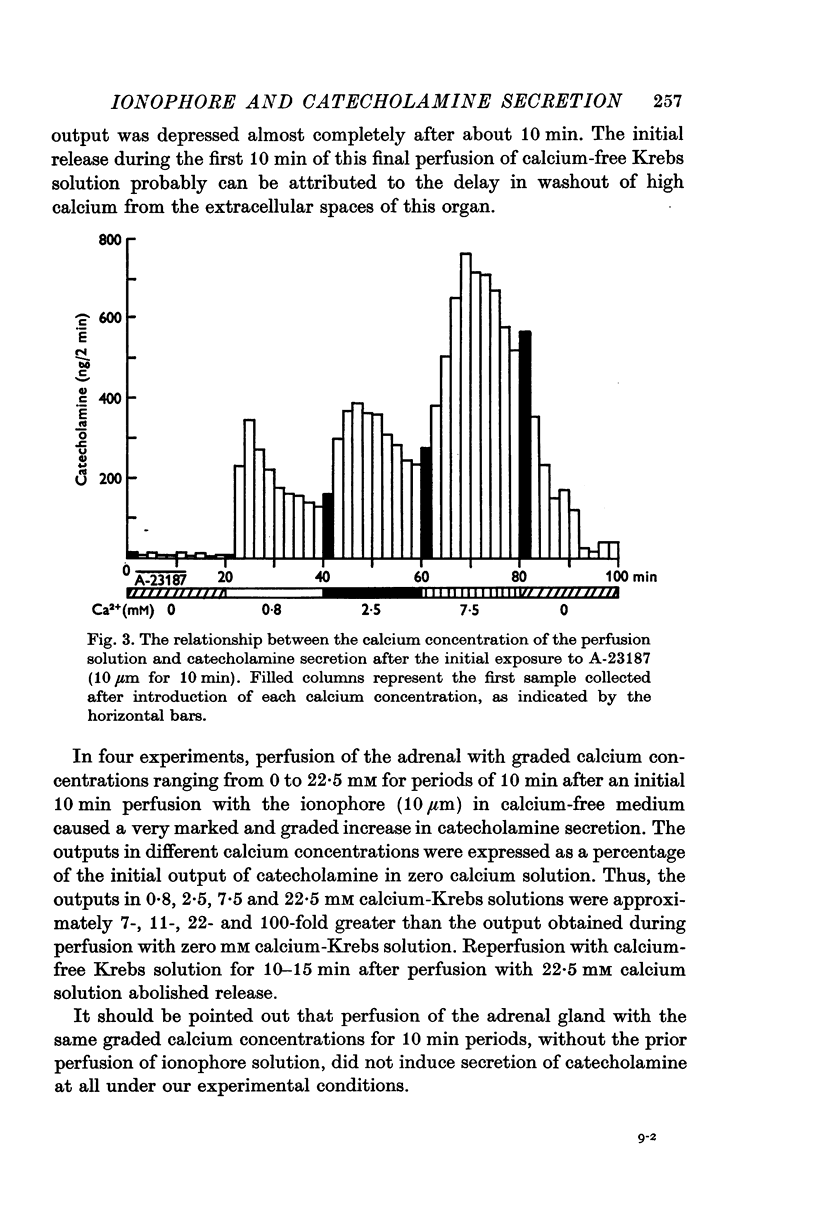
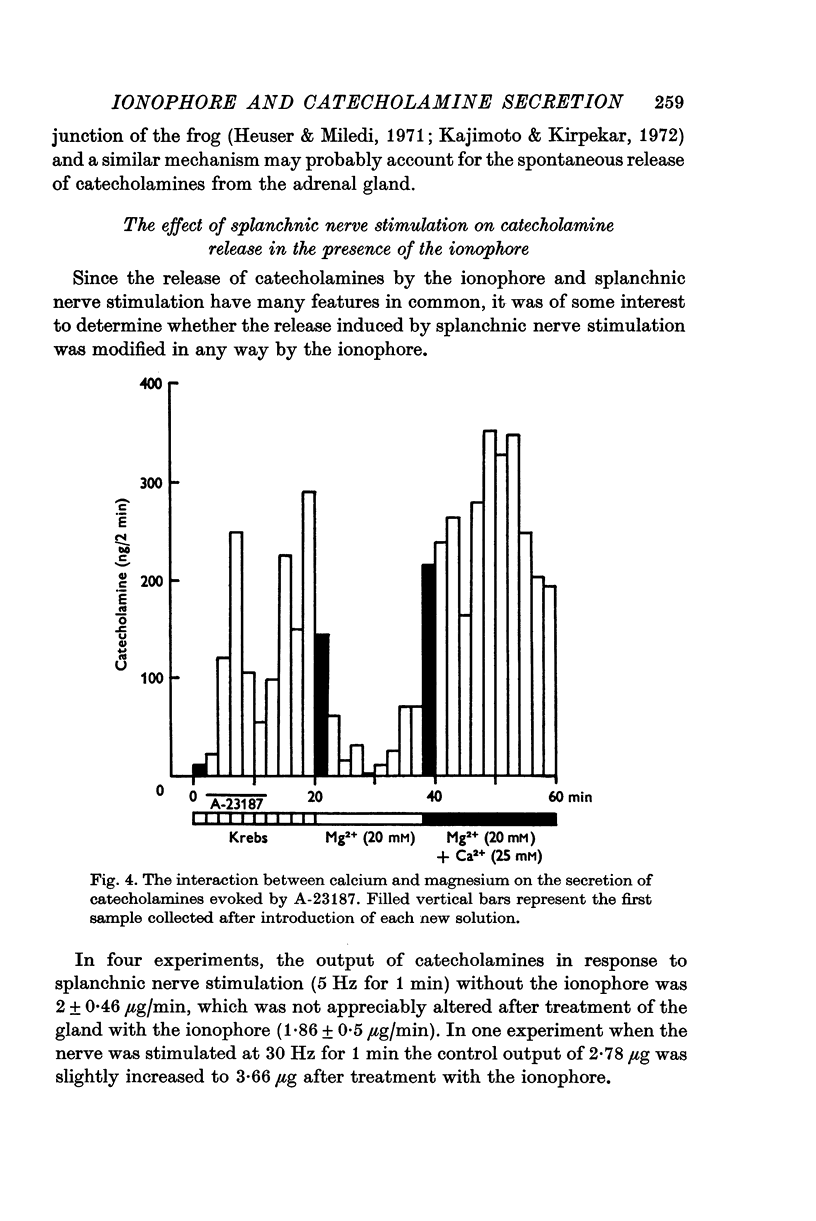
1. Experiments were performed on perfused cat adrenal glands to examine the effect of a calcium ionophore A-23187 in the secretion of catecholamines. 2. Ionophore (1-10 muM) caused a dose-dependent release of catecholamines and the output was about 100-fold greater at 10 mum than at 1 mum. 3. Release of catecholamines by the ionophore was dependent on the calcium concentration of the perfusion medium. Omission of calcium blocked the response to the ionophore while excess calcium facilitated it. 4. Magnesium antagonized the secretory response to the ionophore. Excess calcium overcame the inhibitory effect of magnesium. 5. The ionophore did not modify release of catecholamines by induced splanchnic nerve stimulation. 6. The results suggest that the ionophore, like depolarization, introduces calcium into the chromaffin cell to cause release of catecholamines.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTON A. H., SAYRE D. F. A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxide-trihydroxyindole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Dec;138:360–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Effects of manganese and other agents on the calcium uptake that follows depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):511–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane D. E., Douglas W. W. Calcium-induced extrusion of secretory granules (exocytosis) in mast cells exposed to 48-80 or the ionophores A-23187 and X-537A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):408–412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., ENGBAEK L. The nature of the neuromuscular block produced by magnesium. J Physiol. 1954 May 28;124(2):370–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RUBIN R. P. The role of calcium in the secretory response of the adrenal medulla to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:40–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Rubin R. P. The mechanism of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla and the role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167(2):288–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. C., Mongar J. L., Gomperts B. D. Calcium ionophores and movement of calcium ions following the physiological stimulus to a secretory process. Nature. 1973 Oct 5;245(5423):249–251. doi: 10.1038/245249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. G., Kirpekar S. M. Release of noradrenaline from slices of cat spleen by pre-treatment with calcium, strontium and barium. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):693–713. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J., Miledi R. Effects of lanthanum ions on function and structure of frog neuromuscular junctions. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Dec 14;179(1056):247–260. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajimoto N., Kirpekar S. M. Effect of manganese and lanthanum on spontaneous release of acetylcholine at frog motor nerve terminals. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):29–30. doi: 10.1038/newbio235029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Misu Y. Release of noradrenaline by splenic nerve stimulation and its dependence on calcium. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):219–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Prat J. C., Puig M., Wakade A. R. Modification of the evoked release of noradrenaline from the perfused cat spleen by various ions and agents. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):601–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. V., Cohen J. A., Inesi G. Contractile effects of a calcium ionophore. Nature. 1973 Apr 13;242(5398):461–463. doi: 10.1038/242461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Lanthanum ions abolish the "calcium response" of nerve terminals. Nature. 1971 Feb 5;229(5284):410–411. doi: 10.1038/229410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Slater C. R. The action of calcium on neuronal synapses in the squid. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):473–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C., Harris E. J., Jagger W. S., Johnson J. H. Antibiotic-mediated transport of alkali ions across lipid barriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1949–1956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Properties of ionophores with broad range cation selectivity. Fed Proc. 1973 Jun;32(6):1698–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Eimerl S., Schramm M. A calcium ionophore simulating the action of epinephrine on the alpha-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):128–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


