Abstract
1. A quantitative description of facilitation in the crayfish claw opener muscle is presented. The facilitation of a test response following one or more conditioning stimuli, and the growth of facilitation during a tetanus, are measured.
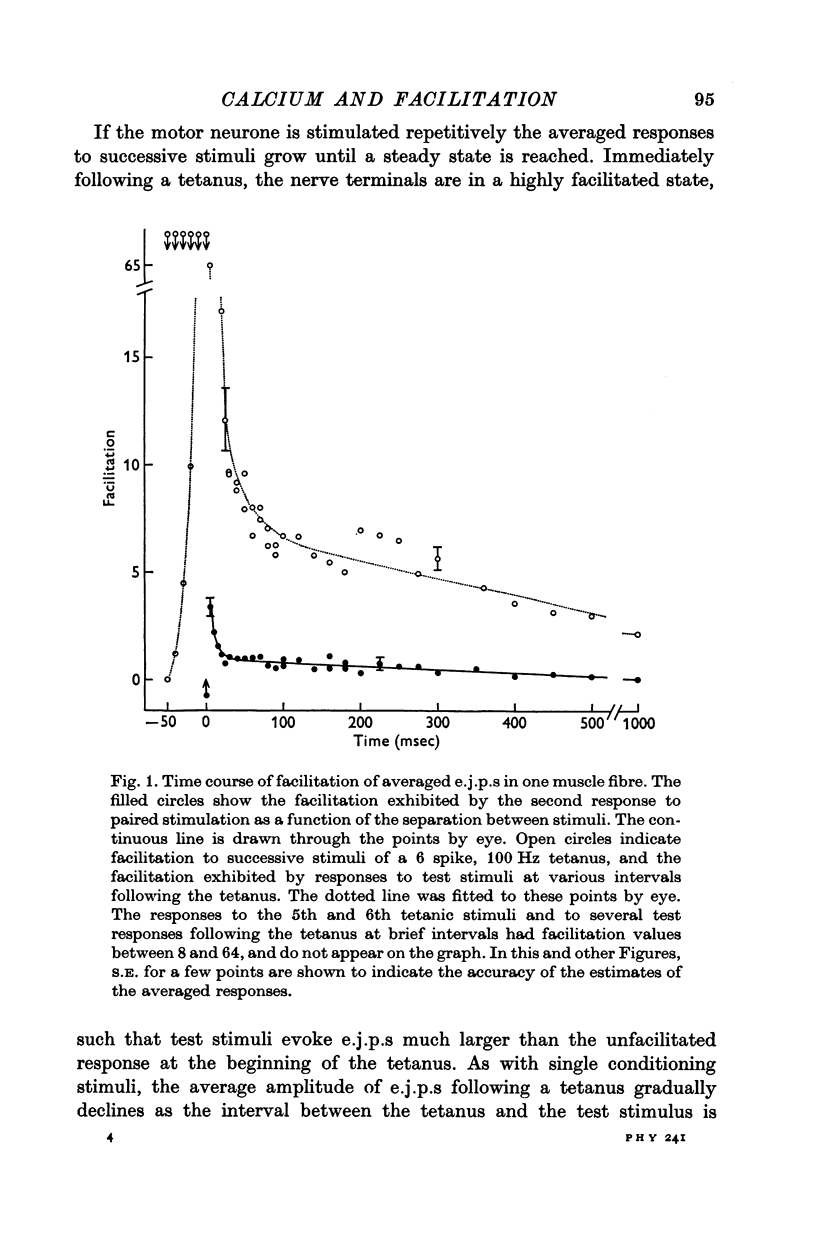
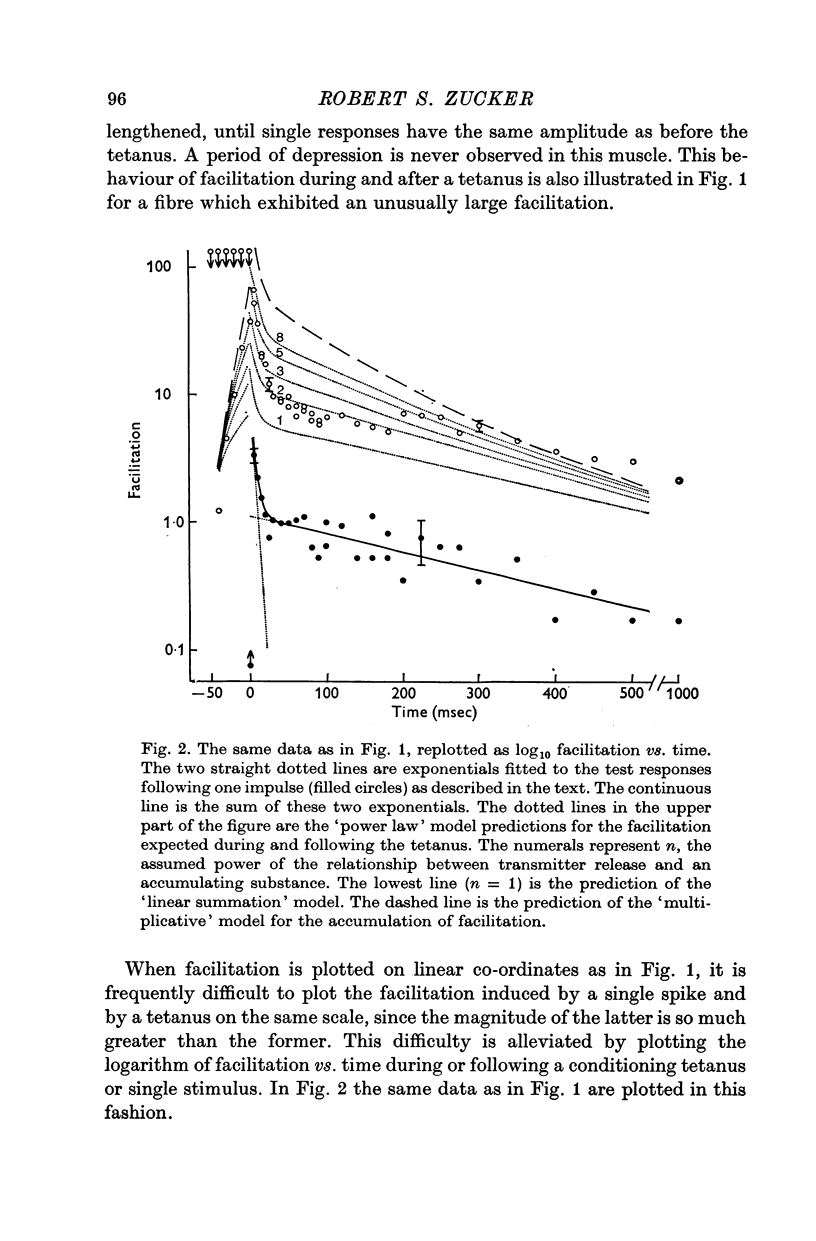
2. In superficial central fibres facilitation following one or more impulses can be described as the sum of two components which are both maximum at the end of the conditioning train and decline simultaneously and exponentially with different time constants thereafter.
3. During a tetanus, facilitation to successive stimuli grows more rapidly than is predicted by assuming that each impulse adds a constant facilitative effect to an accumulating total state of facilitation.
4. Sufficiently large values of tetanic facilitation are predicted by a model which assumes that transmitter release is proportional to the nth power of a substance or factor accumulating in nerve terminals. But no single value of n predicts the correct rise of facilitation in a tetanus and the time course of its subsequent decline from the facilitation following a single spike.
5. A model which assumes that the facilitative effects of successive spikes multiply in a tetanus predicts responses that are larger than those observed.
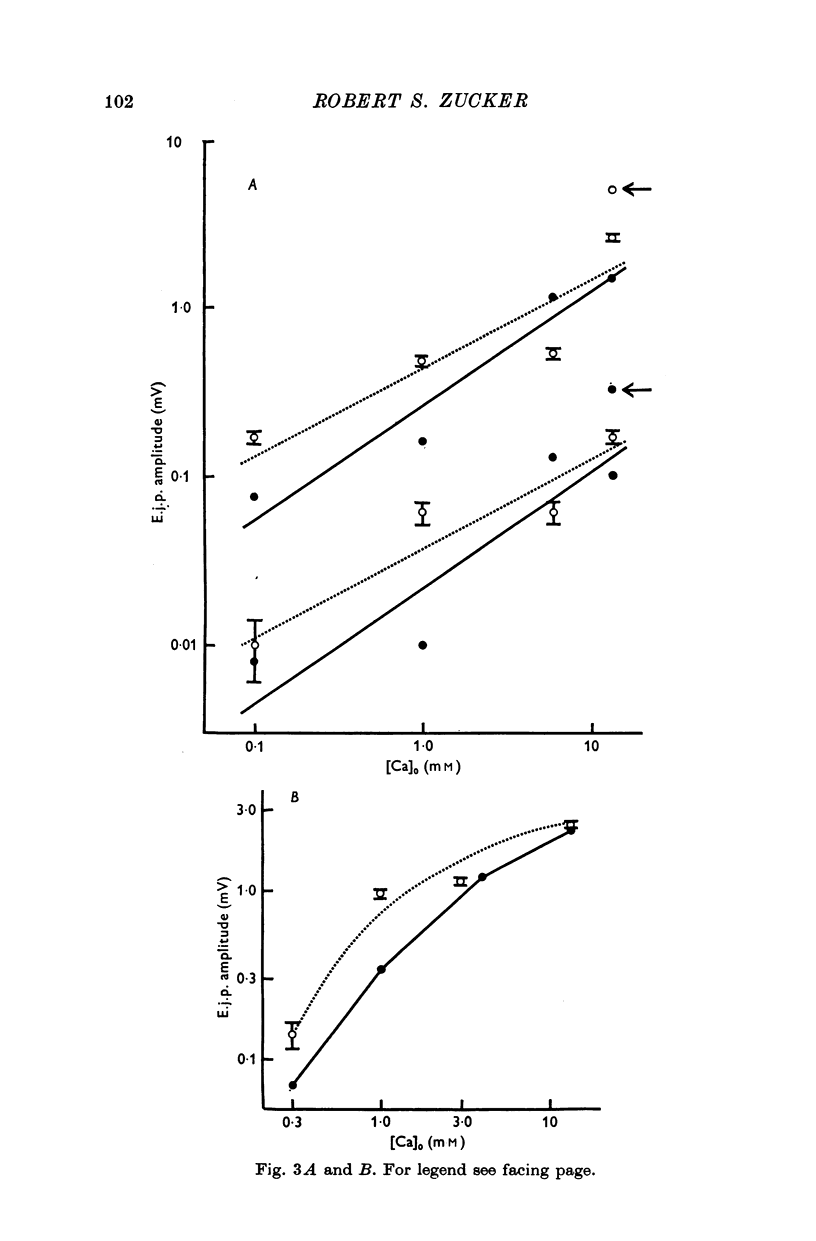
6. The effects of varying the calcium concentration ([Ca2+]) on transmitter release and facilitation were studied. When a magnesium-EDTA buffering system is used to vary [Ca2+], transmitter release is found to be nearly linearly related to [Ca2+] in the range 0·1-13·5 mM.
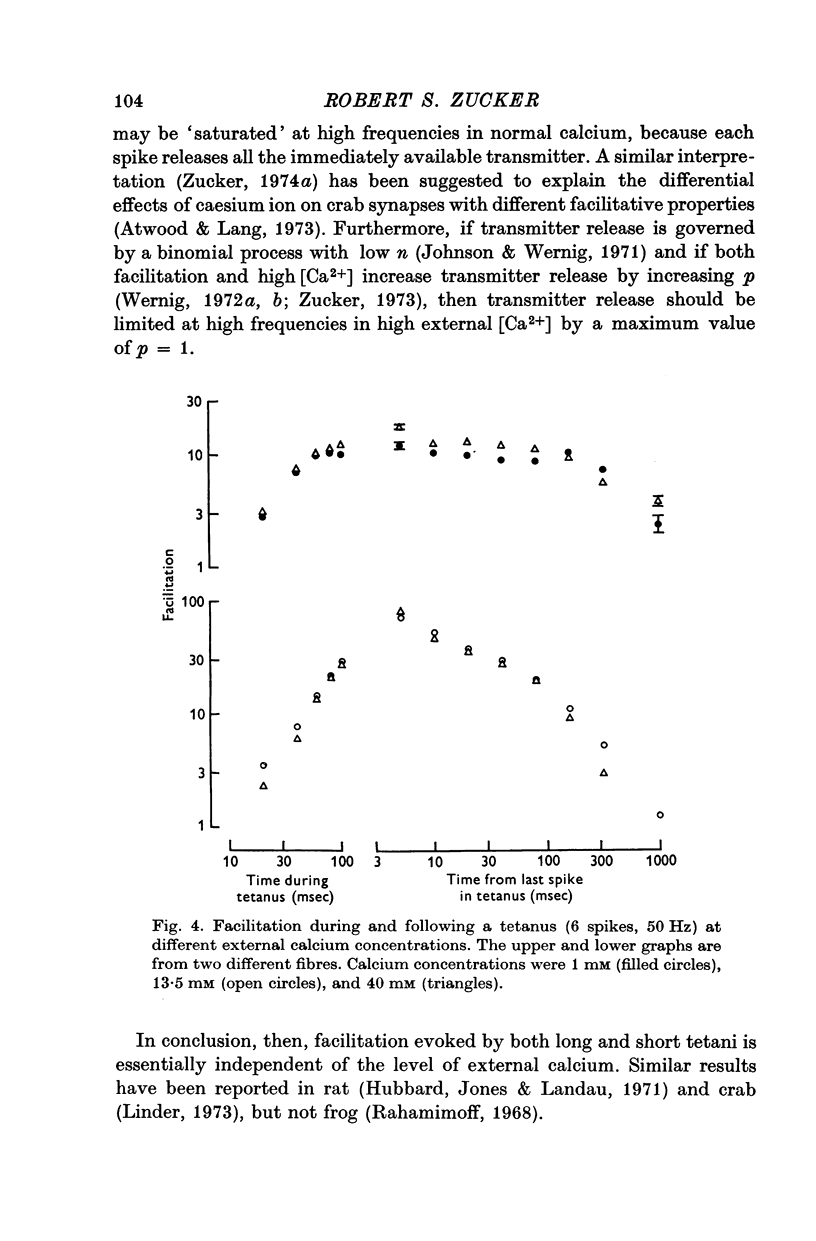
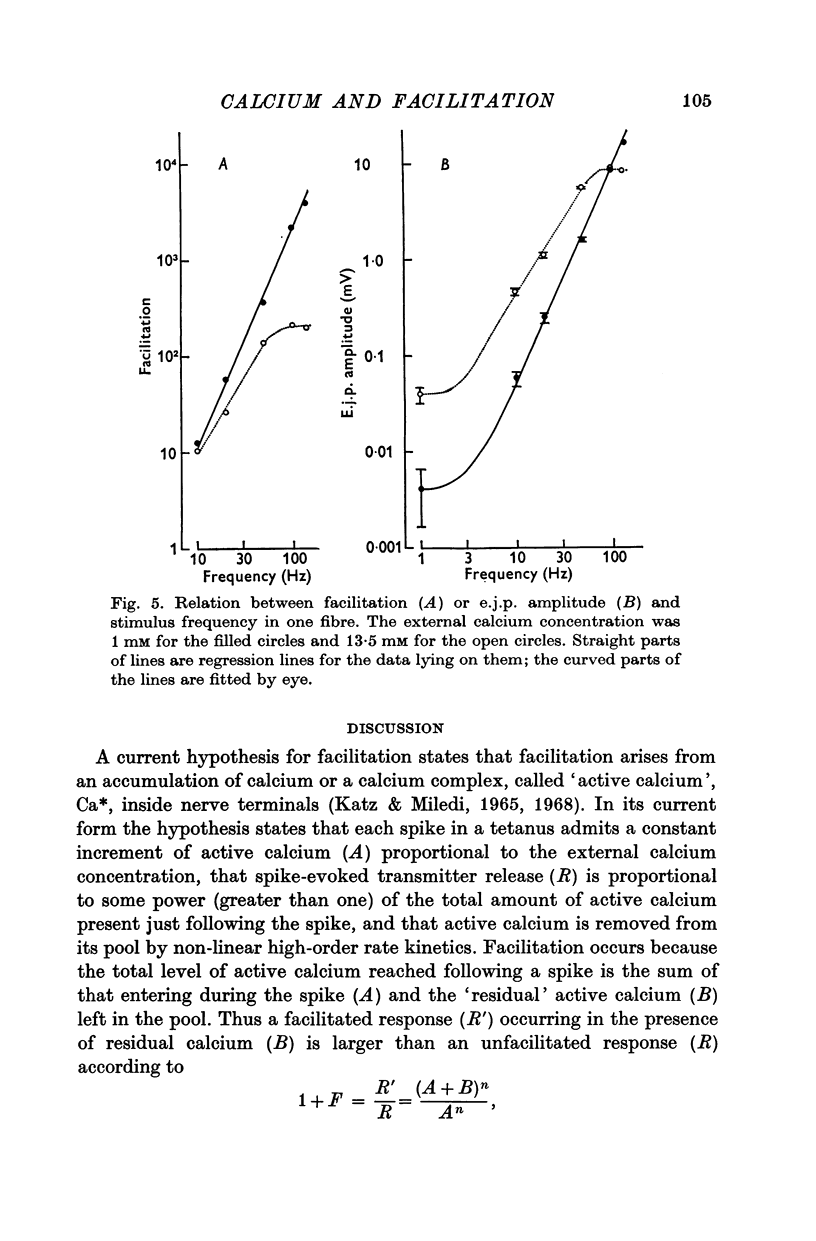
7. The magnitude and time course of facilitation during and following a tetanus are unaffected by varying [Ca2+] between 1·0 and 40 mM.
8. The relation between `steady-state' facilitation and stimulus frequency is also unaffected by changing [Ca2+], except that in high [Ca2+] transmitter release appears to saturate at high frequencies (above 30 Hz).
9. The results are discussed in terms of the `calcium accumulation' hypothesis of facilitation. The findings in crayfish appear to be qualitatively consistent with this hypothesis if certain modifications are made in the hypothesis.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwood H. L., Lang F. Differential responses of crab neuromuscular synapses to cesium ion. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):747–766. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Stevens C. F. The kinetics of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):691–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W. J. Depression of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;206(3):629–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner G. D. Differentiation of nerve terminals in the crayfish opener muscle and its functional significance. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Jun;51(6):731–758. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.6.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner G. D., Kennedy D. Quantitative aspects of transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1970 Dec;47(3):585–592. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracho H., Orkand R. K. Effect of calcium on excitatory neuromuscular transmission in the crayfish. J Physiol. 1970 Jan;206(1):61–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp008997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. D., Quastel D. M. Cumulative and persistent effects of nerve terminal depolarization on transmitter release. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):407–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Statistical factors involved in neuromuscular facilitation and depression. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):574–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDEL J., KUFFLER S. W. Mechanism of facilitation at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:530–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Jones S. F., Landau E. M. The effect of temperature change upon transmitter release, facilitation and post-tetanic potentiation. J Physiol. 1971 Aug;216(3):591–609. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. W., Wernig A. The binomial nature of transmitter release at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):757–767. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE EFFECT OF CALCIUM ON ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:496–503. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):23–38. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The timing of calcium action during neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(3):535–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W., NORTH K. A. An electrical investigation of effects of repetitive stimulation on mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Neurophysiol. 1953 Sep;16(5):509–527. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder T. M. Calcium and facilitation at two classes of crustacean neuromuscular synapses. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jan;61(1):56–73. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L. The effect of repetitive stimulation on facilitation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):327–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Martin A. R. An analysis of facilitation of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):679–694. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Thies R. Tetanic and post-tetanic rise in frequency of miniature end-plate potentials in low-calcium solutions. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):245–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz C. L., Bracho H. Effect of reduced calcium on excitatory transmitter release at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1972 Apr 1;41(4):805–812. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(72)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTZEHL H., CALDWELL P. C., RUEEGG J. C. THE DEPENDENCE OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION OF MUSCLE FIBRES FROM THE CRAB MAIA SQUINADO ON THE INTERNAL CONCENTRATION OF FREE CALCIUM IONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 25;79:581–591. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R. A dual effect of calcium ions on neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):471–480. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R. The use of the Biomac 500 computer for estimating facilitation at single end-plates. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(1):12P–14P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. Post-tetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):121–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman R. G., Atwood H. L. Synaptic facilitation: long-term neuromuscular facilitation in crustaceans. Science. 1971 Mar 26;171(3977):1248–1250. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3977.1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinnakre J., Tauc L. Calcium influx in active Aplysia neurones detected by injected aequorin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 28;242(117):113–115. doi: 10.1038/newbio242113b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraskevich P. S. Reversal potentials of L-glutamate and the excitatory transmitter at the neuromuscular junction of the crayfish. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):700–703. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D. Ionic mechanism of post-tetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernig A. Changes in statistical parameters during facilitation at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):751–759. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernig A. The effects of calcium and magnesium on statistical release parameters at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):761–768. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Changes in the statistics of transmitter release during facilitation. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):787–810. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Crayfish neuromuscular facilitation activated by constant presynaptic action potentials and depolarizing pulses. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):69–89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Excitability changes in crayfish motor neurone terminals. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):111–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


