Abstract
1. The responses of identified cells in the rat cerebral cortex to cholinomimetic and anticholinergic substances has been investigated.
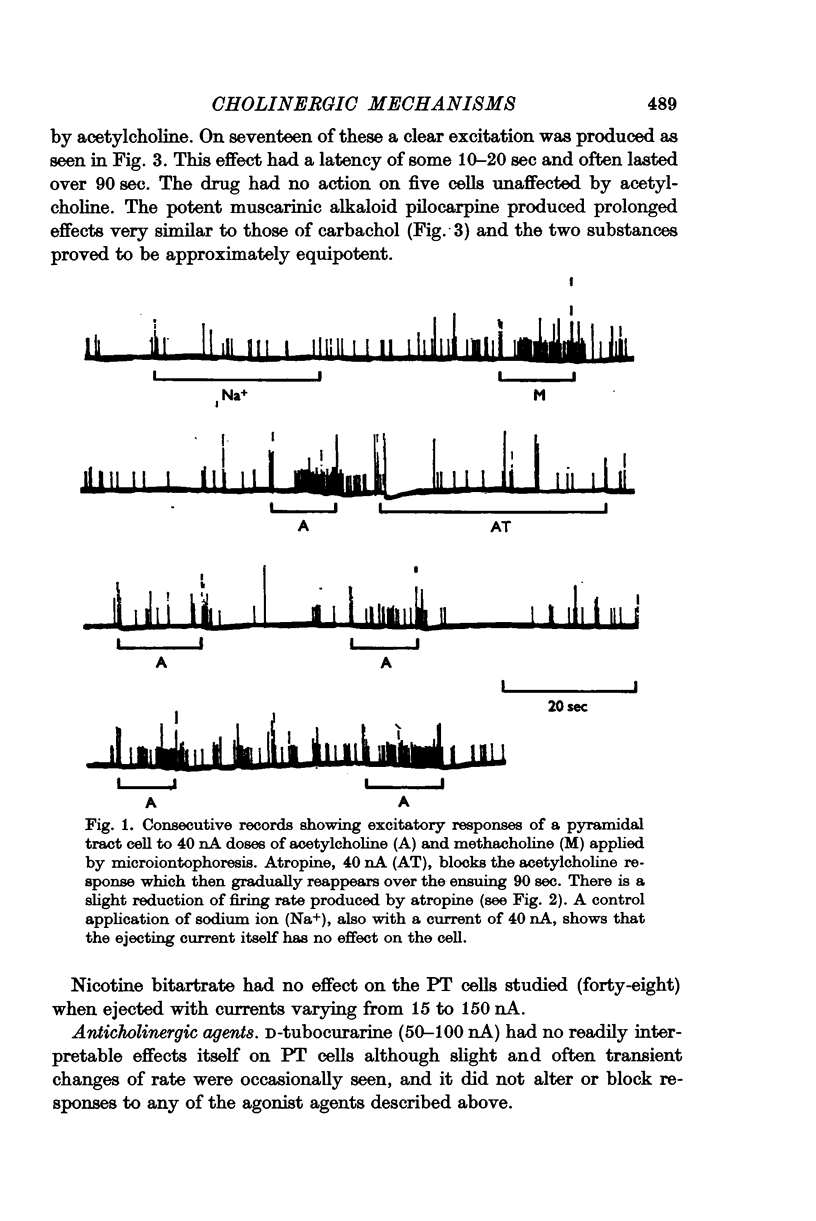
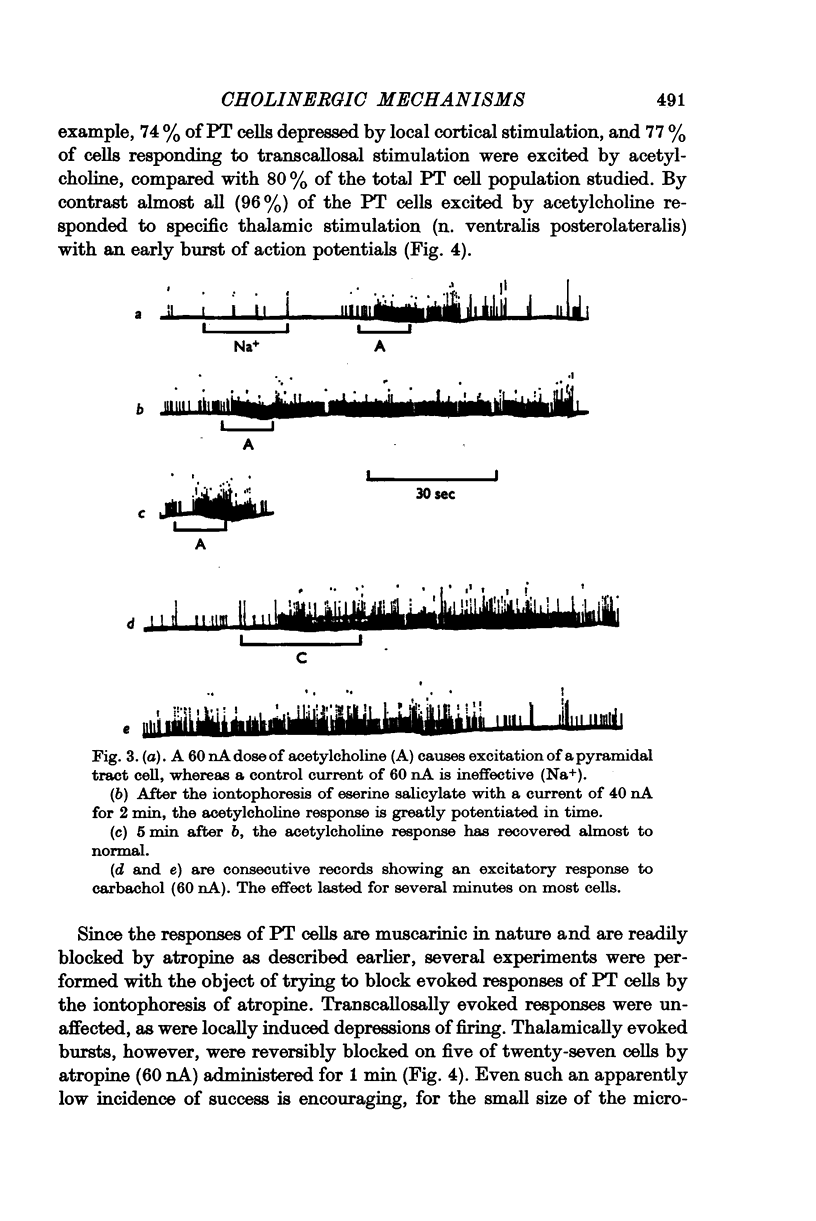
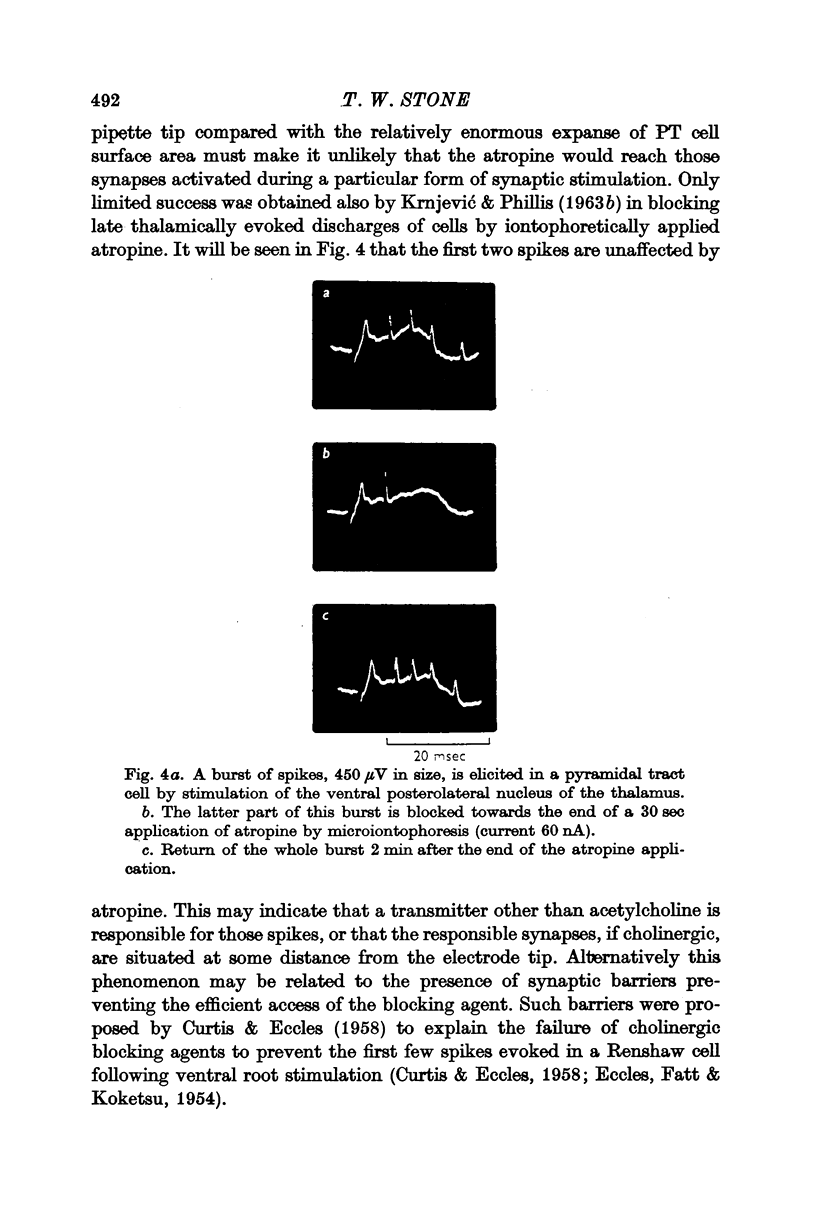
2. Acetylcholine and muscarinic agonists have an excitatory action on 80% of pyramidal tract cells. This response is found especially on cells responding to specific thalamic stimulation and the burst of spikes evoked from this site can sometimes be blocked by the iontophoresis of atropine. This strongly suggests an excitatory transmitter function for acetylcholine in a specific thalamocortical pathway.
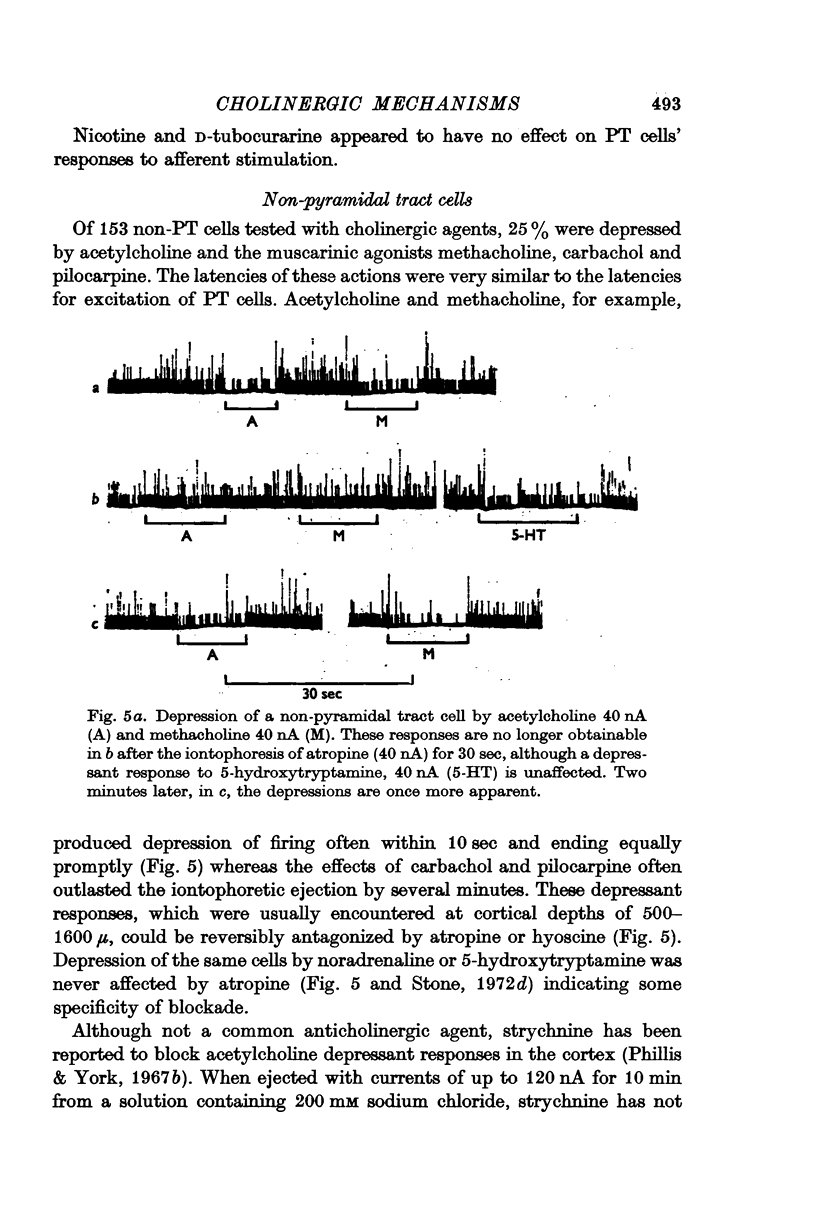
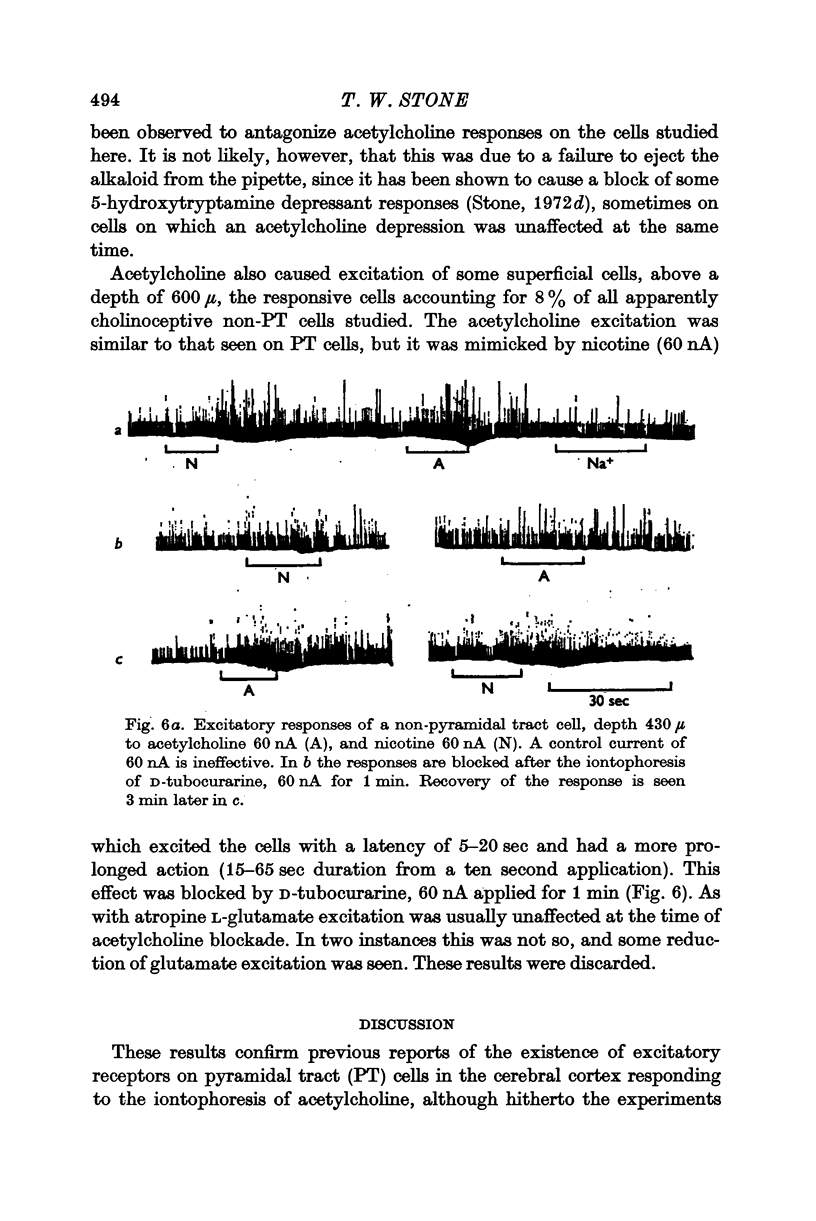
3. Experiments on non-pyramidal tract cells have detected a muscarinic depression of some cells, and a nicotinic excitation of some cells above a depth of 600 μ in the cortex.
4. It is suggested that the increased release of acetylcholine from the cortex produced by atropine administration may be due to an excess of muscarinic inhibitory over excitatory synapses in the cortex.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage A. K., Hall G. H., Sellers C. M. Effects of nicotine on electrocortical activity and acetylcholine release from the cat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):152–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUKIN Y. W. Partial recovery of glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase activity in the infarcted areas of the myocardium in rabbits during stimulation of protein synthesis. Nature. 1963 May 18;198:692–693. doi: 10.1038/198692b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Candy J. M. Iontophoretic release of acetylcholine, noradrenaline, 5-hydroxytryptamine and D-lysergic acid diethylamide from micropipettes. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Oct;40(2):194–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Dhawan B. N., Wolstencroft J. H. Pharmacological properties of cholinoceptive neurones in the medulla and pons of the cat. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):658–674. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG H. T. Similarity in action between curare and strychnine on cortical neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1953 May;16(3):221–233. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., ECCLES R. M. The effect of diffusional barriers upon the pharmacology of cells within the central nervous system. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):446–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier B., Mitchell J. F. The central release of acetylcholine during stimulation of the visual pathway. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):239–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. M., Curtis D. R. Pharmacological studies on feline Betz cells. J Physiol. 1966 Sep;186(1):121–138. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross B. A., Silver I. A. Electrophysiological studies on the hypothalamus. Br Med Bull. 1966 Sep;22(3):254–260. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., KOKETSU K. Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):524–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MALCOLM J. L., SHERWOOD S. L. Some effects of tubocurarine on the electrical activity of the cat's brain. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):130–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Vogt M. Acetylcholine synthesis in different regions of the central nervous system. J Physiol. 1948 Jun 25;107(3):372–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson R. C., Jordan L. M., Phillis J. W. The action of noradrenaline on cortical neurons: effects of pH. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 24;35(2):556–560. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90500-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT W. E., O'LEARY J. L. Form of thalamic response evoked by peripheral nerve stimulation. J Comp Neurol. 1952 Dec;97(3):491–514. doi: 10.1002/cne.900970304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Roberts M. H., Sobieszek A., Straughan D. W. Noradrenaline sensitive cells in cat cerebral cortex. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Dec;8(6):549–566. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLUVER H., BARRERA E. A method for the combined staining of cells and fibers in the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1953 Oct;12(4):400–403. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195312040-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:296–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Phillis J. W. Pharmacological properties of acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 May;166(2):328–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Randić M., Straughan D. W. Pharmacology of cortical inhibition. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):78–105. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Silver A. A histochemical study of cholinergic fibres in the cerebral cortex. J Anat. 1965 Oct;99(Pt 4):711–759. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legge K. F., Randic M., Straughan D. W. The pharmacology of neurones in the pyriform cortex. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Jan;26(1):87–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm J. L., Saraiva P., Spear P. J. Cholinergic and adrenergic inhibition in the rat cerebral cortex. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1967 Nov;6(6):509–527. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(67)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. F. The spontaneous and evoked release of acetylcholine from the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Jan;165(1):98–116. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Tebecis A. K. The responses of thalamic neurons to iontophoretically applied monoamines. J Physiol. 1967 Oct;192(3):715–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., York D. H. Cholinergic inhibition in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1967 Aug;5(4):517–520. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(67)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., York D. H. Pharmacological studies on a cholinergic inhibition in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1968 Sep;10(3):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDIC M., SIMINOFF R., STRAUGHAN D. W. ACETYLCHOLINE DEPRESSION OF CORTICAL NEURONS. Exp Neurol. 1964 Mar;9:236–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(64)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. H., Straughan D. W. Excitation and depression of cortical neurones by 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):269–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmoiraghi G. C., Stefanis C. N. Patterns of central neurons responses to suspected transmitters. Arch Ital Biol. 1965 Dec 10;103(4):705–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Are noradrenaline excitations artefacts? Nature. 1971 Nov 19;234(5325):145–146. doi: 10.1038/234145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Cholinergic mechanisms in the rat cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):155P–156P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Noradrenaline effects and pH. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 May;24(5):422–423. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb09024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Responses of blood vessels to various amines applied by microiontophoresis. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Apr;24(4):318–323. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb08992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez A. J., Krip G., Pinsky C. [vidence for a muscarinic inhibitory mechanism in the cerebral cortex]. Exp Neurol. 1969 Mar;23(3):318–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAKER V. P., SHERIDAN M. N. THE MORPHOLOGY AND ACETYLCHOLINE CONTENT OF ISOLATED CEREBRAL CORTICAL SYNAPTIC VESICLES. J Neurochem. 1965 May;12:363–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


