Abstract
1. The metabolism of rat renal cortex slices was inhibited by iodoacetate and anoxia, and swelling was prevented by the presence in the medium of 7·2 g polyethylene glycol 6000/100 ml. (referred to as PEG medium).
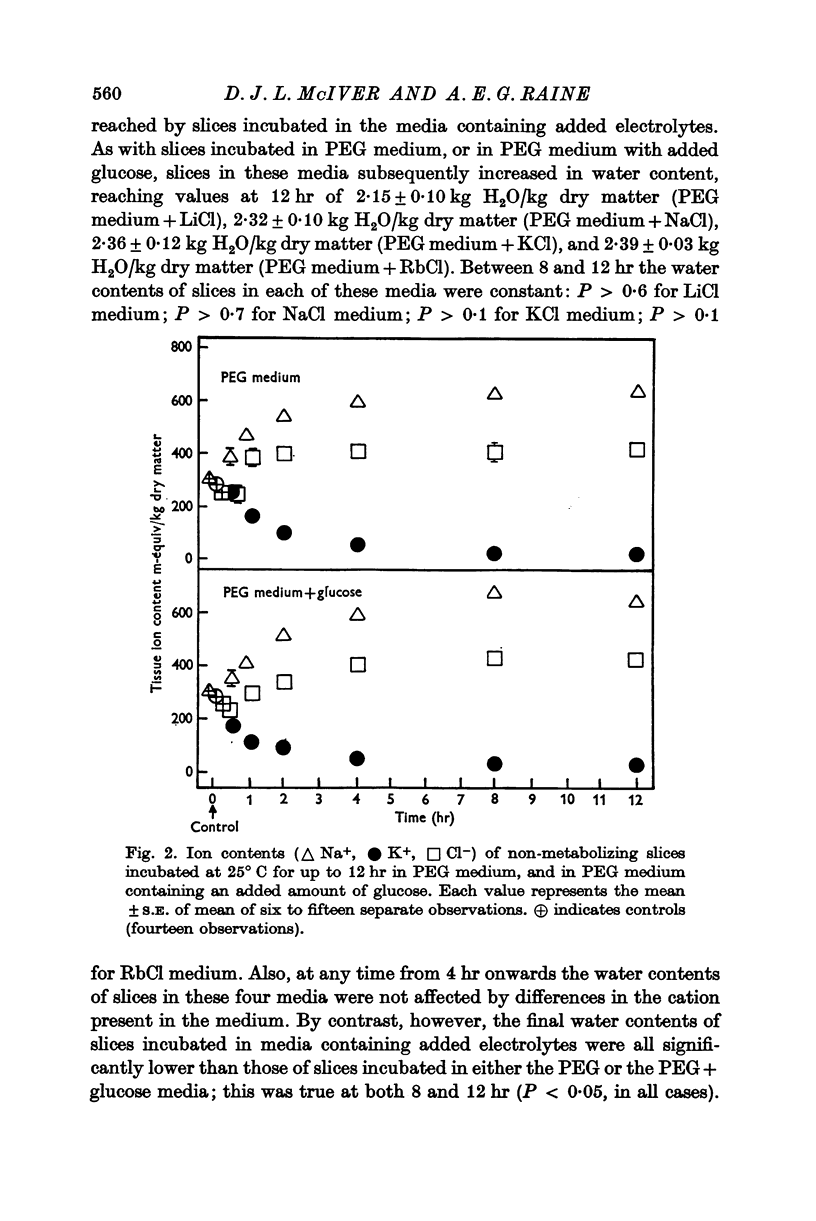
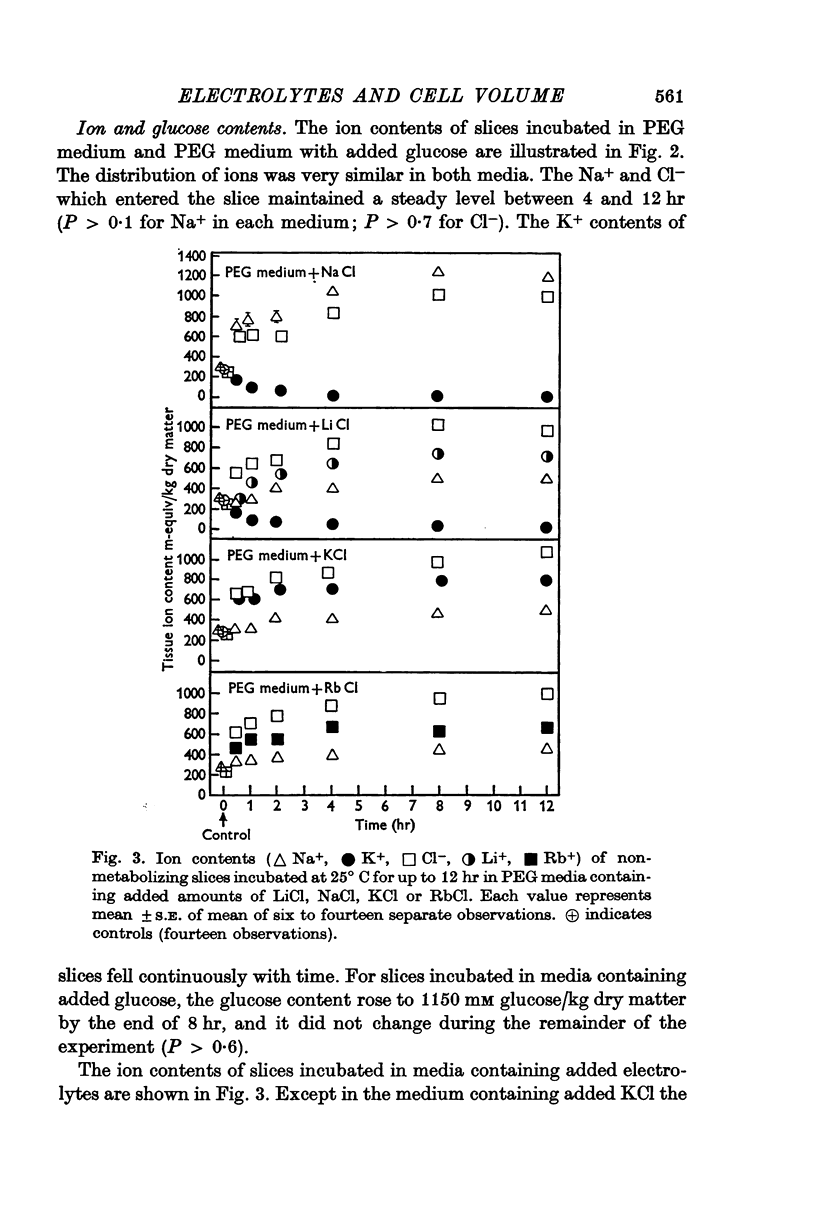
2. Slices were incubated for up to 12 hr in PEG medium, and in PEG media containing 440 m-osmole/kg H2O of an electrolyte (LiCl, NaCl, KCl or RbCl), or a non-electrolyte (glucose).
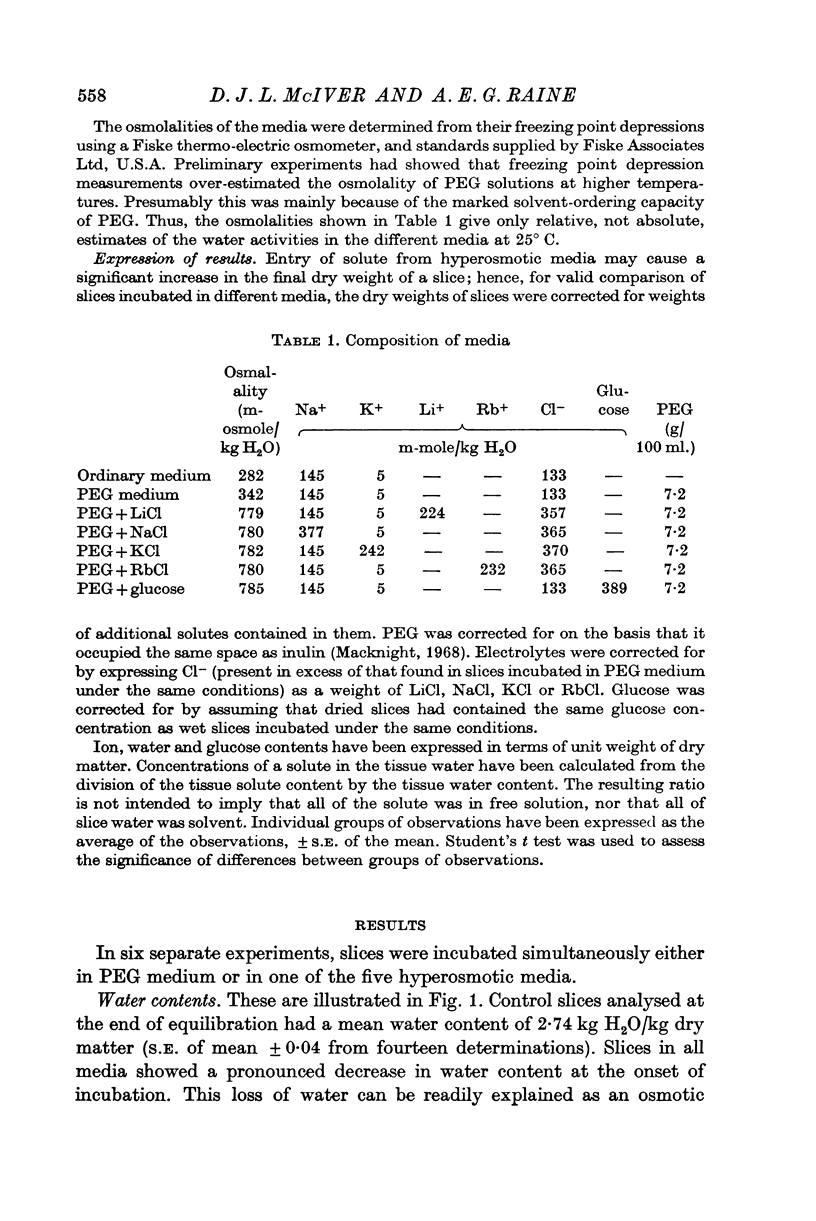
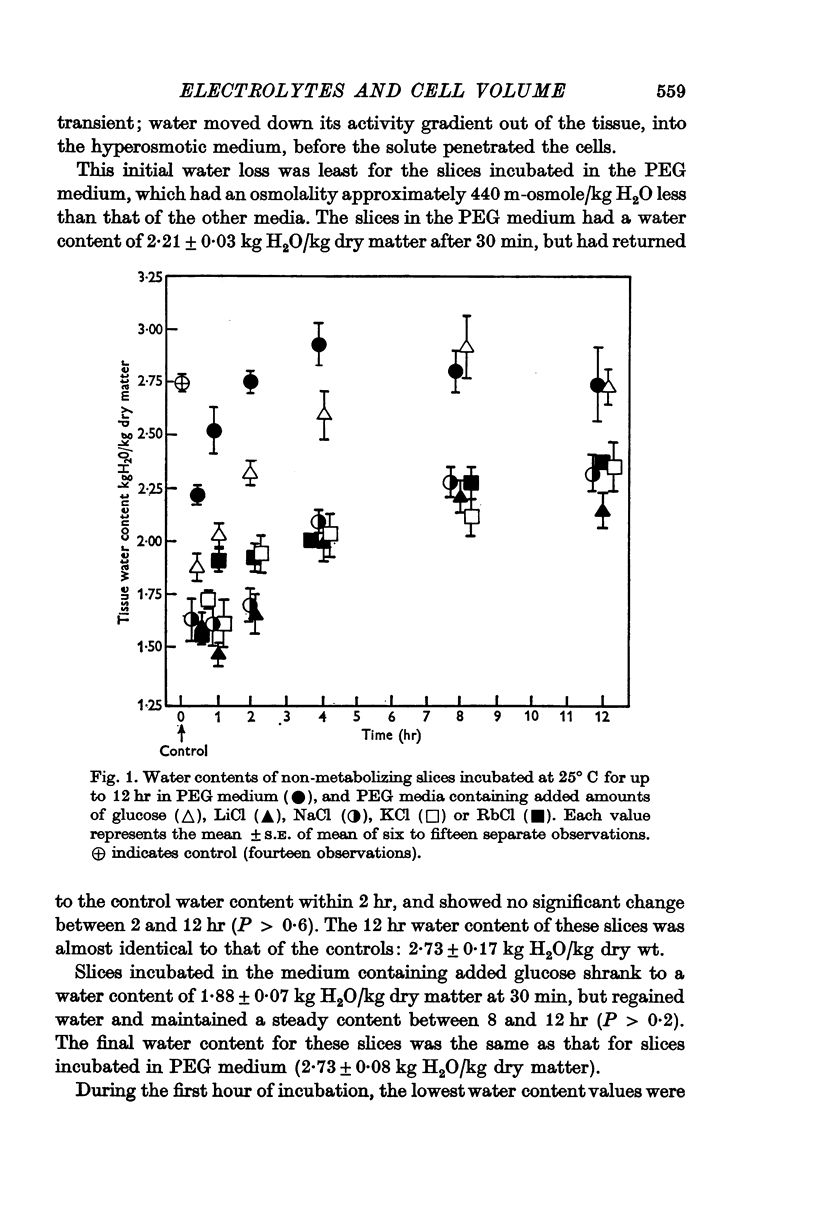
3. It was concluded that the slices in all media were at equilibrium with the medium after incubation for 8 hr.
4. Slices in the medium containing glucose reached the same equilibrium water content as those in the PEG medium, but slices in all the electrolyte media had significantly lower equilibrium water contents, although these did not differ significantly from each other.
5. It is suggested that the results demonstrate a non-specific effect of electrolytes on the swelling of non-metabolizing cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COTLOVE E., TRANTHAM H. V., BOWMAN R. L. An instrument and method for automatic, rapid, accurate, and sensitive titration of chloride in biologic samples. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Mar;51(3):461–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEYRUP I. A study of the fluid uptake of rat kidney slices in vitro. J Gen Physiol. 1953 Jul;36(6):739–749. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.6.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey K. J., Skegg D. C. The effects of high concentrations of an electrolyte on the swelling of non-metabolizing tissue slices. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;212(3):641–653. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaister D., Kerly M. The oxygen consumption and carbohydrate metabolism of the retractor muscle of the foot of Mytilus edulis. J Physiol. 1936 Jun 10;87(1):56–66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A. Maintenance of concentration gradients and regulation of cell volume. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Feb 6;72(12):396–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A. On the mechanism of fluid exchange of tissues in vitro. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):241–248. doi: 10.1042/bj0620241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLE J. R. DETERMINATION OF WATER AND ELECTROLYTES IN TISSUE SLICES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:87–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight A. D. The extracellular space in rat renal cortical slices incubated at 0.5 degrees and 25 degrees. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug;163(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON J. R. Exchanges of water and ions by kidney slices determined by a balance method. J Physiol. 1961 Oct;158:449–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON J. R. Osmoregulation in surviving slices from the kidneys of adult rats. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1950 Oct 13;137(888):378–402. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1950.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. R. Control of water content of non-metabolizing kidney slices by sodium chloride and polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000). J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):227–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. R. Some effects of glucose and calcium upon the metabolism of kidney slices from adult and newborn rats. Biochem J. 1949;45(1):68–74. doi: 10.1042/bj0450068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


