Abstract
1. The effect of restricted water intake and rapid rehydration was studied in three conscious sheep with respect to plasma renin concentration (PRC), blood corticosteroid levels, plasma protein and electrolyte concentrations, and the renal and faecal excretion of sodium and potassium.
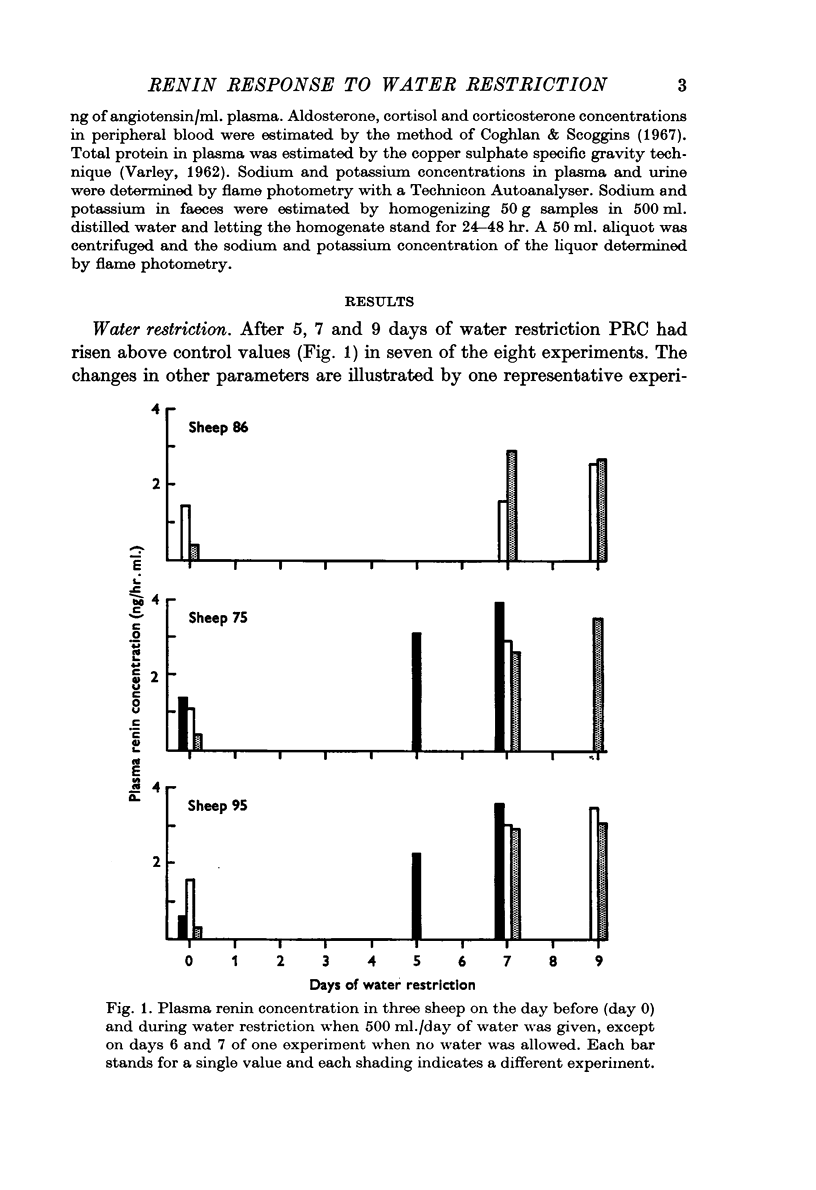
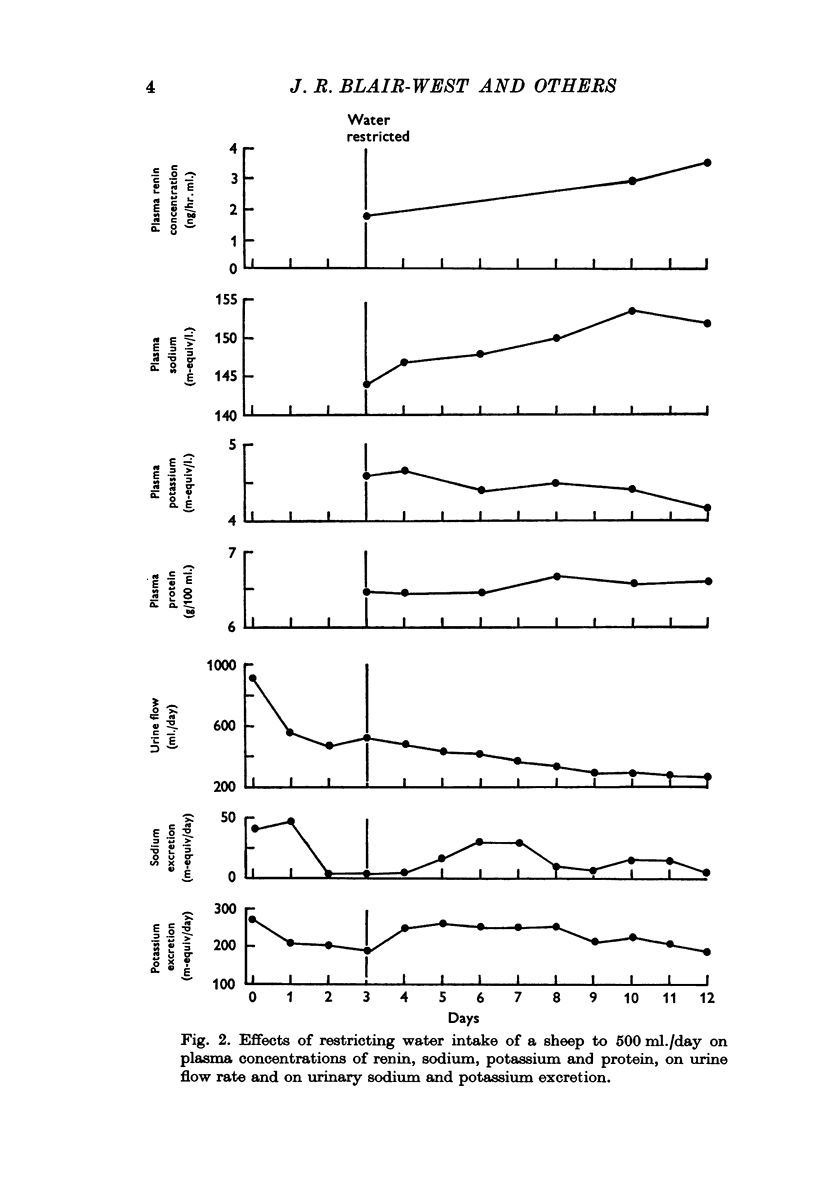
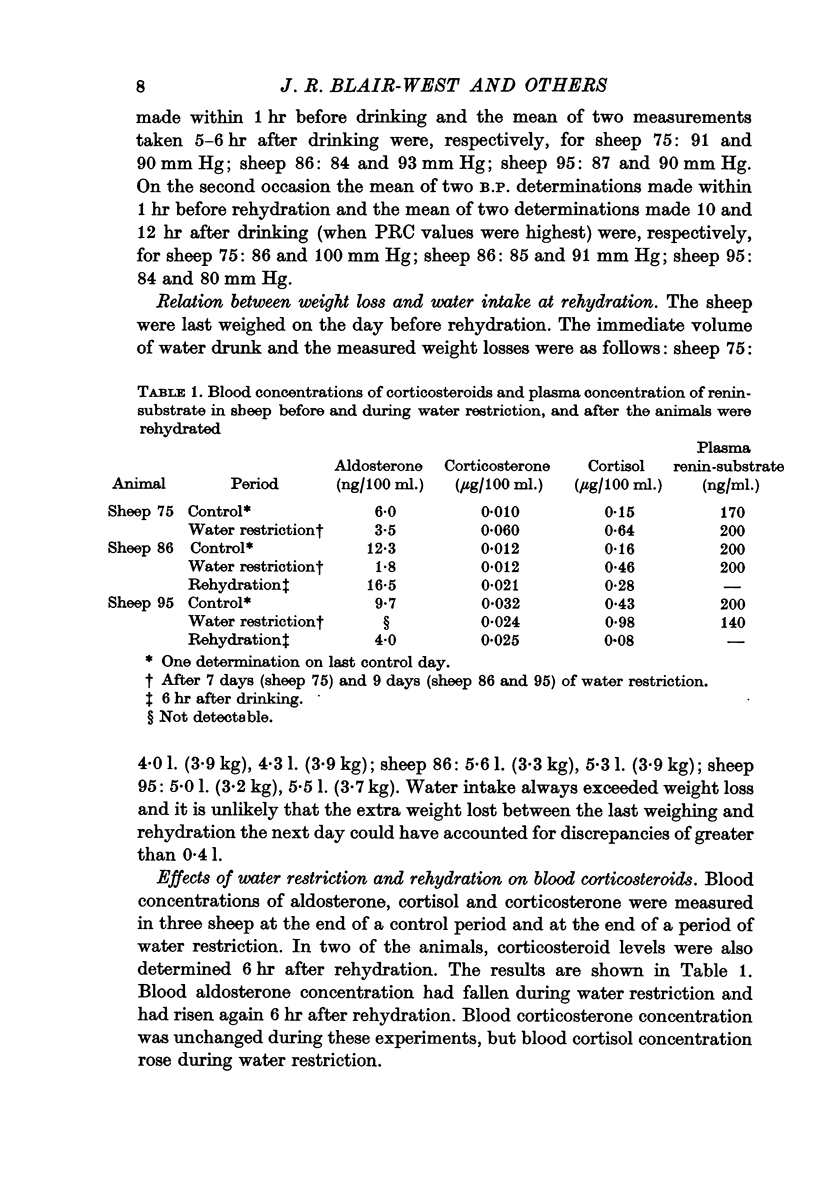
2. During water restriction the plasma concentrations of renin, protein and sodium rose while aldosterone levels were low or undetectable. Plasma potassium levels were unchanged. External sodium and potassium balance appeared to be unaffected.
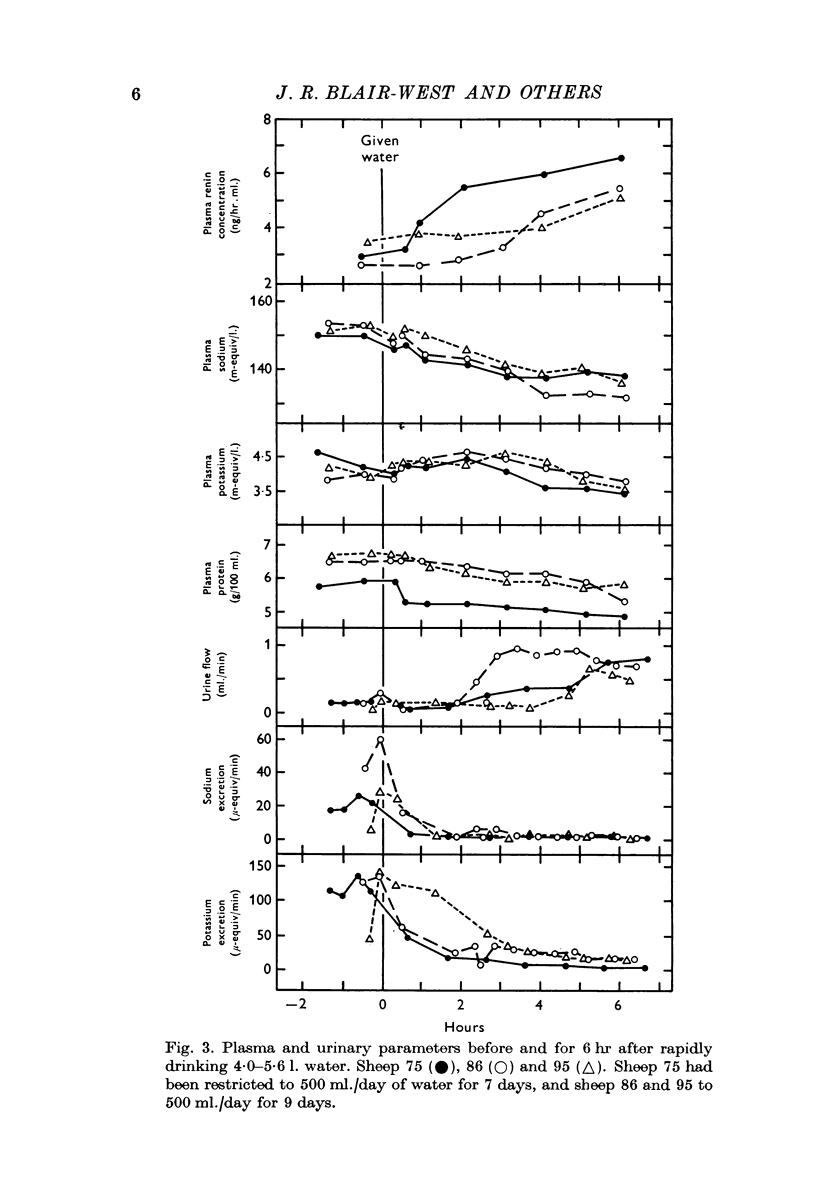
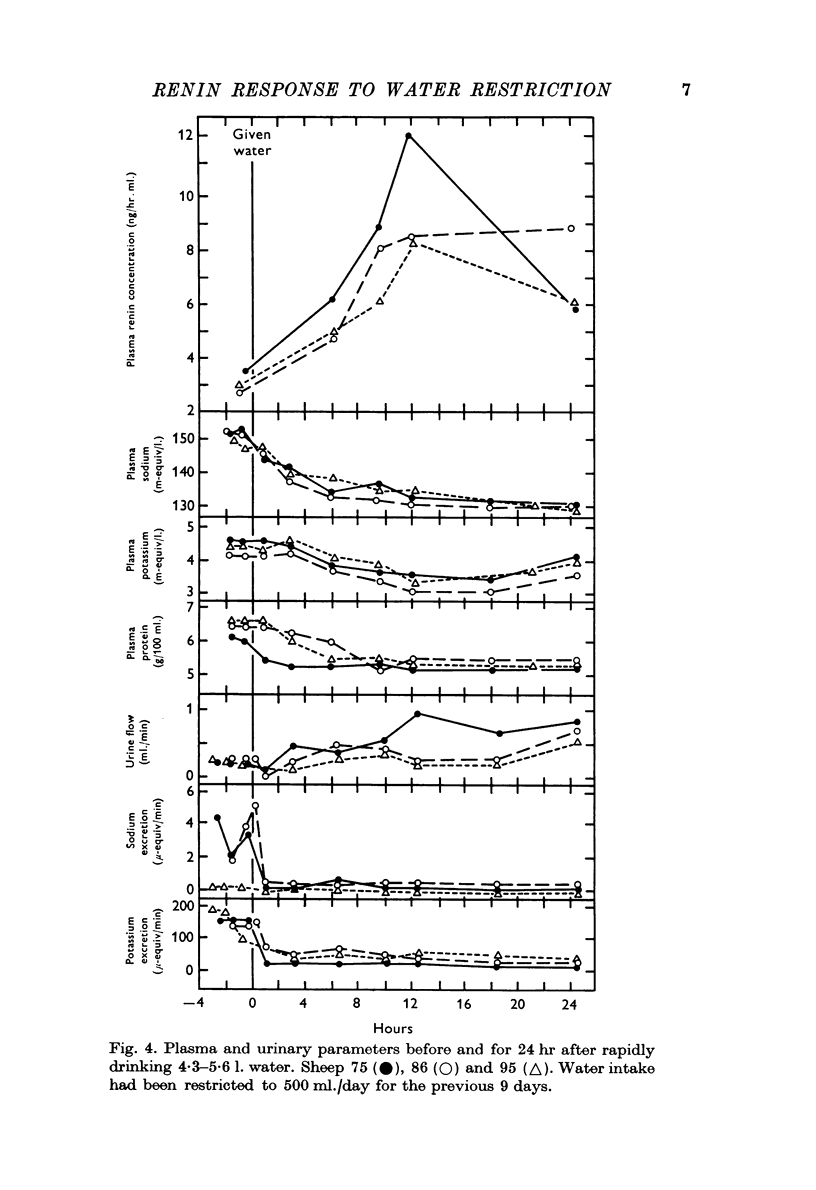
3. During rehydration the sheep drank more than their estimated water deficit in 3-4 min with the following effects: PRC rose three- to fourfold during the ensuing 12 hr. Aldosterone levels too rose, while plasma protein, sodium and potassium concentrations fell. Urinary sodium excretion virtually ceased for 24 hr, and urine flow rate increased only little during this period.
4. If there was a single stimulus to renin release during water restriction and rehydration, it was not an alteration in vascular or extravascular volume, total body sodium, systemic B.P. or plasma sodium concentration.
5. It is concluded that the rise in PRC in these experiments is compatible with the theory that altered sodium transport at the macula densa was the stimulus for renin release.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARGER A. C., BERLIN R. D., TULENKO J. F. Infusion of aldosterone, 9-alpha-fluorohydrocortisone and antidiuretic hormone into the renal artery of normal and adrenalectomized, unanesthetized dogs: effect on electrolyte and water excretion. Endocrinology. 1958 Jun;62(6):804–815. doi: 10.1210/endo-62-6-804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair-West J. R., Brook A. H. Circulatory changes and renin secretion in sheep in response to feeding. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):15–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair-West J. R., Cain M. D., Catt K. J., Coghlan J. P., Denton D. A., Funder J. W., Scoggins B. A., Wright R. D. The dissociation of aldosterone secretion and systemic renin and angiotensin II levels during the correction of sodium deficiency. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1971 Feb;66(2):229–247. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0660229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair-West J. R., Coghlan J. P., Denton D. A., Funder J. W., Scoggins B. A., Wright R. D. The effect of adrenal arterial infusion of hypertonic NaHCO3 solution on aldosterone secretion in sodium deficient sheep. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1971 Mar;66(3):448–461. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0660448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair-West J. R., Coghlan J. P., Denton D. A., Goding J. R., Wintour M., Wright R. D. The direct effect of increased sodium concentration in adrenal arterial blood on corticosteroid secretion in sodium deficient sheep. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Oct;44(5):455–474. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair-West J. R., Coghlan J. P., Denton D. A., Scoggins B. A., Wintour M., Wright R. D. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in sodium depletion. Med J Aust. 1967 Aug 12;2(7):290–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair-West J. R., Coghlan J. P., Denton D. A., Scott D., Wright R. D. The role of aldosterone in renal sodium conservation during sodium depletion. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Oct;46(5):525–529. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonjour J. P., Malvin R. L. Stimulation of ADH release by the renin-angiotensin system. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jun;218(6):1555–1559. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.6.1555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Falchuk K. H., Keimowitz R. I., Berliner R. W. The relationship between peritubular capillary protein concentration and fluid reabsorption by the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1519–1531. doi: 10.1172/JCI106118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunag R. D., Page I. H., McCubbin J. W. Inhibition of renin release by vasopressin and angiotensin. Cardiovasc Res. 1967 Jan;1(1):67–73. doi: 10.1093/cvr/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunag R. D., Page I. H., McCubbin J. W. Neural stimulation of release of renin. Circ Res. 1966 Oct;19(4):851–858. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.4.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coghlan J. P., Scoggins B. A. Measurement of aldosterone in peripheral blood of man and sheep. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Oct;27(10):1470–1486. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-10-1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS F., BRUNNER H., ZIEGLER M. RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM, ALDOSTERONE, AND SODIUM BALANCE. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1965;21:119–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. D., Küchel O., Liddle G. W., Island D. P. Role of the sympathetic nervous system in regulating renin and aldosterone production in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):599–605. doi: 10.1172/JCI105561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge R. L., Lowe R. D., Vane J. R. The effects of alteration of blood-volume on the concentration of circulating angiotensin in anaesthetized dogs. J Physiol. 1966 Aug;185(3):613–626. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maebashi M., Yoshinaga K. Effect of dehydration on plasma renin activity. Jpn Circ J. 1967 Apr;31(4):609–613. doi: 10.1253/jcj.31.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogil R. A., Itskovitz H. D., Russell J. H., Murphy J. J. Renal innervation and renin activity in salt metabolism and hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):693–697. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash F. D., Rostorfer H. H., Bailie M. D., Wathen R. L., Schneider E. G. Renin release: relation to renal sodium load and dissociation from hemodynamic changes. Circ Res. 1968 Apr;22(4):473–487. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.4.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J., Boucher R., Rojo-Ortega J. M., Genest J. Renin activity in aortic tissue of rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;47(1):53–56. doi: 10.1139/y69-009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKINNER S. L., MCCUBBIN J. W., PAGE I. H. CONTROL OF RENIN SECRETION. Circ Res. 1964 Jul;15:64–76. doi: 10.1161/01.res.15.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. A., Blair-West J. R. Renin levels in the kangaroo, the wombat and other marsupial species. J Endocrinol. 1971 Sep;51(1):79–90. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0510079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VEYRAT R., DE CHAMPLAIN J., BOUCHER R., GENEST J. MEASUREMENT OF HUMAN ARTERIAL RENIN ACTIVITY IN SOME PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PATHOLOGICAL STATES. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Jan 25;90:215–220. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J., Carlson J. Mechanism of the effects of furosemide on renin secretion in anesthetized dogs. Circ Res. 1969 Aug;25(2):145–152. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.2.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Control of renin release. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jul;47(3):359–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Effect of catecholamines and the renal nerves on renin secretion in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):659–662. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Inhibition of renin release in the dog by vasopressin and vasotocin. Circ Res. 1968 Nov;23(5):605–609. doi: 10.1161/01.res.23.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


