Abstract
Experiments are presented in support of the hypothesis that acetylcholine functions as a sensory transmitter in the lobster nervous system.
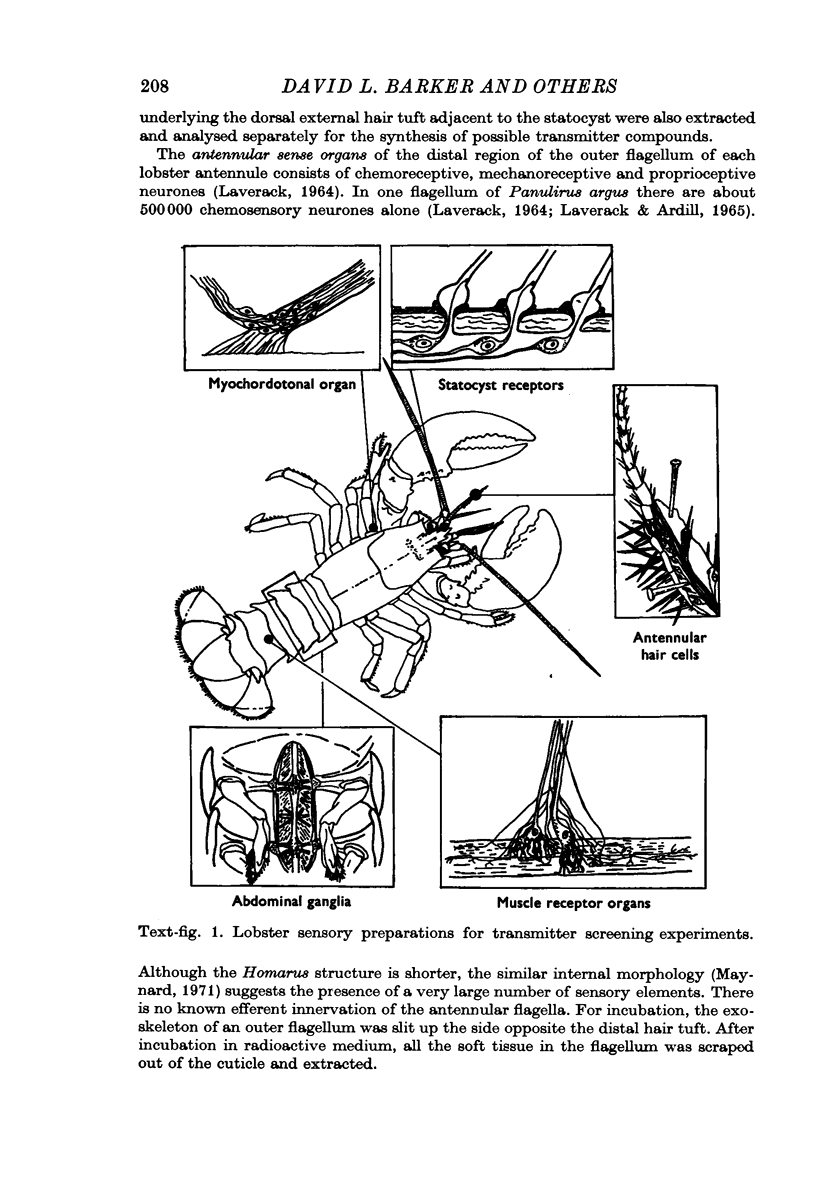
1. Several different peripheral sensory structures incorporate radioactive choline into acetylcholine. The preparation most enriched in sensory as opposed to other nervous elements (the antennular sense organs of the distal outer flagellum) does not incorporate significant amounts of glutamate, tyrosine or tryptophan into any of the other major transmitter candidates.
2. There is a parallel between the distribution of the enzyme choline acetyltransferase and the proportion of sensory fibres in nervous tissue from many parts of the lobster nervous system.
3. Isolated sensory axons contain at least 500 times as much choline acetyltransferase per cm of axon as do efferent excitatory and inhibitory fibres.
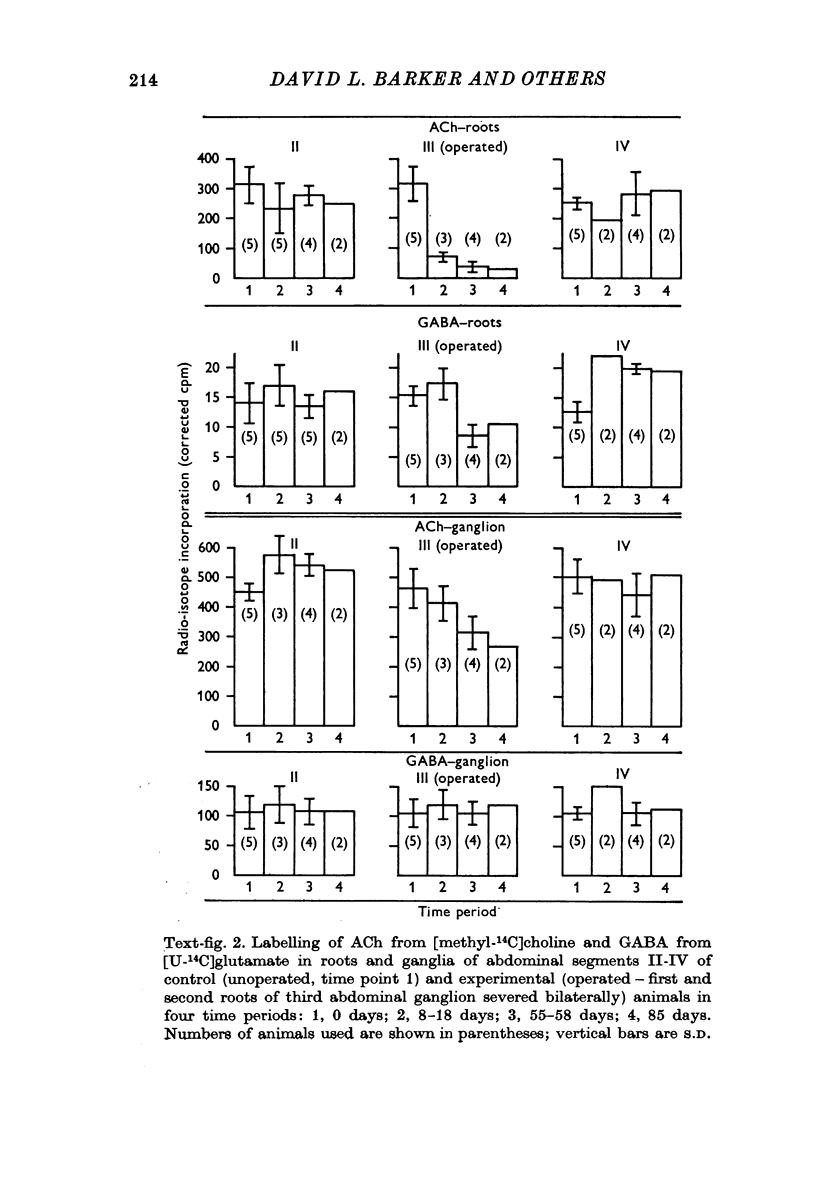
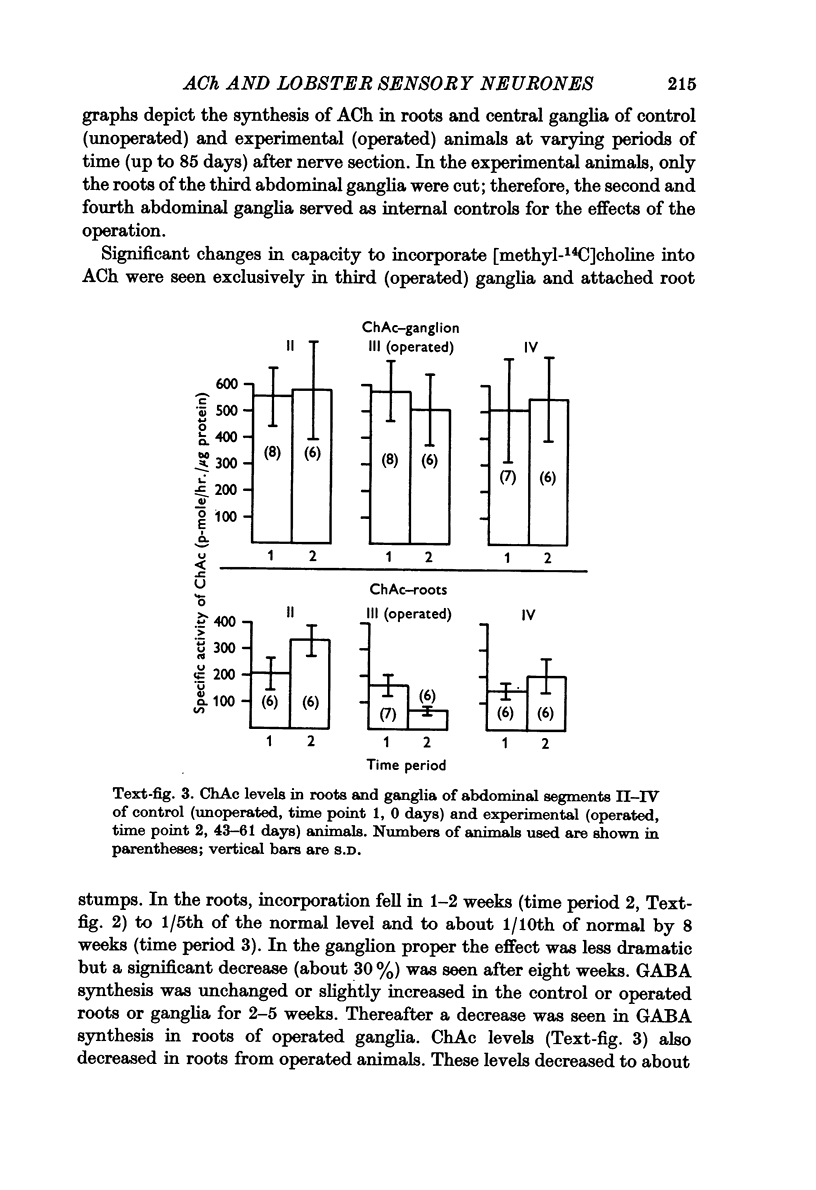
4. Abdominal ganglia and root stumps show a decline in the rate of incorporation of choline into acetylcholine 2 to 8 weeks after severing the first and second roots bilaterally (leaving the connectives and third roots intact). Extracts of the root stumps exhibit a significantly lower level of choline acetyltransferase 2 weeks after this operation.
5. Curare and atropine partially block an identified sensory synapse in the lobster abdominal ganglion.
Full text
PDF







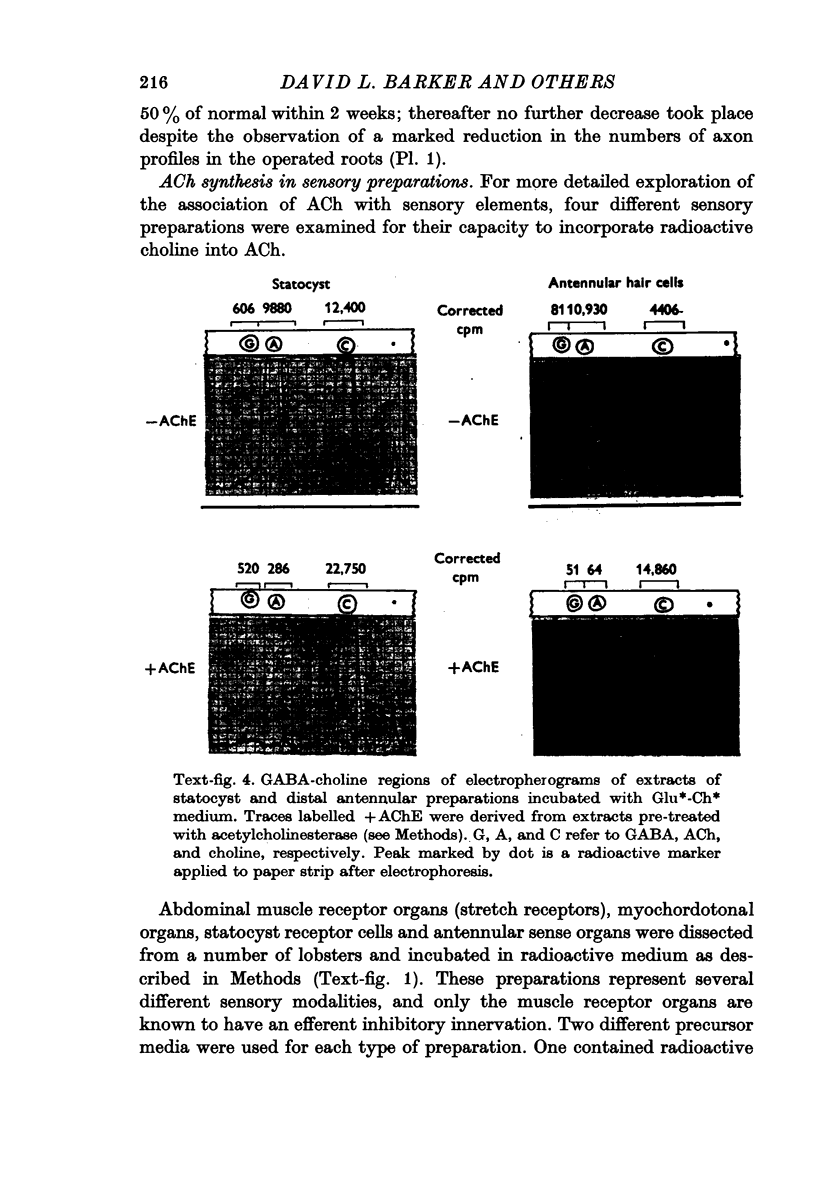

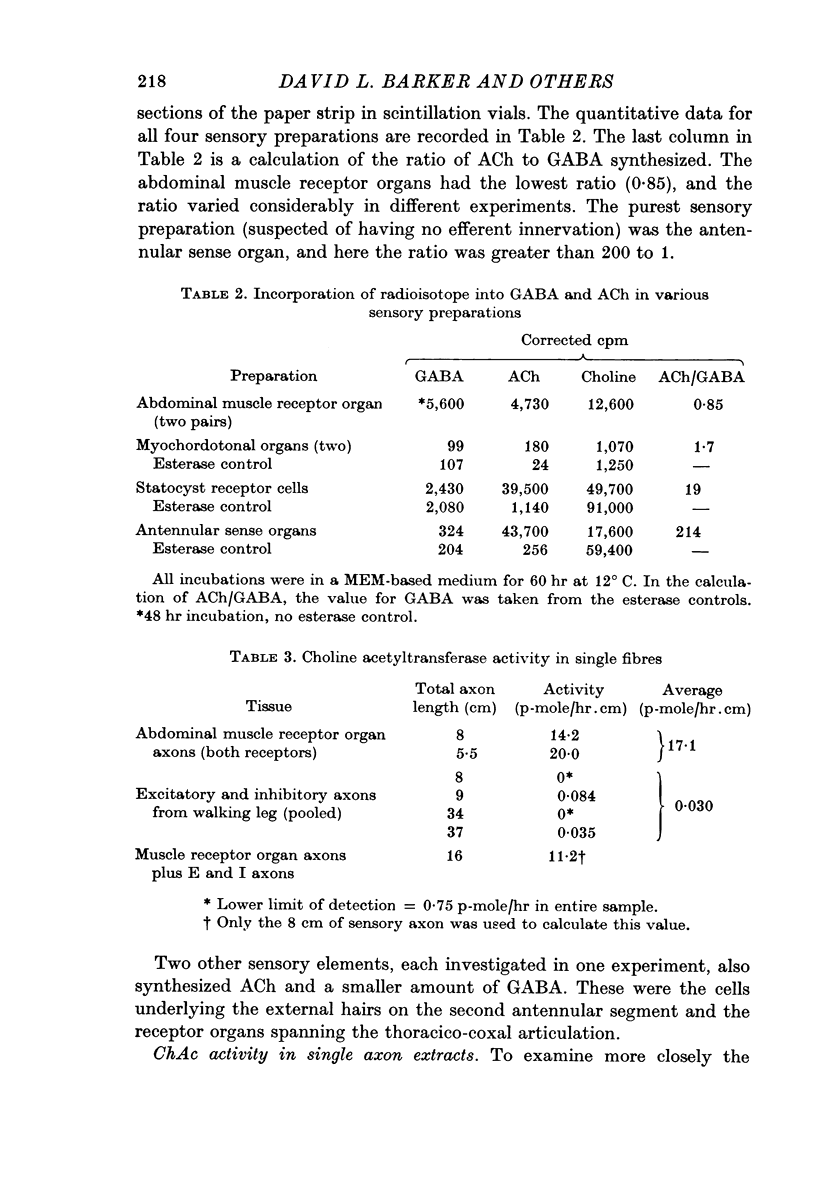

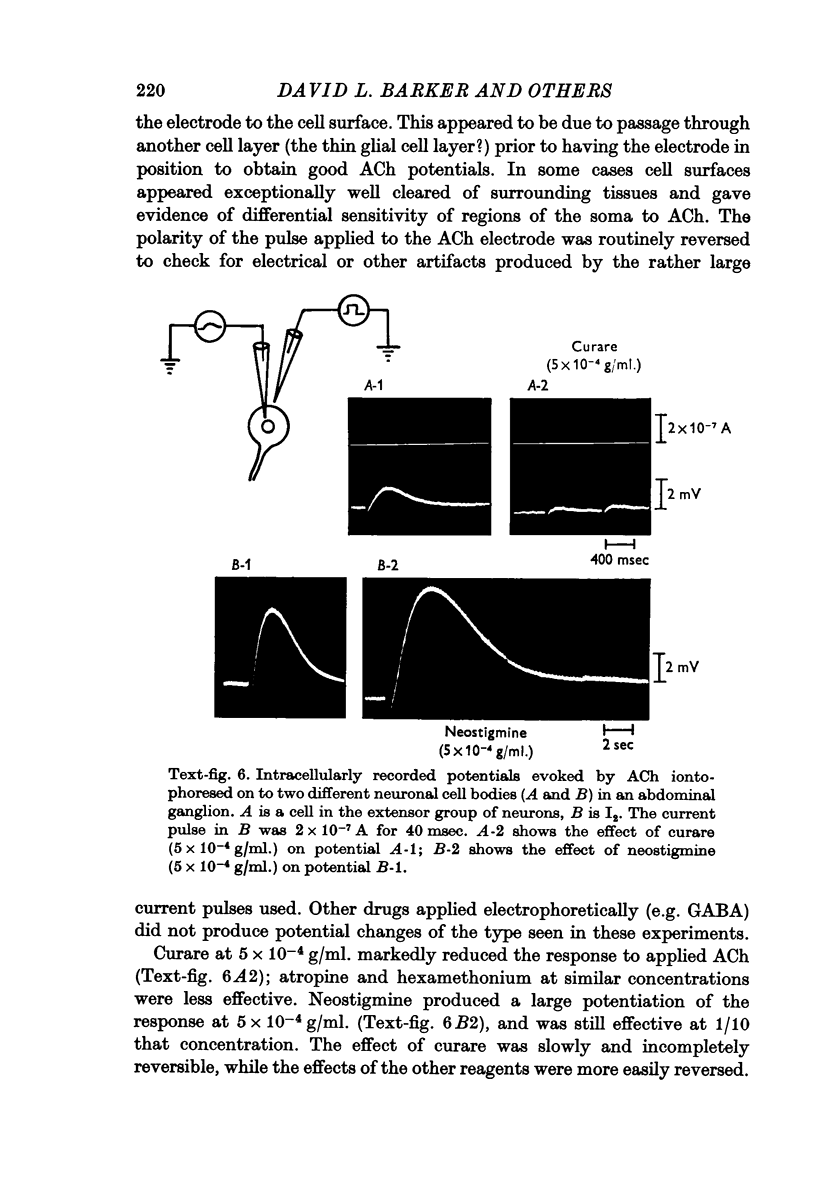
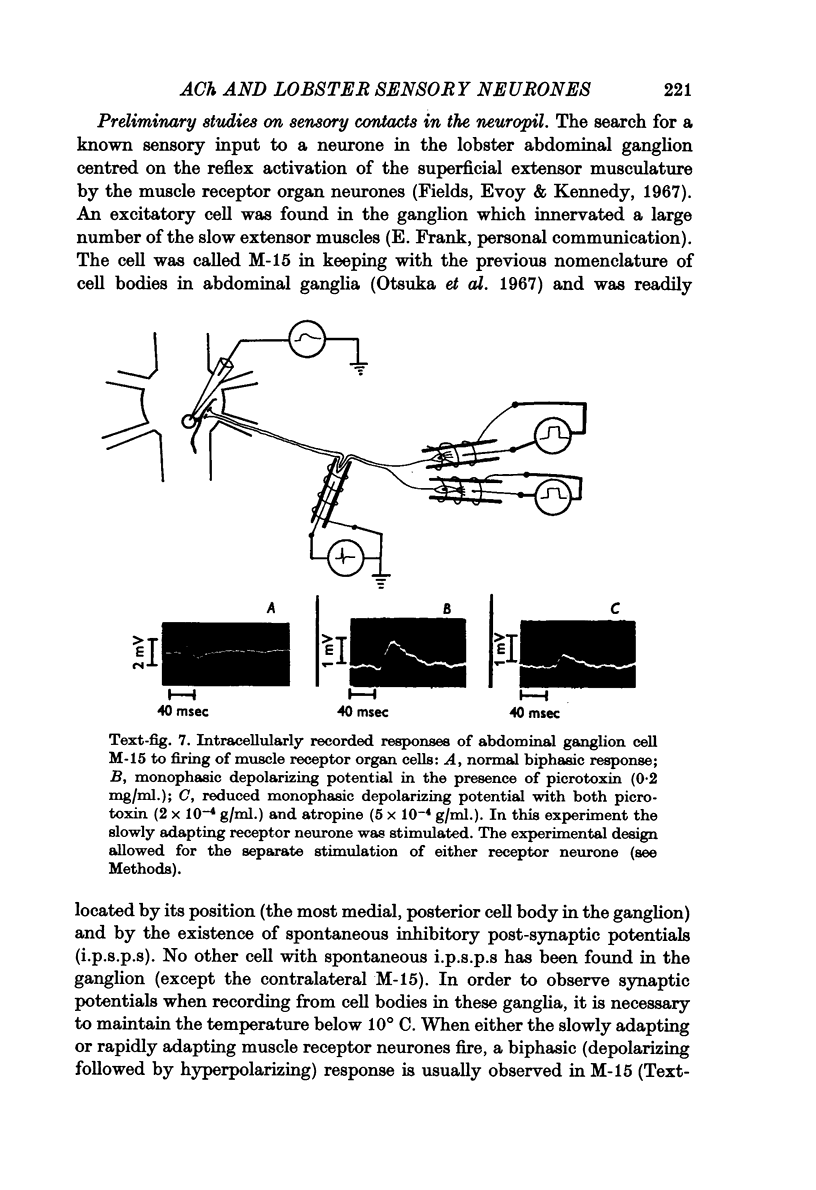








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano T., Richelson E., Nirenberg M. Neurotransmitter synthesis by neuroblastoma clones (neuroblast differentiation-cell culture-choline acetyltransferase-acetylcholinesterase-tyrosine hydroxylase-axons-dendrites). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):258–263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denburg J. L., Eldefrawi M. E., O'Brien R. D. Macromolecules from lobster axon membranes that bind cholinergic ligands and local anesthetics (recpetors-procaine-acetylcholine-nicotine-Na + and K + gates). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):177–181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dettbarn W. D., Rosenberg P. Effect of ions on the efflux of acetylcholine from peripheral nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Nov;50(2):447–460. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EASTON D. M. Synthesis of acetylcholine in crustacean nerve and nerve extract. J Biol Chem. 1950 Aug;185(2):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOREY E., BIEDERMAN M. A. Studies on the distribution of factor I and acetylcholine in crustacean peripheral nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:509–522. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields H. L., Evoy W. H., Kennedy D. Reflex role played by efferent control of an invertebrate stretch receptor. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Jul;30(4):859–874. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.4.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florey E. Neurotransmitters and modulators in the animal kingdom. Fed Proc. 1967 Jul-Aug;26(4):1164–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giller E., Jr, Schwartz J. H. Acetylcholinesterase in identified neurons of abdominal ganglion of Aplysia californica. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):108–115. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giller E., Jr, Schwartz J. H. Choline acetyltransferase in identified neurons of abdominal ganglion of Aplysia californica. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):93–107. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESTRIN S. The reaction of acetylcholine and other carboxylic acid derivatives with hydroxylamine, and its analytical application. J Biol Chem. 1949 Aug;180(1):249–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Bownds M. D., Kravitz E. A. The metabolism of gamma aminobutyric acid in the lobster nervous system. Enzymes in single excitatory and inhibitory axons. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):290–299. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand J. G., Barker D. L., Herbert E., Kravitz E. A. Screening for neurotransmitters: a rapid radiochemical procedure. J Neurobiol. 1971;2(3):231–246. doi: 10.1002/neu.480020305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoy R. R., Bittner G. D., Kennedy D. Regeneration in crustacean motoneurons: evidence for axonal fusion. Science. 1967 Apr 14;156(3772):251–252. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3772.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B. Neuro-muscular transmission in crabs. J Physiol. 1936 Aug 19;87(3):199–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAVERACK M. S. THE ANTENNULAR SENSE ORGANS OF PANULIRUS ARGUS. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1964 Dec;13:301–321. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(64)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard E. A. Microscopic localization of cholinesterases in the nervous systems of the lobsters, Panulirus argus and Homarus americanus. Tissue Cell. 1971;3(2):215–250. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(71)80020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkand P. M., Kravitz E. A. Localization of the sites of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) uptake in lobster nerve-muscle preparations. J Cell Biol. 1971 Apr;49(1):75–89. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Kravitz E. A., Potter D. D. Physiological and chemical architecture of a lobster ganglion with particular reference to gamma-aminobutyrate and glutamate. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Jul;30(4):725–752. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.4.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHALLEK W., WEIRSMA C. A. G. The influence of various drugs on a crustacean synapse. J Cell Physiol. 1948 Feb;31(1):35–47. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030310104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsch F., Dettbarn W. D. The subcellular distribution of acetylcholine, choline acetyltransferase and cholinesterases in lobster walking leg nerves. J Neurochem. 1970 Jul;17(7):927–940. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb02246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]