Abstract
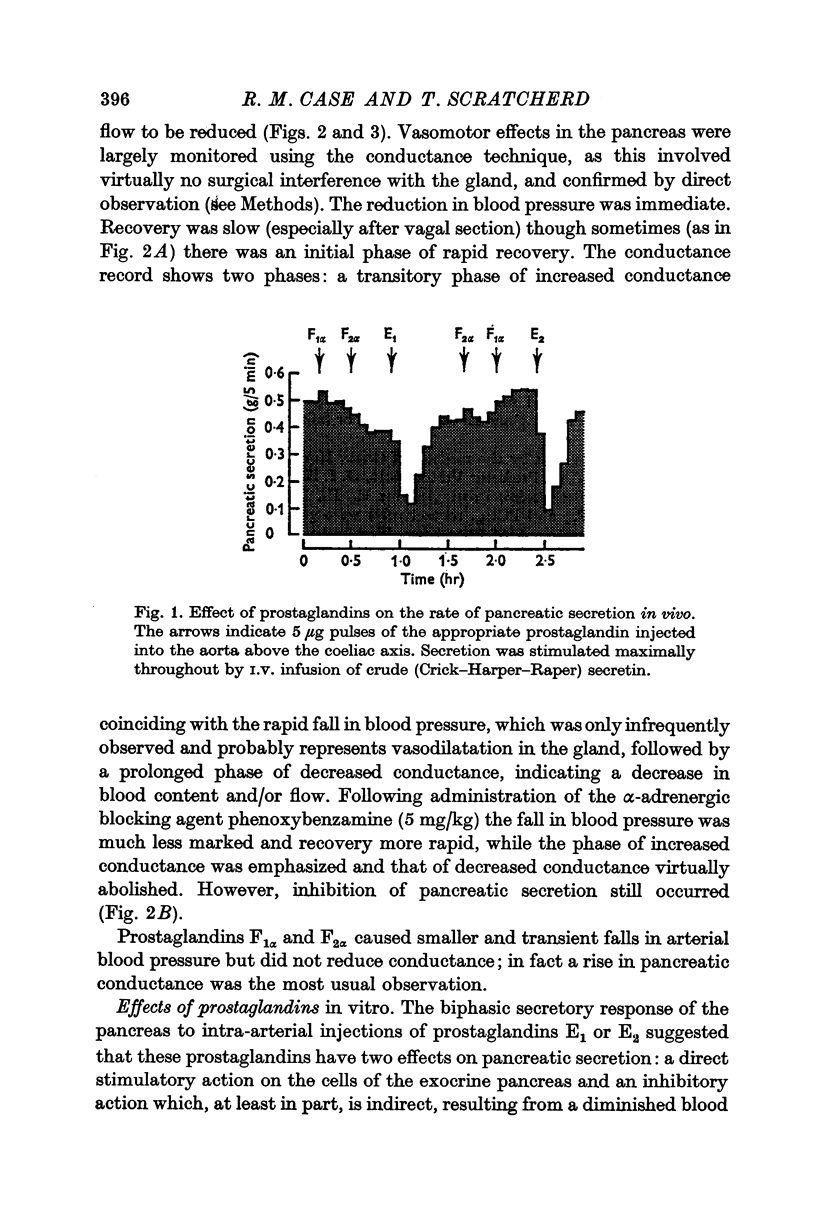
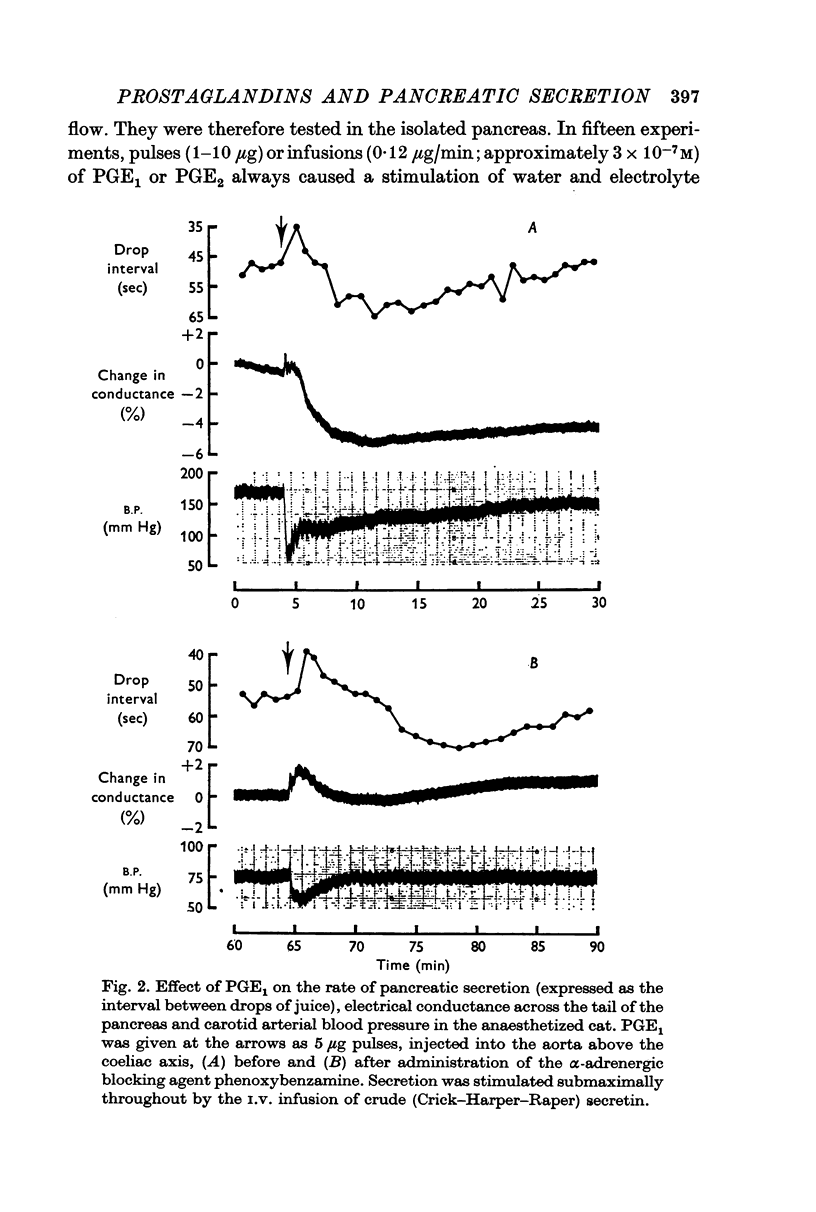
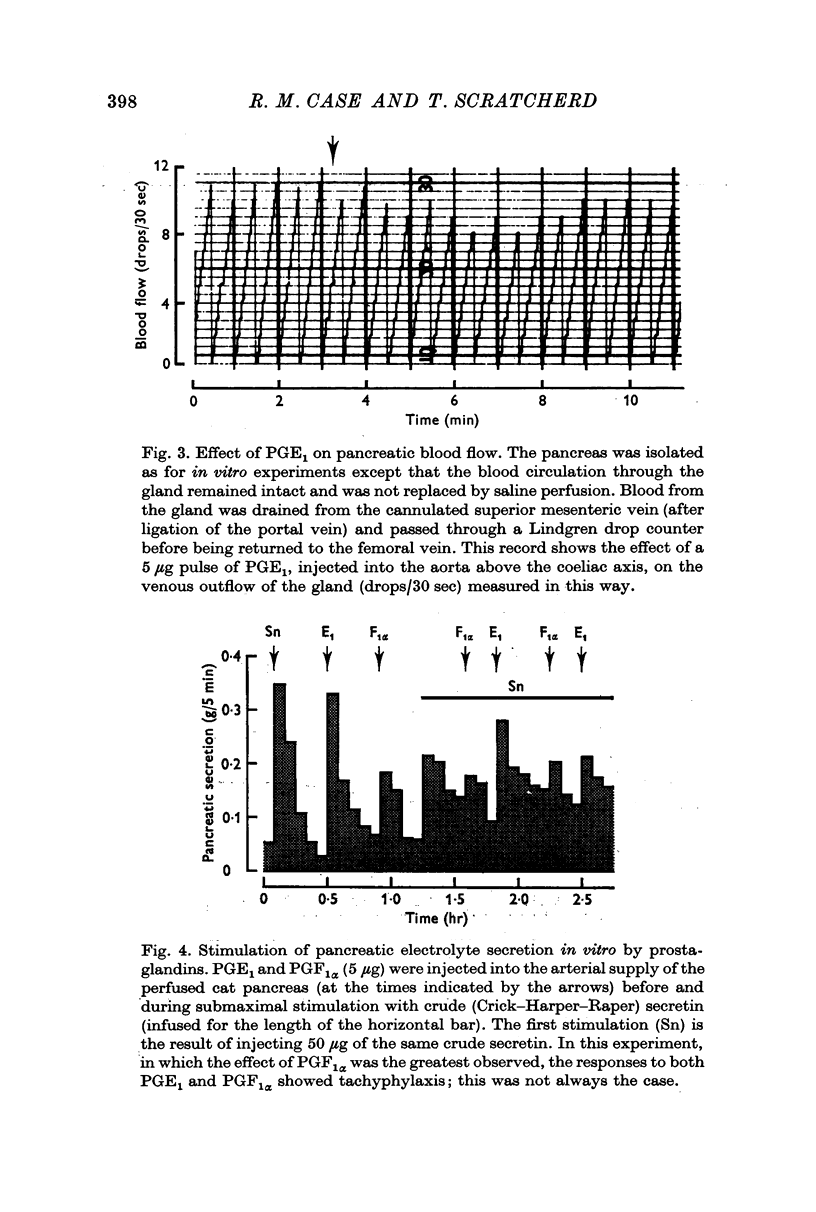
1. Intra-arterial injection or infusion of prostaglandins E1 and E2 into anaesthetized cats caused a fall in arterial blood pressure, a reduction in pancreatic blood flow and an inhibition of secretin-stimulated pancreatic electrolyte secretion. In some experiments these effects were preceded by a transient increase in blood flow and secretion.
2. The fall in blood pressure and reduction in blood flow, but not the inhibition of secretion, were much less marked following administration of the α-adrenergic blocking agent phenoxybenzamine.
3. Prostaglandins F1α and F2α caused only a slight reduction in blood pressure and had very little effect on pancreatic blood flow or electrolyte secretion.
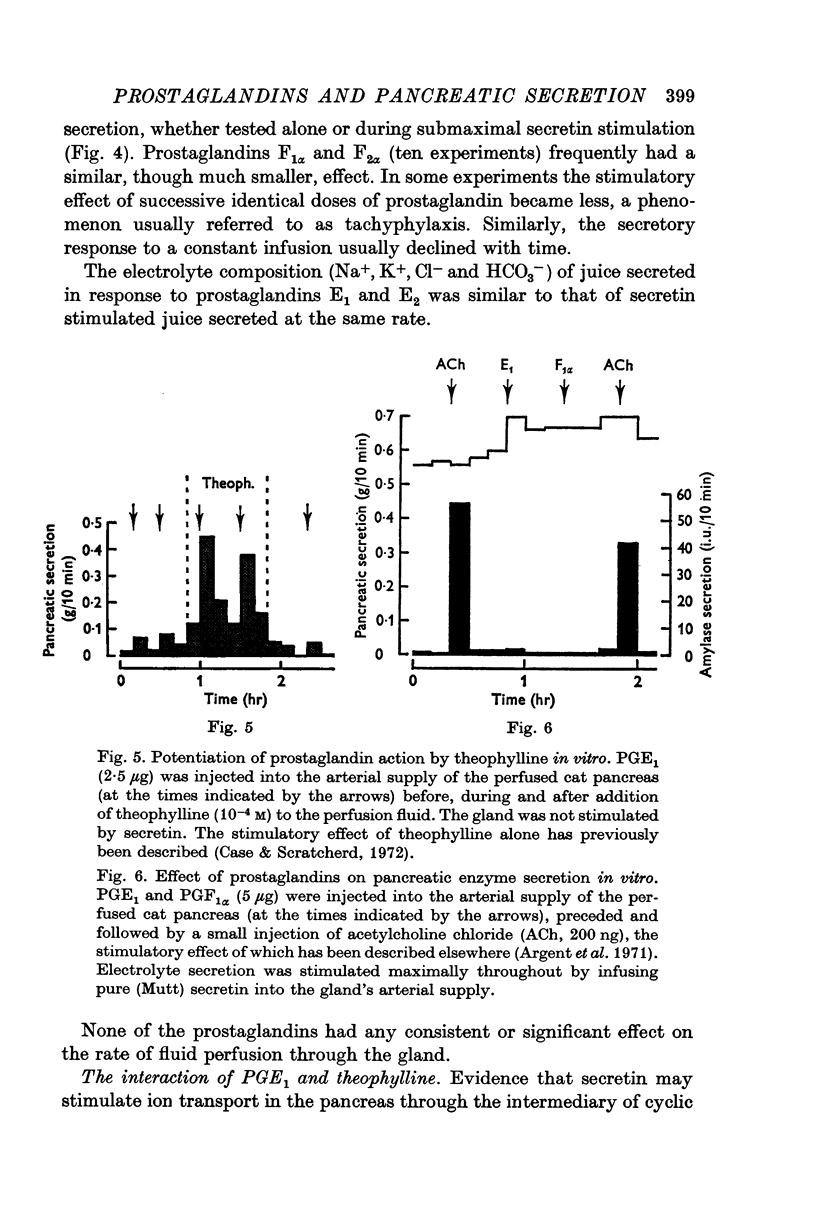
4. Addition of prostaglandins to the perfusate of the saline-perfused cat pancreas stimulated electrolyte secretion, with E1 = E2 ≫ F1α = F2α. This stimulatory action was markedly potentiated by theophylline.
5. Enzyme secretion was not stimulated by any of the prostaglandins, even in the presence of theophylline.
6. It is concluded that prostaglandins can stimulate electrolyte transport by exocrine pancreas, perhaps through a mechanism involving adenylate cyclase, but that in vivo this action is masked by a secondary inhibition resulting either from vasoconstriction, or from the libration of an antisecretory agent, or both.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argent B. E., Case R. M., Scratcherd T. Stimulation of amylase secretion from the perfused cat pancreas by potassium and other alkali metal ions. J Physiol. 1971 Aug;216(3):611–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow T. E., Greenwell J. R., Harper A. A., Scratcherd T. The effect of adrenaline and noradrenaline on the blood flow, electrical conductance and external secretion of the pancreas. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(3):665–678. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Carlson L. A., Orö L. Effect of different doses of prostaglandin E on free fatty acids of plasma, blood glucose and heart rate in the nonanesthetized dog. Prostaglandin and related factors 53. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jun;67(2):185–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Carlson L. A., Weeks J. R. The prostaglandins: a family of biologically active lipids. Pharmacol Rev. 1968 Mar;20(1):1–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S. Prostaglandins: members of a new hormonal system. These physiologically very potent compounds of ubiquitous occurrence are formed from essential fatty acids. Science. 1967 Jul 28;157(3787):382–391. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3787.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke G. Effects of prostaglandins on basal and stimulated thyroid function. Am J Physiol. 1970 May;218(5):1445–1452. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.5.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher R. W., Ho R. J., Meng H. C., Sutherland E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in biological materials. II. The measurement of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in tissues and the role of the cyclic nucleotide in the lipolytic response of fat to epinephrine. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4515–4523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRICK J., HARPER A. A., RAPER H. S. On the preparation of secretin and pancreozymin. J Physiol. 1949 Dec;110(3-4):367–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Orö L. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on blood pressure and heart rate in the dog. Prostaglandin and related factors 48. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 May;67(1):89–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. M., Harper A. A., Scratcherd T. The secretion of electrolytes and enzymes by the pancreas of the anaesthetized cat. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):335–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. M., Harper A. A., Scratcherd T. Water and electrolyte secretion by the perfused pancreas of the cat. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):133–149. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. M., Johnson M., Scratcherd T., Sherratt H. S. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate concentration in the pancreas following stimulation by secretin, cholecystokinin-pancreozymin and acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(3):669–684. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. M., Scratcherd T. The actions of dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and methyl xanthines on pancreatic exocrine secretion. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(3):649–667. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., Greenwell J. R., Harper A. A., Sankey A. M., Scratcherd T. The electrical properties of resting and secreting pancreas. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):247–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claycomb W. C., Kilsheimer G. S. Effect of glucagon, adenosine-3',5'-monophosphate and theophylline on free fatty acid release by rat liver slices and on tissue levels of coenzyme A esters. Endocrinology. 1969 May;84(5):1179–1183. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-5-1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggena P., Schwartz I. L., Walter R. Threshold and receptor reserve in the action of neurohypophyseal peptides. A study of synergists and antagonists of the hydroosmotic response of the toad urinary bladder. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Aug;56(2):250–271. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.2.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins: their disappearance from and release into the circulation. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):868–873. doi: 10.1038/216868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. II. Effects of cyclic 3', 5'-AMP. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):992–997. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Burg M. B. Effect of vasopressin and cyclic AMP on permeability of isolated collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):255–259. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Orloff J. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on the permeability response of the isolated collecting tubule to vasopressin, adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, and theophylline. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1154–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI105804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORTON E. W. ACTION OF PROSTAGLANDIN E1 ON TISSUES WHICH RESPOND TO BRADYKININ. Nature. 1963 Nov 30;200:892–893. doi: 10.1038/200892b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. B., Nigon K., Alonso D. Adenosine-3',5'-monophosphate: intracellular mediator for methyl xanthine stimulation of gastric secretion. Gastroenterology. 1969 Oct;57(4):377–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P. Studies on the effect of prostaglandins E1 and E2 on the sympathetic neuromuscular transmission in some animal tissues. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1970;345:1–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayaalp S. O., Türker R. K. Release of catecholamines from the adrenal medulla by prostaglandin E1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1967 Dec;2(3):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(67)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson L. C., Sharp G. W. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on sodium transport and osmotic water flow in the toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1046–1052. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezamis J. E., Robert A., Stowe D. F. Inhibition by prostaglandin E 1 of gastric secretion in the dog. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):369–383. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOFF J., HANDLER J. S., BERGSTROM S. EFFECT OF PROSTAGLANDIN (PGE-1) ON THE PERMEABILITY RESPONSE OF TOAD BLADDER TO VASOPRESSIN, THEOPHYLLINE AND ADENOSINE 3',5'-MONOPHOSPHATE. Nature. 1965 Jan 23;205:397–398. doi: 10.1038/205397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOFF J., HANDLER J. S. The similarity of effects of vasopressin, adenosine-3',5'-phosphate (cyclic AMP) and theophylline on the toad bladder. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:702–709. doi: 10.1172/JCI104528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Carpenter C. C., Jr, Elliott H. L., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effects of prostaglandins, theophylline, and cholera exotoxin upon transmucosal water and electrolyte movement in the canine jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jan;60(1):22–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E. Biological significance of the prostaglandins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:139–187. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A., Nezamis J. E., Phillips J. P. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on gastric secretion and ulcer formation in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1968 Oct;55(4):481–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A., Nezamis J. E., Phillips J. P. Inhibition of gastric secretion by prostaglandins. Am J Dig Dis. 1967 Oct;12(10):1073–1076. doi: 10.1007/BF02233268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison G. A., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W. Cyclic AMP. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:149–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudick J., Gonda M., Dreiling D. A., Janowitz H. D. Effects of prostaglandin E1 on pancreatic exocrine function. Gastroenterology. 1971 Feb;60(2):272–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERSON P. H. Potentiometric determination of chloride in biological fluids. Biochem J. 1952 Nov;52(3):502–505. doi: 10.1042/bj0520502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way L., Durbin R. P. Inhibition of gastric acid secretion in vitro by prostaglandin E1. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):874–875. doi: 10.1038/221874a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems C., Rocmans P. A., Dumont J. E. Stimulation in vitro by thyrotropin, cyclic 3',5'-AMP, dibutyryl cylclic 3',5'-AMP and prostaglandin E1, of secretion by dog thyroid slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 24;222(2):474–481. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


