Abstract
1. The specific radioactivities of isotopically pure oxytocin and vasopressin prepared from the neural lobe of the pituitary gland have been measured at various times after an intracisternal injection of [3H]tyrosine.
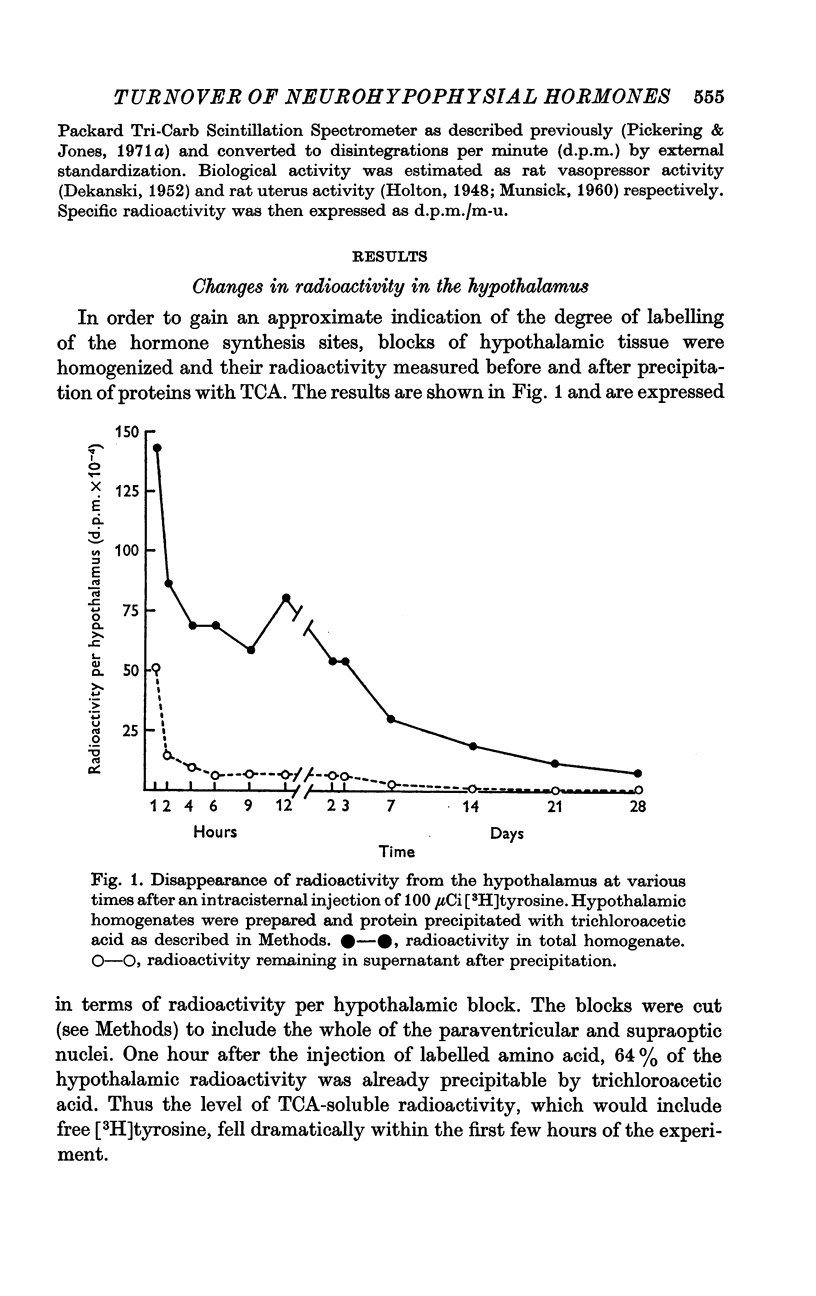
2. Radioactive hormone began to appear in the gland 1-2 hr after the injection which suggests an intra-axonal transport velocity of 1-2 mm/hr.
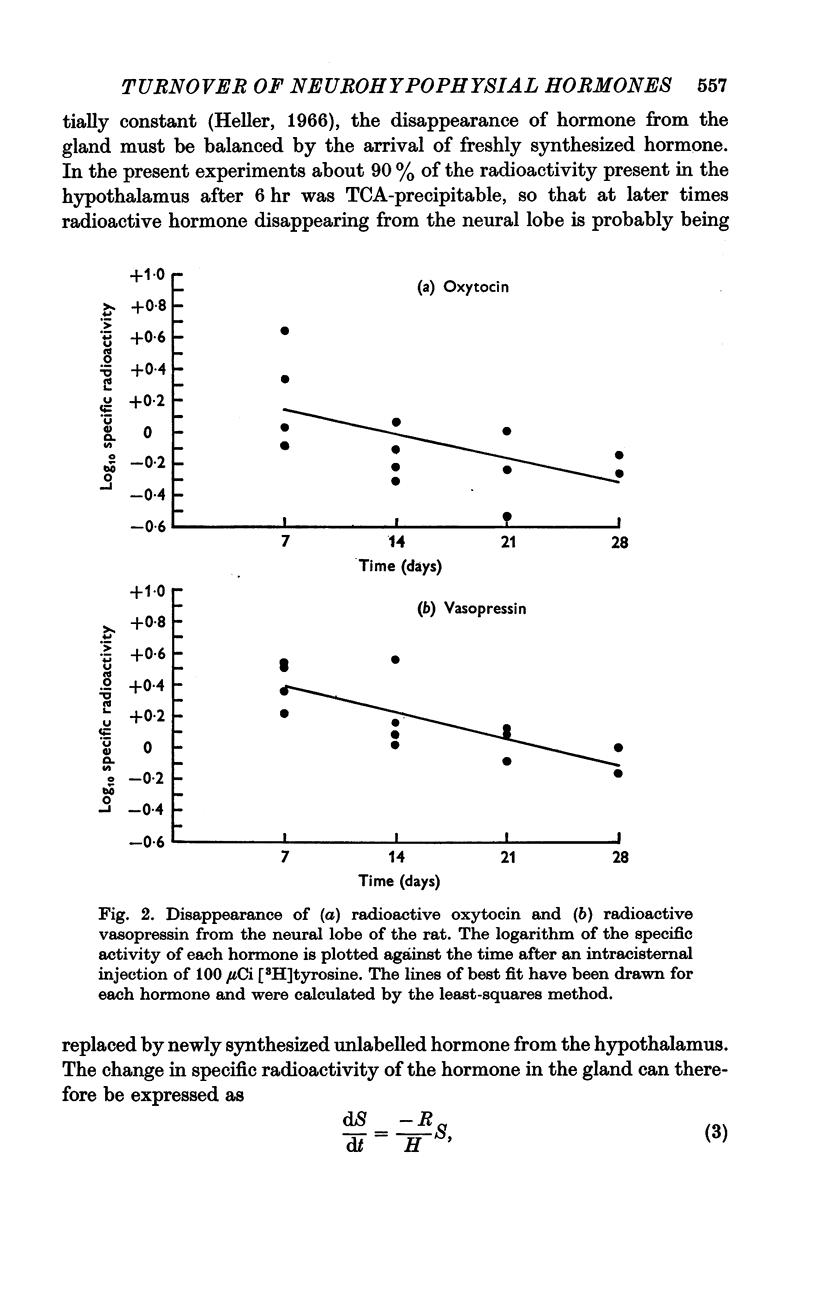
3. From 7 days onwards the specific radioactivity of each hormone declined exponentially with the same rate constant and a half-life of about 13 days.
4. If the decline in radioactivity can be equated with the release of the hormones, the rates of secretion for the male rat in water balance are 18·7 m-u./day for oxytocin and 28·9 m-u./day for vasopressin.
5. Calculation from the secretion rates gave steady-state plasma concentrations of about 3 μu./ml. for each hormone.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bie P., Thorn N. A. In vitro studies of the release mechanism for vasopressin in rats. II. Studies of the possible release of hormone from hypothalamic tissue. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Sep;56(1):139–145. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0560139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burford G. D., Jones C. W., Pickering B. T. Tentative identification of a vasopressin-neurophysin and an oxytocin-neurophysin in the rat. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):809–813. doi: 10.1042/bj1240809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burford G. D., Pickering B. T. The number of neurophysins in the rat. Influence of the concentration of Bromophenol Blue, used as a tracking dye, on the resolution of proteins by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):941–944. doi: 10.1042/bj1280941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CZACZKES J. W., KLEEMAN C. R. THE EFFECT OF VARIOUS STATES OF HYDRATION AND THE PLASMA CONCENTRATION ON THE TURNOVER OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE IN MAMMALS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1649–1658. doi: 10.1172/JCI105040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEKANSKI J. The quantitative assay of vasopressin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Dec;7(4):567–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb00723.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian M., Forsling M. L., Jones J. J., Lee J. The release, clearance and plasma protein binding of oxytocin in the anaesthetized rat. J Endocrinol. 1969 Feb;43(2):175–189. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0430175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsling M. L., Jones J. J., Lee J. Factors influencing the sensitivity of the rat to vasopressin. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(2):495–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller H. The hormone content of the vertebrate hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Br Med Bull. 1966 Sep;22(3):227–231. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Pickering B. T. Comparison of the effects of water deprivation and sodium chloride imbibition on the hormone content of the neurohypophysis of the rat. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):449–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOBAYASHI H., OOTA Y., HIRANO T. Acid phosphatase activity of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal system of dehydrated rats and pigeons in relation to neurosecretion. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1962 Oct;2:495–498. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(62)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNSICK R. A. Effect of magnesium ion on the response of the rat uterus to neurohypophysial hormones and analogues. Endocrinology. 1960 Mar;6:451–457. doi: 10.1210/endo-66-3-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilly A. S., Legros J. J., Forsling M. L. Release of oxytocin, vasopressin and neurophysin in the goat. J Endocrinol. 1972 Jan;52(1):209–210. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0520209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka R. S., Zambrano D., Bern H. A. Electron microscope radioautography of amino acid incorporation by supraoptic neurons of the rat. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1970 Dec;15(3):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(70)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norström A., Sjöstrand J. Axonal transport of proteins in the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system of the rat. J Neurochem. 1971 Jan;18(1):29–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norström A., Sjöstrand J., Livett B. G., Uttenthal L. O., Hope D. B. Electrophoretic and immunological characterization of rat neurophysin. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(5):671–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1220671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering B. T., Jones C. W. Isolation of radioactive oxytocin and vasopressin from the posterior pituitary gland of the rat after the injection of labelled tyrosine into the cerebrospinal fluid. J Endocrinol. 1971 Jan;49(1):93–103. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0490093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLOPER J. C., ARNOTT D. J., KING B. C. Sulphur metabolism in the pituitary and hypothalamus of the rat: a study of radioisotope-uptake after the injection of 35S DL-cysteine, methionine, and sodium sulphate. J Endocrinol. 1960 Feb;20:9–23. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0200009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H., Fawcett P., Takabatake Y., Portanova R. Biosynthesis and release of vasopressin and neurophysin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:447–491. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H., Haller E. W. Further studies on the capacity of the neurohypophysis to release vasopressin. Endocrinology. 1968 Aug;83(2):251–262. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H. Neurosecretion. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:327–372. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H., Share L., Osinchak J., Carpi A. Capacity of the neurohypophysis to release vasopressin. Endocrinology. 1967 Oct;81(4):755–770. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-4-755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKABATAKE Y., SACHS H. VASOPRESSIN BIOSYNTHESIS. 3. IN VITRO STUDIES. Endocrinology. 1964 Dec;75:934–942. doi: 10.1210/endo-75-6-934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata P. S., Buzalkov R. Vasopressin studies in the rat. 3. Inability of ethanol anesthesia to prevent ADH secretion due to pain and hemorrhage. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;290(4):294–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttenthal L. O., Livett B. G., Hope D. B. Release of neurophysin together with vasopressin by a Ca 2 dependent mechanism. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Jun 17;261(839):379–380. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker S., LaBella F. S. Ultrastructural localization of acid phosphatase in the posterior pituitary of the dehydrated rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;125(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00306838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


