Abstract
1. Cat spleens were perfused with Krebs-bicarbonate solution at a rate of about 7 ml./min at 33-35° C. Noradrenaline release after splenic nerve stimulation at 10 or 30 Hz was measured. Effects of various ions and drugs on noradrenaline release were determined.
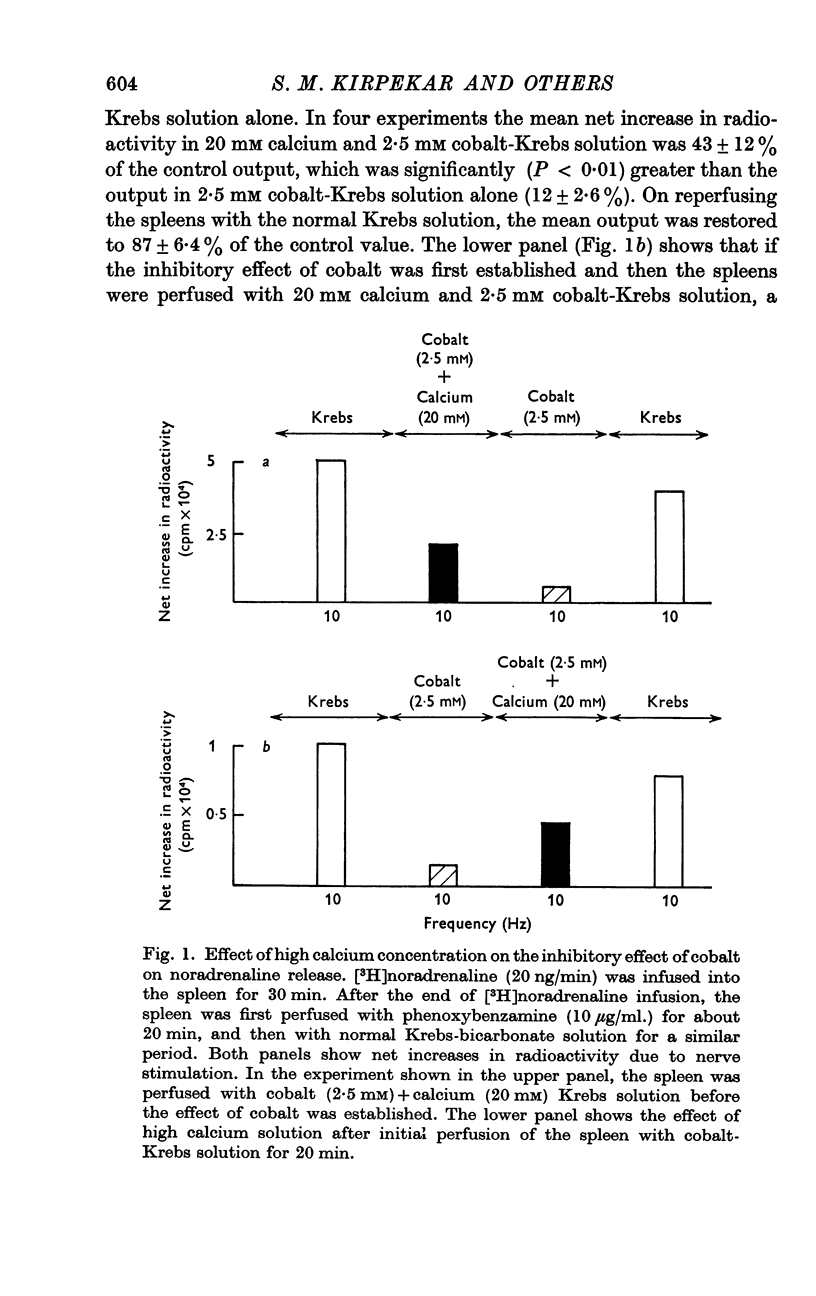
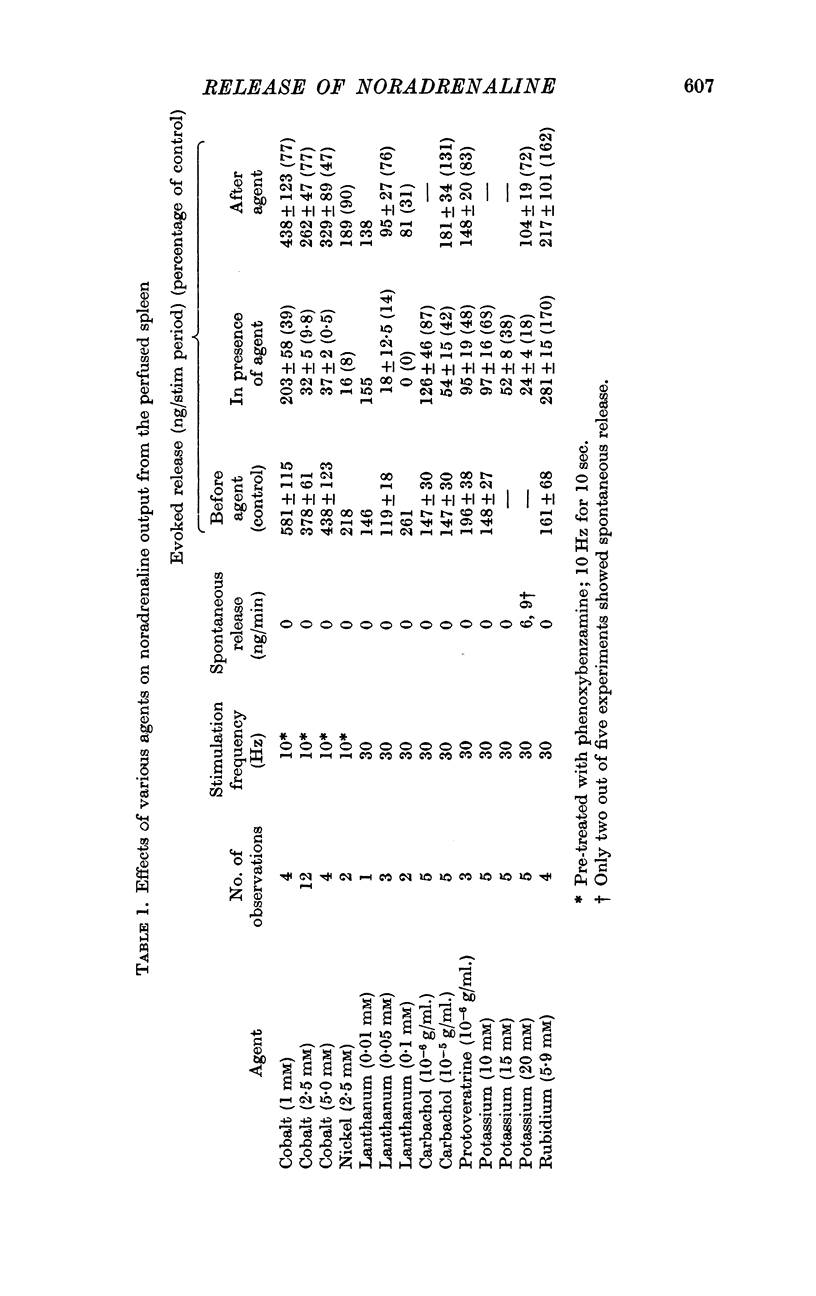
2. Perfusion of phenoxybenzamine- and [3H]noradrenaline-treated spleens with 1, 2·5 and 5 mM cobalt or nickel—2 Krebs solution markedly reduced the release of noradrenaline by nerve stimulation. Lanthanum was the most potent inhibitor of noradrenaline release. Increasing the calcium concentration or adding tetraethylammonium chloride (TEA) partially counteracted the inhibitory effects of cobalt on release. Cobalt did not inhibit release induced by tyramine.
3. Calcium did not cause spontaneous release of noradrenaline either when high concentrations were injected directly into the spleen or after first perfusing the spleen with calcium-free medium.
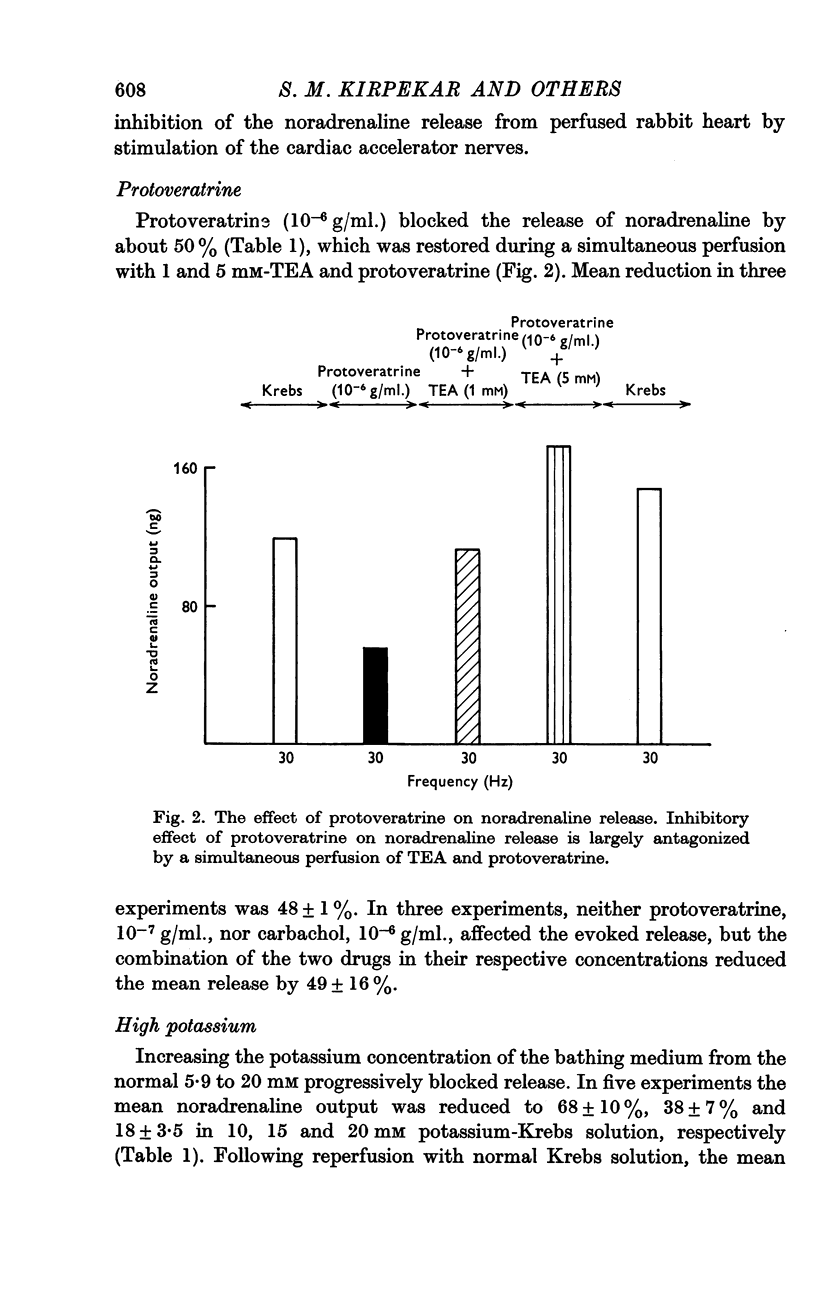
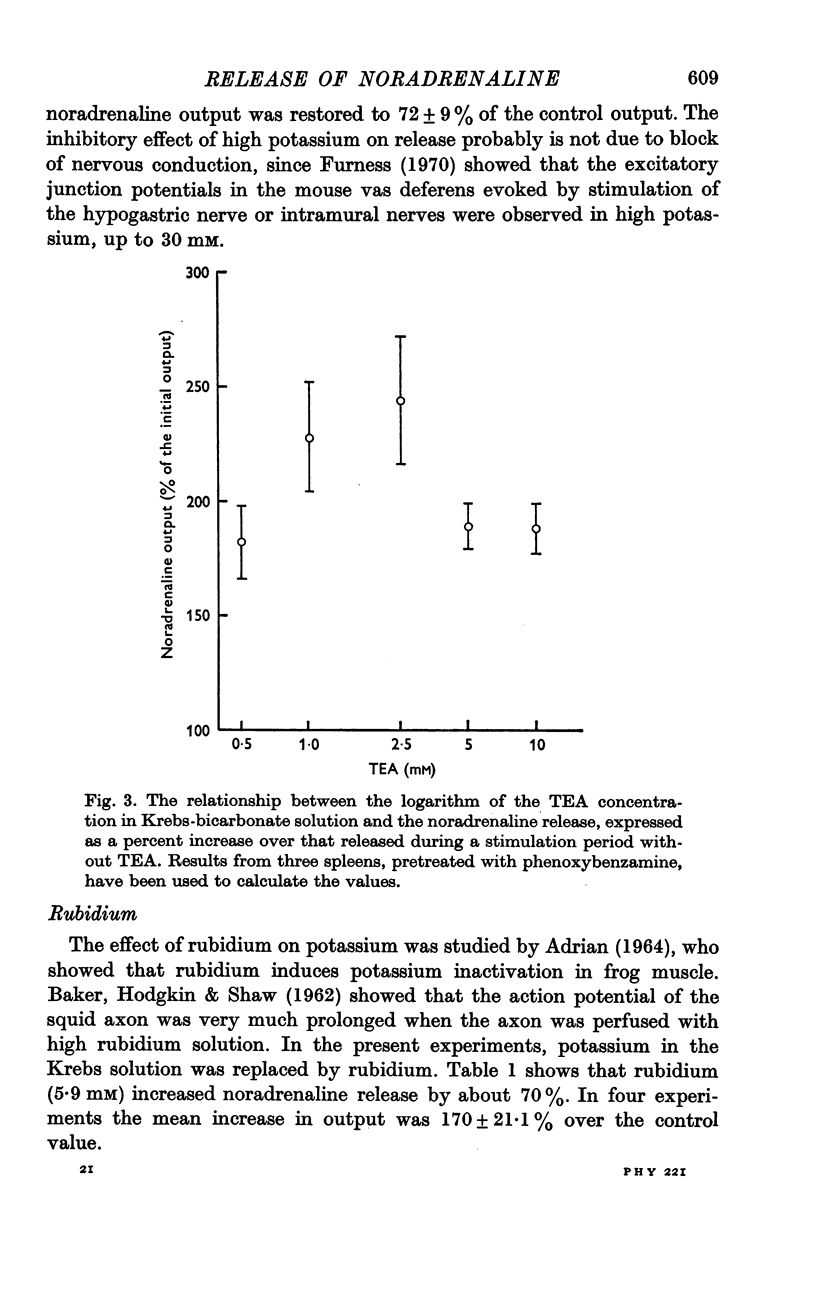
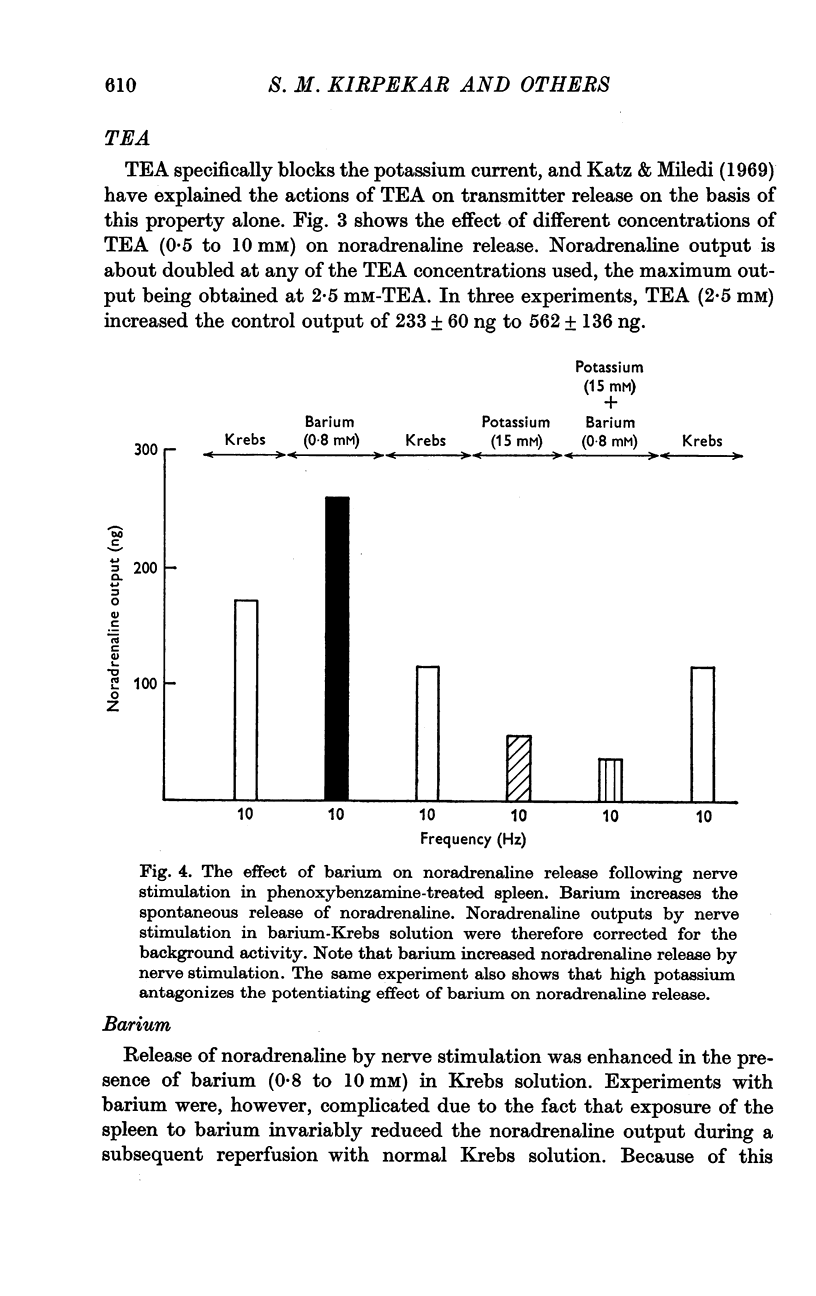
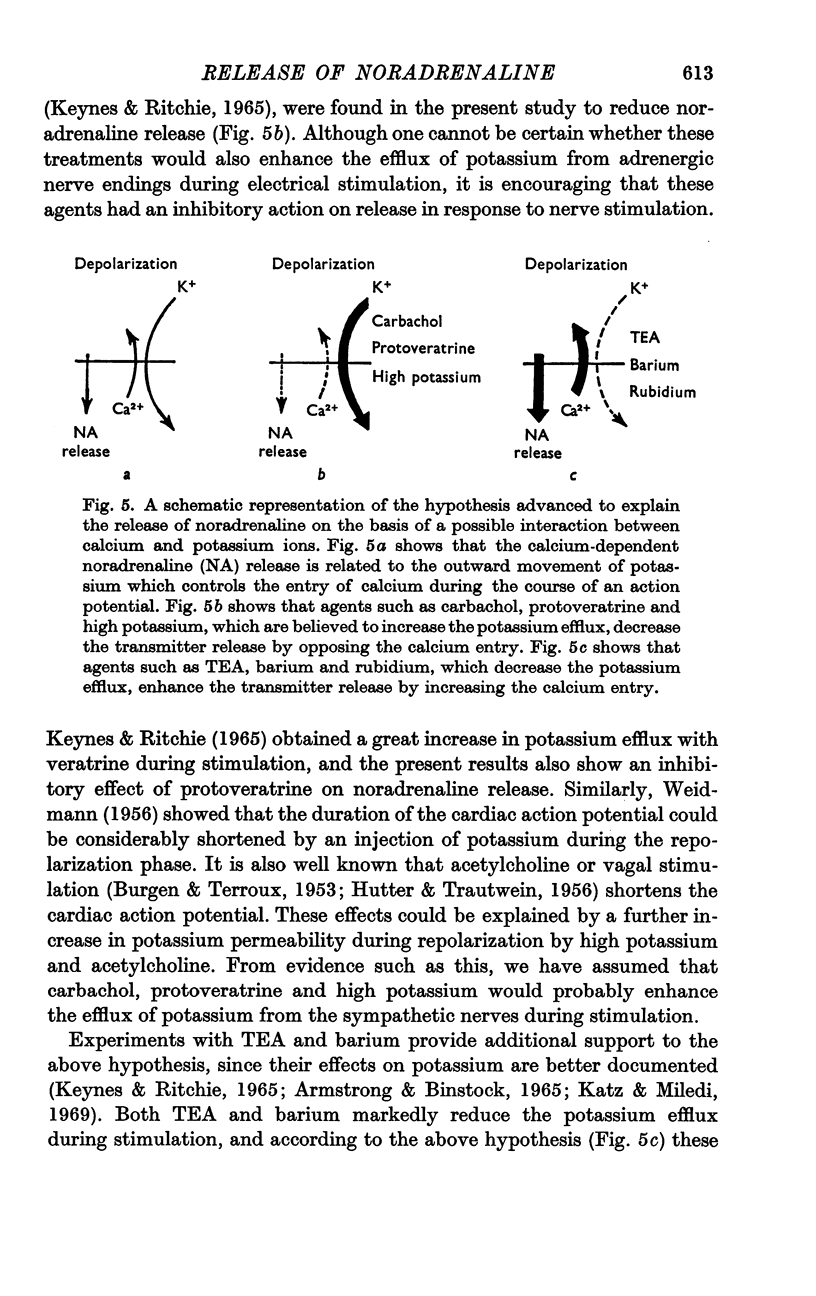
4. Carbachol, protoveratrine and high potassium inhibit, whereas TEA, barium and rubidium enhance, the evoked release of noradrenaline.
5. The relation of noradrenaline release to influx of calcium ions and its modification by various agents has been discussed.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. THE RUBIDIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY OF FROG MUSCLE MEMBRANE. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:134–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANTON A. H., SAYRE D. F. A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxide-trihydroxyindole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Dec;138:360–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMSTRONG C. M., BINSTOCK L. ANOMALOUS RECTIFICATION IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON INJECTED WITH TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:859–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. The effects of changes in internal ionic concentrations on the electrical properties of perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:355–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN G. L., GILLESPIE J. S. The output of sympathetic transmitter from the spleen of the cat. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):81–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGEN A. S., TERROUX K. G. On the negative inotropic effect in the cat's auricle. J Physiol. 1953 Jun 29;120(4):449–464. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Phasic entry of calcium in response to depolarization of giant axons of Loligo forbesi. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):70P–71P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J. The action of extracellular cations on the release of the sympathetic transmitter from peripheral nerves. J Physiol. 1967 Mar;189(1):85–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn J. H., Gibbons W. R. The release of noradrenaline from sympathetic fibres in relation to calcium concentration. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(1):214–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coraboeuf E., Vassort G. Effets de la tétrodotoxine, du tétraéthylammonium et du manganèse sur l'activité du myocarde de rat et de cobaye. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Feb 20;264(8):1072–1075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Rubin R. P. The mechanism of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla and the role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167(2):288–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B. The effect of external potassium ion concentration on autonomic neuro-muscular transmission. Pflugers Arch. 1970;317(4):310–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00586580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Kirpekar S. M. The uptake and release of radioactive noradrenaline by the splenic nerves of cats. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(1):51–68. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTTING G., AXELROD J. Fate of tritiated noradrenaline at the sympathetic nerve-endings. Nature. 1961 Oct 14;192:172–173. doi: 10.1038/192172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., TRAUTWEIN W. Vagal and sympathetic effects on the pacemaker fibers in the sinus venosus of the heart. J Gen Physiol. 1956 May 20;39(5):715–733. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.5.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Differences in Na and Ca spikes as examined by application of tetrodotoxin, procaine, and manganese ions. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):793–806. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. Surface density of calcium ions and calcium spikes in the barnacle muscle fiber membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jan;50(3):583–601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Ritchie J. M. The movements of labelled ions in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1965 Jul;179(2):333–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Dixon W., Prat J. C. Inhibitory effect of manganese on norepinephrine release from the splenic nerves of cats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Jul;174(1):72–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Misu Y. Release of noradrenaline by splenic nerve stimulation and its dependence on calcium. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):219–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Wakade A. R. Release of noradrenaline from the cat spleen by potassium. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):595–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindmar R., Löffelholz K., Muscholl E. Unterschiede zwischen Tyramin und Dimethylphenylpiperzin in der Ca-Abhangigkeit und im zeitlichen Verlauf der Noradrenalin-Freisetzung am isolierten Kaninchenherzen. Experientia. 1967 Nov 15;23(11):933–934. doi: 10.1007/BF02136230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löffelholz K., Muscholl E. A muscarinic inhibition of the noradrenaline release evoked by postganglionic sympathetic nerve stimulation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1969;265(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01417206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Lanthanum ions abolish the "calcium response" of nerve terminals. Nature. 1971 Feb 5;229(5284):410–411. doi: 10.1038/229410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Haefely W., Staehelin H. Potentiation by tetraethylammonium of the response of the cat spleen to postganglionic sympathetic nerve stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Sep;157(3):532–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. Shortening of the cardiac action potential due to a brief injection of KCl following the onset of activity. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):157–163. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


