Abstract
1. An electron microscopic method has been developed and used to study cation binding sites in smooth muscle.
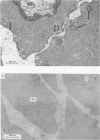
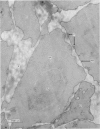
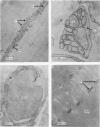
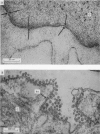
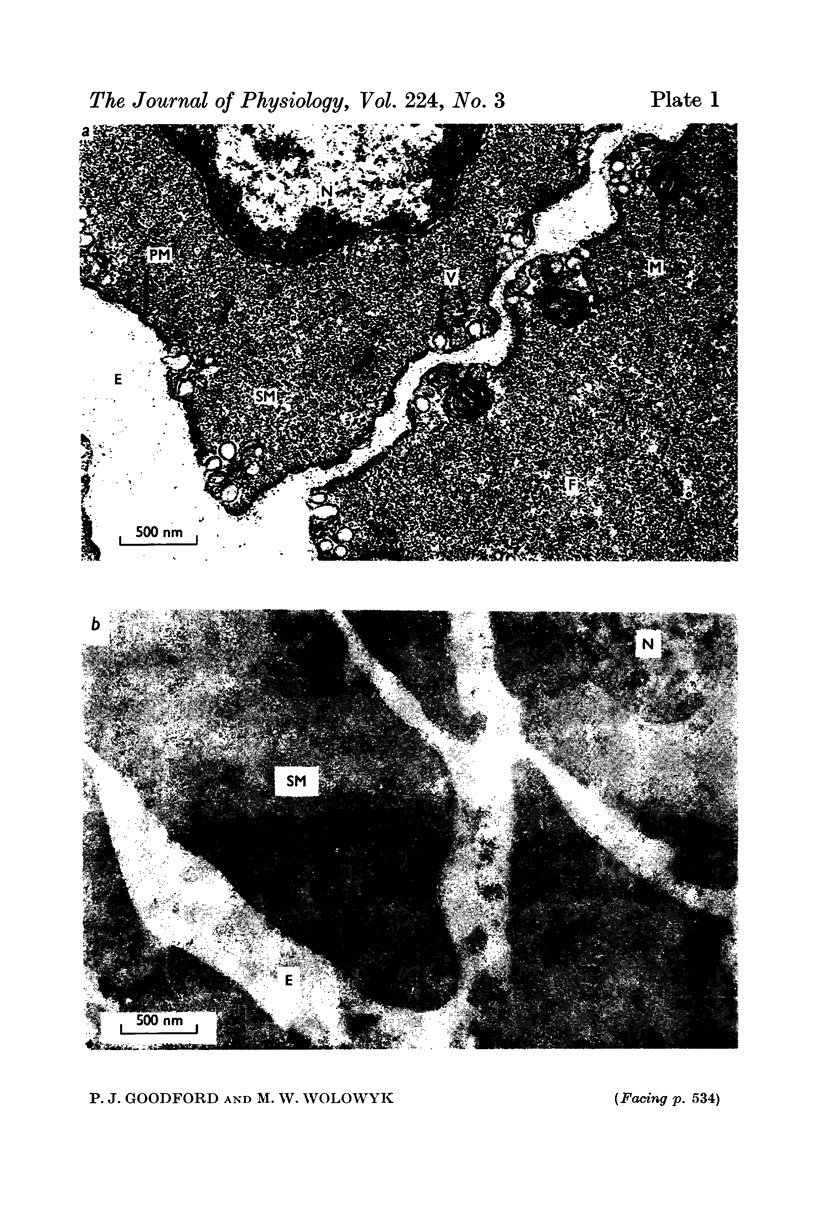
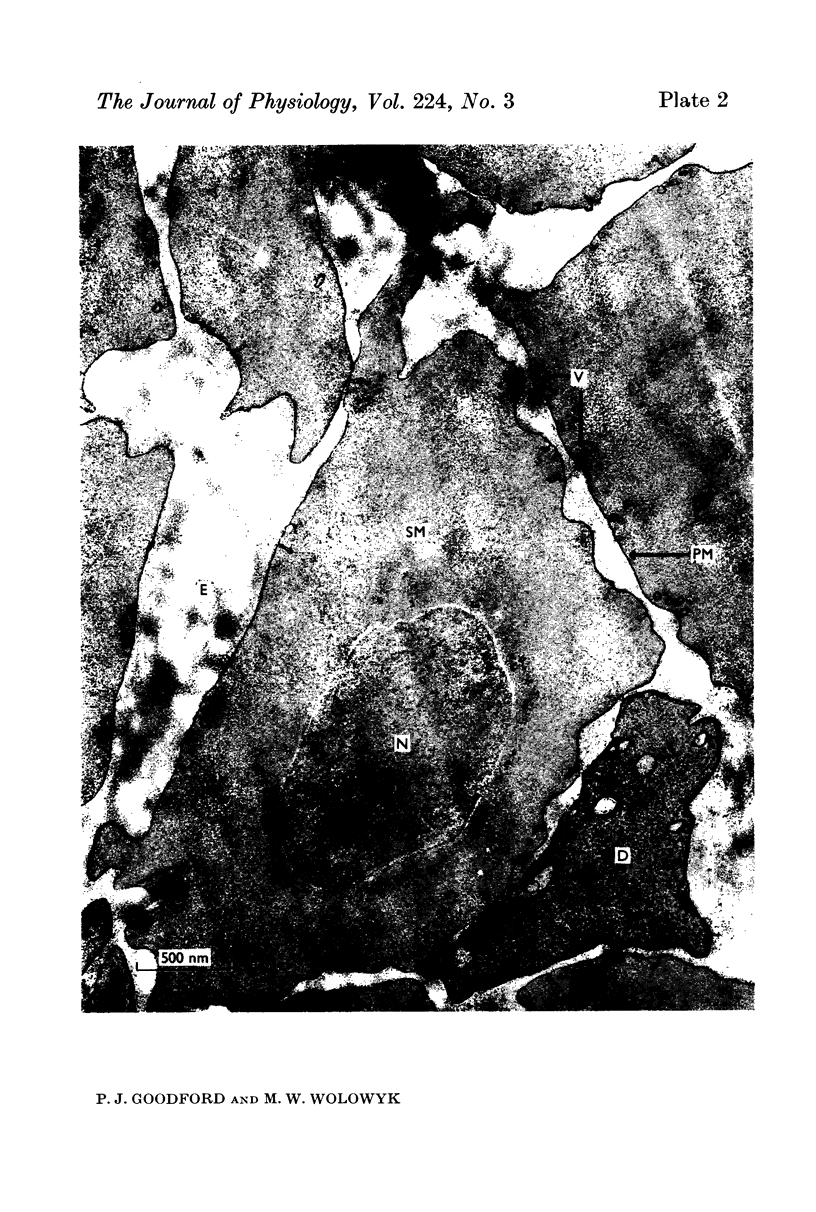
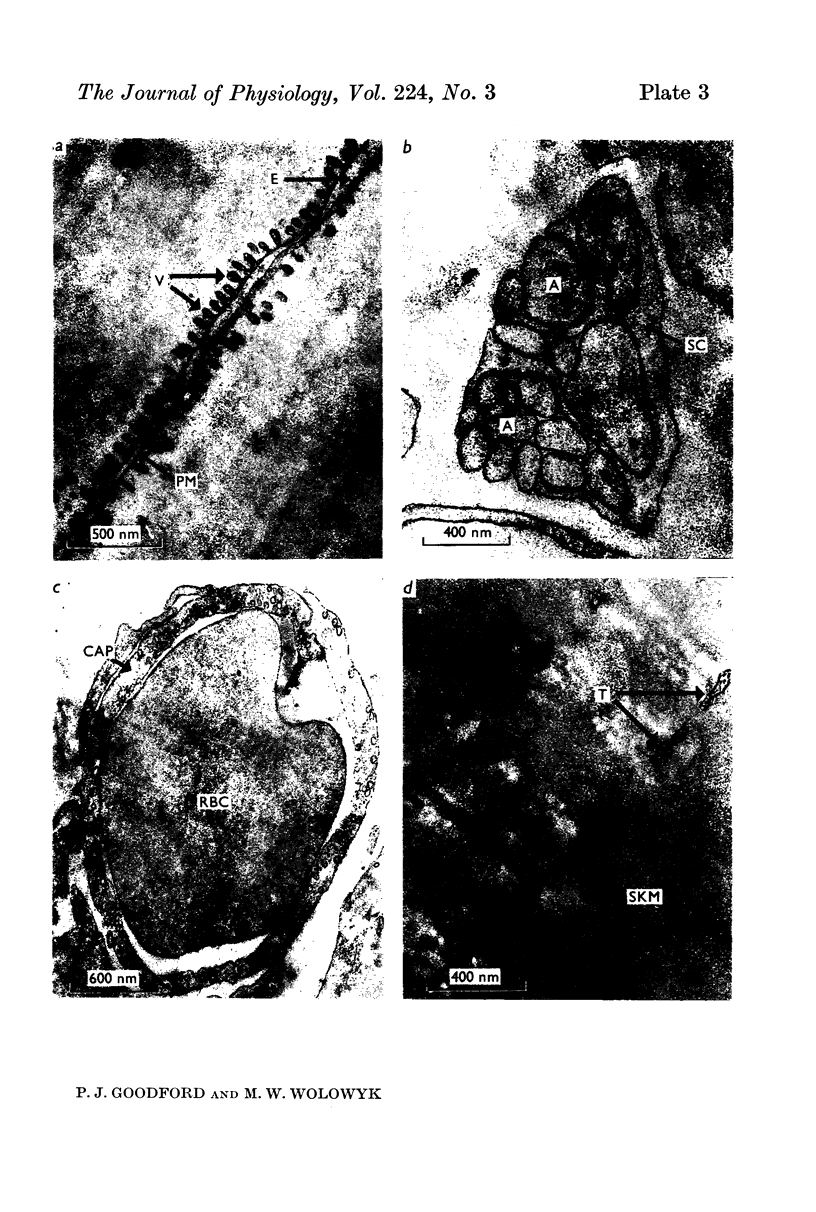
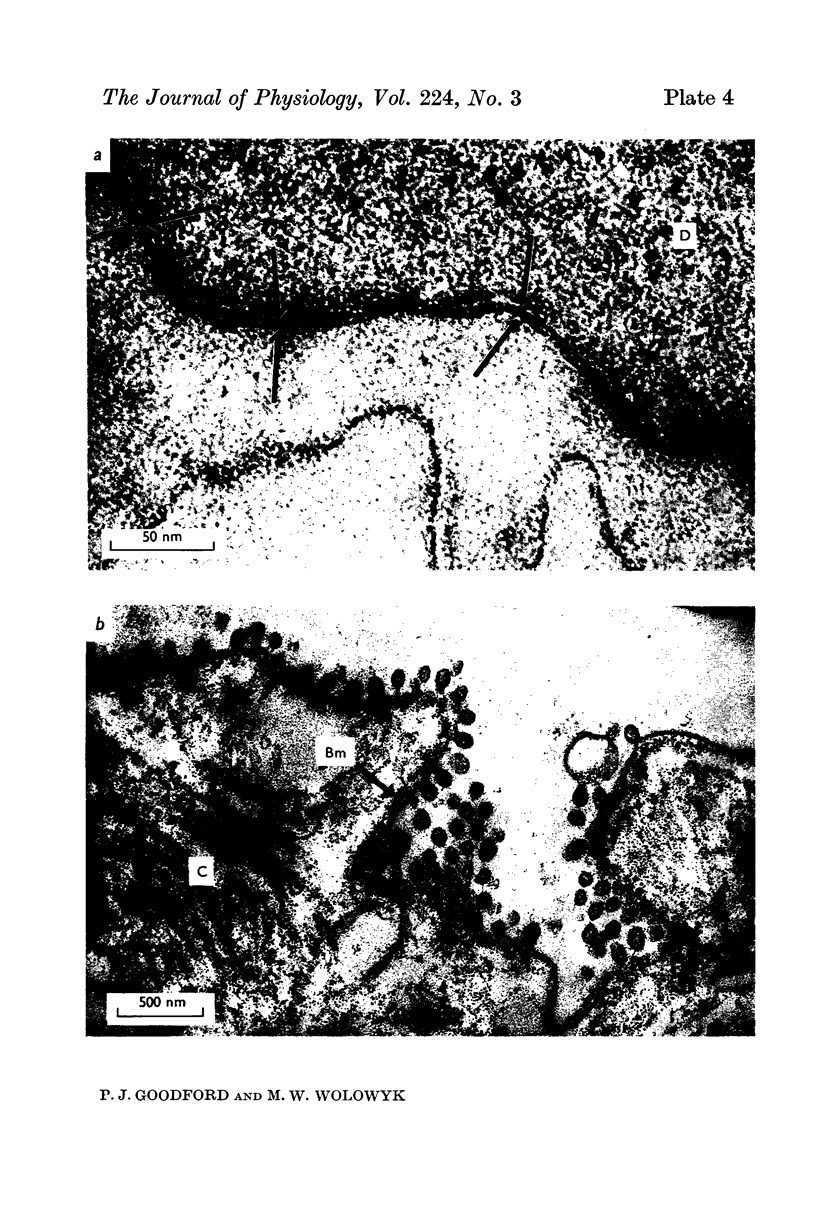
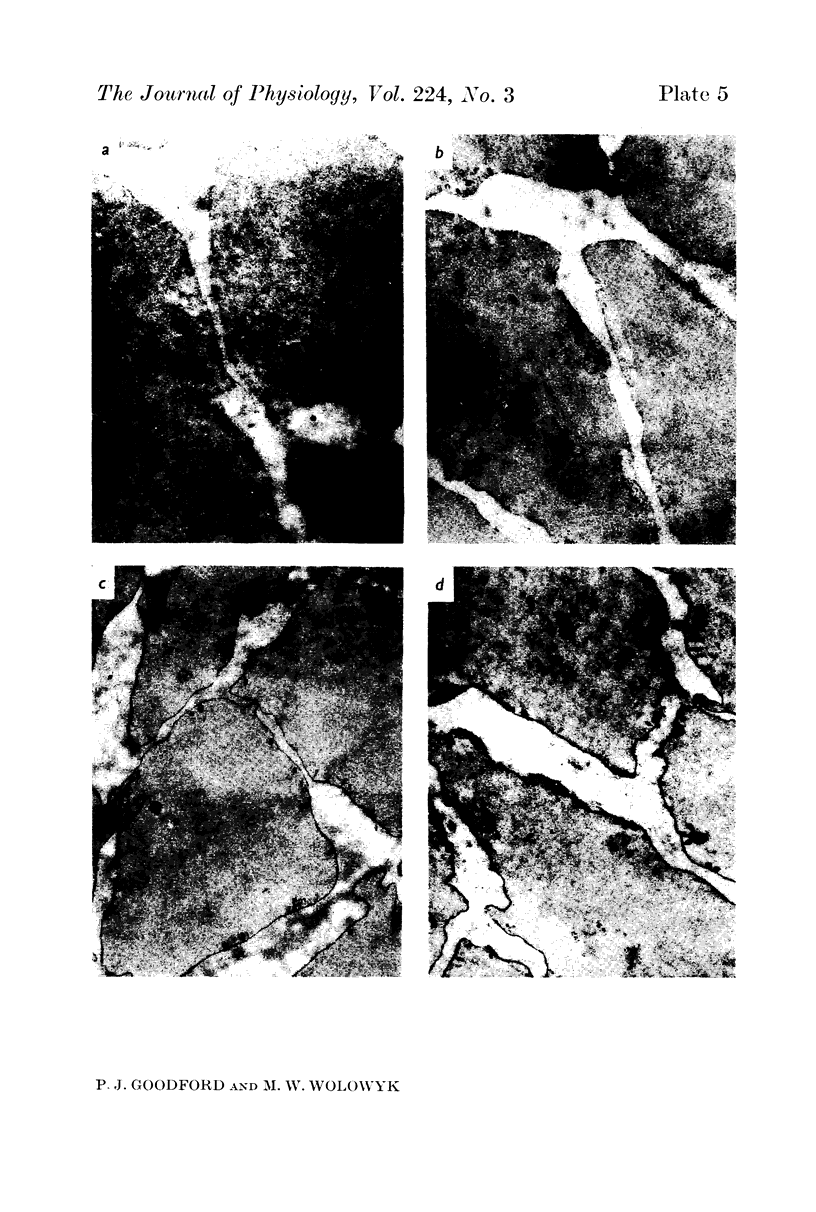
2. Uranyl cations normally bind to the external surface of the plasma membrane. However, uranyl also binds to the inner surface when it is accessible. Similar binding has been observed in skeletal muscle, nerve and red blood cells.
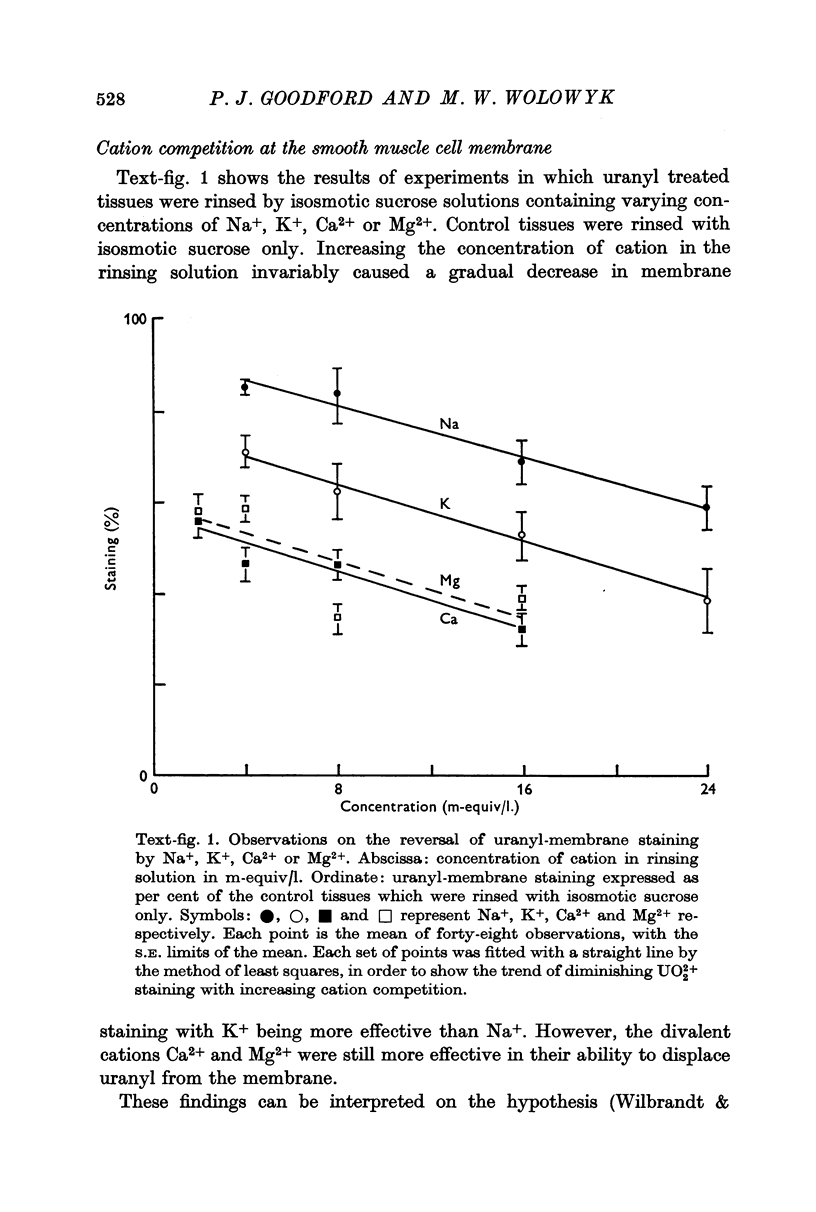
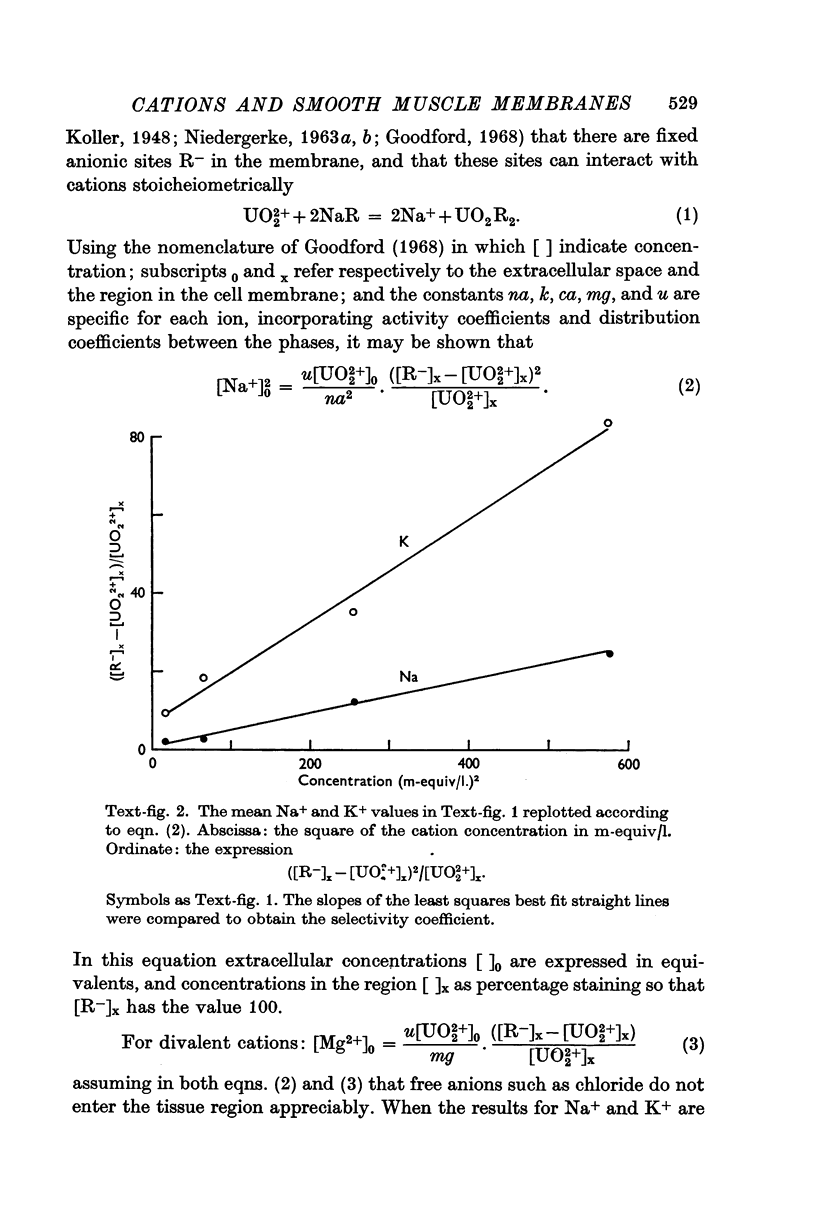
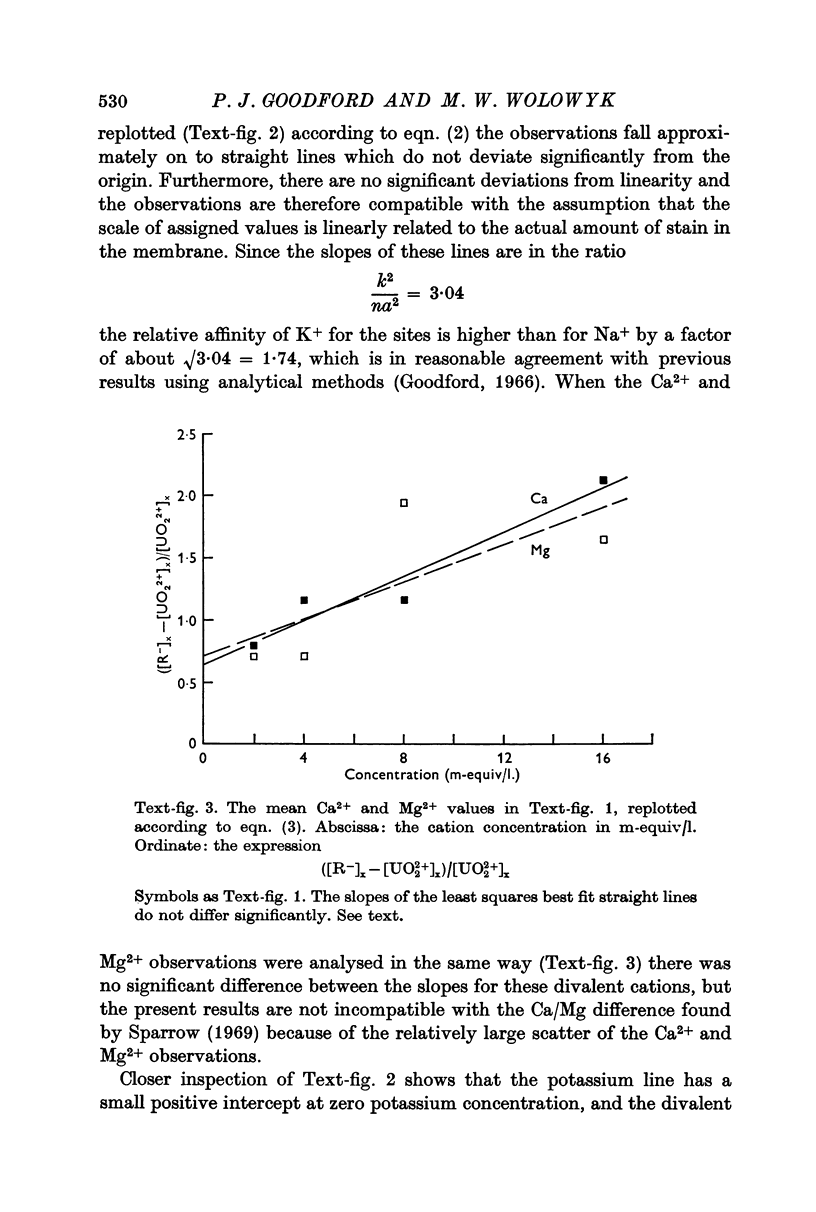
3. Uranyl binds electrostatically, and the binding can be competitively reversed by other cations. By a quantitative procedure the relative affinities Ca2+ ≃ Mg2+ ≫ K+ > Na+ for the membrane sites have been determined. This sequence is in agreement with previous values determined analytically.
4. The results support a counter-cation hypothesis for the plasma membrane surfaces of the taenia coli, and may explain features of the electrical activity in smooth muscle.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bone Q., Denton E. J. The osmotic effects of electron microscope fixatives. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):571–581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck B., Goodford P. J. The distribution of ions in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):551–569. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANSLER H. [Structure and function of smooth musculature. II. Light and electron microscope findings on cavitary organs of rats, guinea pigs and man]. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1961;55:724–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodford P. J. An interaction between potassium and sodium in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 Sep;186(1):11–26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodford P. J. The calcium content of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):145–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D., Callen C. R., McCabe M. The reactions between glutaraldehyde and various proteins. An investigation of their kinetics. Histochem J. 1970 Mar;2(2):137–150. doi: 10.1007/BF01003541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. Fixatives and fixation: a review. Histochem J. 1969 May;1(4):323–360. doi: 10.1007/BF01003278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi L., Prenna G., Okolicsanyi L., Gautier A. Electron staining with uranyl acetate. Possible role of free amino groups. J Histochem Cytochem. 1971 Mar;19(3):161–168. doi: 10.1177/19.3.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEDERGERKE R., LUTTGAU H. C. Antagonism between calcium and sodium ions. Nature. 1957 May 25;179(4569):1066–1067. doi: 10.1038/1791066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEDERGERKE R. MOVEMENTS OF CA IN FROG HEART VENTRICLES AT REST AND DURING CONTRACTURES. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:515–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEDERGERKE R. Movements of Ca in beating ventricles of the frog heart. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167:551–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSTEIN A. Functional implications of interactions of extracellular ions with ligands of the cell membrane. Circulation. 1962 Nov;26:1189–1200. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.26.5.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSTEIN A., MEIER R. The relationship of the cell surface to metabolism. VI. The chemical nature of uranium-complexing groups of the cell surface. J Cell Physiol. 1951 Oct;38(2):245–270. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030380209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. Vascular smooth muscle. I. Normal structure, pathology, biochemistry, and biophysics. Pharmacol Rev. 1968 Dec;20(4):197–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow M. P. Interaction of 28Mg with Ca and K in the smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(1):19–38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]