Abstract
1. When a steady dose of acetylcholine (ACh) is applied to an end-plate, the resulting depolarization is accompanied by a significant increase in voltage noise.
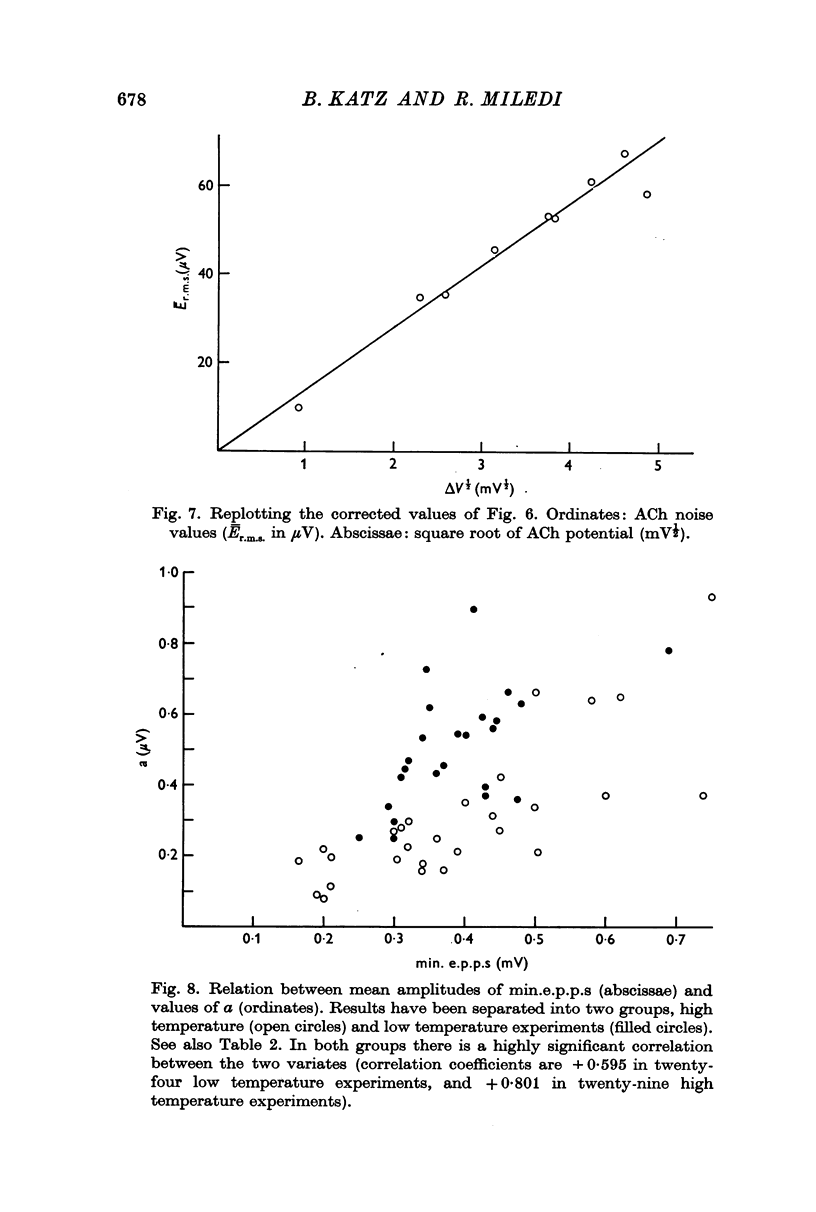
2. The characteristic properties of this ACh noise (amplitude and time course) are examined under various experimental conditions. The voltage noise is analysed on the assumption that it arises from statistical fluctuations in reaction rate, and in the frequency of the elementary current pulses (`shot effects') produced by the action of ACh molecules.
3. The elementary ACh current pulse (amplitude approximately 10-11 A), arises from a conductance change of the order of 10-10 Ω-1 which lasts for approximately 1 ms (at 20° C), and produces a minute depolarization, of the order of 0·3 μV. It is associated with a net charge transfer of nearly 10-14 C, equivalent to approximately 5 × 104 univalent ions.
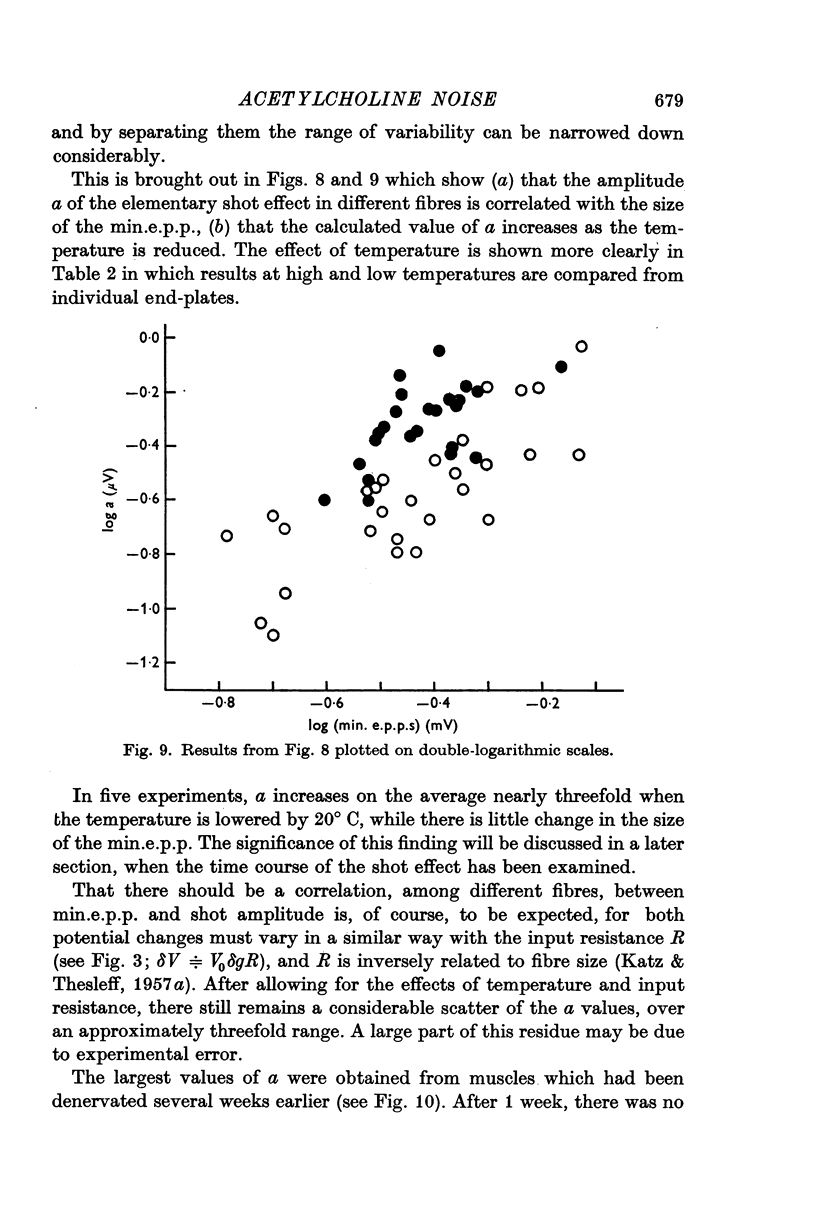
4. At low temperature, and during chronic denervation, the duration of the elementary current pulse increases, and the elementary voltage change becomes correspondingly larger.
5. Curare has little or no effect on the characteristics of the elementary event.
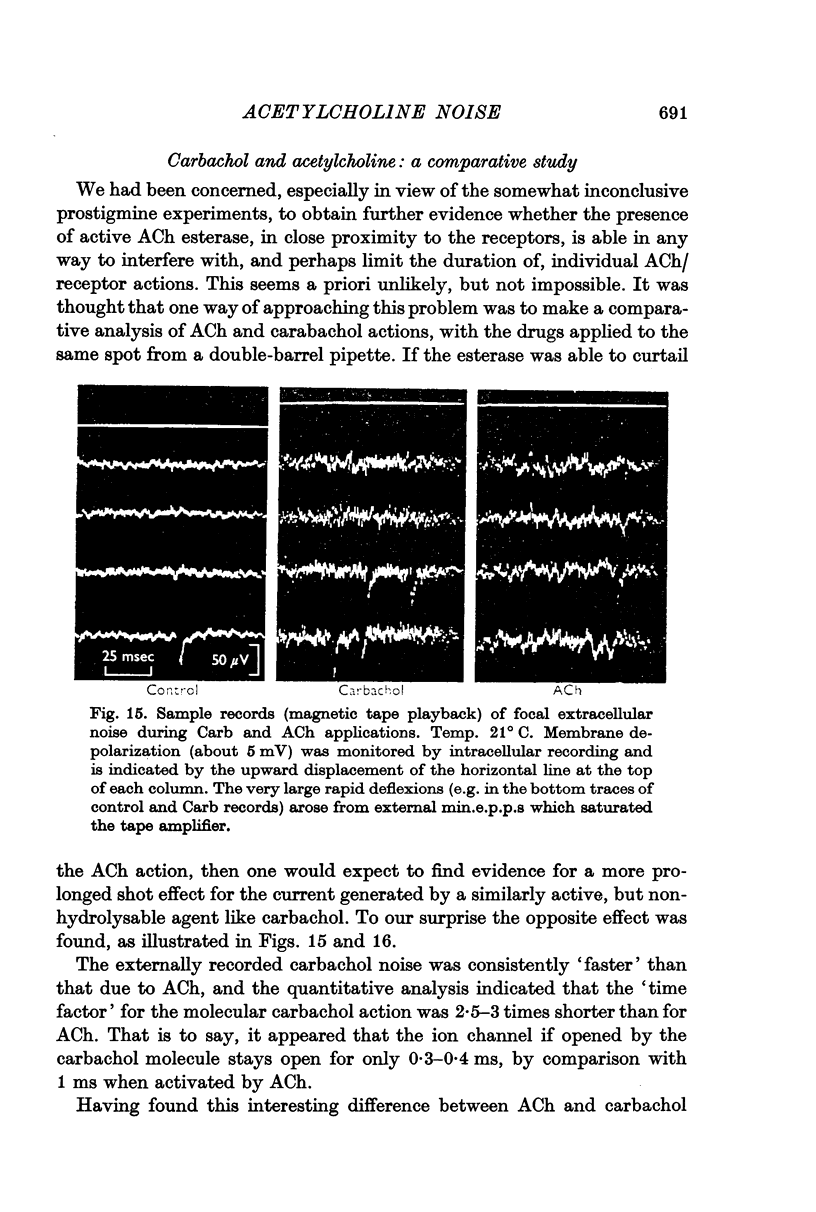
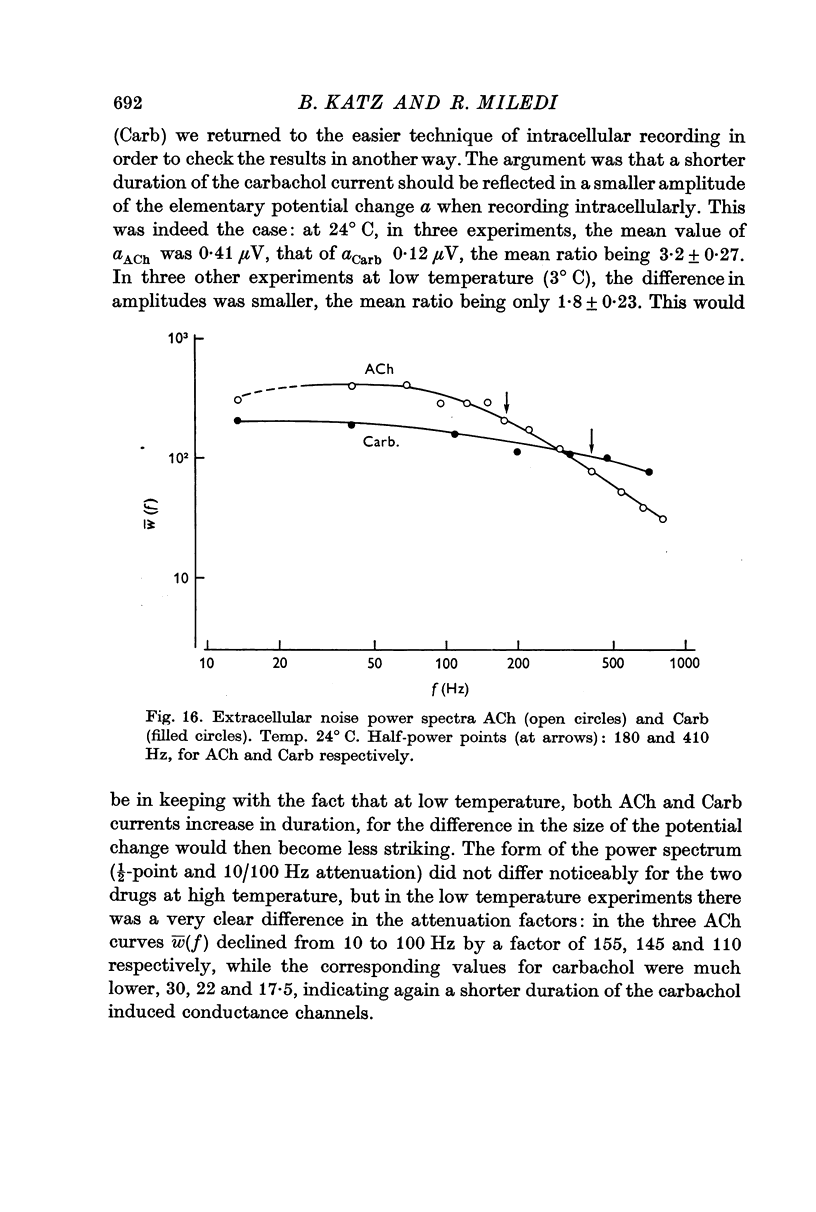
6. A comparative study of ACh and carbachol actions shows that carbachol produces considerably briefer, and therefore less effective, current pulses than ACh.
Full text
PDF







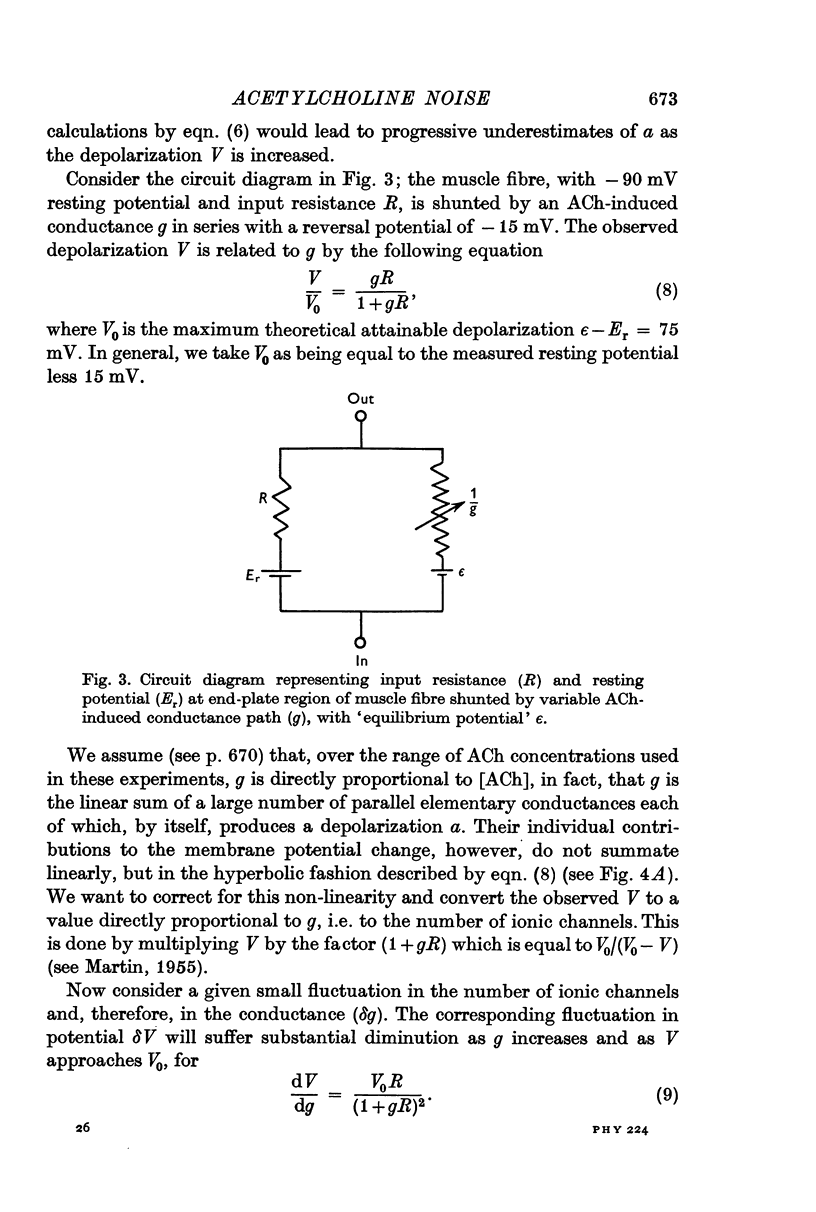
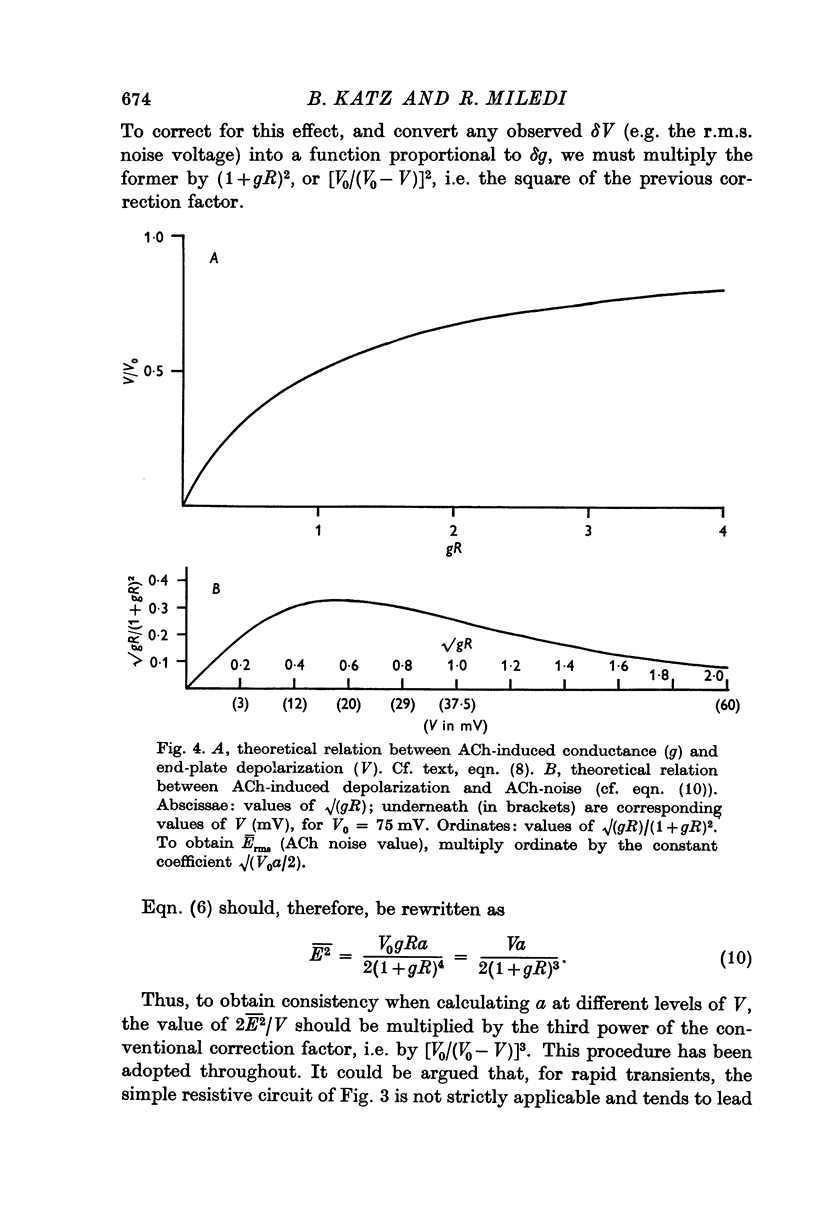

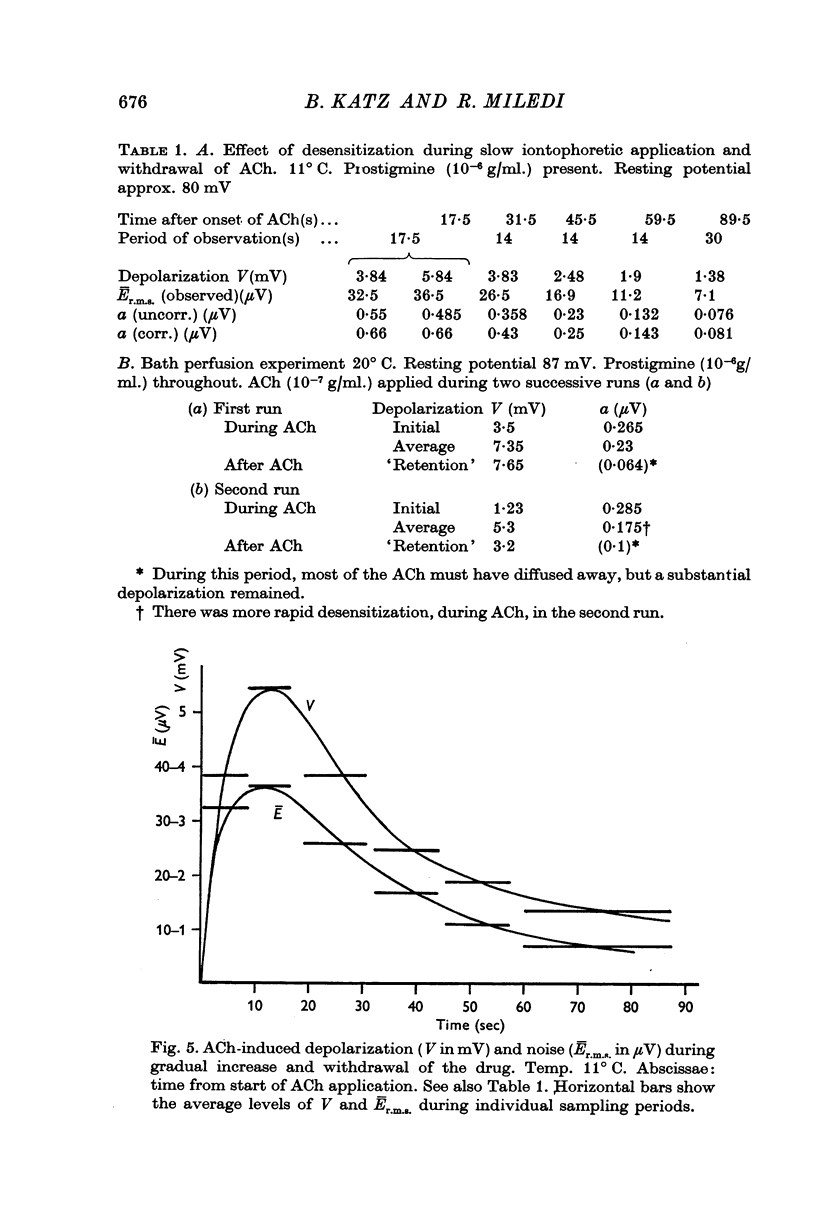
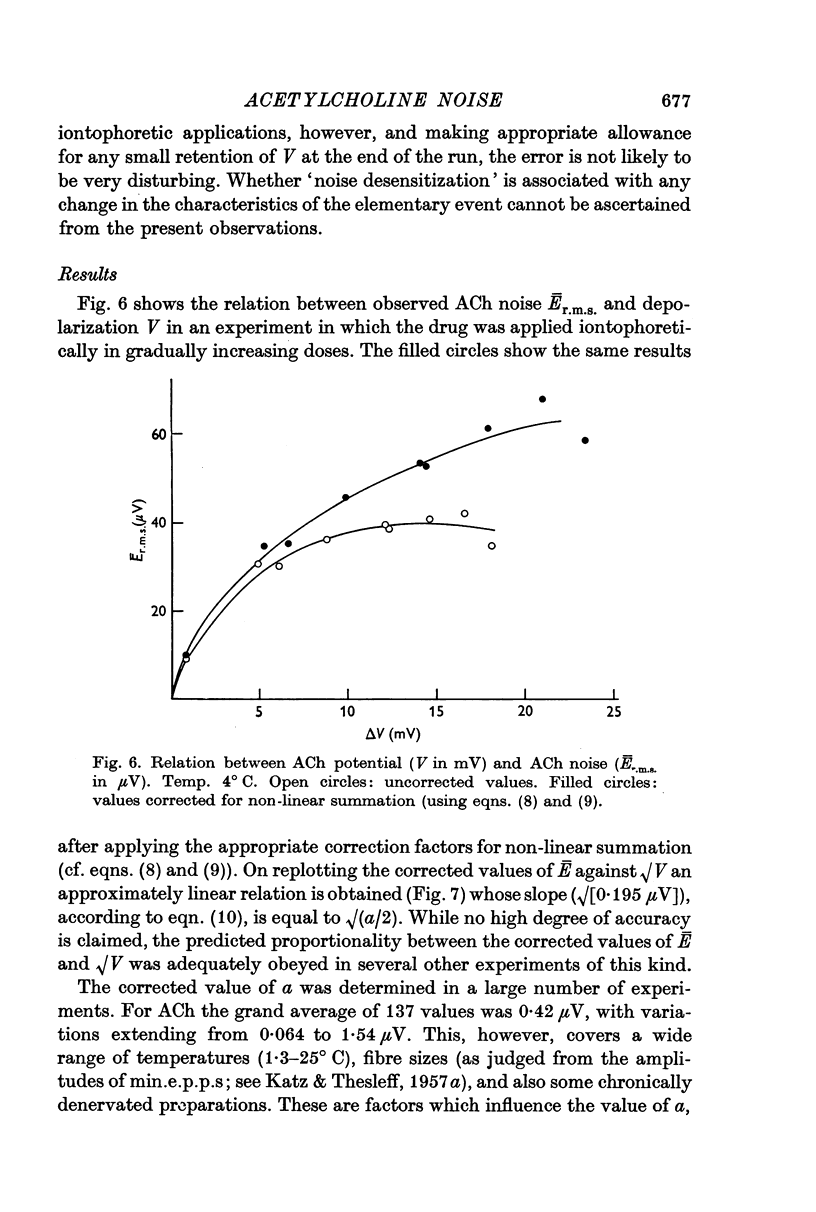


















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach A., Betz W. Does curare affect transmitter release? J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):691–705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. The membrane change produced by the neuromuscular transmitter. J Physiol. 1954 Sep 28;125(3):546–565. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., MACHNE X. Effect of temperature on the passive electrical properties of the muscle fibre membrane. J Physiol. 1953 May 28;120(3):431–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK G., FATT P. LINEAR ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF STRIATED MUSCLE FIBRES OBSERVED WITH INTRACELLULAR ELECTRODES. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Apr 14;160:69–123. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Schmidt R. F., Yokota T. The effect of acetylcholine upon mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(4):810–829. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The antagonism between tubocurarine and substances which depolarize the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:309–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. PROPAGATION OF ELECTRIC ACTIVITY IN MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:453–482. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. On the factors which determine the amplitude of the miniature end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):267–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MITCHELL J. F. Diffusion of acetylcholine in agar gels and in the isolated rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1960 Oct;153:562–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Further observations on acetylcholine noise. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):124–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio232124b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of local blockage of motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(3):729–741. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of temperature on the synaptic delay at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):656–670. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. The acetylcholine sensitivity of frog muscle fibres after complete or partial devervation. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthey A. A. The effect of calcium on the desensitization of membrane receptors at the neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):963–976. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLLS J. G. The electrical properties of denervated skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Jan 27;131(1):1–12. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastuk W. L., Parsons R. L. Factors in the inactivation of postjunctional membrane receptors of frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Aug;56(2):218–249. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straughan D. W. The release of acetylcholine from mammalian motor nerve endings. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1960 Sep;15(3):417–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1960.tb01266.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


