Abstract
1. Electrophysiological techniques were utilized to study the mechanisms underlying adrenergic inhibition in the urinary bladder of the cat.
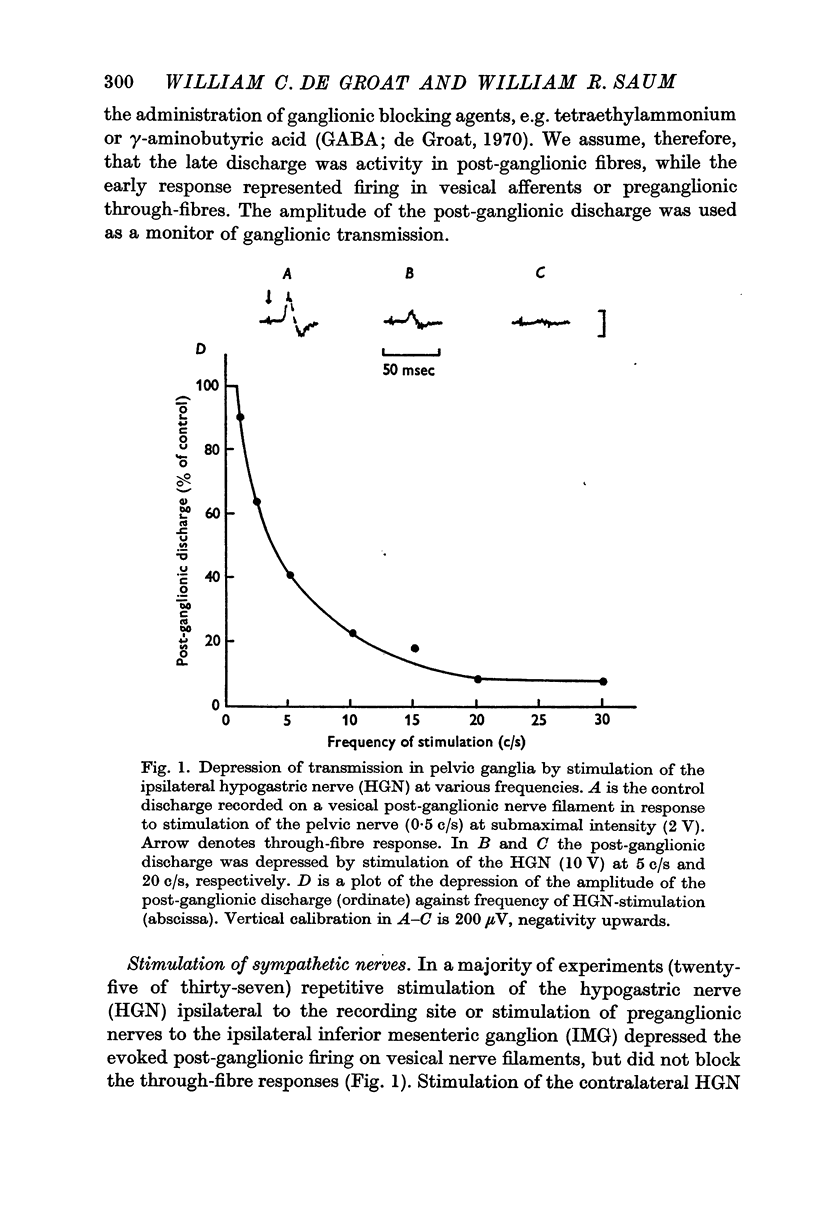
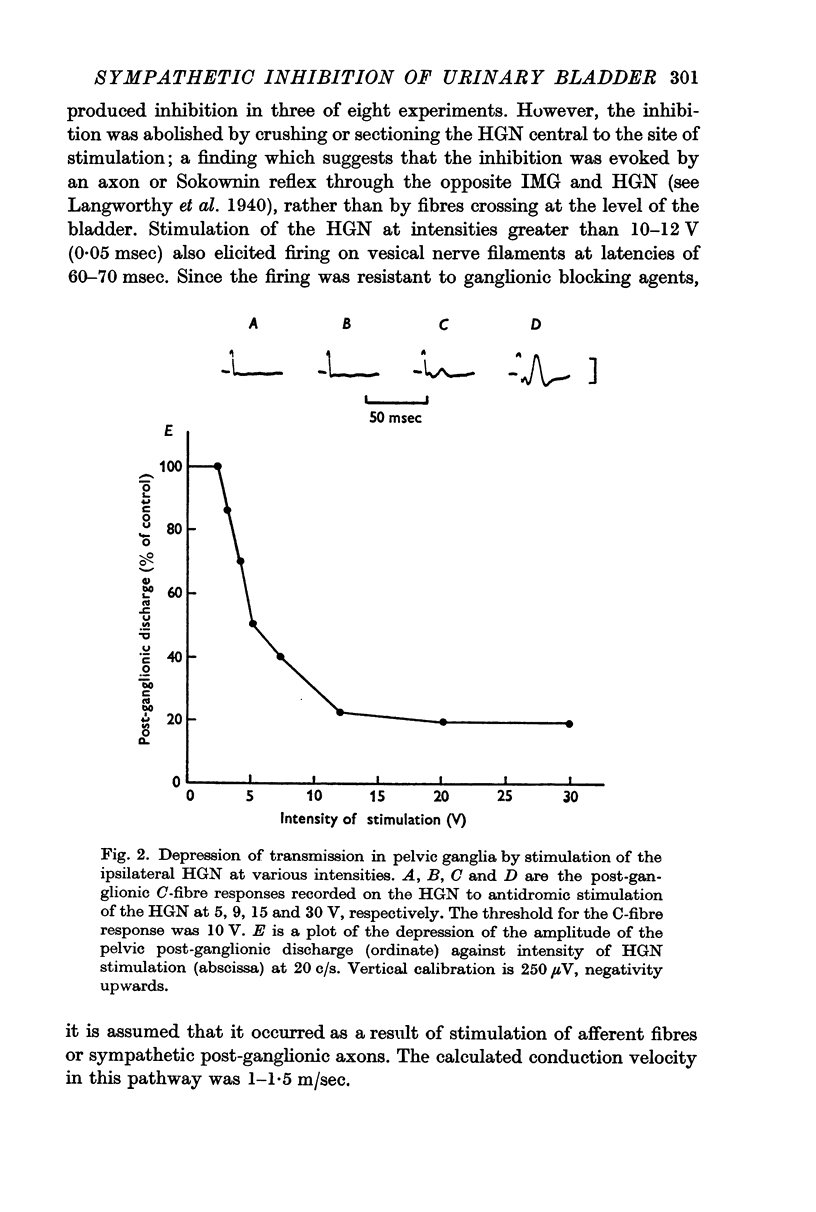
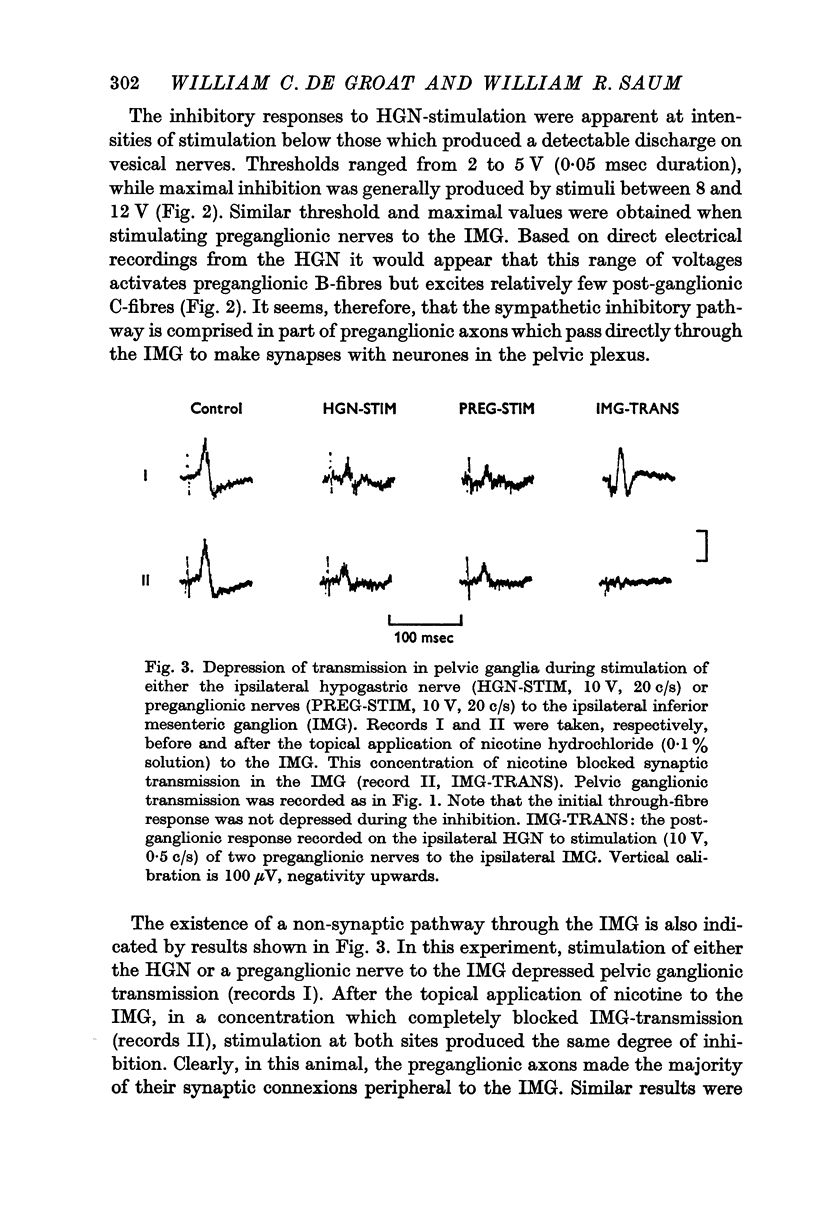
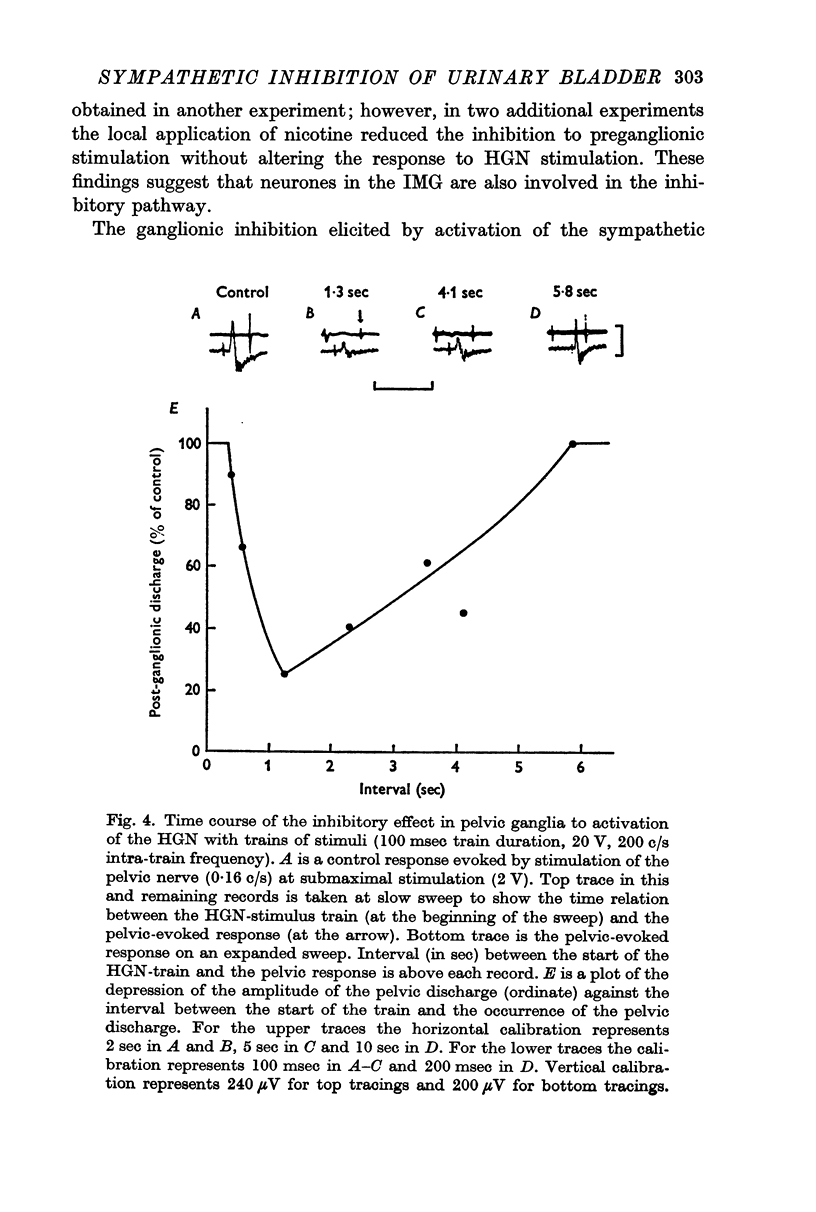
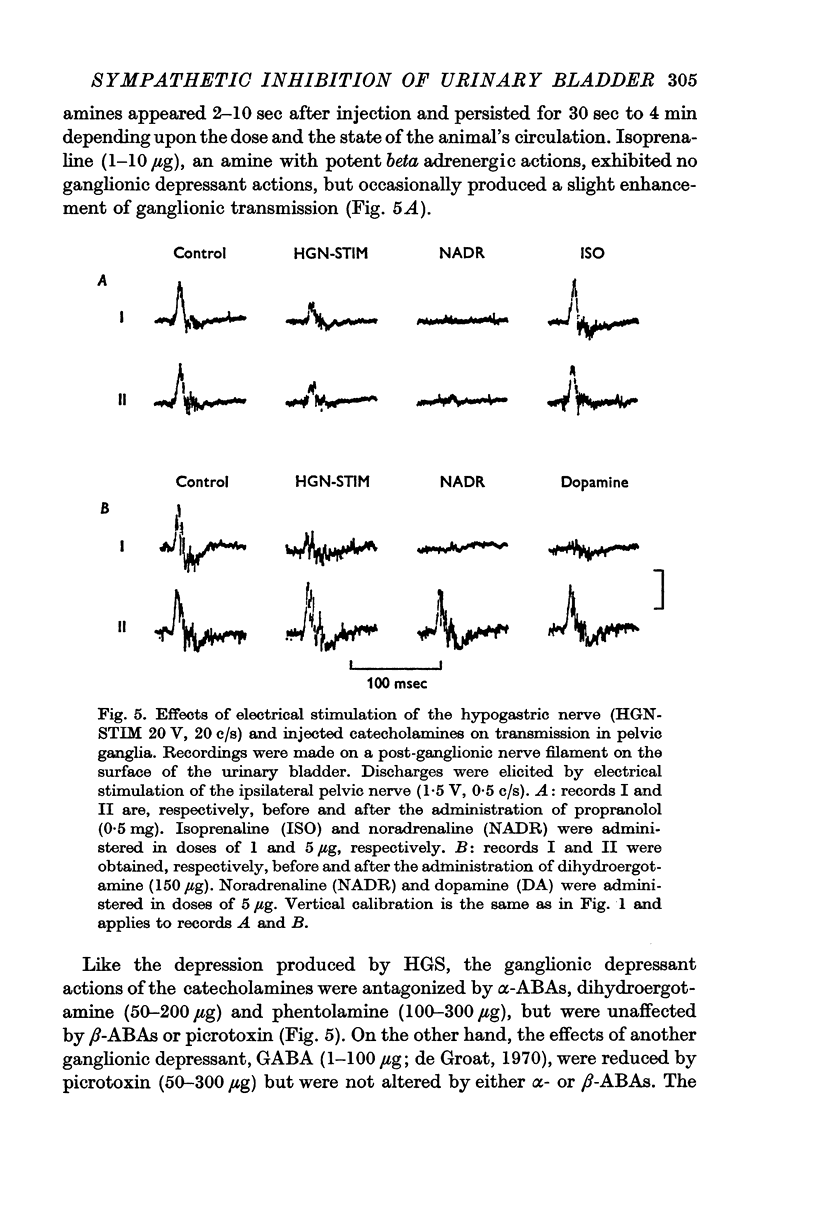
2. It has been shown that catecholamines administered by close intraarterial injection or released endogenously by electrical stimulation of the hypogastric nerves elicit two distinct inhibitory responses in the bladder: (1) a direct depression of the vesical smooth muscle and (2) a depression of transmission in vesical parasympathetic ganglia.
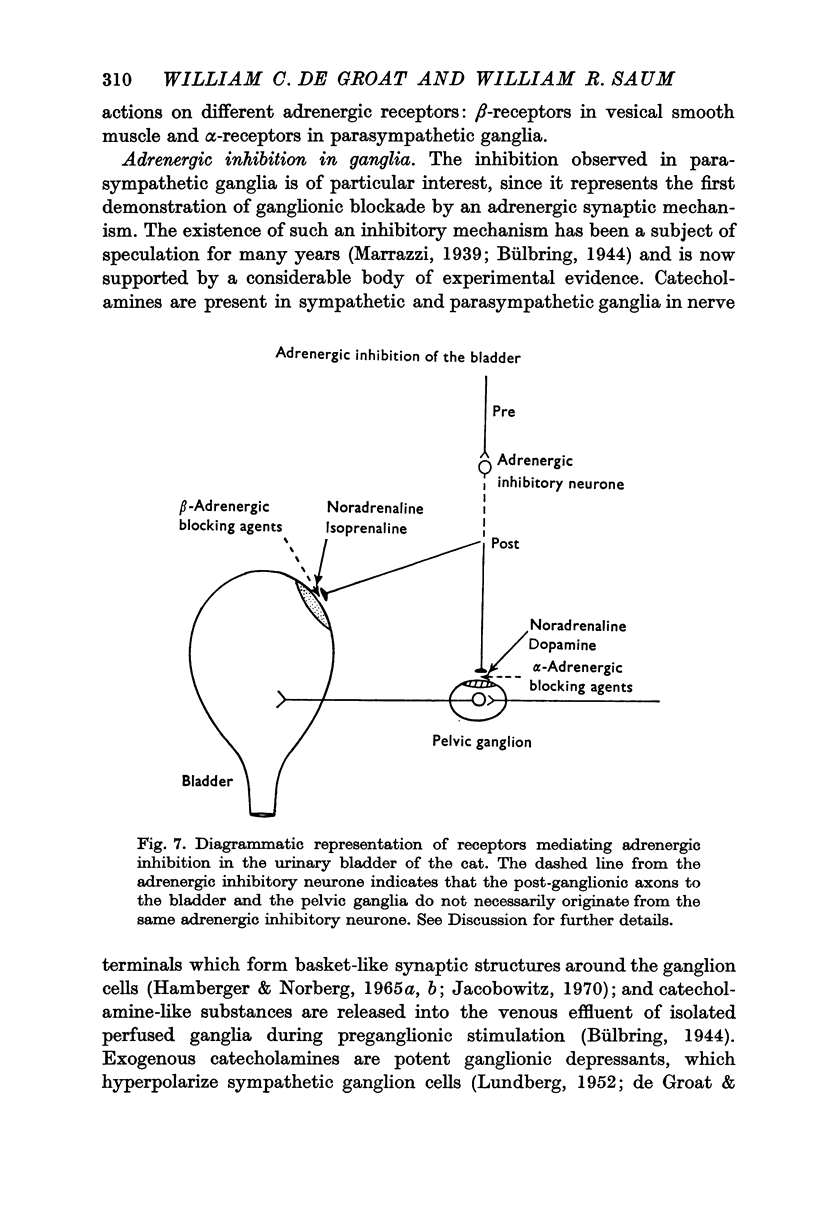
3. Pharmacological studies revealed that the inhibitory mechanisms were mediated via different adrenergic receptors: β-receptors on the smooth muscle and α-receptors in the parasympathetic ganglia.
4. We have been unable, however, to demonstrate that either of these mechanisms is activated by naturally occurring sympathetic firing.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOURA A. L., GREEN A. F. ADRENERGIC NEURONE BLOCKING AGENTS. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1965;5:183–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.05.040165.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E. The action of adrenaline on transmission in the superior cervical ganglion. J Physiol. 1944 Jun 15;103(1):55–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1944.sp004062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christ D. D., Nishi S. Effects of adrenaline on nerve terminals in the superior cervical ganglion of the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Feb;41(2):331–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb08033.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groat W. C., Ryall R. W. Recurrent inhibition in sacral parasympathetic pathways to the bladder. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):579–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groat W. C., Saum W. R. Adrenergic inhibition in mammalian parasympathetic ganglia. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 9;231(23):188–189. doi: 10.1038/newbio231188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groat W. C., Volle R. L. Interactions between the catecholamines and ganglionic stimulating agents in sympathetic ganglia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Nov;154(2):200–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groat W. C., Volle R. L. The actions of the catecholamines on transmission in the superior cervical ganglion of the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Oct;154(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LIBET B. Origin and blockade of the synaptic responses of curarized sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1961 Aug;157:484–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvardsen P. Nervous control of urinary bladder in cats. I. The collecting phase. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Jan-Feb;72(1):157–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb03838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvardsen P. Nervous control of urinary bladder in cats. IV. Effects of autonomic blocking agents on responses to peripheral nerve stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Jan-Feb;72(1):234–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb03845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbadawi A., Schenk E. A. A new theory of the innervation of bladder musculature. 3. Postganglionic synapses in uretero-vesico-urethral autonomic pathways. J Urol. 1971 Mar;105(3):372–374. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)61529-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjone R. Peripheral autonomic influence on the motility of the urinary bladder in the cat. I. Rhythmic contractions. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Dec;65(4):370–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMBERGER B., NORBERG K. A. ADRENERGIC SYNAPTIC TERMINALS AND NERVE CELLS IN BLADDER GANGLIA OF THE CAT. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1965 Feb;4:41–45. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(65)90045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberger B., Norberg K. A. Studies on some systems of adrenergic synaptic terminals in the abdominal ganglia of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Nov;65(3):235–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobowitz D. Catecholamine fluorescence studies of adrenergic neurons and chromaffin cells in sympathetic ganglia. Fed Proc. 1970 Nov-Dec;29(6):1929–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURU M. NERVOUS CONTROL OF MICTURITION. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jul;45:425–494. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A. Adrenaline and transmission in the sympathetic ganglion of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952 Sep 10;26(2-3):252–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley J. N., Anderson H. K. The Innervation of the Pelvic and adjoining Viscera: Part II. The Bladder. Part III. The External Generative Organs. Part IV. The Internal Generative Organs. Part V. Position of the Nerve Cells on the Course of the Efferent Nerve Fibres. J Physiol. 1895 Dec 30;19(1-2):71–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1895.sp000587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley J. N., Anderson H. K. The Innervation of the Pelvic and adjoining Viscera: Part VII. Anatomical Observations. J Physiol. 1896 Oct 19;20(4-5):372–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1896.sp000629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libet B., Kobayashi H. Generation of adrenergic and cholinergic potentials in sympathetic ganglion cells. Science. 1969 Jun 27;164(3887):1530–1532. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3887.1530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIGG E. B., SIGG T. D. SYMPATHEIC STIMULATION AND BLOCKADE OF THE URINARY BLADDER IN CAT. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1964 May;3:241–252. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(64)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groat W. C., Ryall R. W. Reflexes to sacral parasympathetic neurones concerned with micturition in the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):87–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groat W. C. The actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid and related amino acids on mammalian autonomic ganglia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Apr;172(2):384–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


