Abstract
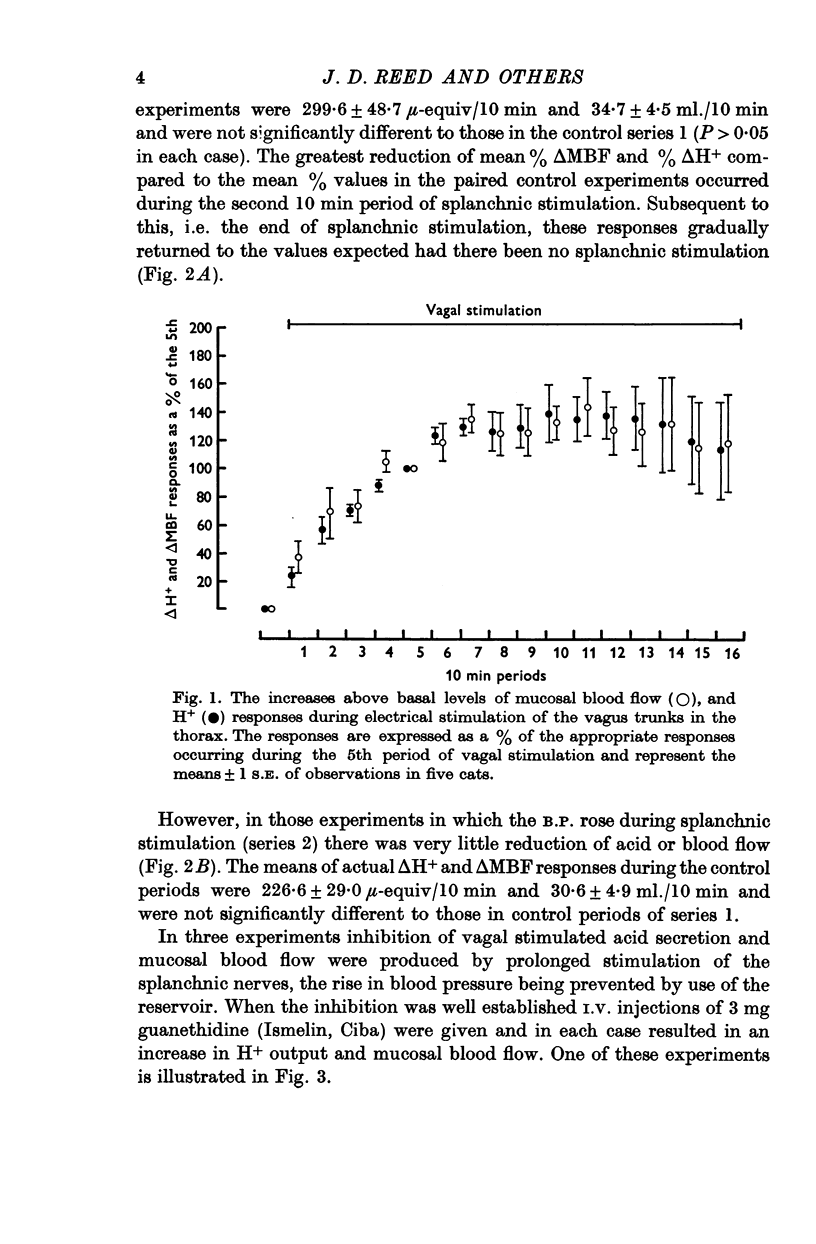
1. Electrical stimulation of the vagus nerves produced a parallel increase in gastric acid secretion and gastric mucosal blood flow.
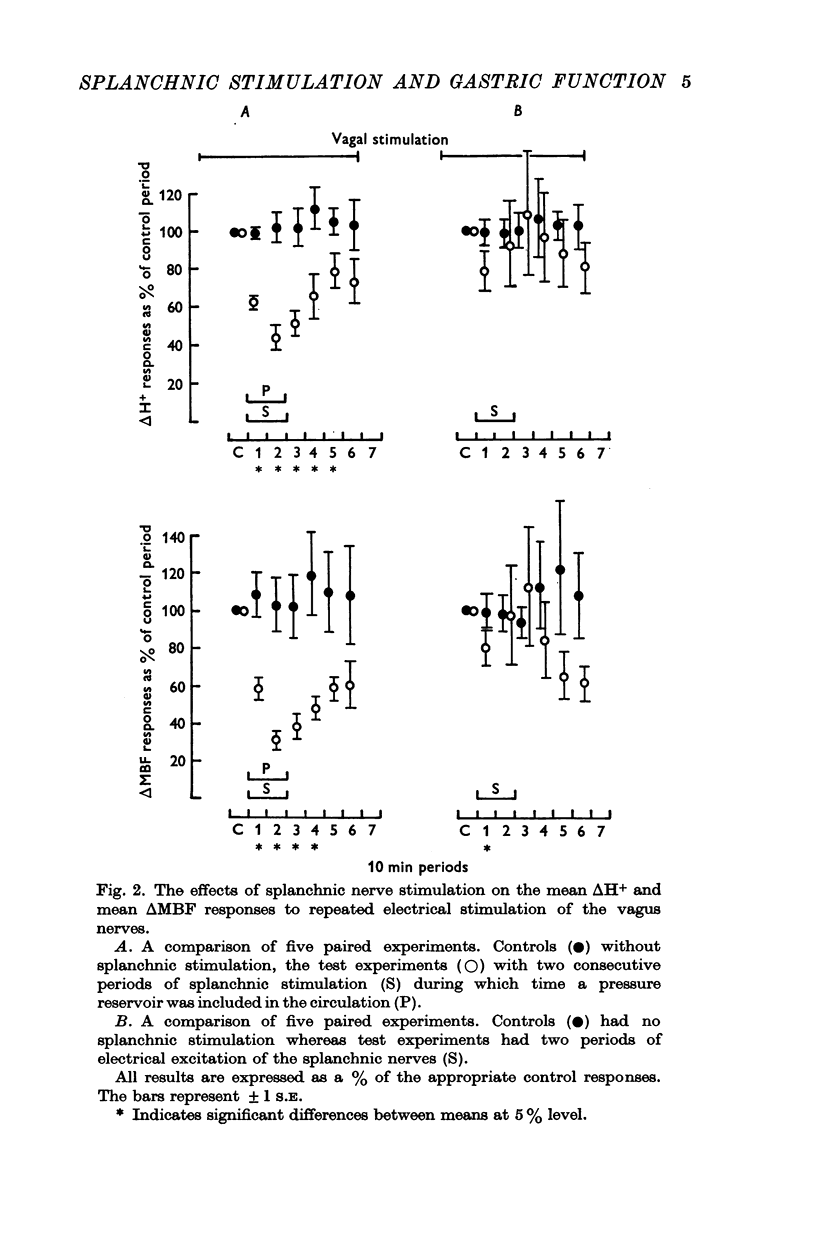
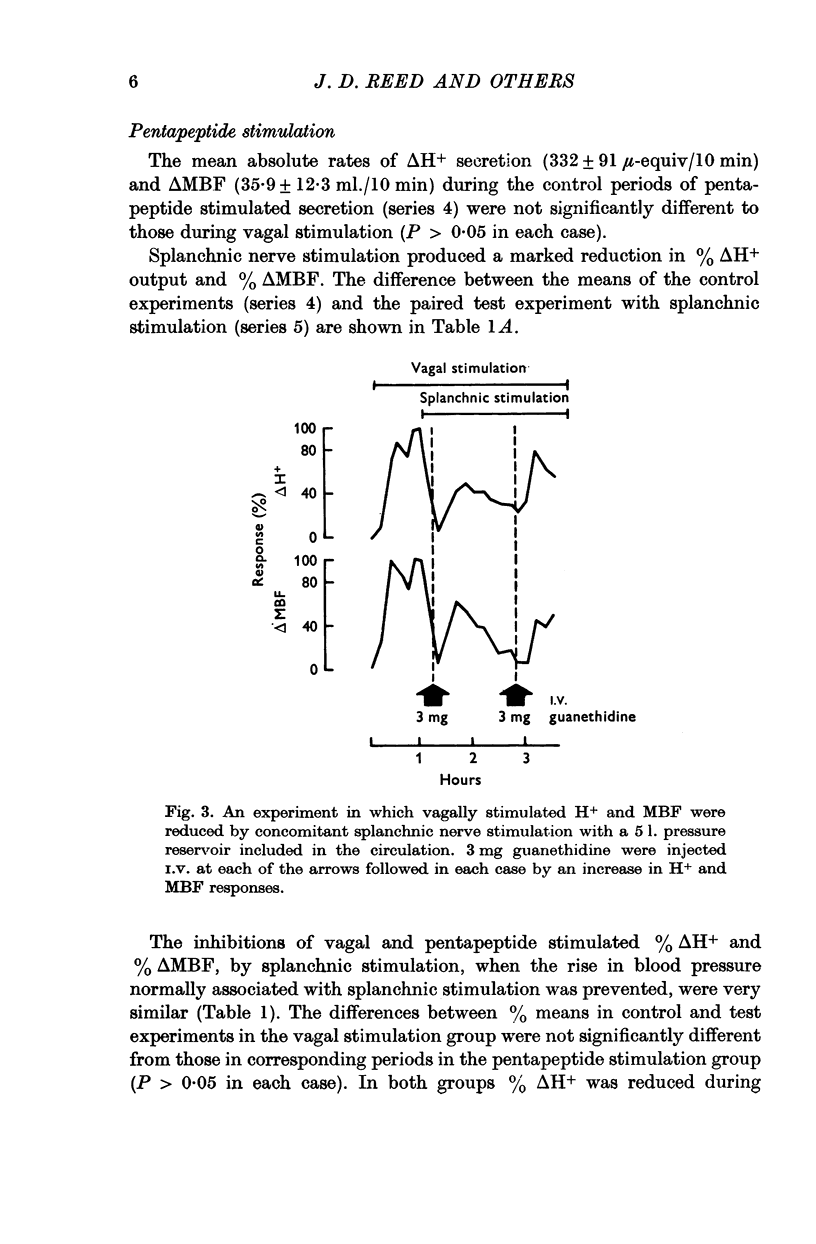
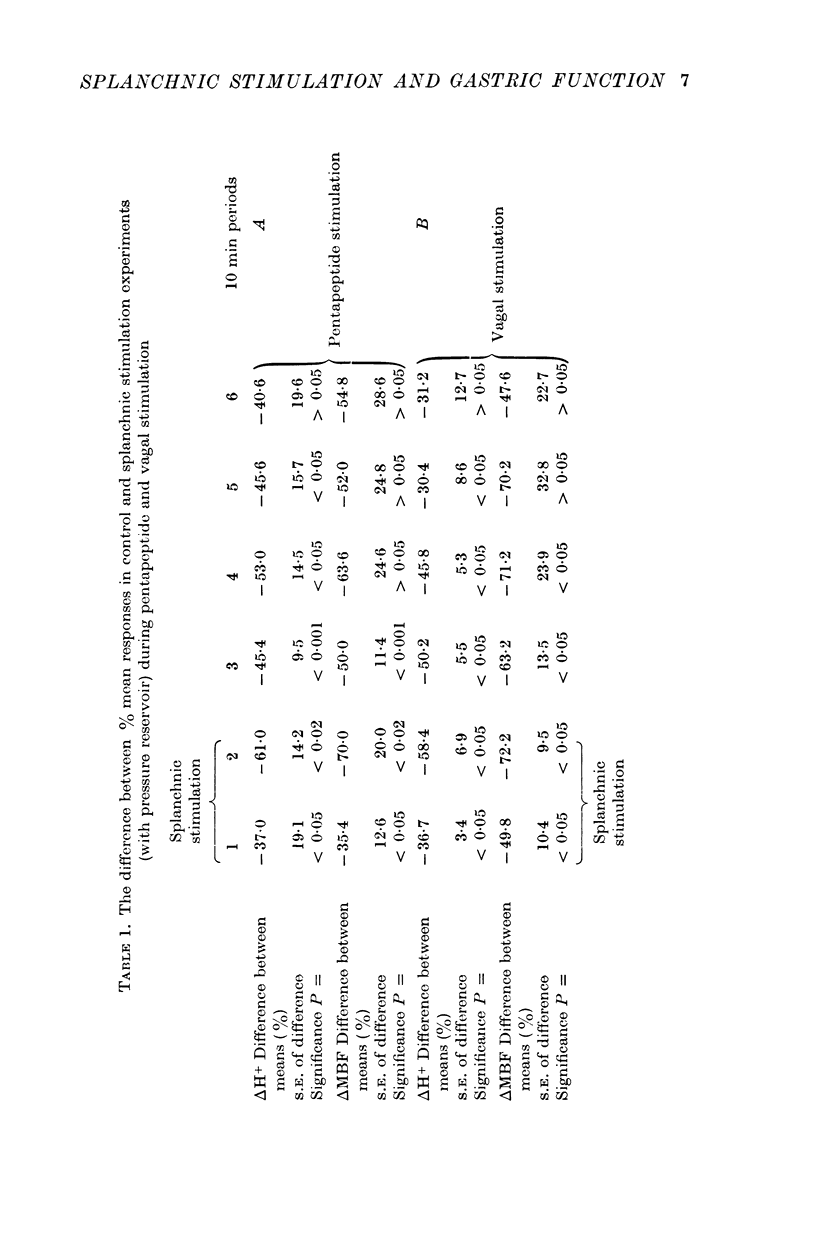
2. Gastric acid secretion and mucosal blood flow, stimulated by pentapeptide infusions or by vagal stimulation, were markedly and equally reduced by electrical stimulation of splanchnic nerve fibres.
3. The splanchnic stimulated reduction in acid and mucosal blood flow occurred only when the rise in blood pressure, normally associated with splanchnic stimulation, was prevented by inclusion of a pressure reservoir in the circulation.
4. There was evidence that the effect of the splanchnic nerves was not mediated by release of adrenaline from the adrenal medulla.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CELANDER O. Are there any centrally controlled sympathetic inhibitory fibres to the musculature of the intesine? Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Dec 12;47:299–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley D. J., Code C. F., Fiasse R. Gastric mucosal blood flow during secretory inhibition by gastrin pentapeptide and gastrone. Gastroenterology. 1969 Apr;56(4):659–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORREST A. P., CODE C. F. The inhibiting effect of epinephrine and norepinephrine on secretion induced by histamine in separated pouches of dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Apr;110(4):447–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIESEN S. R., HEMINGWAY A. The vascular response of the stomach to experimental alterations in the autonomic nervous system of the dog. Am Surg. 1952 Feb;18(2):195–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. A., Reed J. D., Smy J. R. Gastric blood flow in anaesthetized cats. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):795–807. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobowitz D. Histochemical studies of the autonomic innervation of the gut. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Sep;149(3):358–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D. Comparison of prostaglandin E1 and norepinephrine on the gastric mucosal circulation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):516–519. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D., Eisenberg M. M., Swan K. G. Effects of histamine on gastric blood flow in conscious dogs. Gastroenterology. 1966 Oct;51(4):466–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D., Linford R. H., Grossman M. I. Gastric secretion in relation to mucosal blood flow studied by a clearance technic. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):1–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI105313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D., Swan K. G., Grossman M. I. Blood flow and secretion in the stomach. Gastroenterology. 1967 Feb;52(2):414–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody F. G. Gastric blood flow and acid secretion during direct intraarterial histamine administration. Gastroenterology. 1967 Feb;52(2):216–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORBERG K. A. ADRENERGIC INNERVATION OF THE INTESTINAL WALL STUDIED BY FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1964 Sep;3:379–382. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(64)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OBERHELMAN H. A., Jr, WOODWARD E. R., SMITH C. A., DRAGSTEDT L. R. Effect of sympathectomy on gastric secretion in total pouch dogs. Am J Physiol. 1951 Sep;166(3):679–685. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.166.3.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan K. G., Jacobson E. D. Gastric blood flow and secretion in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol. 1967 Apr;212(4):891–896. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.4.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON J. E., VANE J. R. Gastric secretion induced by histamine and its relationship to the rate of blood flow. J Physiol. 1953 Sep;121(3):433–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


