Abstract
1. The spinal integration of cortical, segmental and breathing inputs to thoracic motoneurones was studied in anaesthetized, paralysed cats: the breathing input was intensified by underventilation or abolished by hyperventilation.
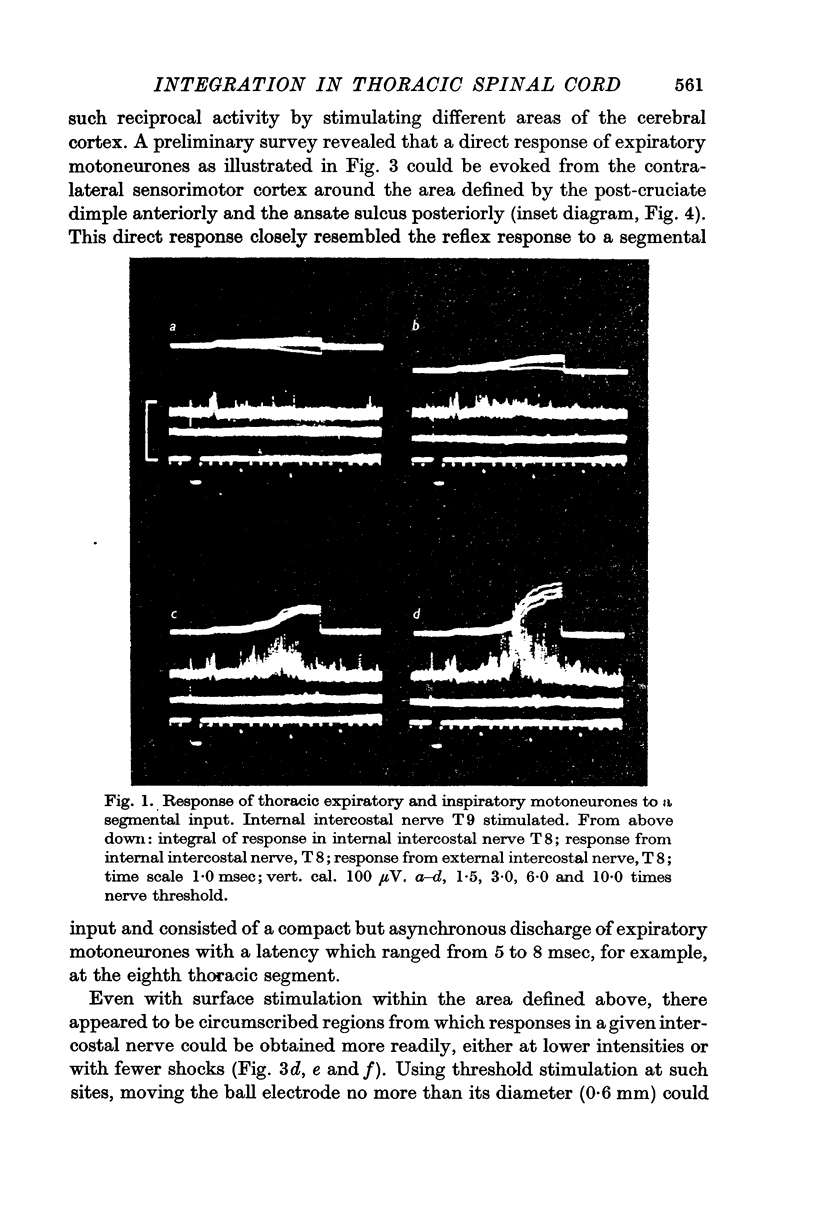
2. In apnoeic animals, low intensity stimulation of an internal intercostal nerve evoked a brief latency polysynaptic reflex discharge of expiratory motoneurones (direct response) in several adjacent segments with no or little response of the inspiratory motoneurones.
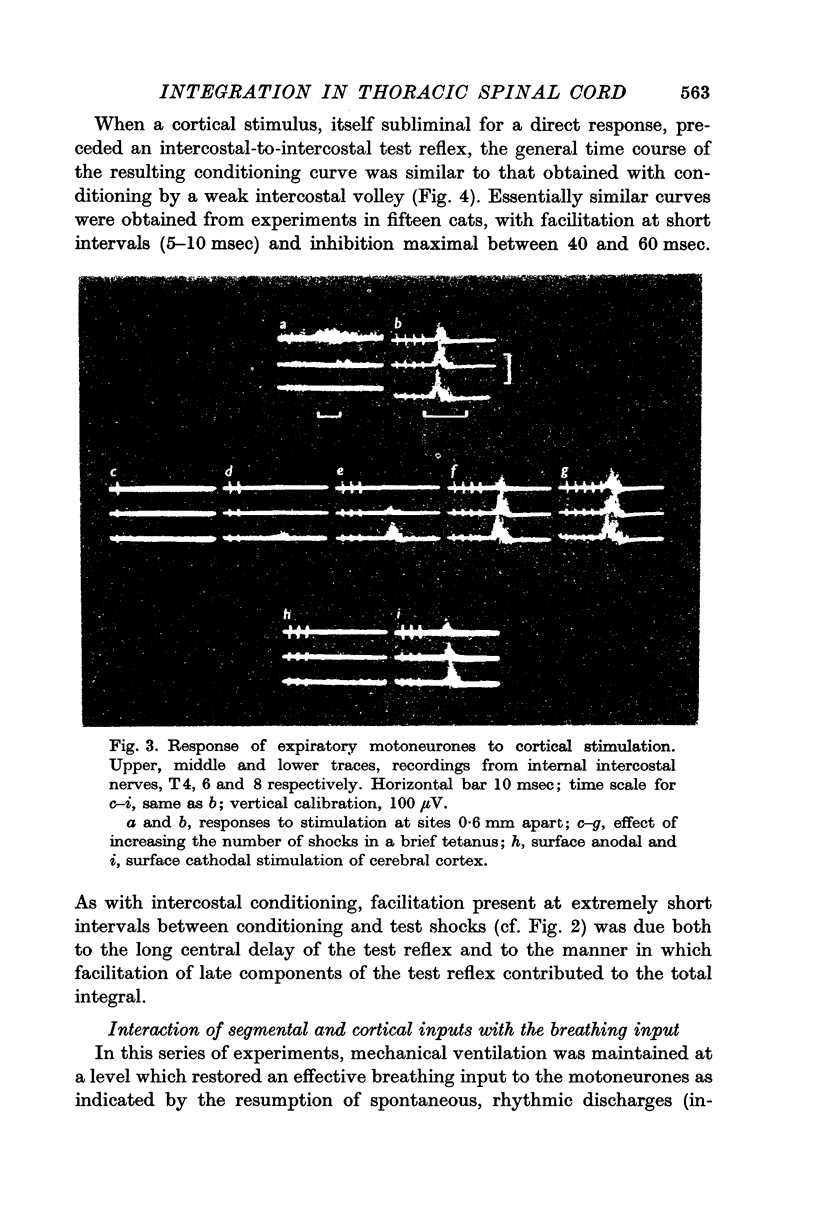
3. A similar direct response of expiratory motoneurones occurred with brief tetanic stimulation of the trunk area in the contralateral sensorimotor cortex.
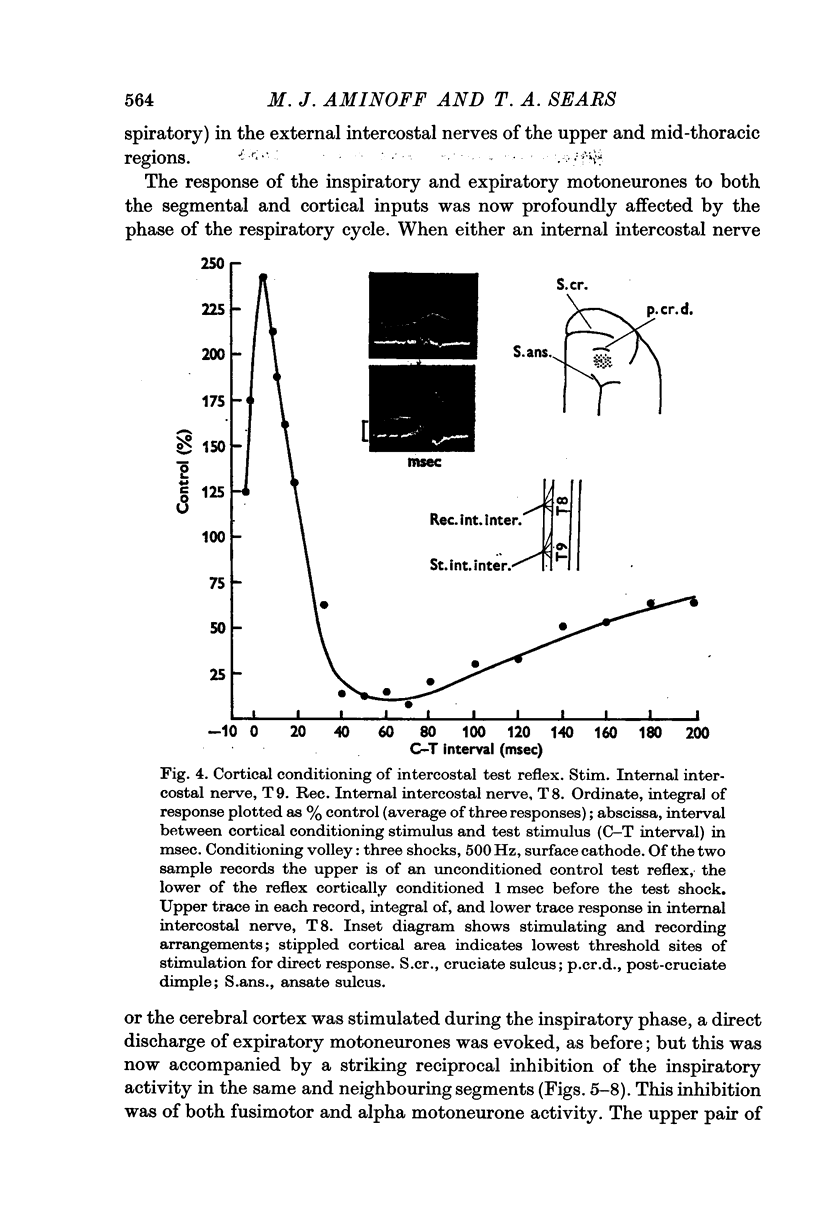
4. Conditioning of an intercostal-intercostal test reflex by a prior stimulus to an intercostal nerve or to the cortex gave conditioning curves showing facilitation of transmission to expiratory motoneurones at short intervals (5-25 msec) and inhibition at long intervals (25-200 msec).
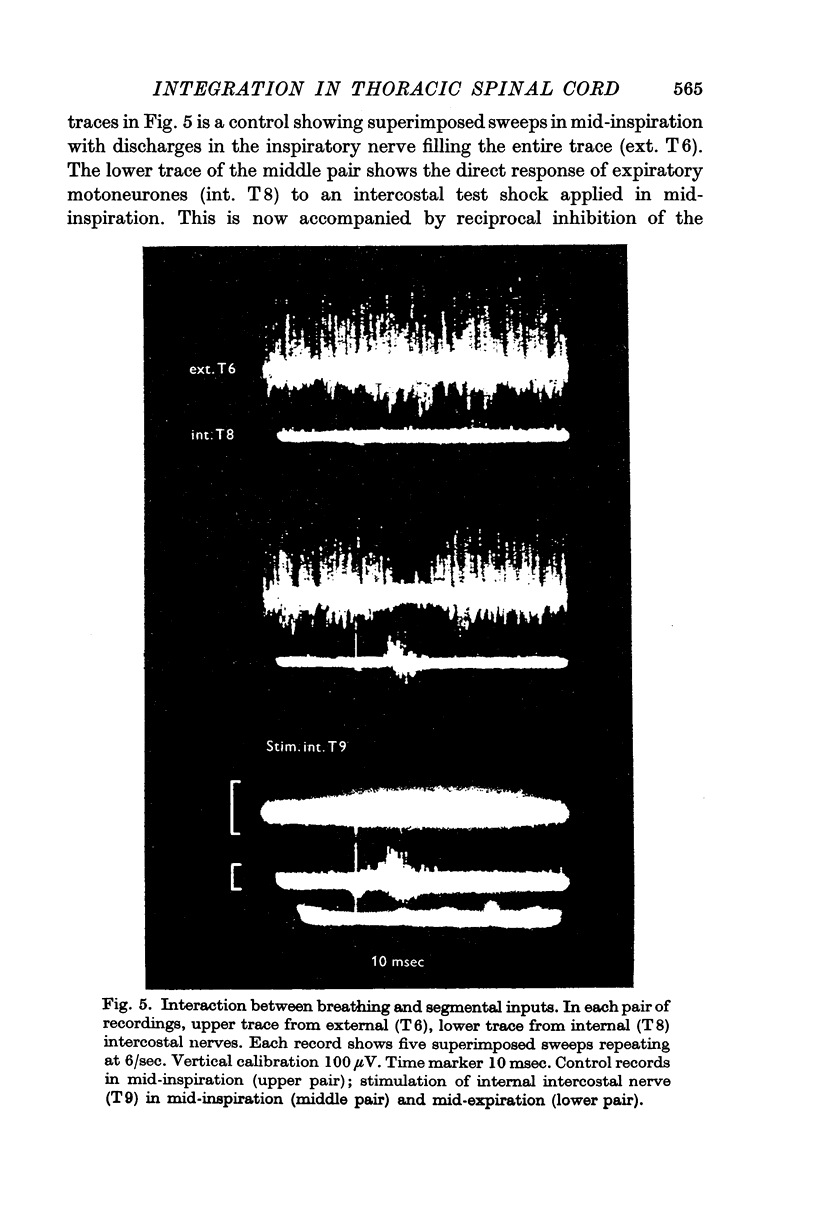
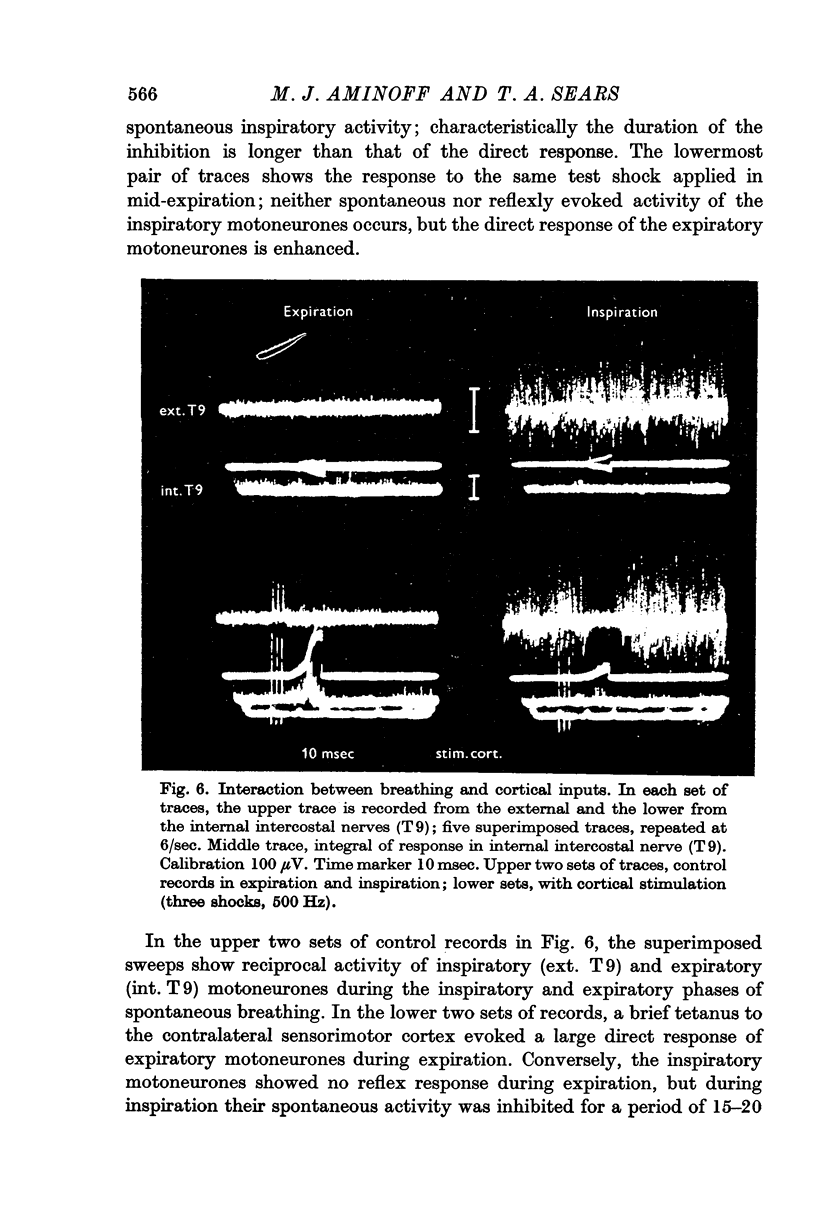
5. The direct response of expiratory motoneurones to the cortical or segmental inputs was depressed during the inspiratory phase when the animal was underventilated; conversely the spontaneous activity of the inspiratory motoneurones was inhibited for a period that corresponded with the direct response or to the phase of facilitated transmission to expiratory motoneurones. During the expiratory phase, the cortically or segmentally induced direct response was facilitated but the inhibition of inspiratory motoneurone activity was concealed by the absence of spontaneous activity.
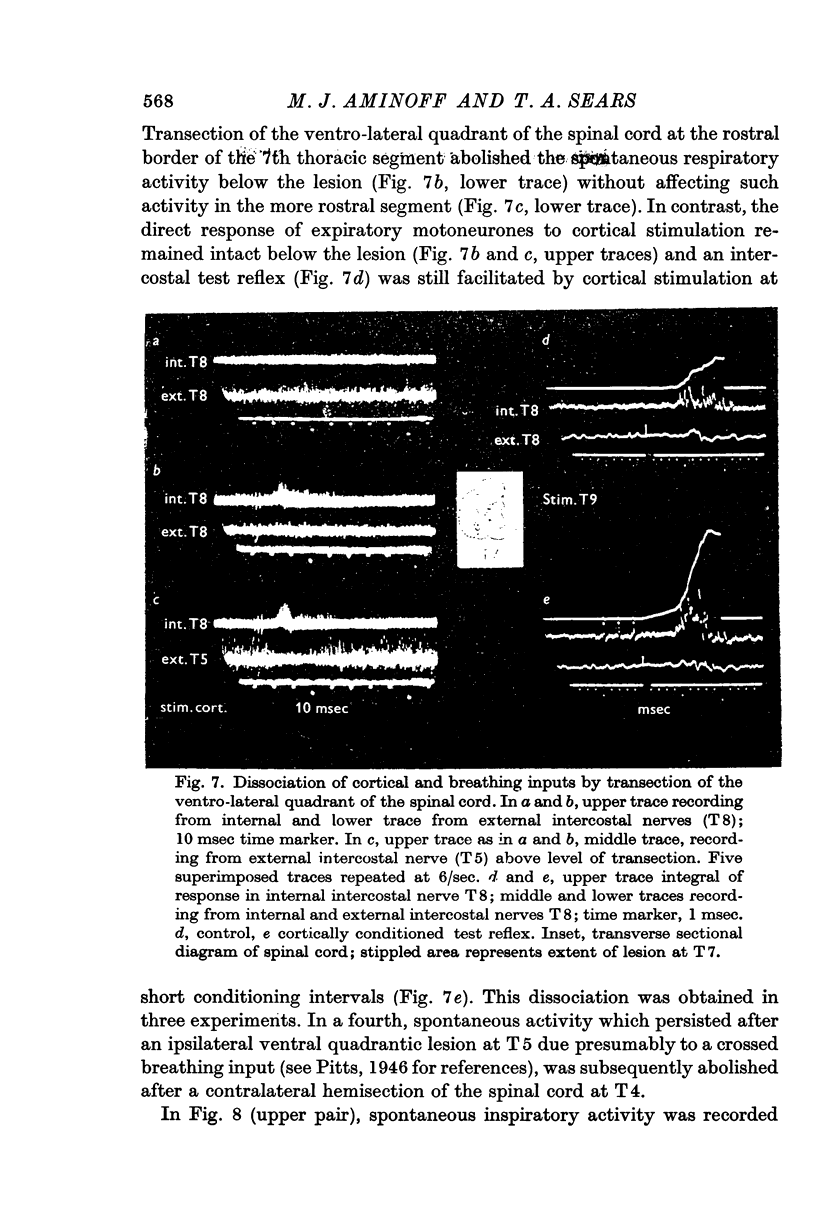
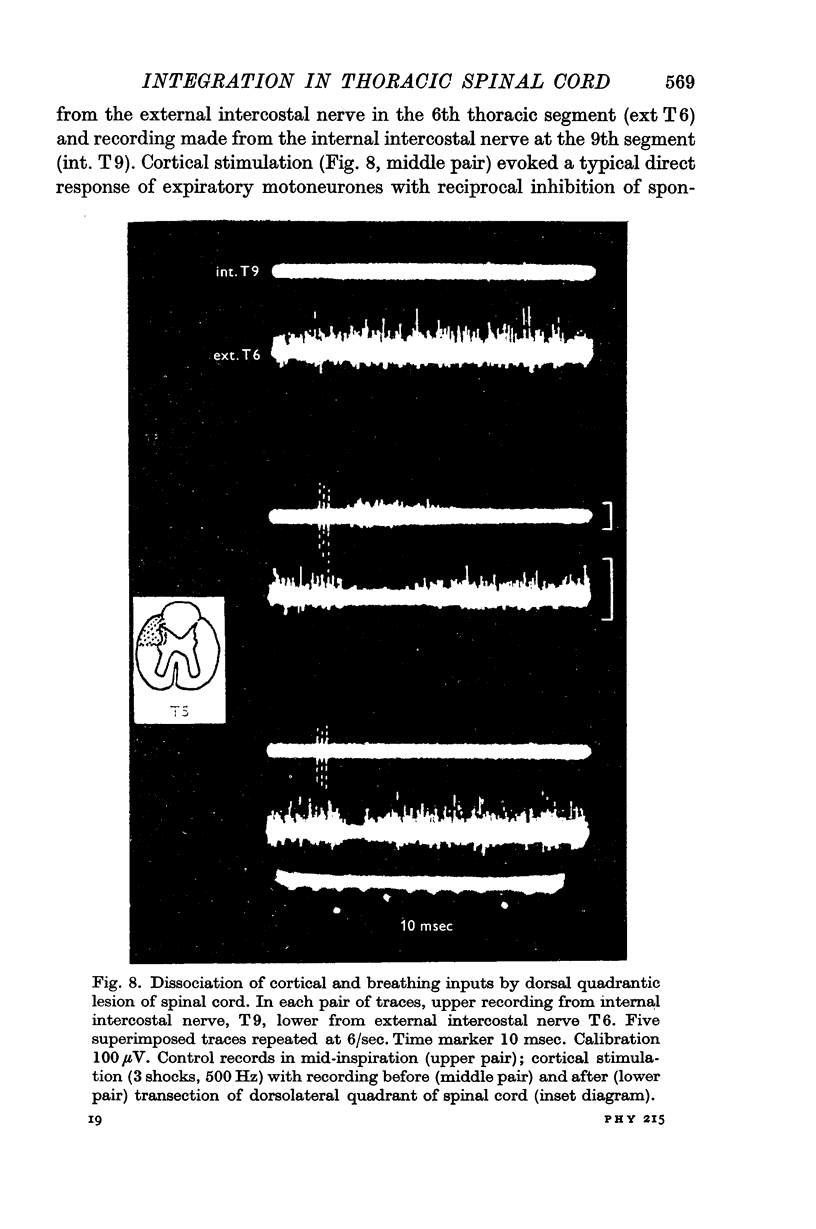
6. It was possible with discrete lesions of the spinal cord to differentiate between the pathways subserving the responses to cortical stimulation and the spontaneous activity due to the breathing input.
7. To account for the results a working hypothesis is proposed utilizing a segmental interneuronal network which transmits mutual reciprocal inhibition between inspiratory and expiratory motoneurones.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P., ECCLES J. C., SEARS T. A. CORTICALLY EVOKED DEPOLARIZATION OF PRIMARY AFFERENT FIBERS IN THE SPINAL CORD. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jan;27:63–77. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Sears T. A. Medullary activation of intercostal fusimotor and alpha motoneurones. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):739–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATFIELD P. O., PURPURA D. P. Factors affecting responses of the inspiratory center to electrical stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1953 Mar;172(3):632–638. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.172.3.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRITCHLOW V., VON EULER INTERCOSTAL MUSCLE SPINDLE ACTIVITY AND ITS GAMMA MOTOR CONTROL. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:820–847. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corda M., von Euler C., Lennerstrand G. Reflex and cerebellar influences on alpha and on 'rhythmic' and 'tonic' gamma activity in the intercostal muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):898–923. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWNMAN C. B., HUSSAIN A. Spinal tracts and supraspinal centres influencing visceromotor and allied reflexes in cats. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):489–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWNMAN C. B. Skeletal muscle reflexes of splanchnic and intercostal nerve origin in acute spinal and decerebrate cats. J Neurophysiol. 1955 May;18(3):217–235. doi: 10.1152/jn.1955.18.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decima E. E., von Euler C., Thoden U. Intercostal-to-phrenic reflexes in the spinal cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Apr;75(4):568–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Integrative pattern of Ia synaptic actions on motoneurones of hip and knee muscles. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 4;144(2):271–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., SEARS T. A., SHEALY C. N. Intra-cellular recording from respiratory motoneurones of the thoracic spinal cord of the cat. Nature. 1962 Mar 3;193:844–846. doi: 10.1038/193844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKLUND G., VON EULER, RUTKOWSKI S. SPONTANEOUS AND REFLEX ACTIVITY OF INTERCOSTAL GAMMA MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1964 May;171:139–163. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S., Hongo T., Lund S. Descending monosynaptic and reflex control of gamma-motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Apr;75(4):592–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S., Hongo T., Lund S. The vestibulospinal tract. Effects on alpha-motoneurones in the lumbosacral spinal cord in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1970;10(1):94–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00340521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERN J. E., LANDGREN S., PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Selective excitation of corticofugal neurones by surface-anodal stimulation of the baboon's motor cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Apr;161:73–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E. Effects from the sensorimotor cortex on the spinal cord in cats with transected pyramids. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(2):117–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00233257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. I. Effects on alpha-motoneurones innervating hindlimb muscles in cats. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(4):344–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00237320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Jukes M. G., Lund S., Lundberg A. The effect of DOPA on the spinal cord. 5. Reciprocal organization of pathways transmitting excitatory action to alpha motoneurones of flexors and extensors. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Jul-Aug;70(3):369–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUGELBERG E., HAGBARTH K. E. Spinal mechanism of the abdominal and erector spinae skin reflexes. Brain. 1958 Sep;81(3):290–304. doi: 10.1093/brain/81.3.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUYPERS H. G. An anatomical analysis of cortico-bulbar connexions to the pons and lower brain stem in the cat. J Anat. 1958 Apr;92(2):198–218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIVINGSTON A., PHILLIPS C. G. Maps and thresholds for the sensorimotor cortex of the cat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1957 Apr;42(2):190–205. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1957.sp001250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., VOORHOEVE P. Effects from the pyramidal tract on spinal reflex arcs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Nov-Dec;56:201–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund S., Pompeiano O. Monosynaptic excitation of alpha motoneurones from supraspinal structures in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 May-Jun;73(1):1–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb04075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSION J., MEULDERS M., COLLE J. [Postural function of the respiratory muscles]. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1960 Mar;68:314–326. doi: 10.3109/13813456009083552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYBERG-HANSEN R., MASCITTI T. A. SITES AND MODE OF TERMINATION OF FIBERS OF THE VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACT IN THE CAT. AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY WITH SILVER IMPREGNATION METHODS. J Comp Neurol. 1964 Jun;122:369–383. doi: 10.1002/cne.901220307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI G. F., BRODAL A. Corticofugal fibres to the brain-stem reticular formation; an experimental study in the cat. J Anat. 1956 Jan;90(1):42–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. Activity of fusimotor fibres innervating muscle spindles in the intercostal muscles of the cat. Nature. 1963 Mar 9;197:1013–1014. doi: 10.1038/1971013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. EFFERENT DISCHARGES IN ALPHA AND FUSIMOTOR FIBRES OF INTERCOSTAL NERVES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:295–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. SOME PROPERTIES AND REFLEX CONNEXIONS OF RESPIRATORY MOTONEURONES OF THE CAT'S THORACIC SPINAL CORD. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. THE FIBRE CALIBRE SPECTRA OF SENSORY AND MOTOR FIBRES IN THE INTERCOSTAL NERVES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1964 Jul;172:150–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. THE SLOW POTENTIALS OF THORACIC RESPIRATORY MOTONEURONES AND THEIR RELATION TO BREATHING. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:404–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMI T. Organization of spinal respiratory neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Jun 24;109:561–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


