Abstract
1. Interneurones monosynaptically excited from large muscle spindle (Ia) afferents and inhibited from motor axon collaterals were searched for in the lumbar spinal cord of the cat.
2. Monosynaptic Ia excitation was found in sixty-seven of sixty-nine interneurones inhibited by antidromic volleys. These interneurones were excited from Ia afferents from one or a few muscles (mainly close synergists). Volleys in high threshold muscle and skin afferents (FRA) evoked polysynaptic excitation or inhibition. Weak inhibition from Ia afferents (from antagonists to those giving Ia excitation) was seen in a few cells. Monosynaptic excitation was evoked from the ventral quadrant of the spinal cord and polysynaptic excitation from the dorsal quadrant.
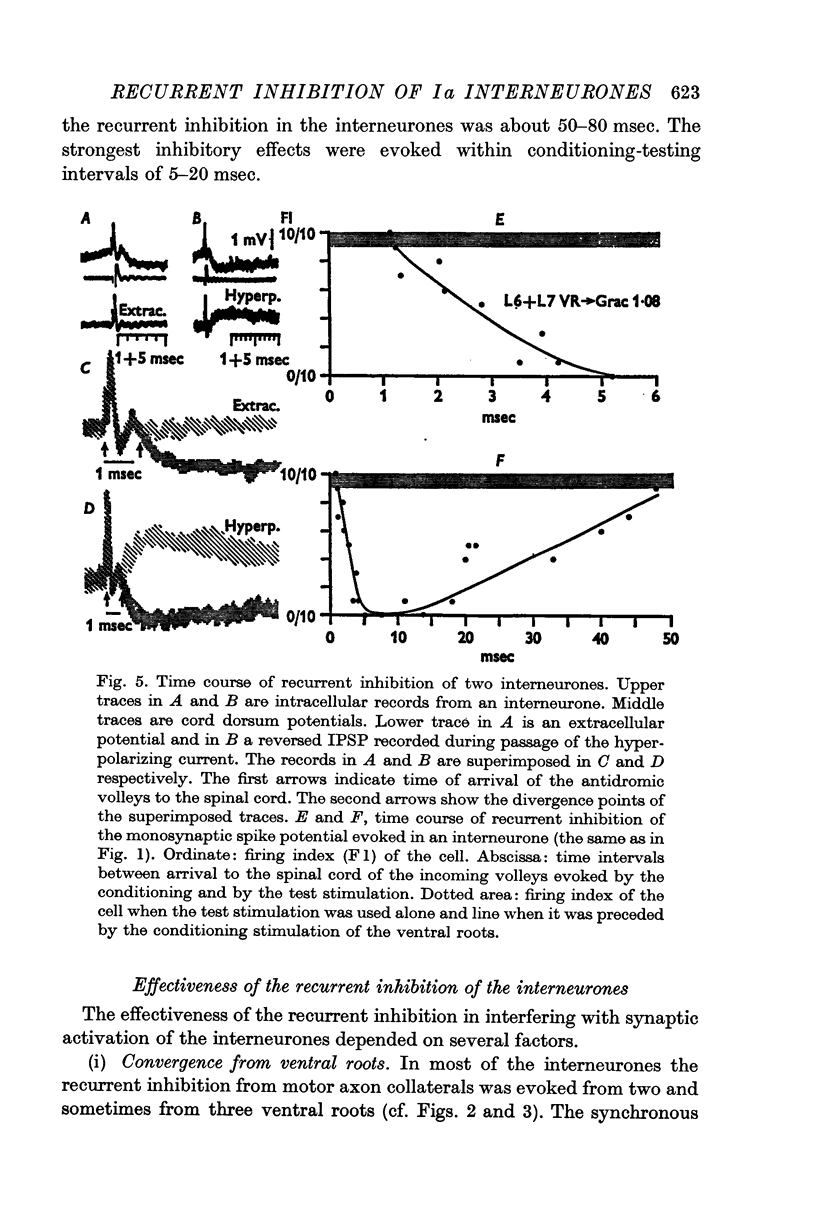
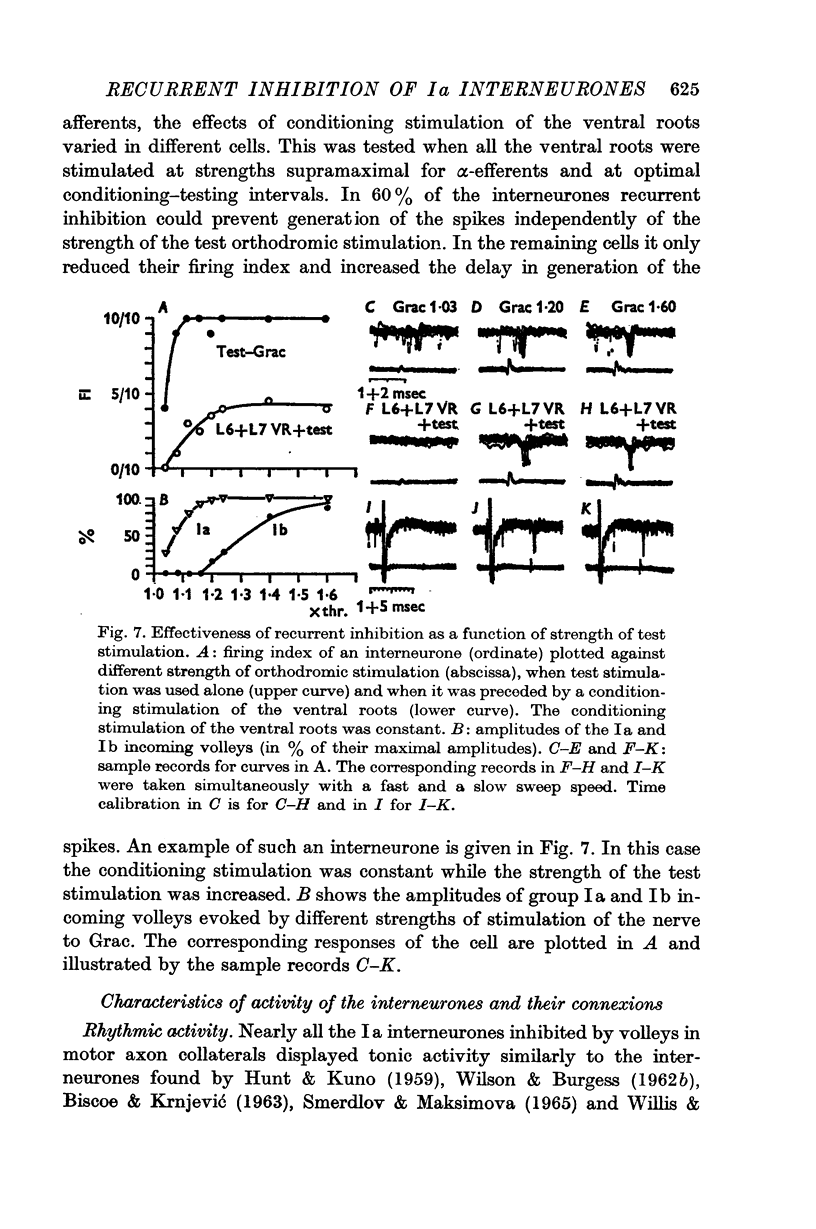
3. Inhibition from motor axon collaterals was evoked with a latency (1·2-2·0 msec) suggesting a disynaptic linkage and had the same time course as in motoneurones. It prevented synaptic activation of 60% of interneurones and decreased the firing index and delayed generation of spikes in the remaining.
4. The interneurones with convergence of monosynaptic Ia excitation and inhibition from motor axon collaterals were found in the ventral horn dorsomedial to motor nuclei. No inhibition by antidromic volleys could be detected in interneurones located in intermediate nucleus and activated monosynaptically from Ia, Ib, group I or cutaneous afferents.
5. It was concluded that the ventral Ia interneurones inhibited by volleys in recurrent motor axon collaterals mediate the reciprocal Ia inhibition to motoneurones.
Full text
PDF





















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., EOCLES J. C., ITO M. Correlation of the inhibitory post-synaptic potential of motoneurones with the latency and time course of inhibition of monosynaptic reflexes. J Physiol. 1960 Dec;154:354–377. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andén N. E., Jukes M. G., Lundberg A., Vyklický L. The effect of DOPA on the spinal cord. 1. Influence on transmission from primary afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jul-Aug;67(3):373–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY K., EASTON D. M., ECCLES J. C. An investigation of primary or direct inhibition. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):474–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY K., ECCLES J. C. Analysis of the fast afferent impulses from thigh muscles. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):462–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK L. G., COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C. Intracellular recording from antidromically activated motoneurones. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):429–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones in relation to the two components of the group I muscle afferent volley. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):527–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Types of neurone in and around the intermediate nucleus of the lumbosacral cord. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:89–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., KOKETSU K. Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):524–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., LANDGREN S. Central pathway for direct inhibitory action of impulses in largest afferent nerve fibres to muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Jan;19(1):75–98. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., LANDGREN S., WINSBURY G. J. Spinal cord potentials generated by volleys in the large muscle afferents. J Physiol. 1954 Sep 28;125(3):590–606. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., RALL W. Repetitive monosynaptic activation of motoneurones. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1951 Oct 30;138(893):475–498. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1951.0036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Integrative pattern of Ia synaptic actions on motoneurones of hip and knee muscles. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 4;144(2):271–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The synaptic linkage of direct inhibition. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 8;43(3-4):204–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIDE E., LUNDBERG A., VOORHOEVE P. Monosynaptically evoked inhibitory post-synaptic potentials in motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Oct;53:185–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Unitary activity of spinal interneurones of cats. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):424–435. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S., Hongo T., Lund S. Reciprocal effects between two descending bulbospinal systems with monosynaptic connections to spinal motoneurones. Brain Res. 1968 Sep;10(3):477–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90221-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., KUNO M. Background discharge and evoked responses of spinal interneurones. J Physiol. 1959 Sep 2;147:364–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. Convergence of excitatory and inhibitory action on interneurones in the lumbosacral cord. Exp Brain Res. 1966;1(4):338–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00237706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. Effects evoked from the rubrospinal tract in cats. Experientia. 1965 Sep 15;21(9):525–526. doi: 10.1007/BF02138973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. II. Facilitation of interneuronal transmission in reflex paths to motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(4):365–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00237321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Recurrent inhibition from motor axon collaterals of transmission in the Ia inhibitory pathway to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):591–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Recurrent inhibition from motor axon collatersls in interneurones monosynaptically activated rom la afferents. Brain Res. 1968 Jul;9(2):367–369. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Relative contribution from different nerves to recurrent depression of Ia IPSPs in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):637–664. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOIZUMI K., USHIYAMA J., BROOKS C. M. A study of reticular formation action on spinal interneurons and motoneurons. Jpn J Physiol. 1959 Sep 15;9:282–303. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.9.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLMODIN G. M. Integrative processes in single spinal interneurones with proprioceptive connections. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1957;40(139):1–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Pilyavsky A. I. A possible direct intereuronal pathway from rubrospinal tract to motoneurones. Brain Res. 1969 Jul;14(2):526–529. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., NORRSELL U., VOORHOEVE P. Pyramidal effects on lumbo-sacral interneurones activated by somatic afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Nov-Dec;56:220–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., VOORHOEVE P. Effects from the pyramidal tract on spinal reflex arcs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Nov-Dec;56:201–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYBERG-HANSEN R., MASCITTI T. A. SITES AND MODE OF TERMINATION OF FIBERS OF THE VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACT IN THE CAT. AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY WITH SILVER IMPREGNATION METHODS. J Comp Neurol. 1964 Jun;122:369–383. doi: 10.1002/cne.901220307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REXED B. A cytoarchitectonic atlas of the spinal cord in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Apr;100(2):297–379. doi: 10.1002/cne.901000205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryall R. W. Renshaw cell mediated inhibition of Renshaw cells: patterns of excitation and inhibition from impulses in motor axon collaterals. J Neurophysiol. 1970 Mar;33(2):257–270. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner R. D., Willis W. D., Hancock M. B. Actions of ventral cord pathways on spinal neurons. Exp Neurol. 1970 May;27(2):318–333. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(70)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smerdlov S. M., Maksimova E. V. Effects of antidromic impulses on spontaneous activity of interneurons in the cat spinal cord. Fed Proc Transl Suppl. 1966 May-Jun;25(3):419–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton A. O., Kravitz E. A. Neuronal geometry: determination with a technique of intracellular dye injection. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):132–134. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C., Wilson V. J. Precise localization of Renshaw cells with a new marking technique. Nature. 1965 Apr 10;206(980):211–213. doi: 10.1038/206211b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. J., BURGESS P. R. Disinhibition in the cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1962 May;25:392–404. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.3.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. J., BURGESS P. R. Effects of antidromic conditioning on some motoneurons and interneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Sep;25:636–650. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.5.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. J. Recurrent facilitation of spinal reflexes. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Mar 20;42(4):703–713. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Bruggencate G., Burke R., Lundberg A., Udo M. Interaction between the vestibulospinal tract, contralateral flexor reflex afferents and la afferents. Brain Res. 1969 Jul;14(2):529–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


