Abstract
1. The interaction between Ca and Sr ions on quantal transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction was studied, using conventional electrophysiological techniques.
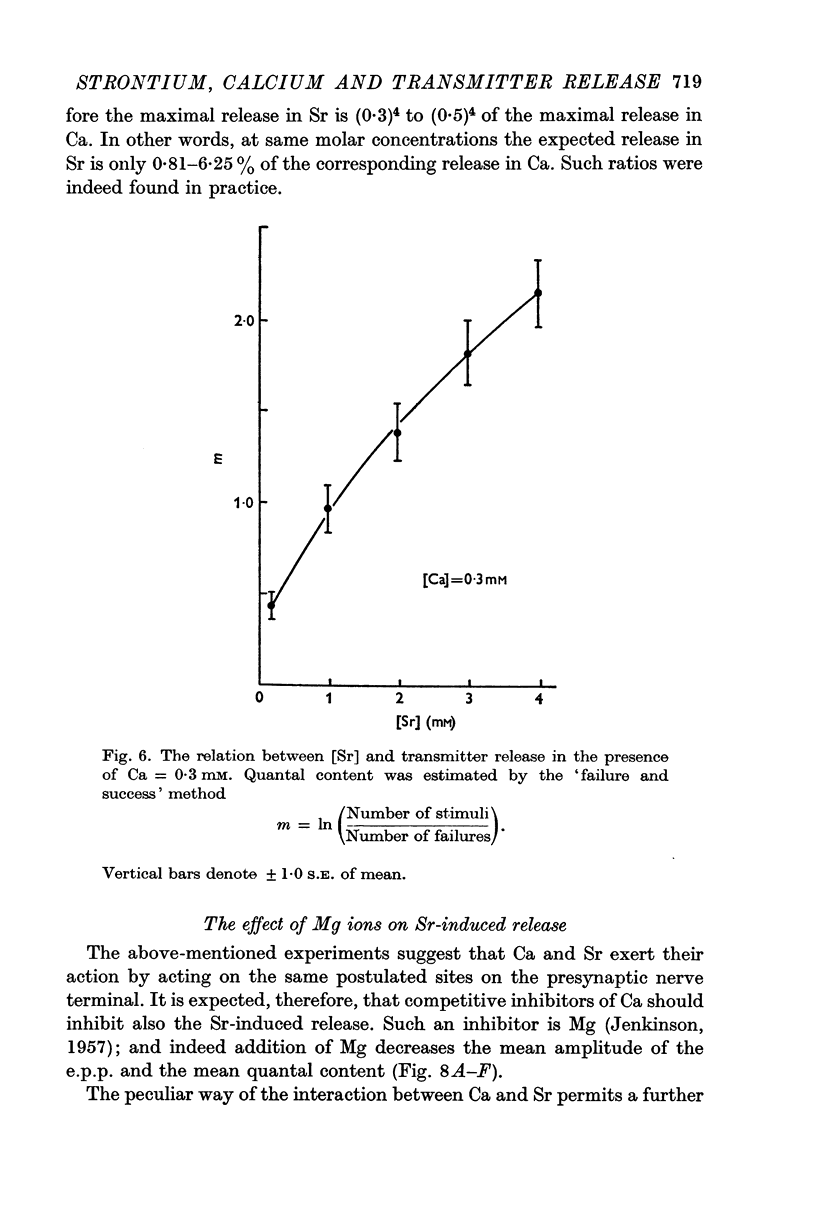
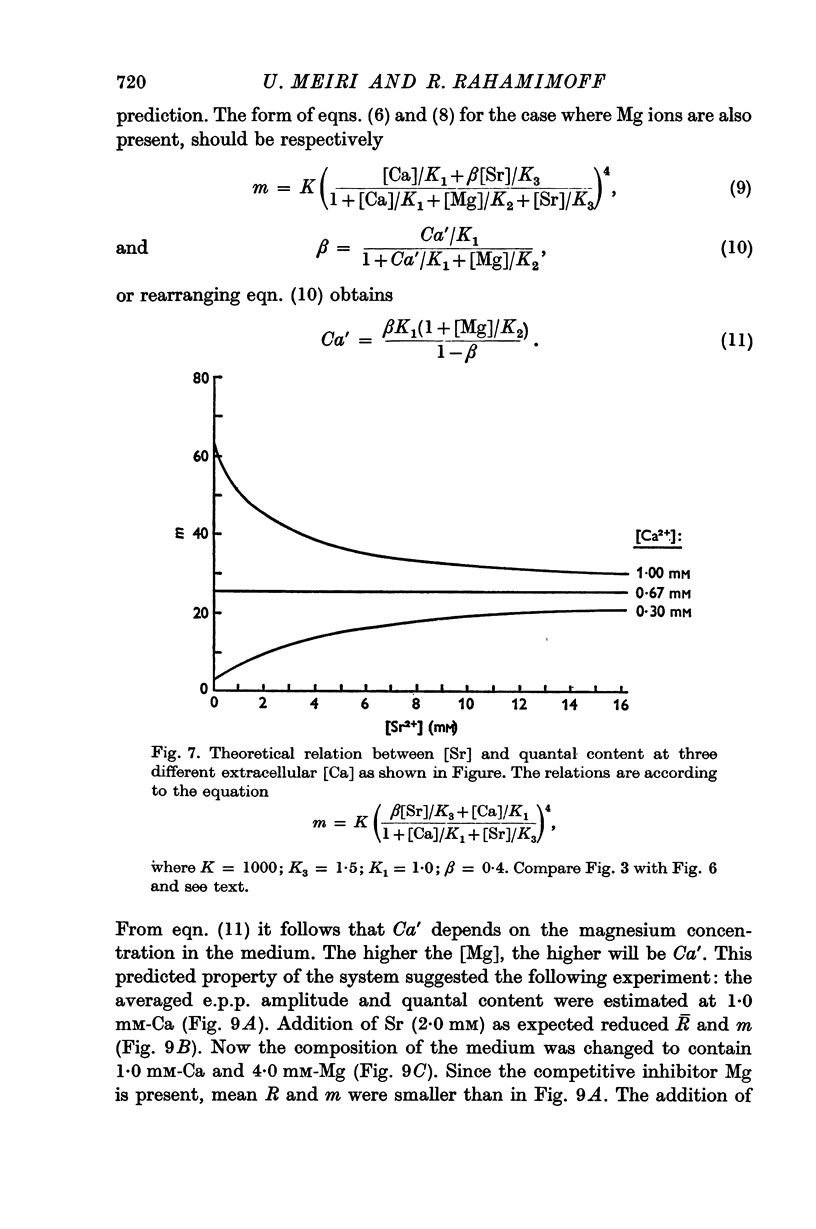
2. While Ca ions always activate transmitter release, the activating action of Sr ions depends on the Ca ion concentration in the medium; at low [Ca], strontium ions enhance the release, but at higher [Ca] they inhibit it. It is postulated that there is a [Ca] at which Sr ions do not affect transmitter liberation.
3. When Sr activates release, its effect and the effect of Ca add in a more than linear fashion.
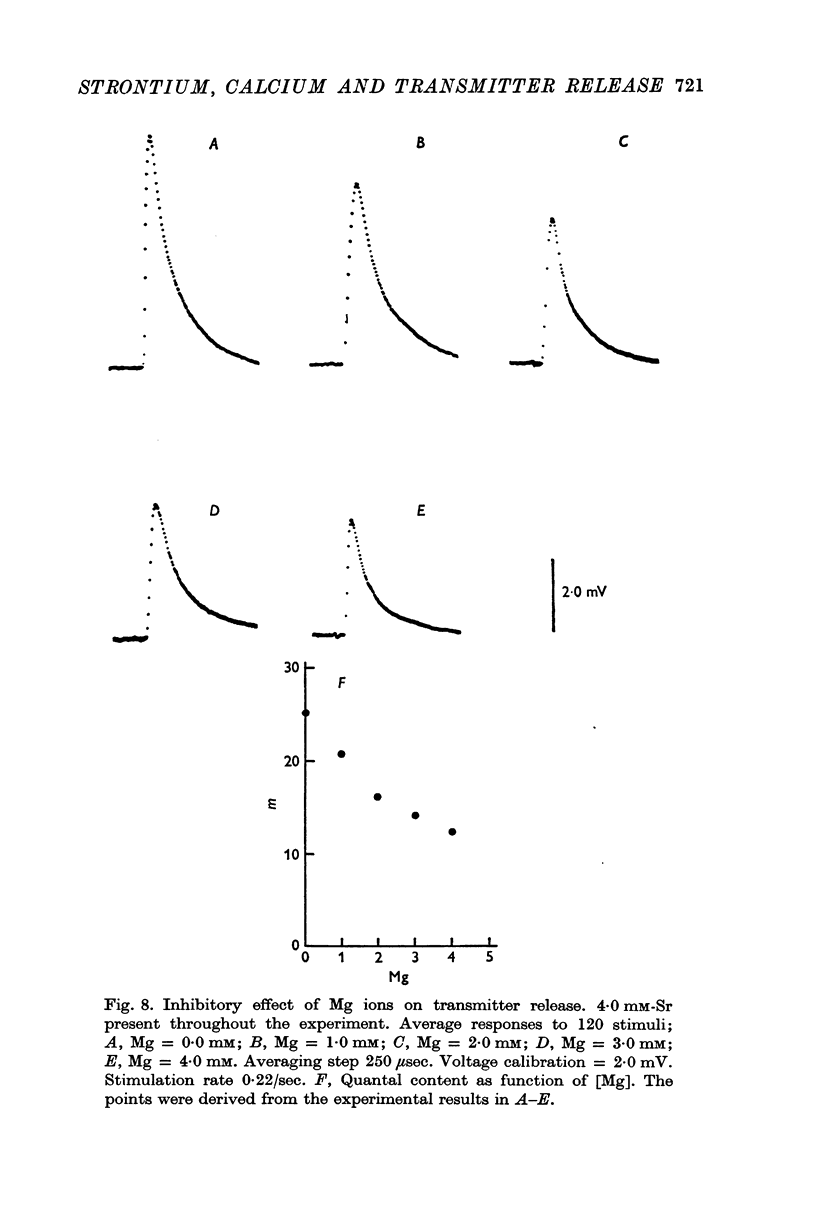
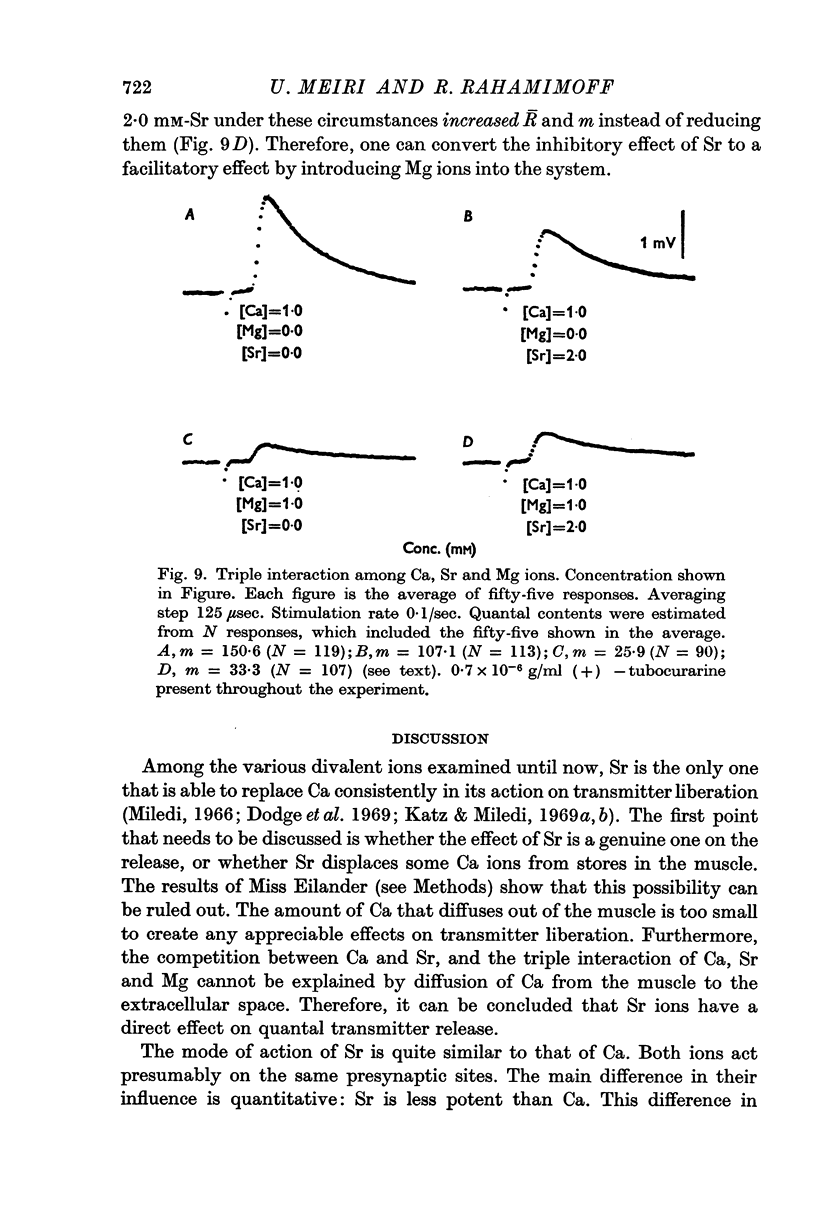
4. Magnesium ions inhibit the release induced by Sr.
5. The results can be explained by assuming that Ca and Sr act on the same site, at some stage of the process of quantal transmitter release. The affinity of both ions towards the sites is approximately the same, but the effectiveness of Sr is much smaller.
Full text
PDF




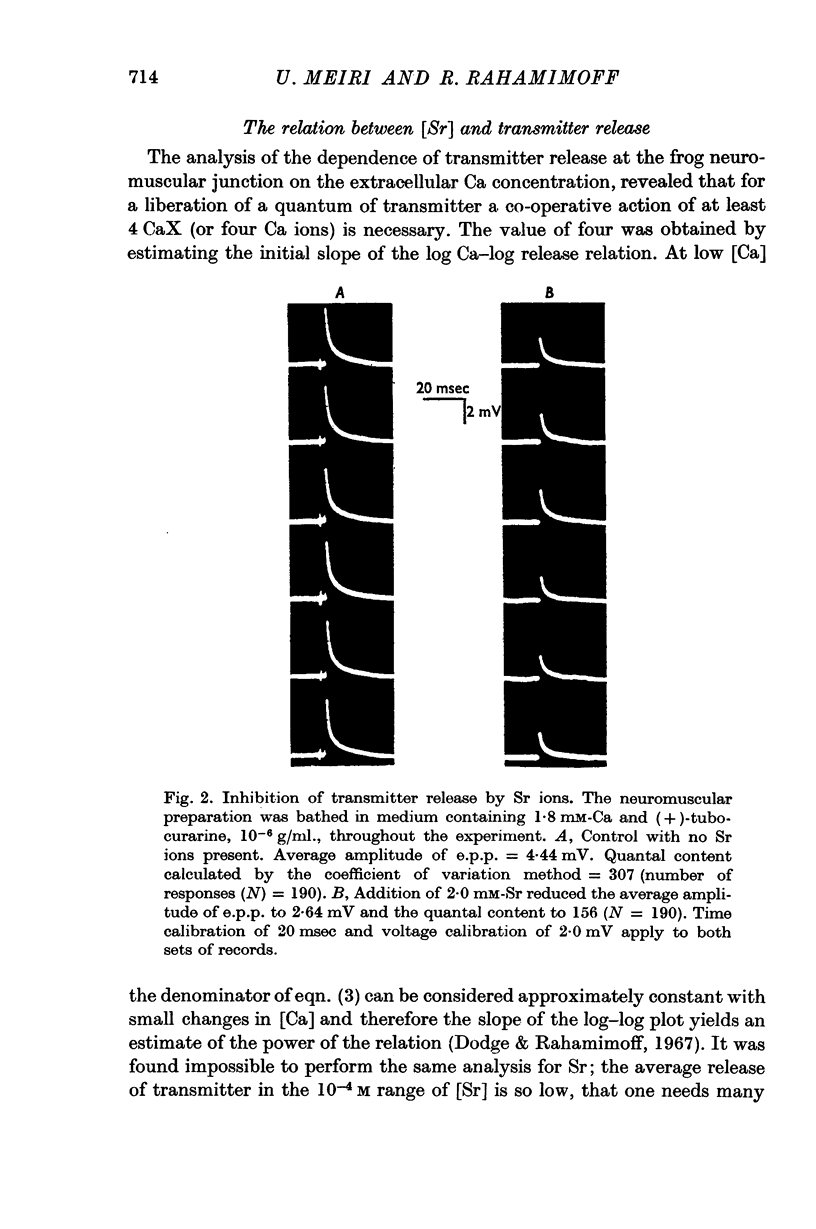
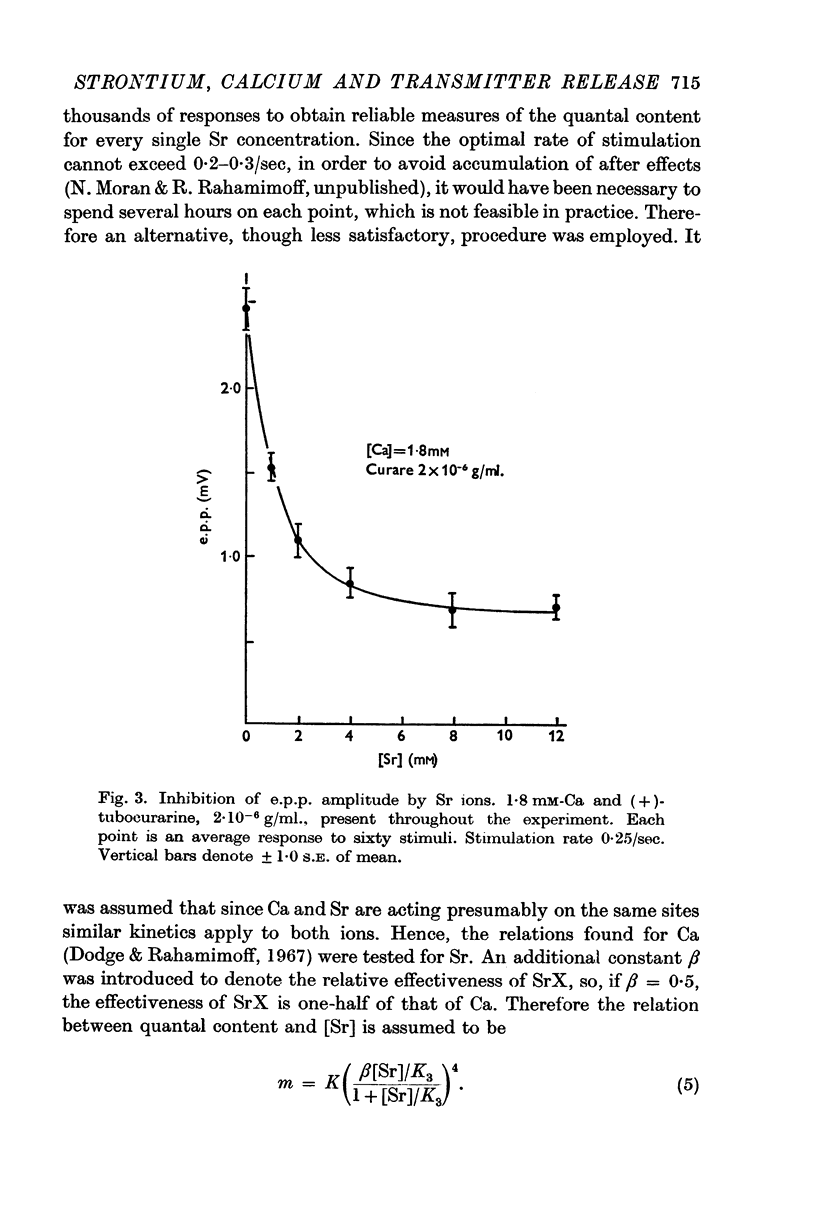

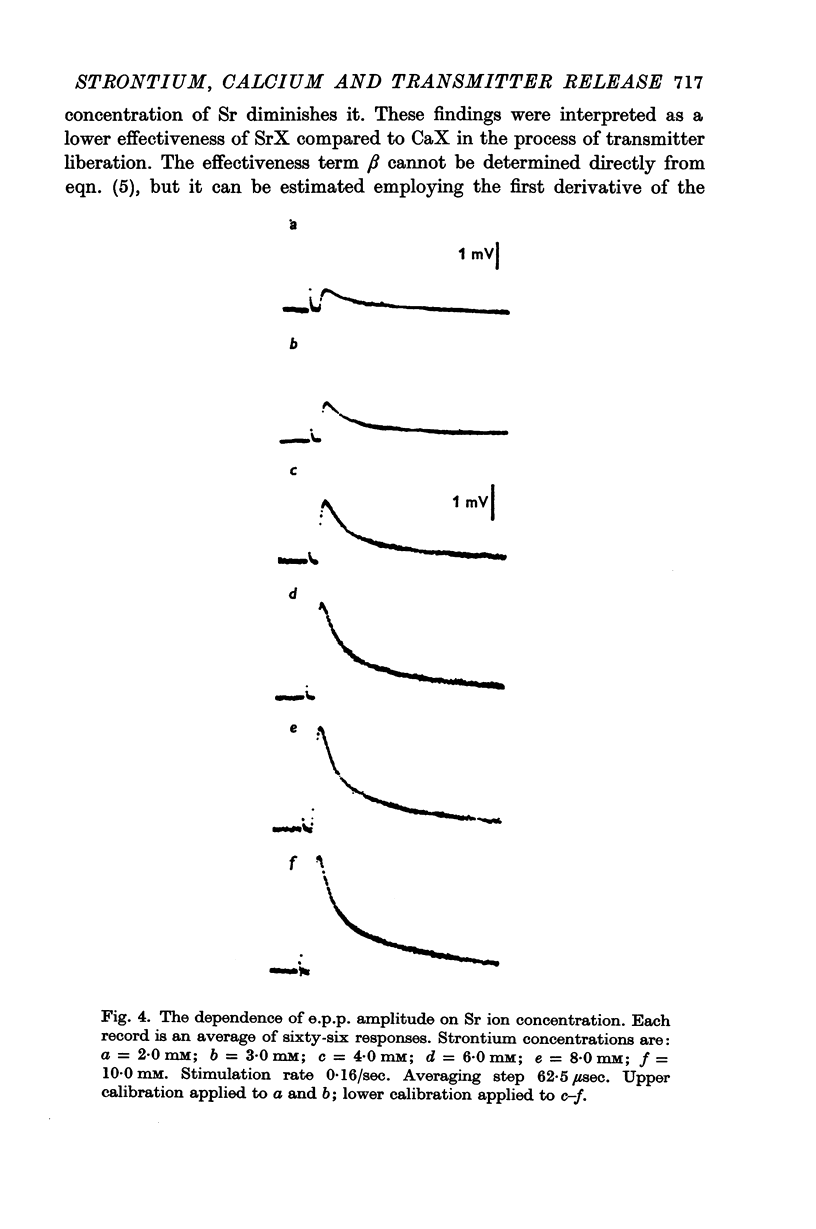
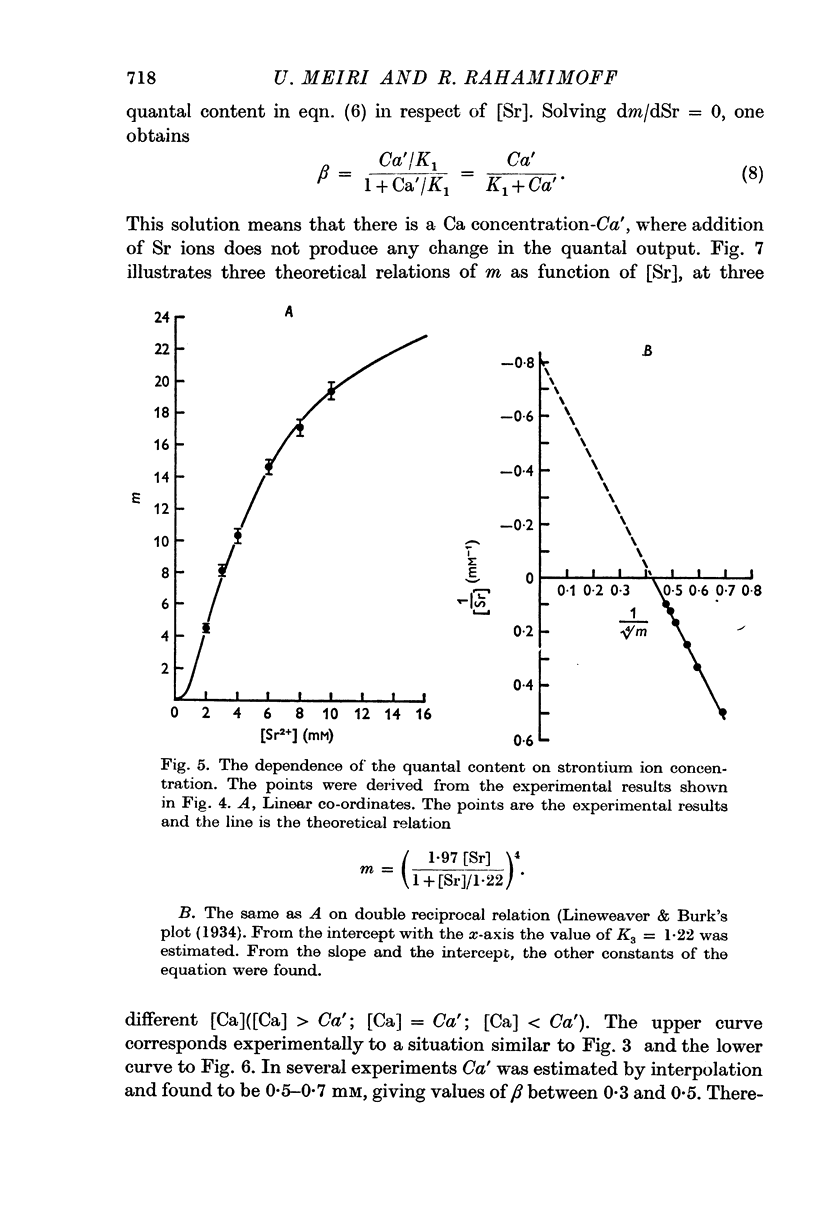



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colomo F., Rahamimoff R. Interaction between sodium and calcium ions in the process of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1968 Sep;198(1):203–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., ENGBAEK L. The nature of the neuromuscular block produced by magnesium. J Physiol. 1954 May 28;124(2):370–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. The effect of magnesium on the activity of motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):553–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Miledi R., Rahamimoff R. Strontium and quantal release of transmitter at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):267–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. The effect of calcium on the myelinated nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):245–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):434–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE EFFECT OF CALCIUM ON ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:496–503. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLY J. S. ANTAGONISM BETWEEN NA+ AND CA2+ AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. Nature. 1965 Jan 16;205:296–297. doi: 10.1038/205296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):23–38. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mines G. R. On the replacement of calcium in certain neuro-muscular mechanisms by allied substances. J Physiol. 1911 Mar 29;42(3):251–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1911.sp001433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran N., Rahamimoff R. Some statistical properties of neuromuscular facilitation. Isr J Med Sci. 1970 Mar-Apr;6(2):201–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastuk W. L., Liu J. H. Muscle postjunctional membrane: changes in chemosensitivity produced by calcium. Science. 1966 Oct 14;154(3746):266–267. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3746.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R., Colomo F. Inhibitory action of sodium ions on transmitter release at the motor end-plate. Nature. 1967 Sep 9;215(5106):1174–1176. doi: 10.1038/2151174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


