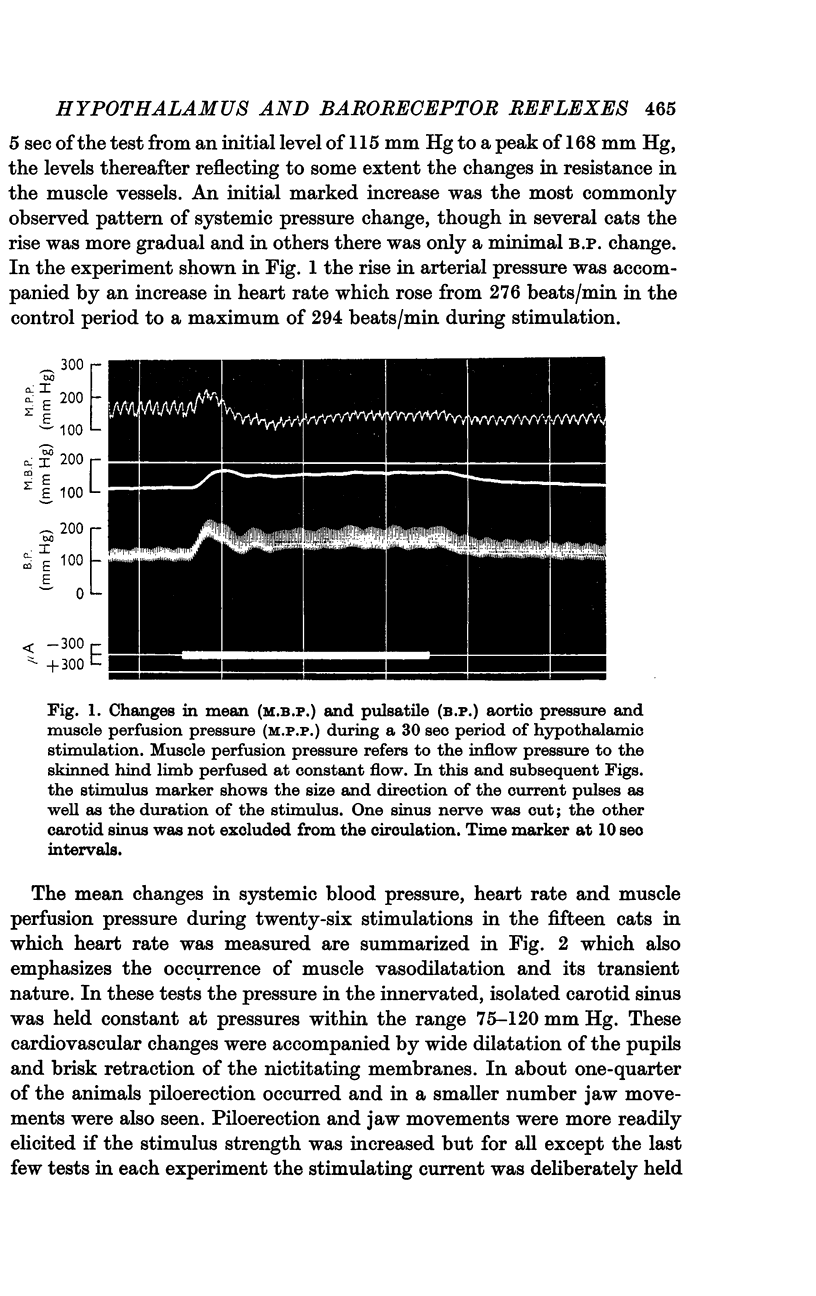
Abstract
1. The effects of stimulation of the hypothalamic defence area on carotid sinus baroreceptor reflexes have been investigated by examining the cardiovascular responses to a 15 sec period of increased pressure within the vascularly isolated carotid sinus before, during, and immediately following a 25 sec period of hypothalamic stimulation.
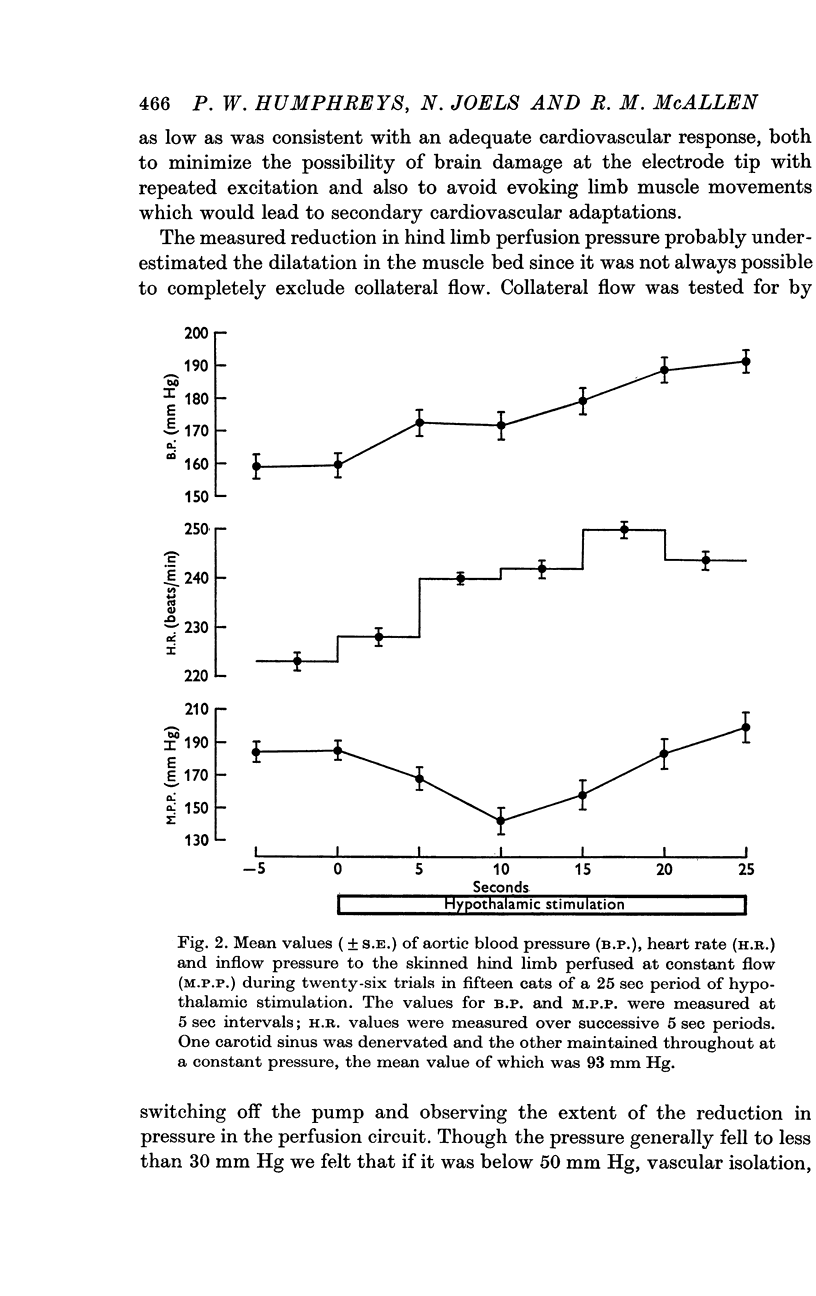
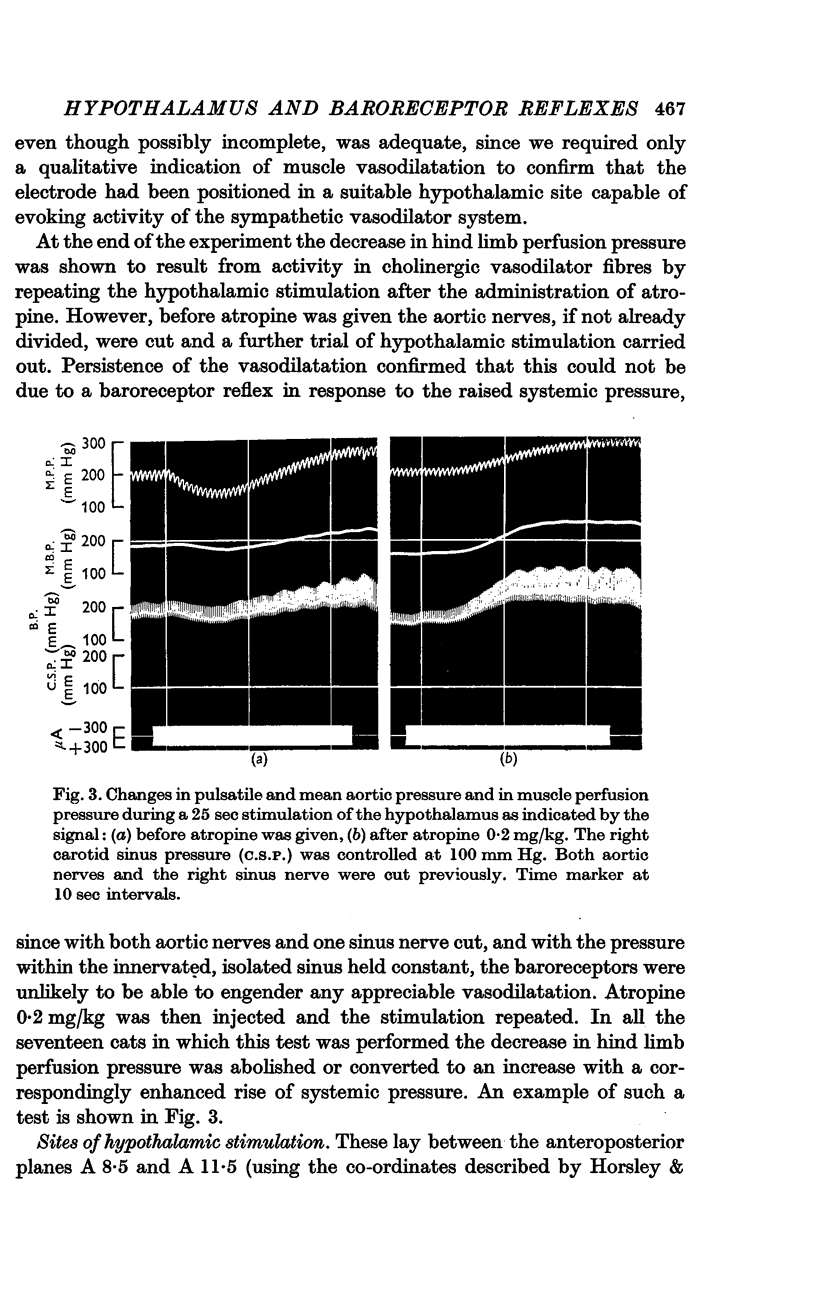
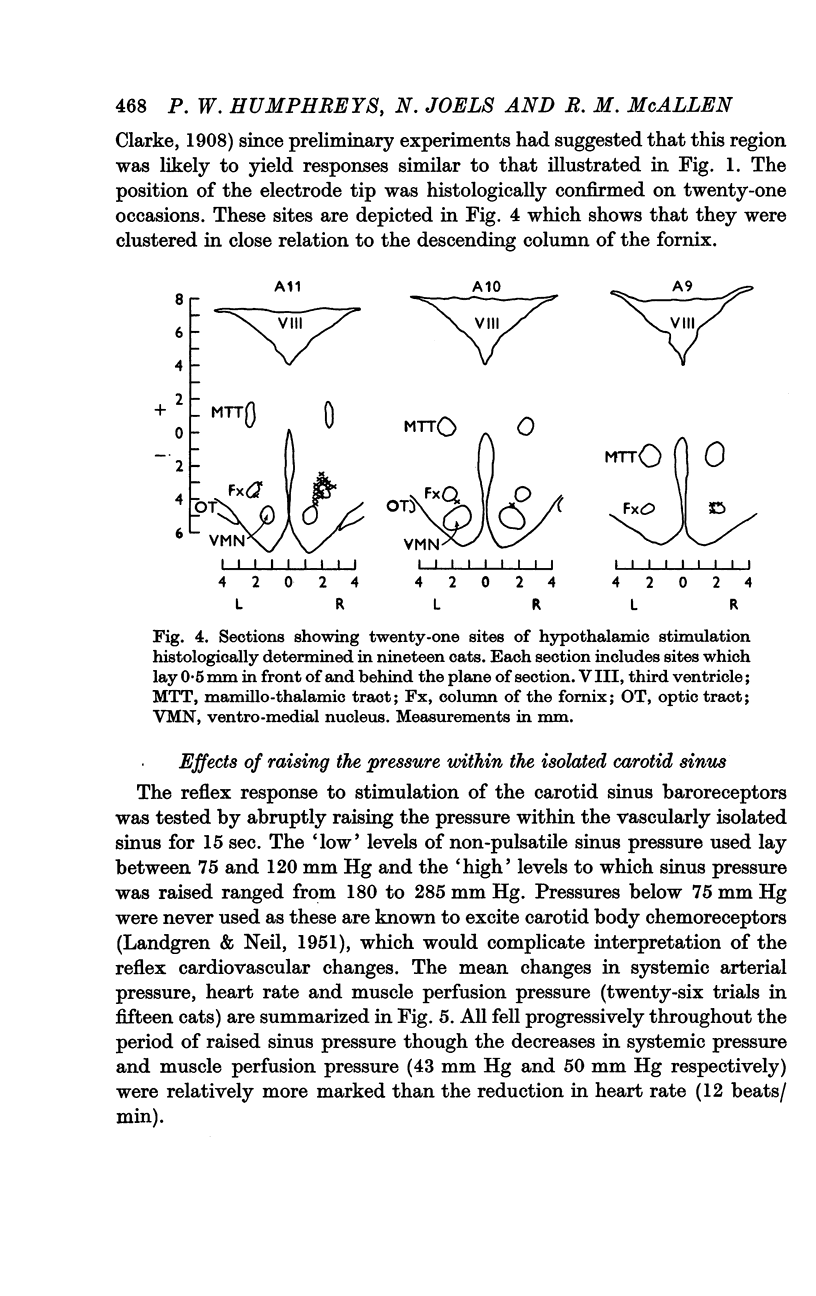
2. Identification of the hypothalamic defence area was based on the occurence of atropine-sensitive muscle vasodilatation. Electrode positions were confirmed by histological examination.
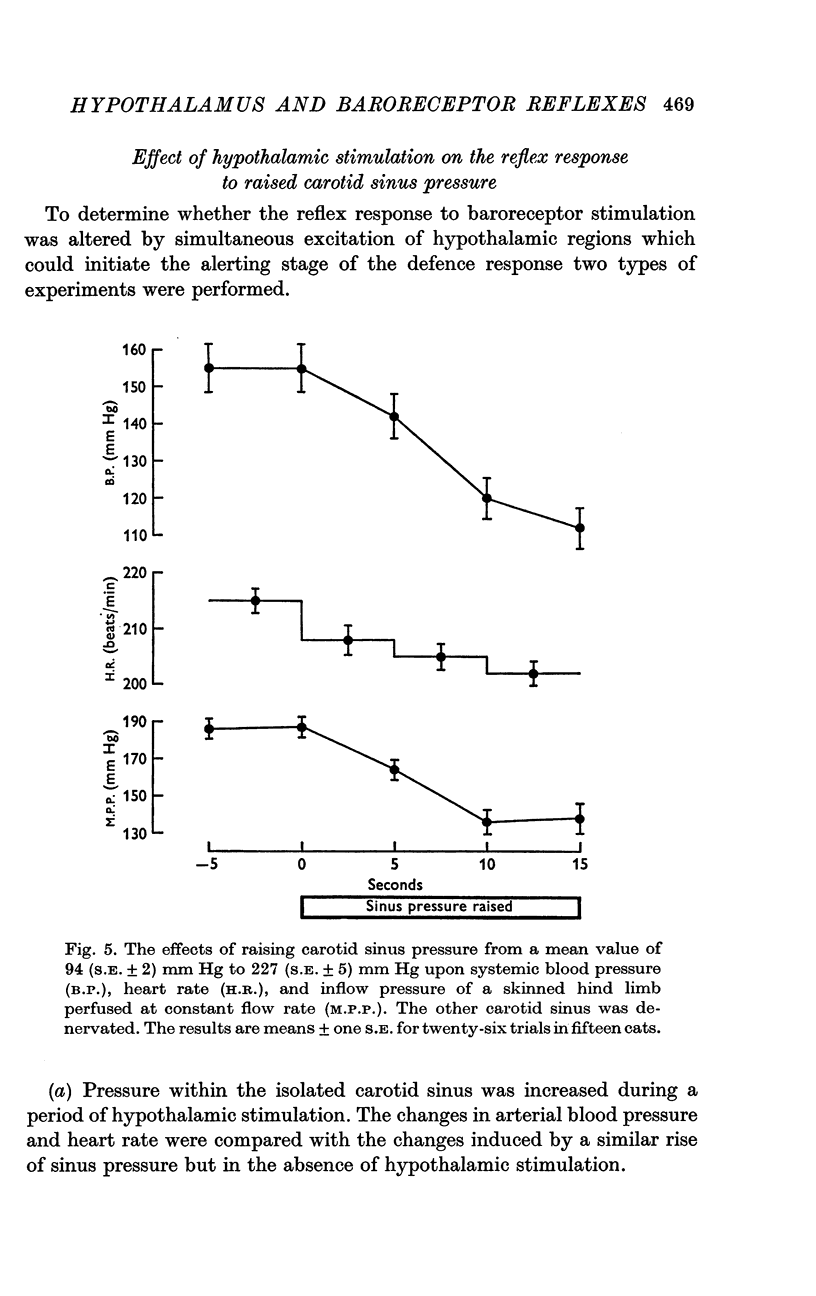
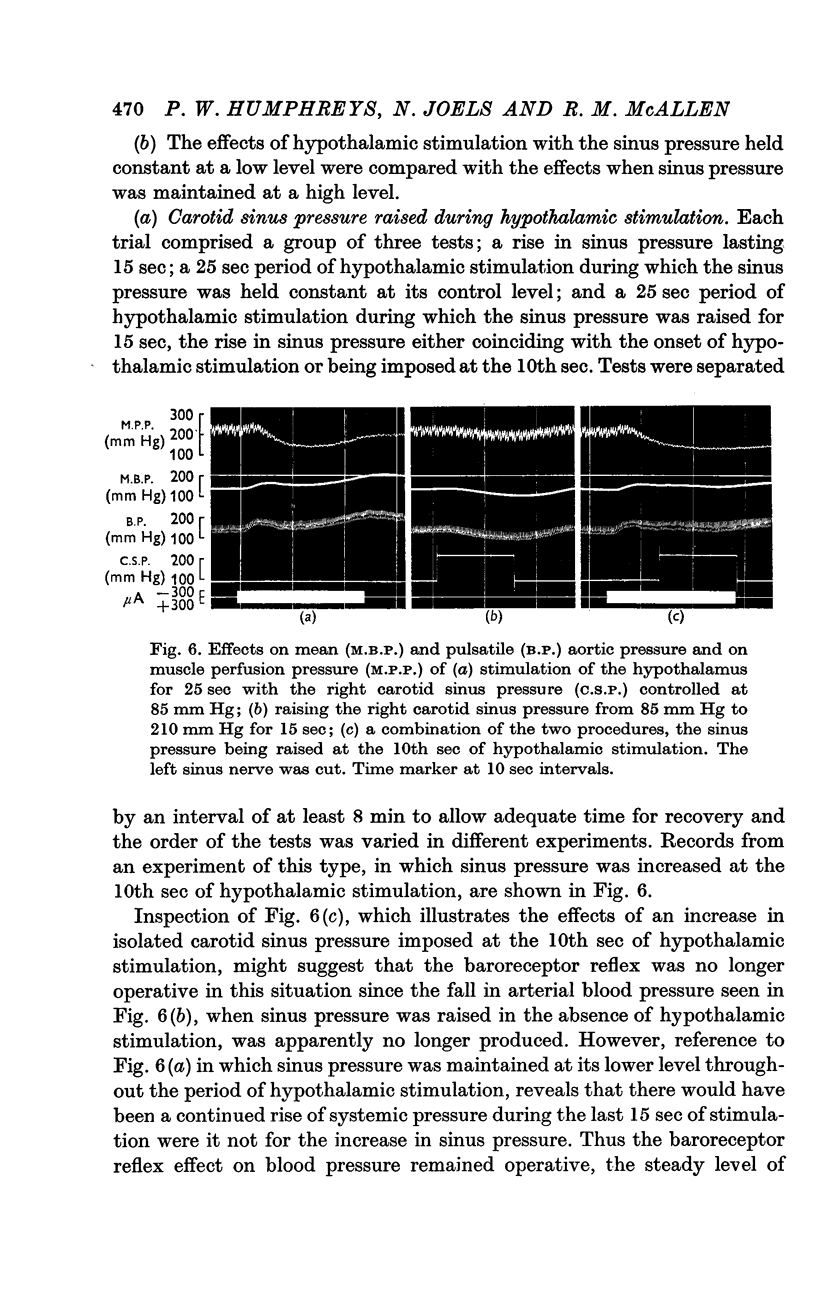
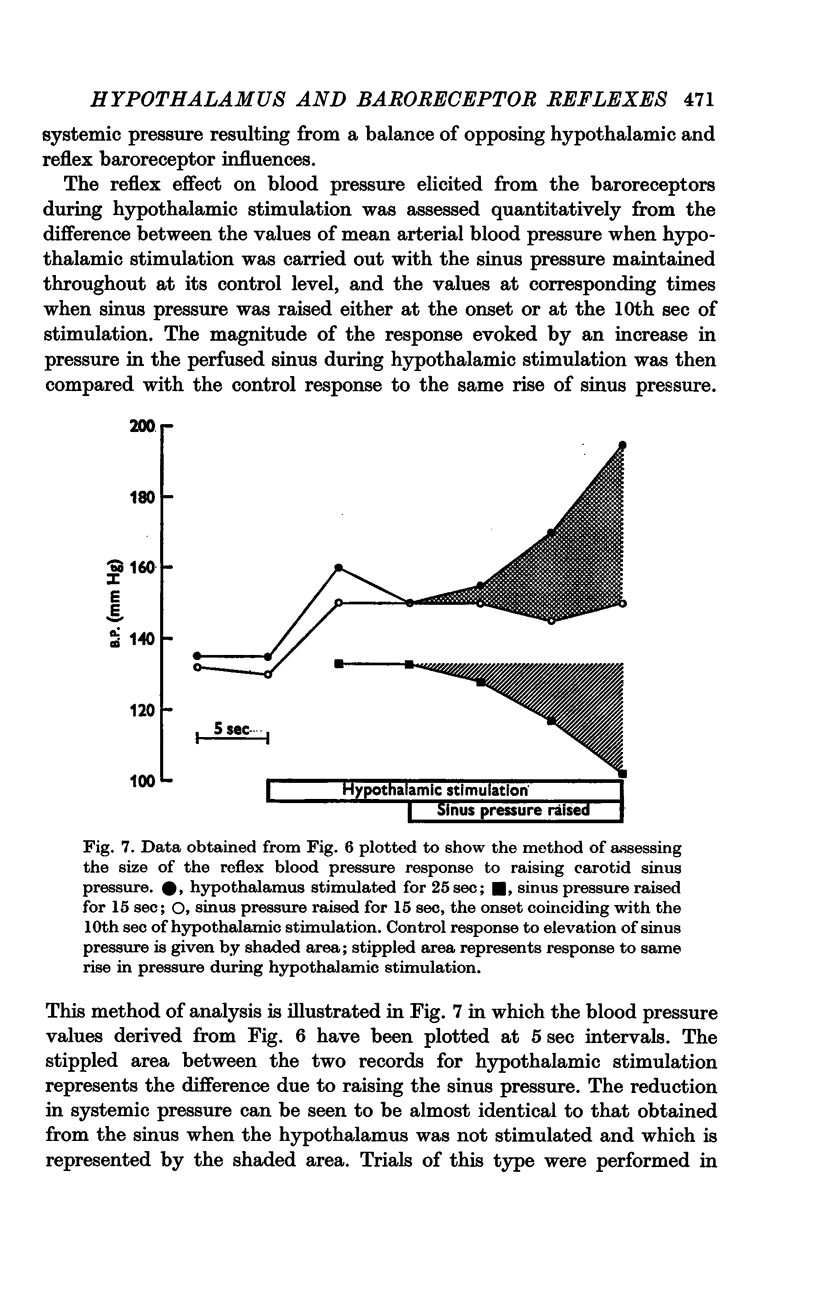
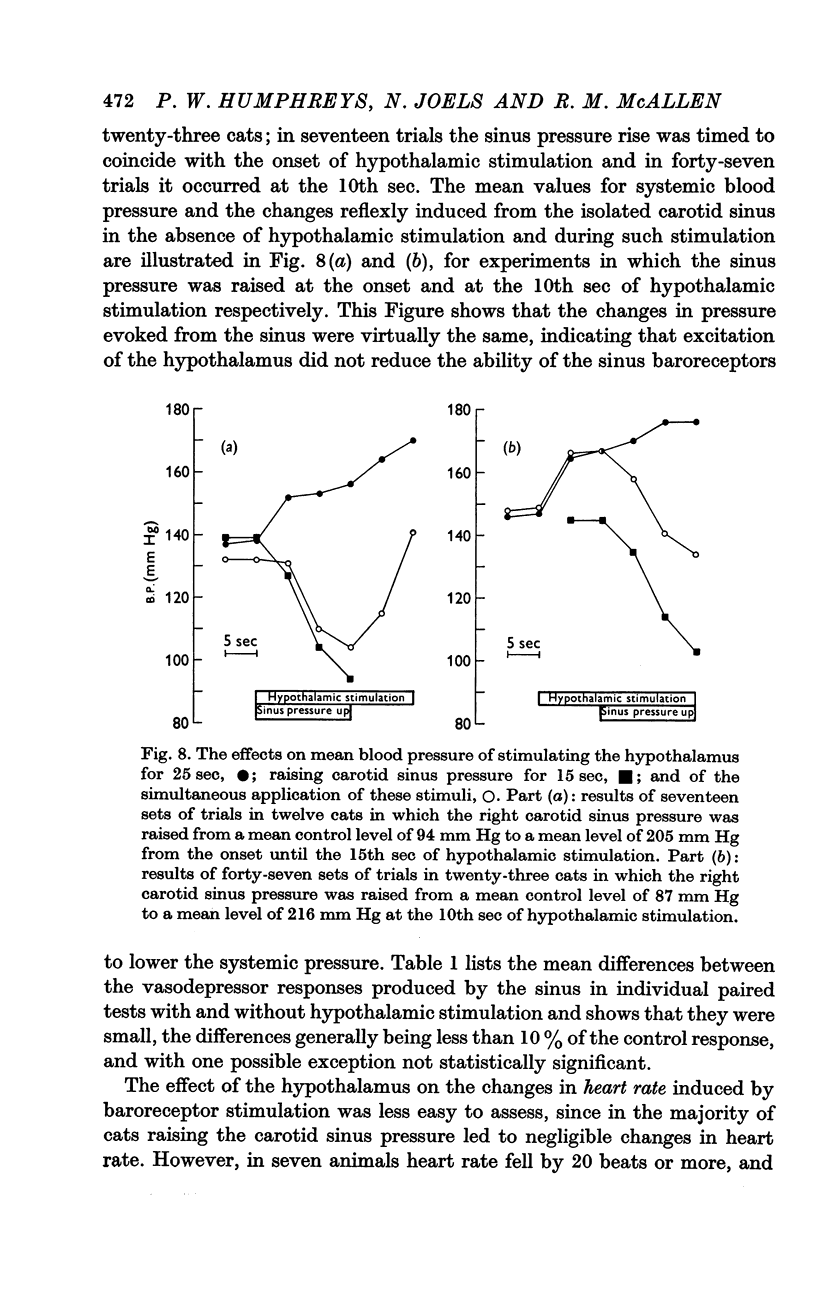
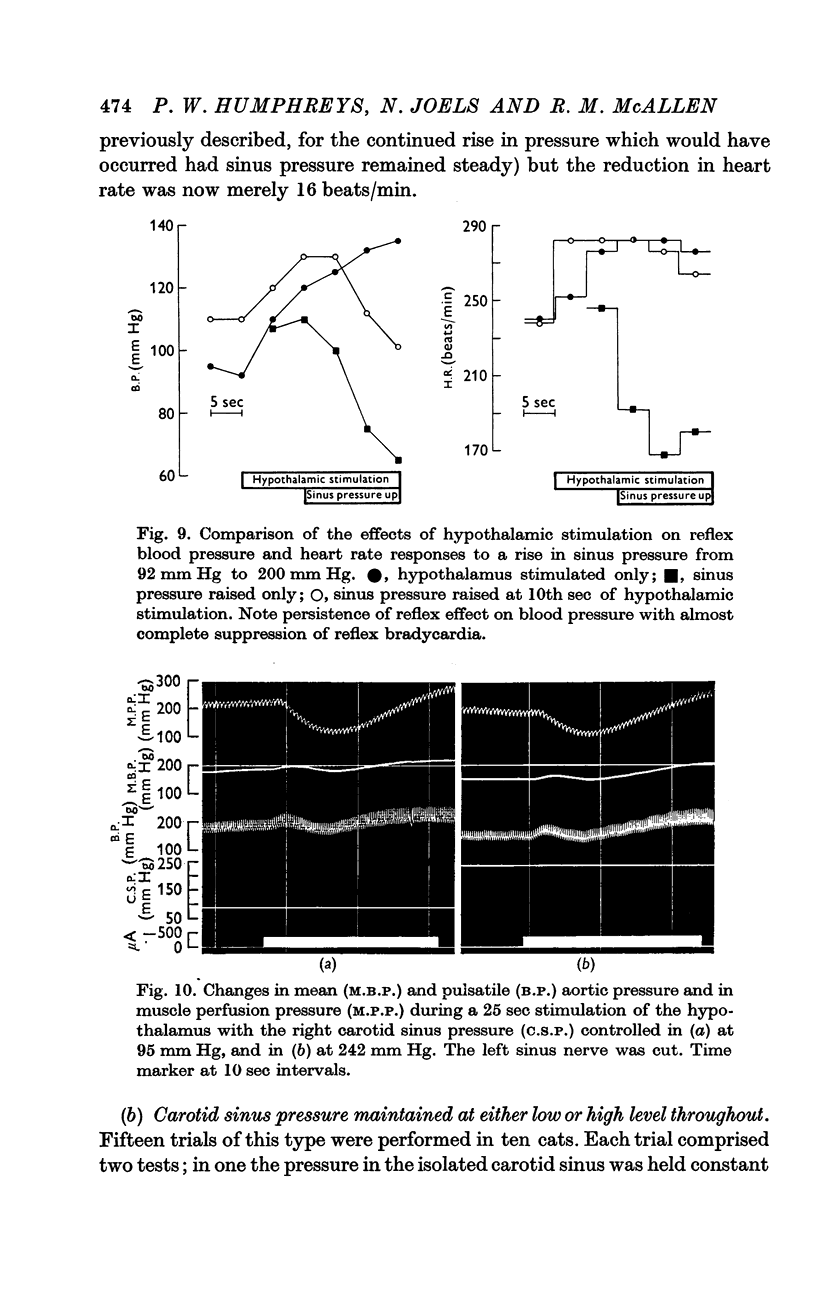
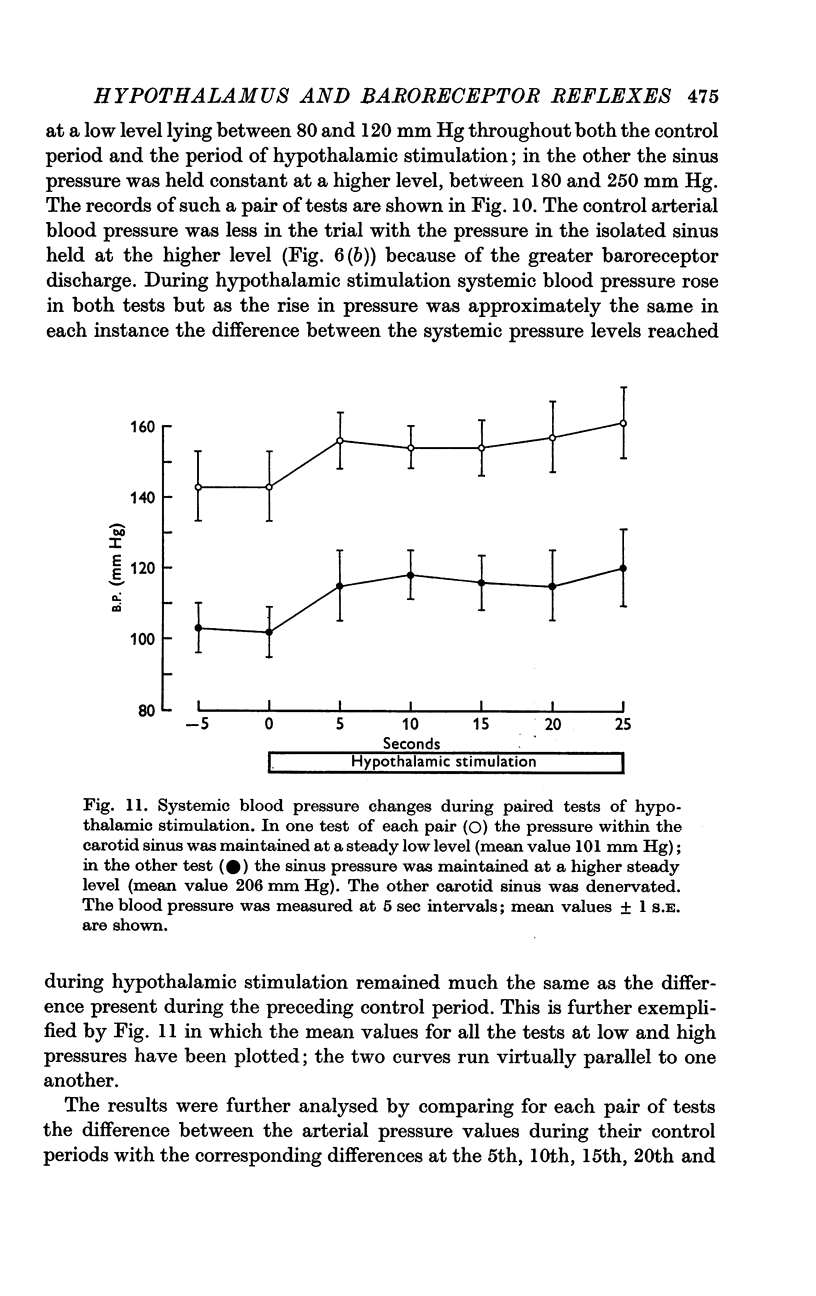
3. During hypothalamic stimulation the reflex fall in blood pressure resulting from a rise in sinus pressure was found to be undiminished whether sinus pressure was raised at the onset or at the 10th sec of hypothalamic stimulation.
4. By contrast, in at least half the cats in which a reflex bradycardia could be evoked from the sinus, this bradycardia was largely if not completely suppressed during hypothalamic stimulation. This suppression of reflex bradycardia occurred when sinus pressure was raised at the onset as well as at the 10th sec of stimulation.
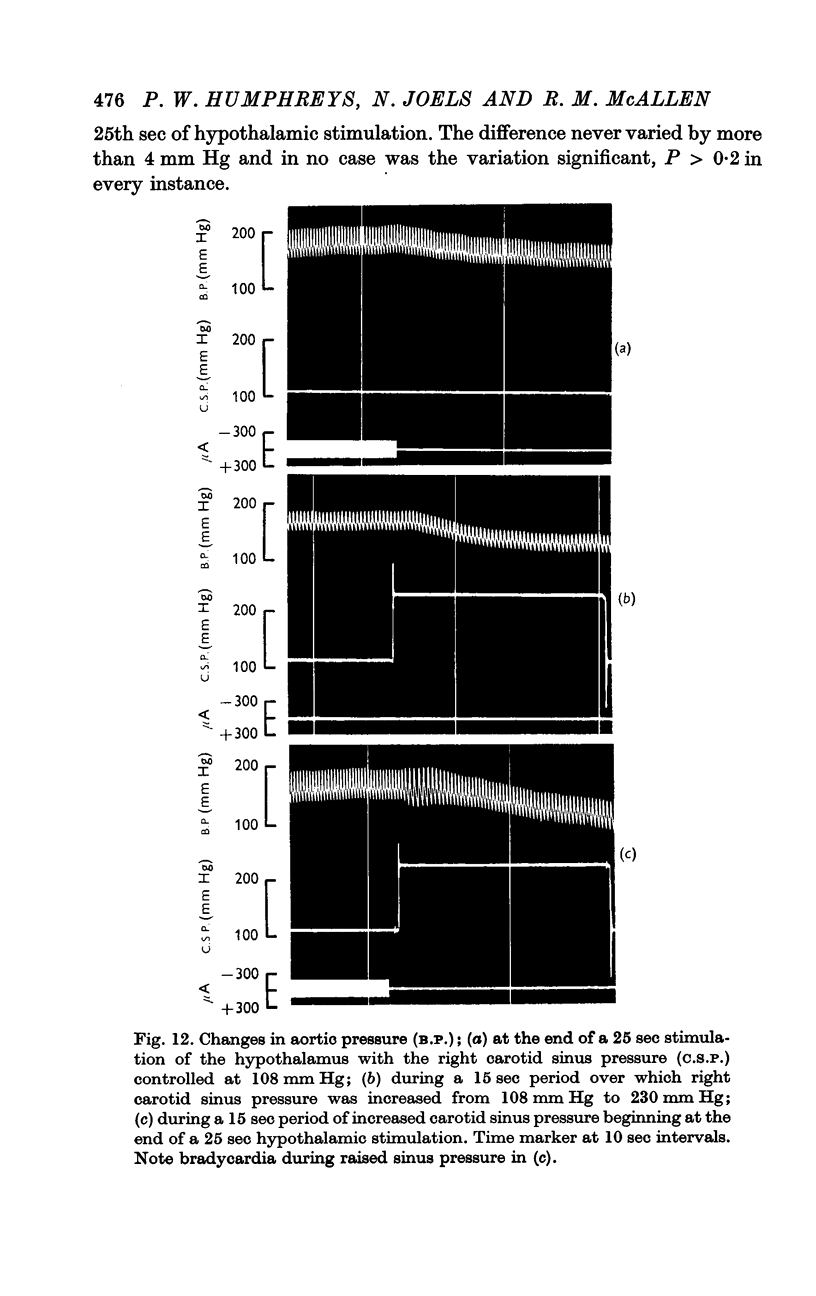
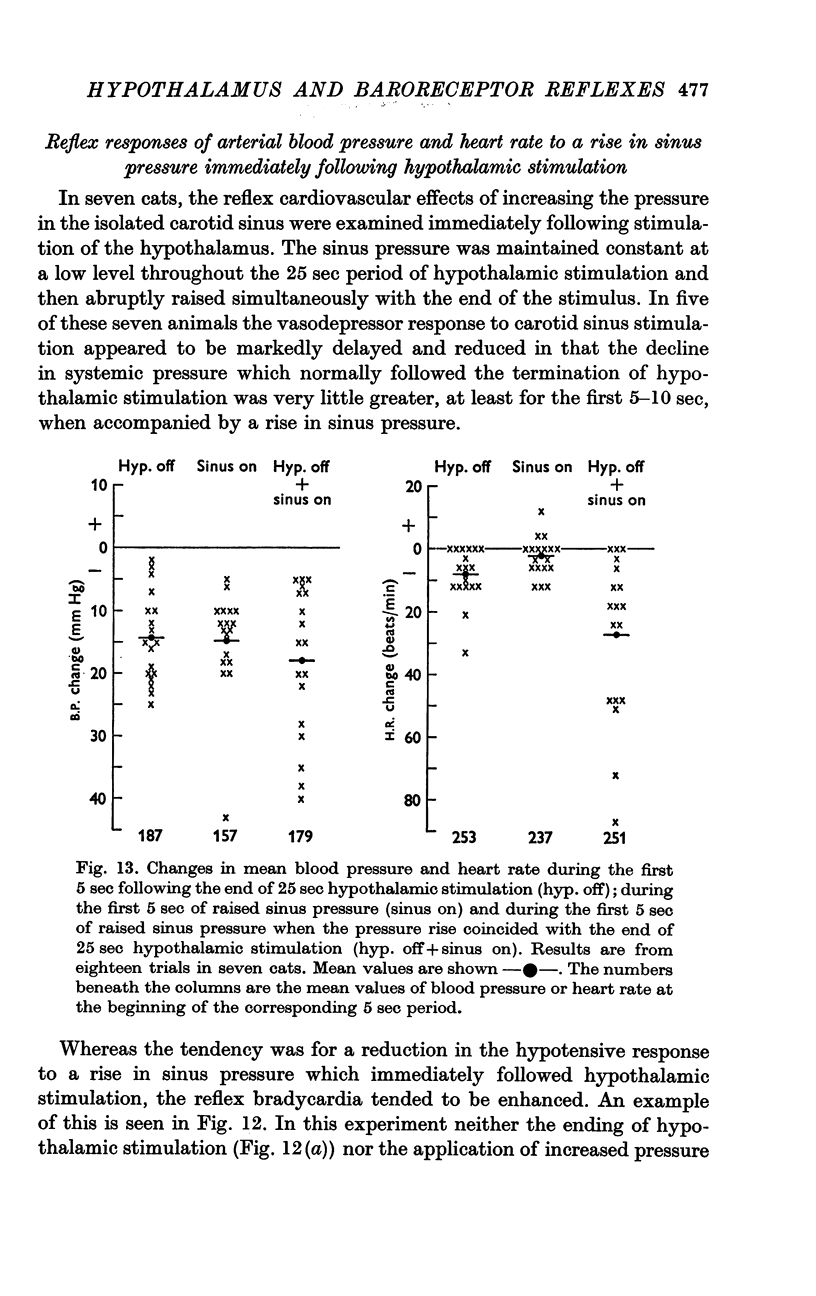
5. During the first 5 sec after hypothalamic stimulation the hypotensive response to an increase in carotid sinus pressure was much reduced; on the other hand the reduction in heart rate was exaggerated, sometimes to a very marked degree.
6. The results suggest that stimulation of the hypothalamic defence area can modify baroreceptor reflexes and that this modification can include selective alterations in the various components of the reflex response.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAHAMS V. C., HILTON S. M., ZBROZYNA A. Active muscle vasodilatation produced by stimulation of the brain stem: its significance in the defence reaction. J Physiol. 1960 Dec;154:491–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djojosugito A. M., Folkow B., Kylstra P. H., Lisander B., Tuttle R. S. Differentiated interaction between the hypothalamic defence reaction and baroreceptor reflexes. I. Effects on heart rate and regional flow resistance. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Mar;78(3):376–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAD H. W., GREEN J. H., NEIL E. A comparison of the effects of pulsatile and non-pulsatile blood flow through the carotid sinus on the reflexogenic activity of the sinus baroceptors in the cat. J Physiol. 1952 Dec;118(4):509–519. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELIASSON S., FOLKOW B., LINDGREN P., UVNAS B. Activation of sympathetic vasodilator nerves to the skeletal muscles in the cat by hypothalamic stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1951 Sep 21;23(4):333–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1951.tb00819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebber G. L., Snyder D. W. Hypothalamic control of baroreceptor reflexes. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jan;218(1):124–131. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton S. M. Hypothalamic control of the cardiovascular responses in fear and rage. Sci Basis Med Annu Rev. 1965:217–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton S. M. Hypothalamic regulation of the cardiovascular system. Br Med Bull. 1966 Sep;22(3):243–248. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockman C. H., Talesnik J., Livingston K. E. Central nervous system modulation of baroceptor reflexes. Am J Physiol. 1969 Dec;217(6):1681–1689. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.6.1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLUVER H., BARRERA E. A method for the combined staining of cells and fibers in the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1953 Oct;12(4):400–403. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195312040-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kylstra P. H., Lisander B. Differentiated interaction between the hypothalamic defence area and baroreceptor reflexes. II. Effects on aortic blood flow as related to work load on the left ventricle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Mar;78(3):386–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDGREN S., NEIL E. Chemoreceptor impulse activity following haemorrhage. Acta Physiol Scand. 1951 Aug 25;23(2-3):158–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1951.tb00805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis D. J., Cuénod M. Central neural regulation of carotid baroreceptor reflexes in the cat. Am J Physiol. 1965 Dec;209(6):1267–1277. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.6.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON M. F., CLARKE N. P., SMITH O. A., RUSHMER R. F. Interrelation between central and peripheral mechanisms regulating blood pressure. Circ Res. 1961 May;9:491–496. doi: 10.1161/01.res.9.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


