Abstract
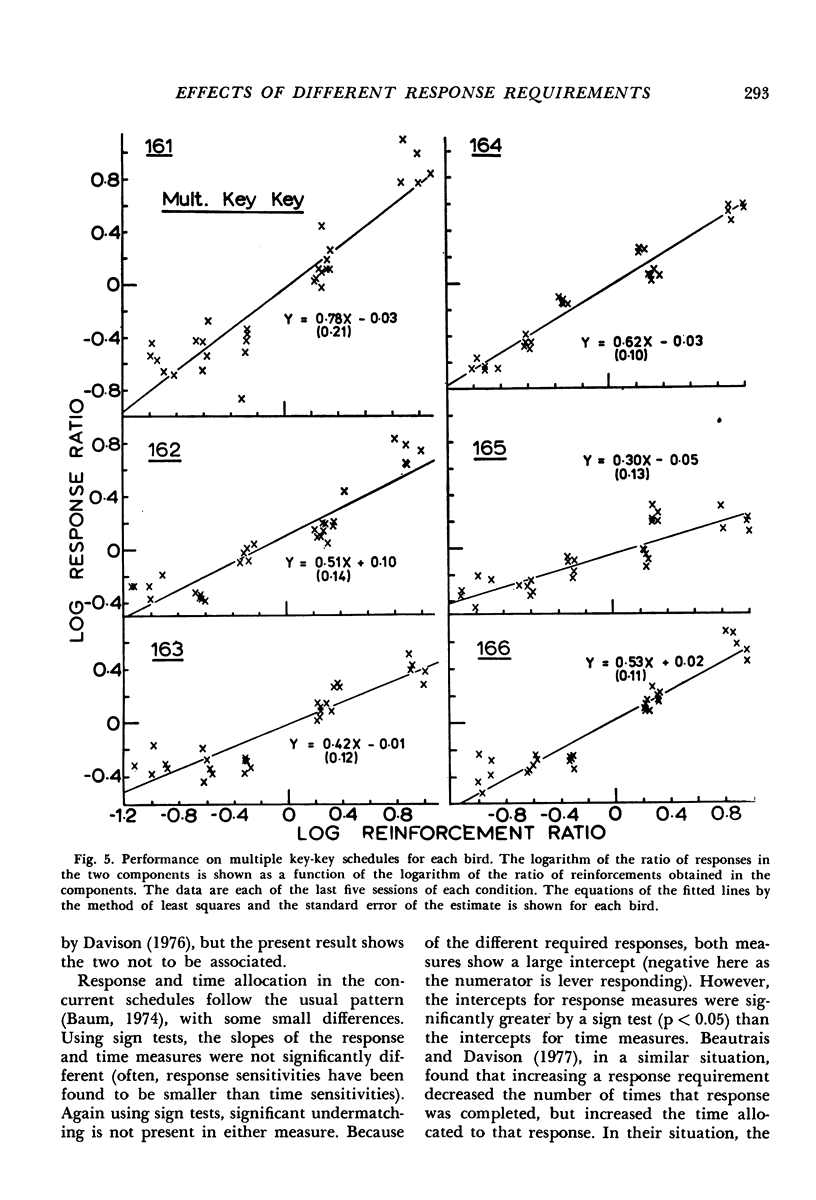
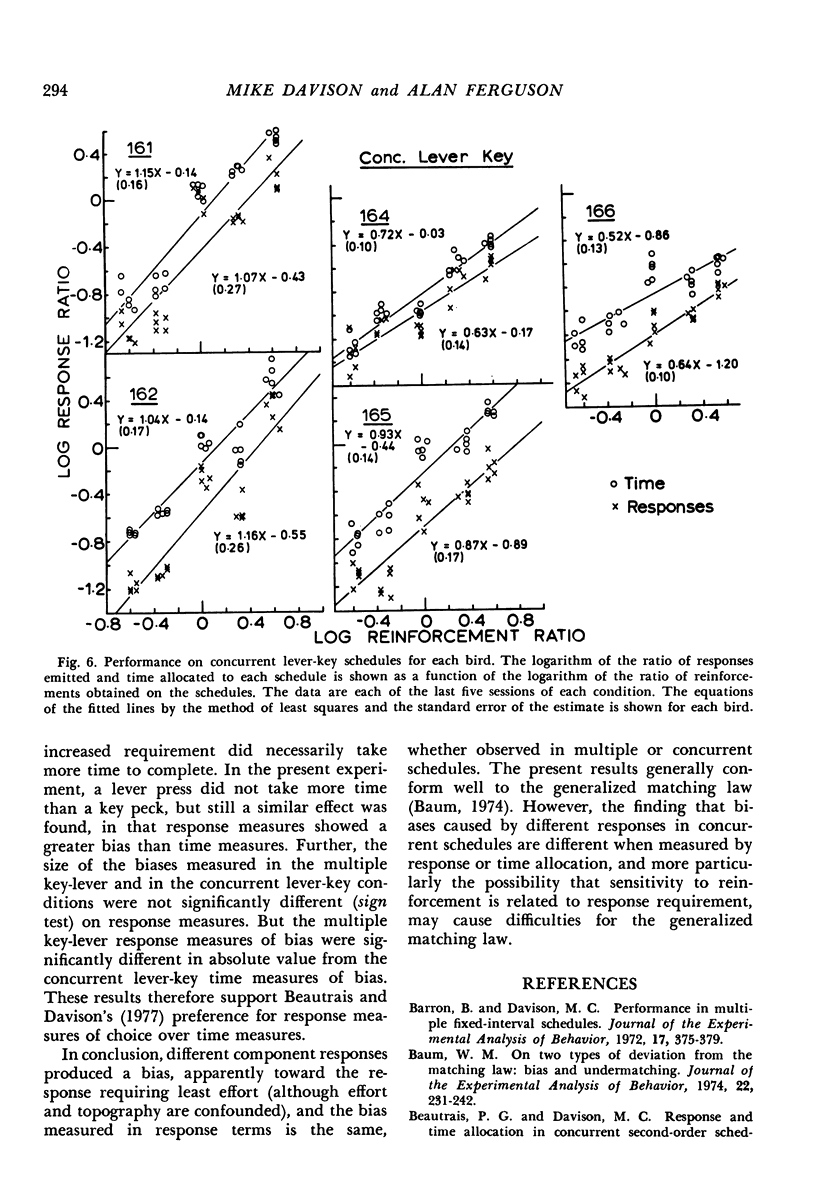
Six pigeons were trained on multiple and concurrent schedules. The reinforcement rates were varied systematically (a) when lever pressing was required in one component and key pecking in the successive component; (b) when lever pressing was required in both multiple components; (c) when key pecking was required in both multiple components; and (d) when key pecking was required on one schedule and lever pressing was required on the concurrently-available schedule. Only the absolute level of responding was changed by different response requirements. Analyzed by the generalized matching law, performance under different response requirements resulted in a bias toward key pecking, and the measured response bias was the same in multiple and concurrent schedule arrangements. The bias in time measures obtained from concurrent schedule performance was reliably smaller than the obtained response biases. The sensitivity to reinforcement-rate changes was ordered: concurrent key-lever; multiple key-key; multiple lever-key; and, the least sensitive, multiple lever-lever. The results confirm that requirements of different topographical responses can be handled by the generalized matching law mainly in the bias parameter, but problems for this type of analysis may be caused by the changing sensitivity to reinforcement in multiple schedule performance as response requirements are changed.
Keywords: multiple schedules, concurrent schedules, bias, contrast, lever pressing, key pecking, pigeons
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barron B., Davison M. C. Performance in multiple fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 May;17(3):375–379. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. On two types of deviation from the matching law: bias and undermatching. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):231–242. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beautrais P. G., Davison M. C. Response and time allocation in concurrent second-order schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jan;27(1):61–69. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C. Preference for fixed-interval schedules: effects of unequal initial links. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 May;25(3):371–376. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmes N. S. Behavioral contrast in pigeons depends upon the operant. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1973 Oct;85(1):171–178. doi: 10.1037/h0034883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander D. G., Irwin R. J. Multiple schedules: effects of the distribution of reinforcements between component on the distribution of responses between conponents. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):517–524. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb B., Davison M. C. Multiple and concurrent schedule performance: independence from concurrent and successive schedule contexts. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jul;28(1):27–39. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.28-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb B., Davison M. C. Performance in concurrent interval schedules: a systematic replication. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Sep;24(2):191–197. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSweeney F. K. Matching and contrast on several concurrent treadle-press schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Mar;23(2):193–198. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers D. L., Myers L. E. Undermatching: a reappraisal of performance on concurrent variable-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jan;27(1):203–214. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scull J., Westbrook R. F. Interactions in multiple schedules with different responses in each of the components. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):511–519. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P., Wheatley K. L. Matching to relative reinforcement frequency in multiple schedules with a short component duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Mar;15(2):205–210. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A., Pliskoff S. S. Concurrent responding with fixed relative rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):887–895. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook R. F. Failure to obtain positive contrast when pigeons press a bar. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):499–510. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


