Abstract
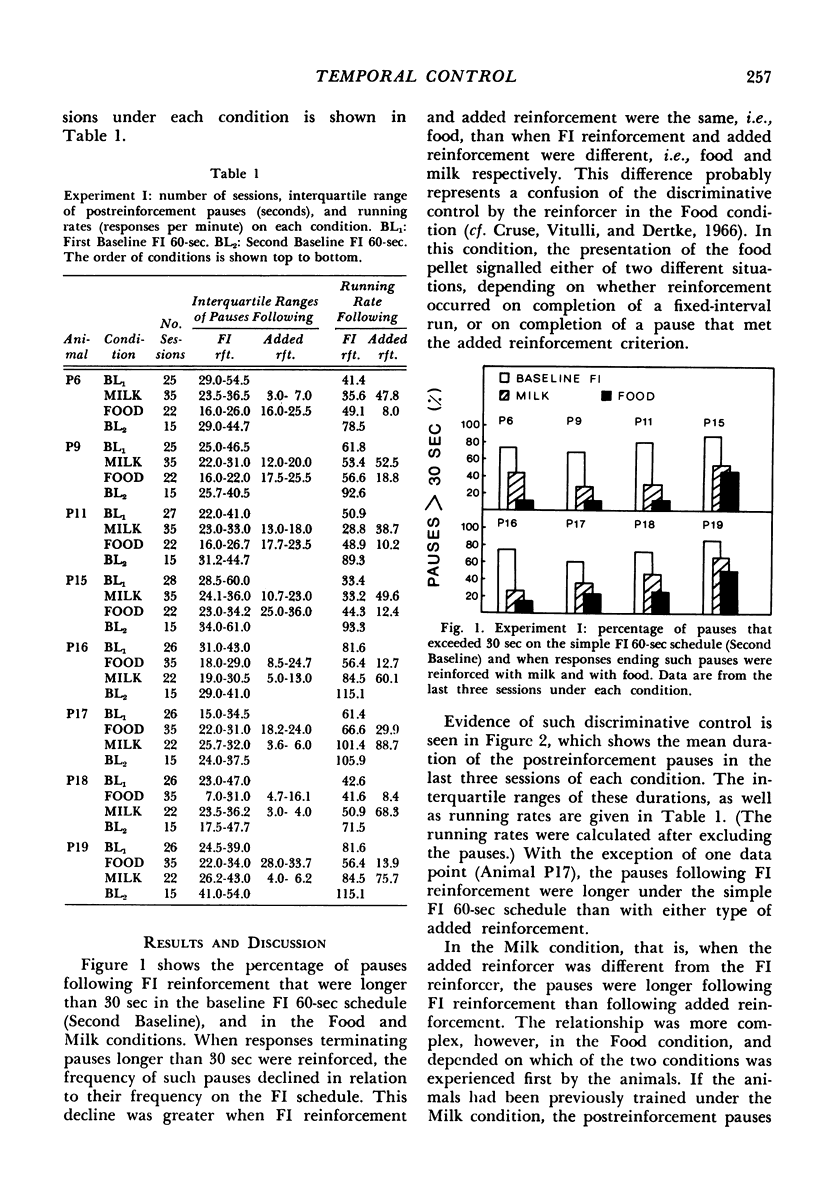
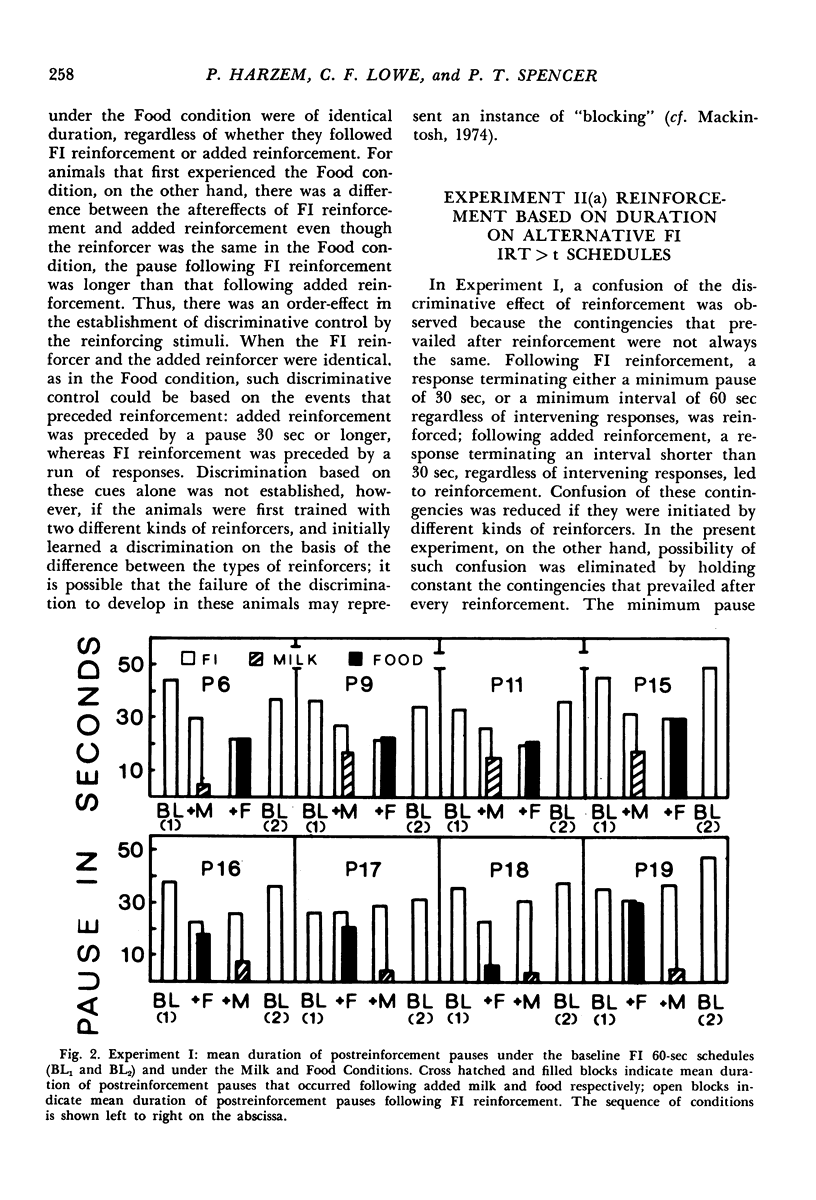
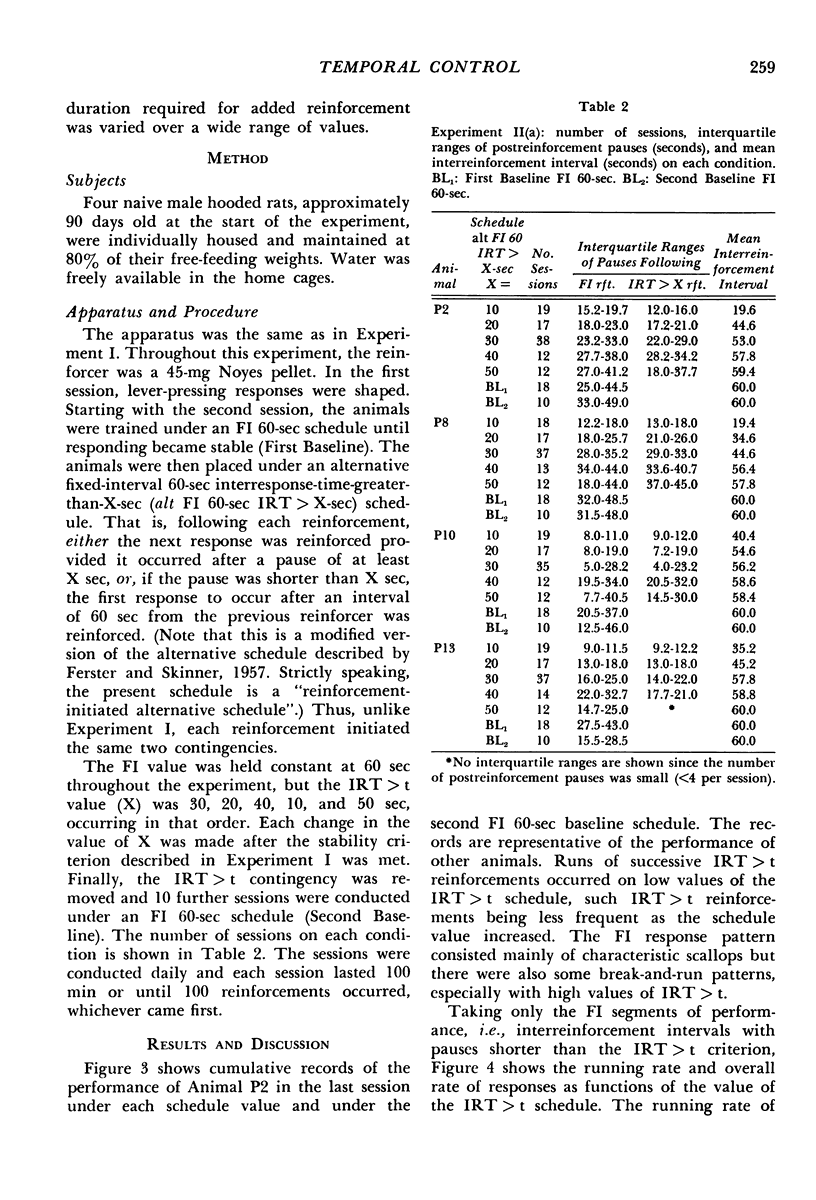
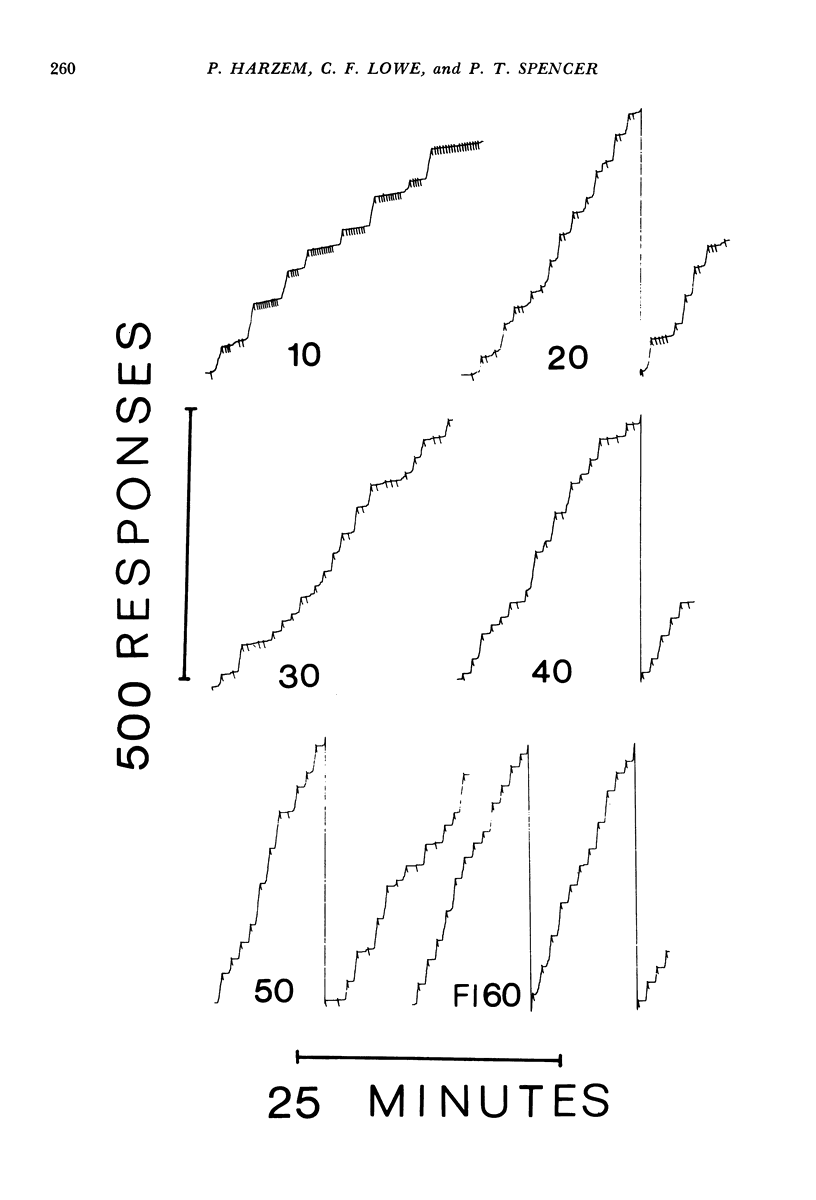
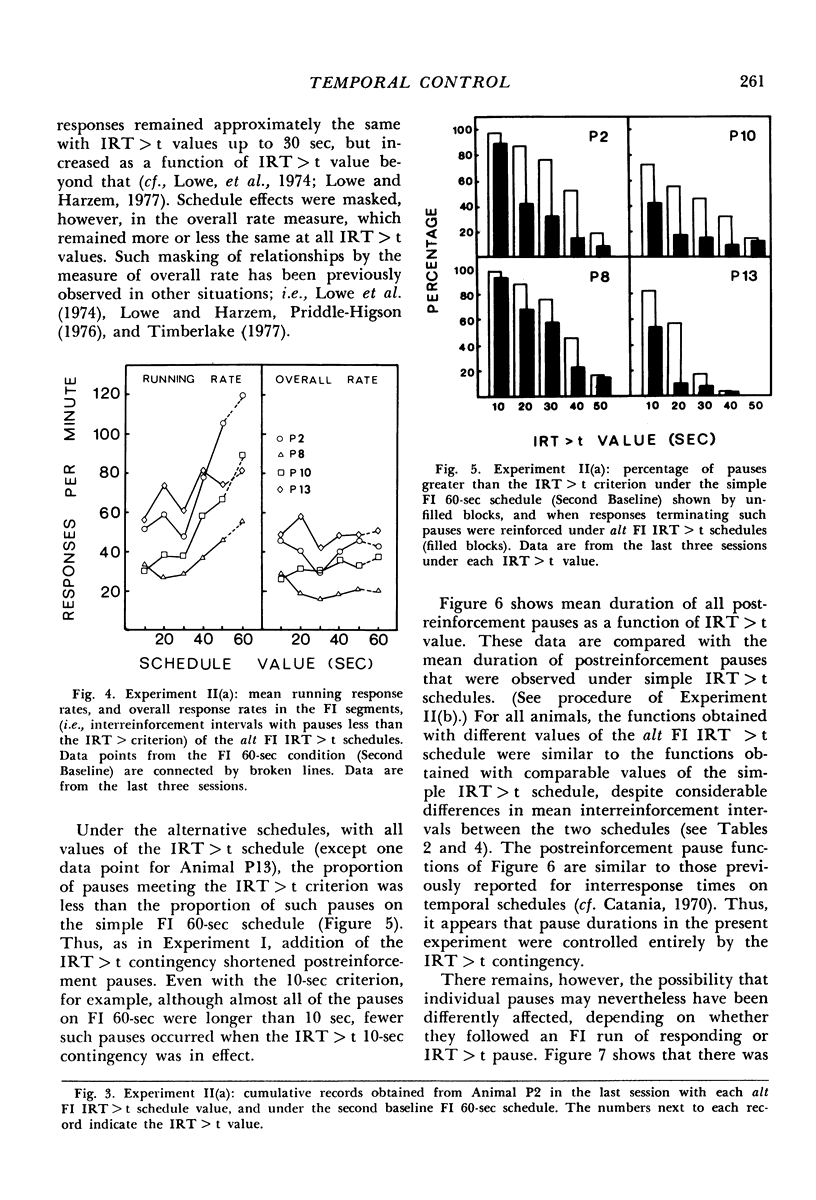
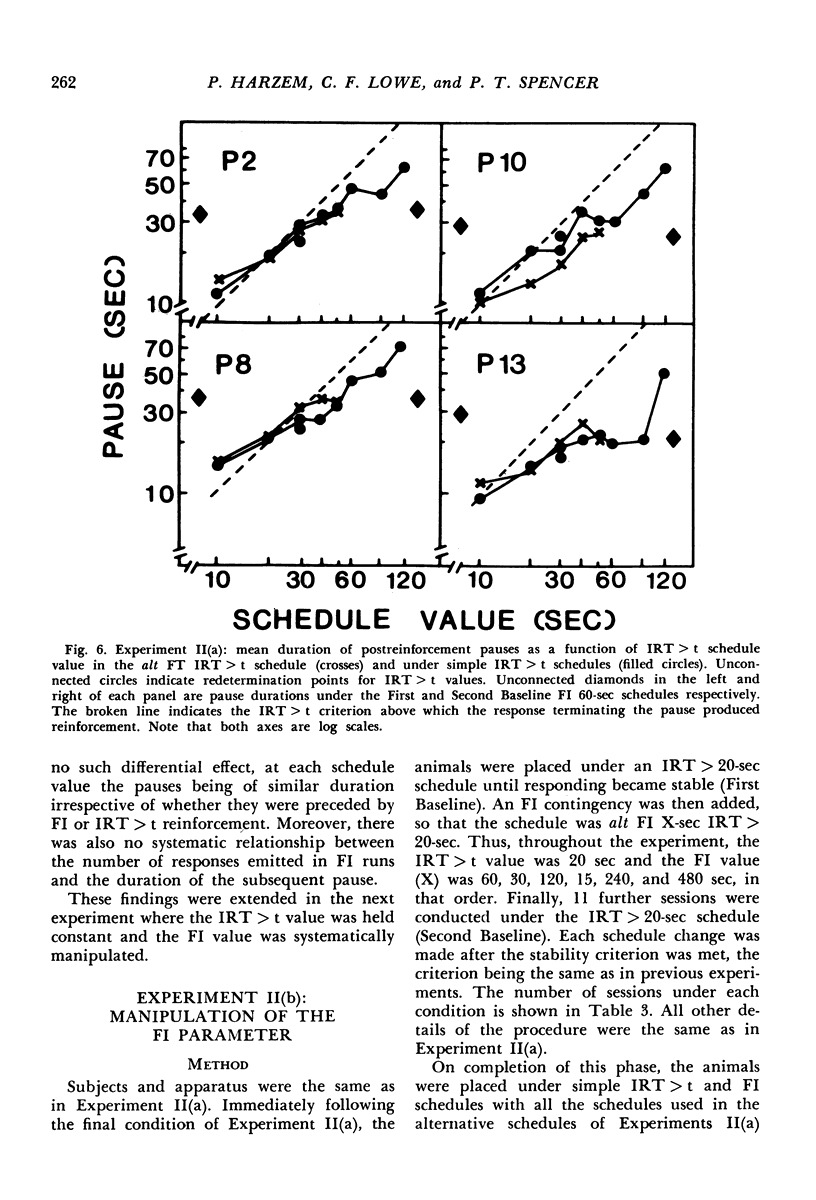
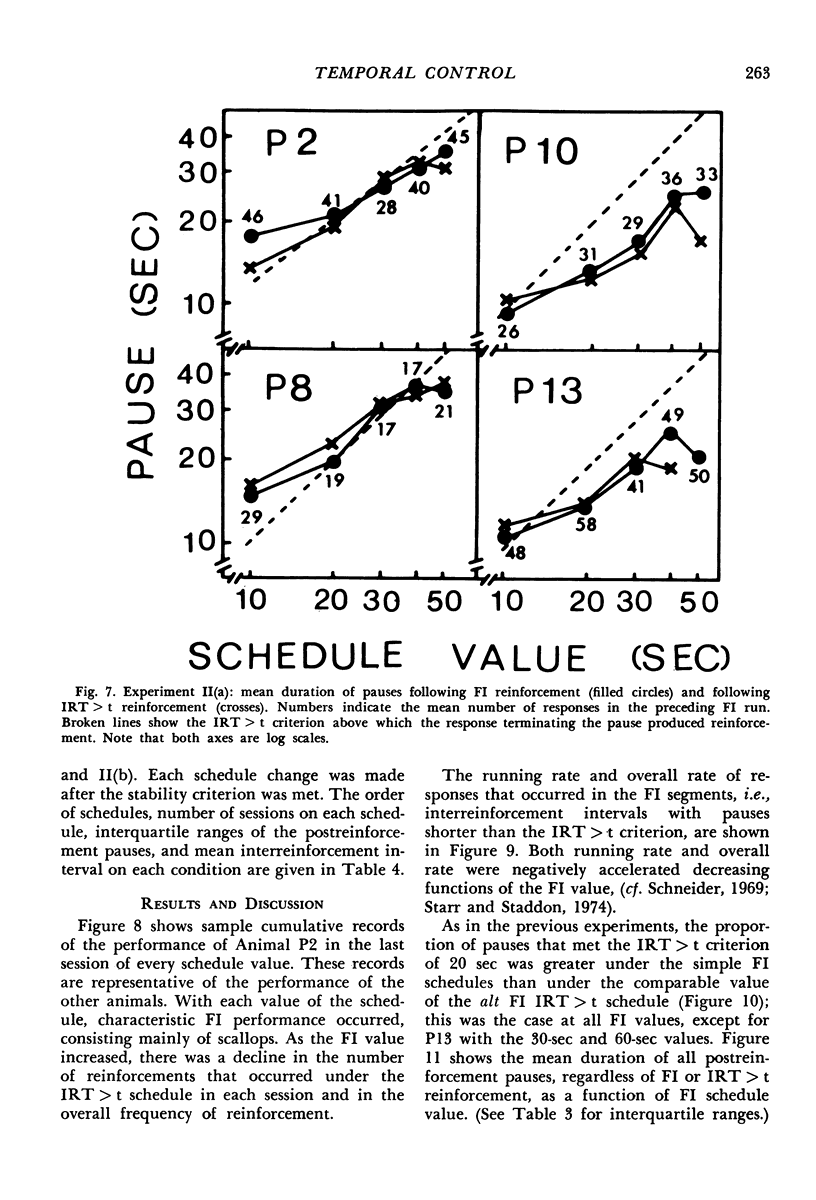
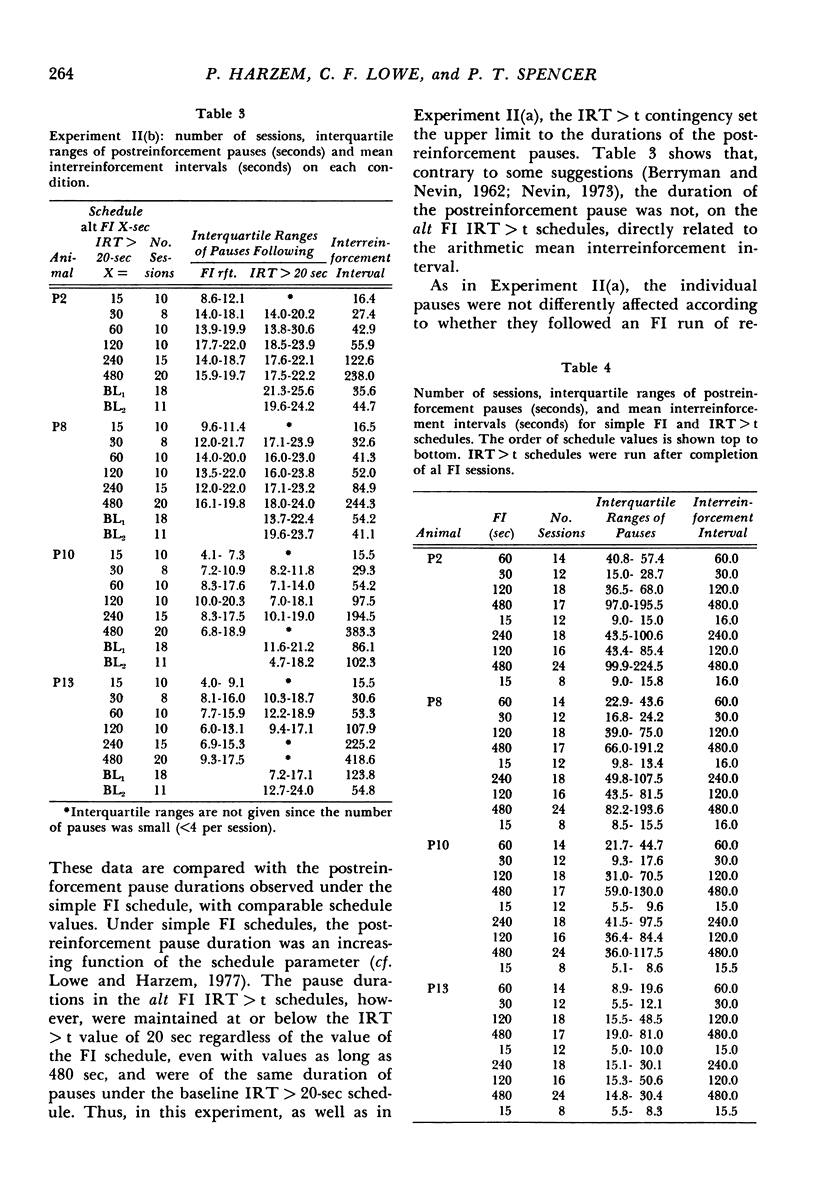
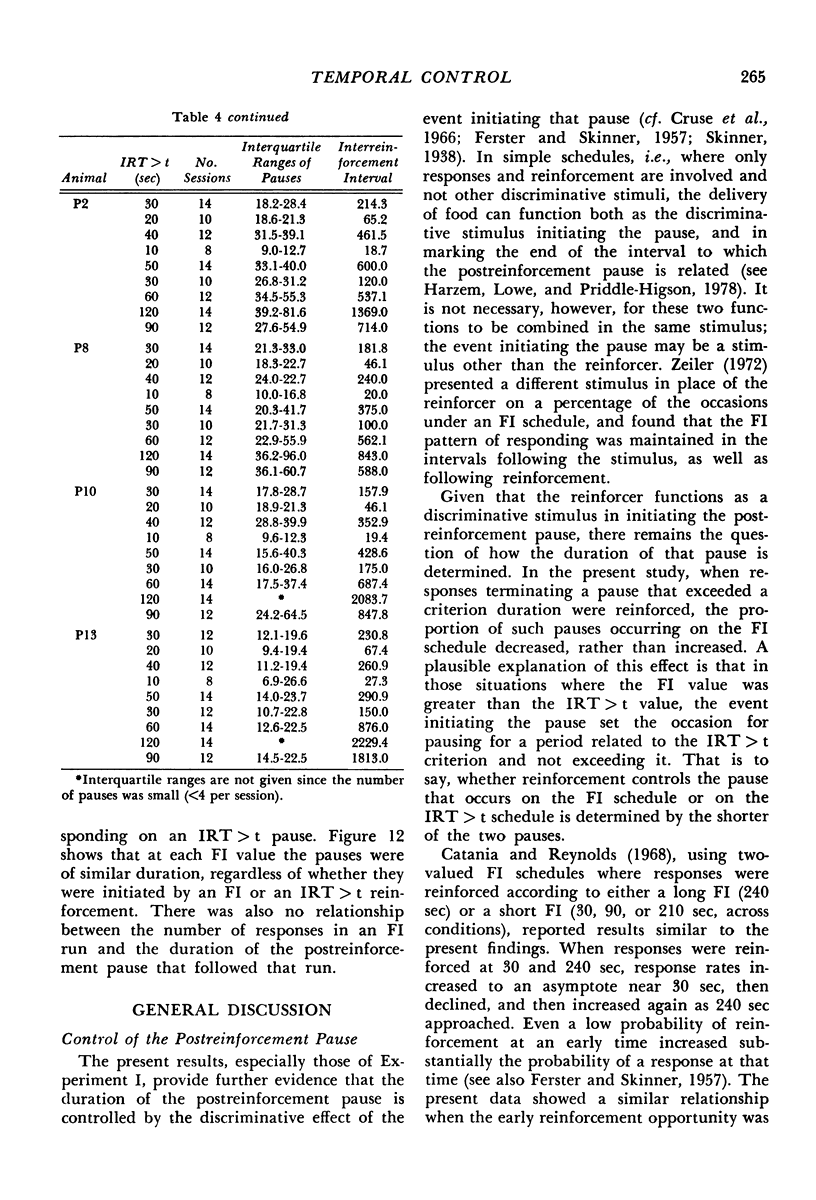
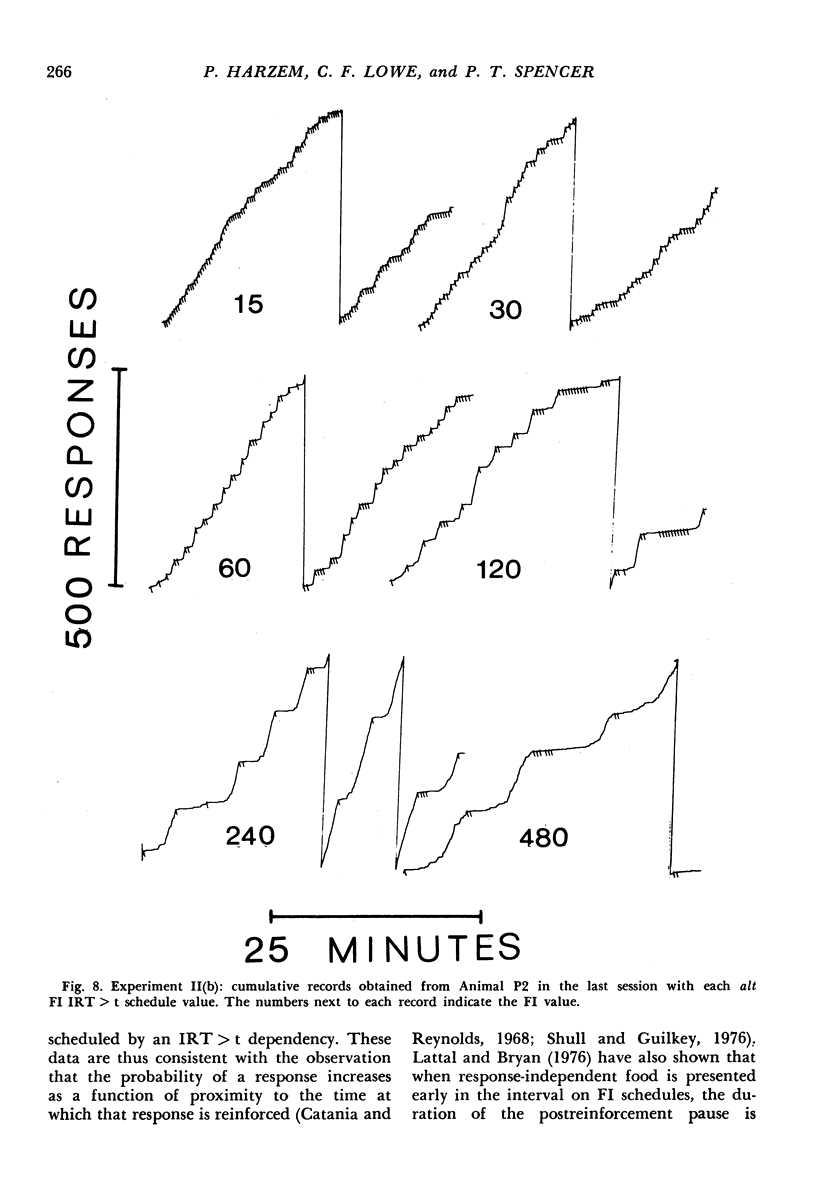
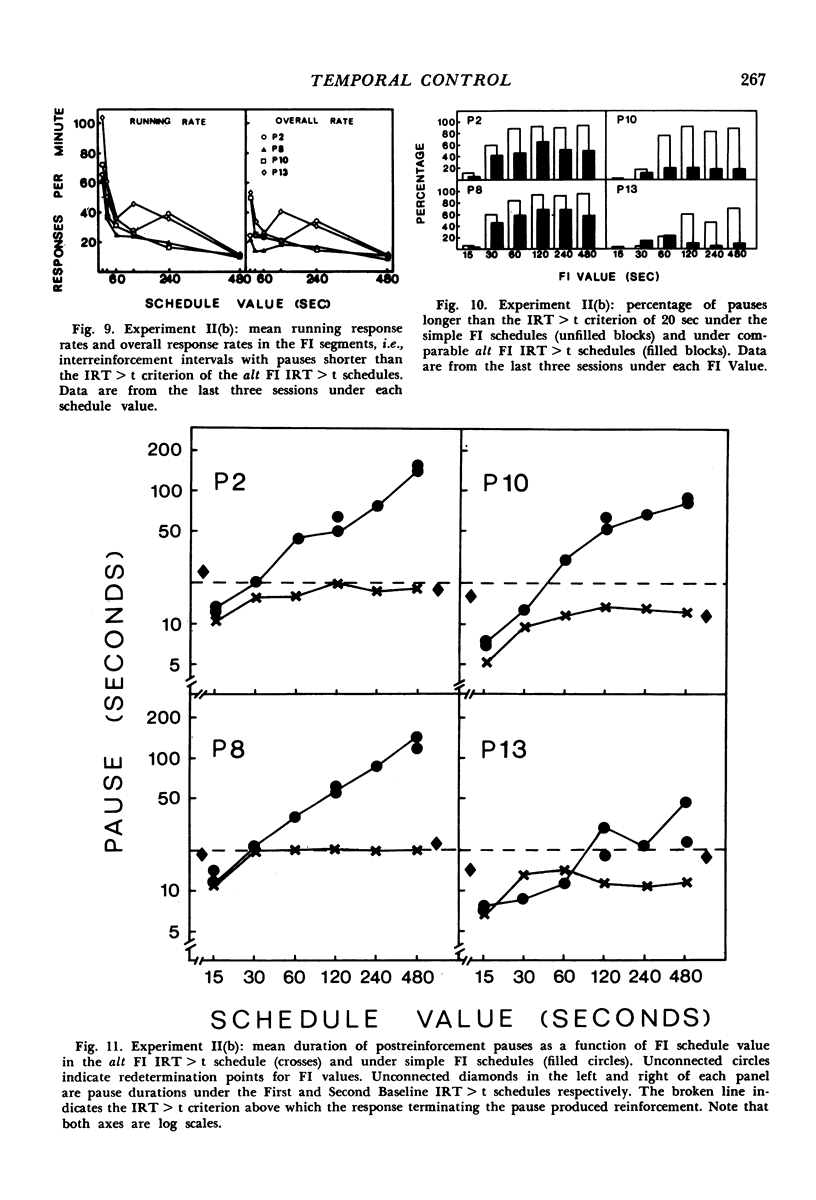
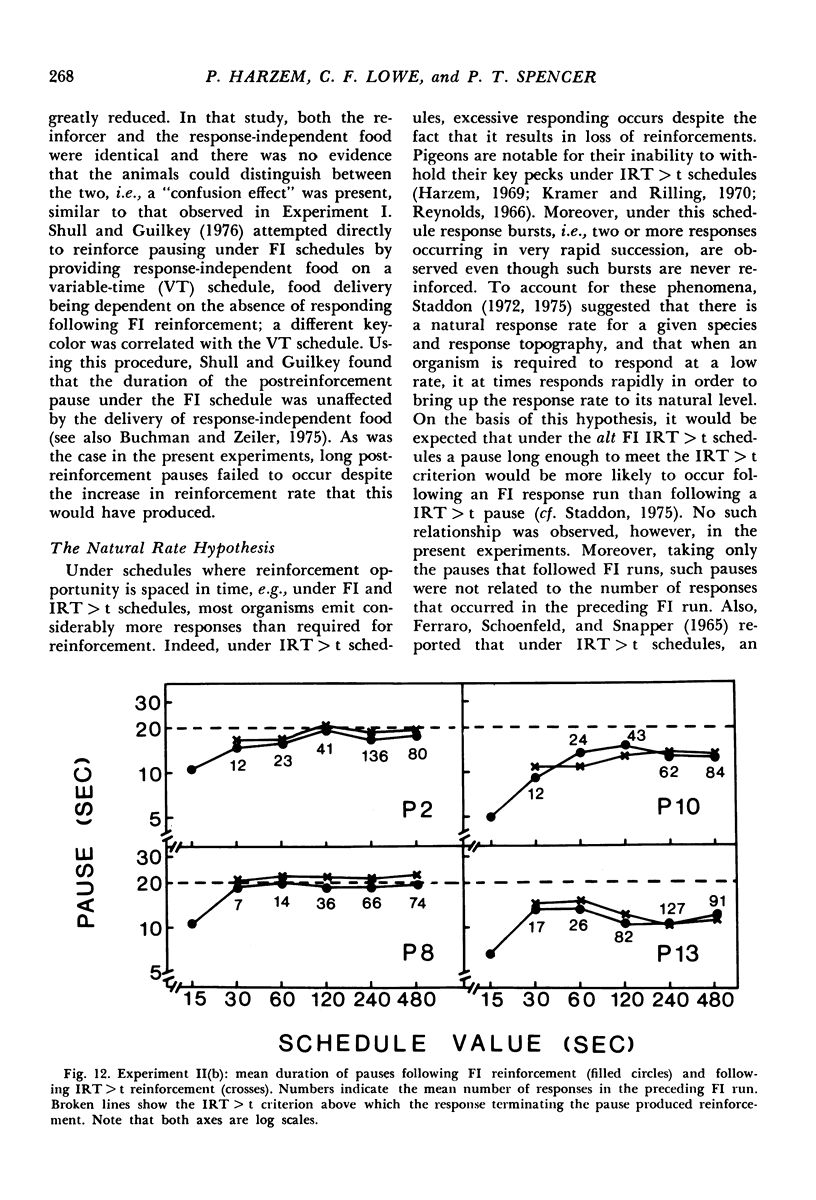
In Experiment I the response that terminated the postreinforcement pauses occurring under a fixed-interval 60-second schedule was reinforced, if the pause duration exceeded 30 seconds. The percentage of such pauses, rather than increasing, decreased. There were complex effects on the discriminative control of the pause by the reinforcer terminating the previous fixed interval, depending on whether the fixed interval and the added reinforcer were the same or different. In Experiments II(a) and II(b), each reinforcement initiated an alternative fixed-interval interresponse-time-greater-than-t-sec schedule, the schedule values being systematically varied. When the response following a pause exceeding a given duration was reinforced, fewer such pauses occurred than when they were not reinforced, i.e., on the comparable simple fixed-interval schedule. There was no systematic relationship between mean interrinforcement interval and duration of the postreinforcement pause. The pause duration initiated by reinforcement was directly related to the dependency controlling the shortest pause at that time, regardless of changes in mean interreinforcement interval.
Keywords: postreinforcement pause, discriminative control, temporal control, natural response rate, fixed interval, interresponse time greater than t seconds, rats
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AZRIN N. H., HOLZ W. C. Punishment during fixed-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Oct;4:343–347. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERRYMAN R., NEVIN J. A. Interlocking schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:213–223. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch M. N., Gollub L. R. A detailed analysis of the effects of d-amphetamine on behavior under fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):519–539. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman I. B., Zeiler M. D. Stimulus properties of fixed-interval responses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Nov;24(3):369–375. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER G. Consummatory and instrumental responding as functions of deprivation. J Exp Psychol. 1962 Oct;64:410–414. doi: 10.1037/h0044157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruse D. B., Vitulli W., Dertke M. Discriminative and reinforcing properties of two types of food pellets. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 May;9(3):293–303. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dews P. B. Studies on responding under fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement: II. The scalloped pattern of the cumulative record. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Jan;29(1):67–75. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRARO D. P., SCHOENFELD W. N., SNAPPER A. G. SEQUENTIAL RESPONSE EFFECTS IN THE WHITE RAT DURING CONDITIONING AND EXTINCTION ON A DRL SCHEDULE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jul;8:255–260. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harzem P., Lowe C. F., Davey G. C. Two-component schedules of differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Jul;24(1):33–42. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harzem P., Lowe C. F., Priddle-Higson P. J. Inhibiting function of reinforcement: magnitude effects on variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Jul;30(1):1–10. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattal K. A., Bryan A. J. Effects of concurrent response-independent reinforcement on fixed-interval schedule performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Nov;26(3):495–504. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe C. F., Davey G. C., Harzem P. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on interval and ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Nov;22(3):553–560. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe C. F., Harzem P. Species differences in temporal control of behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Nov;28(3):189–201. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.28-189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priddle-Higson P. J., Lowe C. F., Harzem P. Aftereffects of reinforcement on variable-ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 May;25(3):347–354. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. S. Discrimination and emission of temporal intervals by pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jan;9(1):65–68. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. K. A test of the effectiveness of the differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):385–391. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. A. A two-state analysis of fixed-interval responding in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):677–687. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. L., Brownstein A. J. Interresponse time duration in fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement: control by ordinal position and time since reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jul;14(1):49–53. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. L., Guilkey M. Food deliveries during the pause on fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Nov;26(3):415–423. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. L., Guilkey M., Witty W. Changing the response unit from a single peck to a fixed number of pecks in fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Mar;17(2):193–200. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E. Effect of reinforcement duration on fixed-interval responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jan;13(1):9–11. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr B. C., Staddon J. E. Temporal control of periodic schedules: signal properties of reinforcement and blackout. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Nov;22(3):535–545. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. The application of the matching law to simple ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jan;27(1):215–217. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler M. D. Fixed-interval behavior: effects of percentage reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Mar;17(2):177–189. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


