Abstract
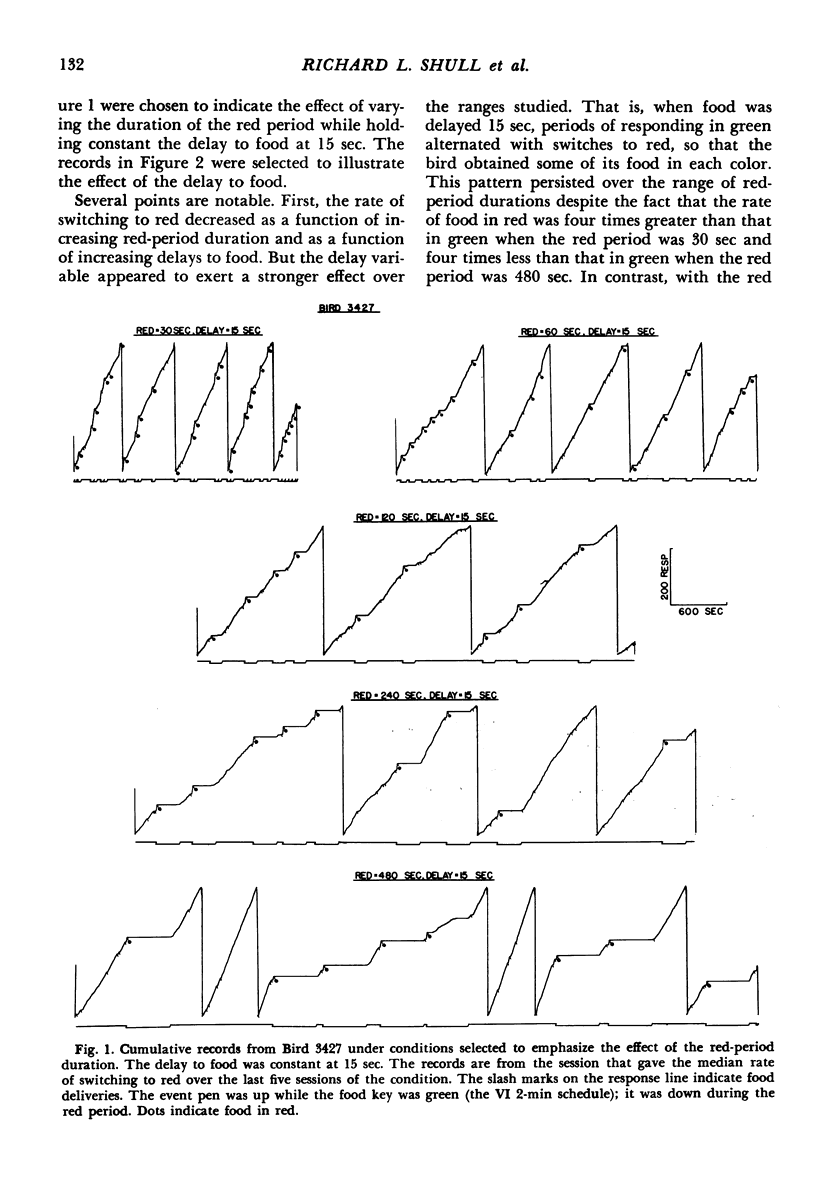
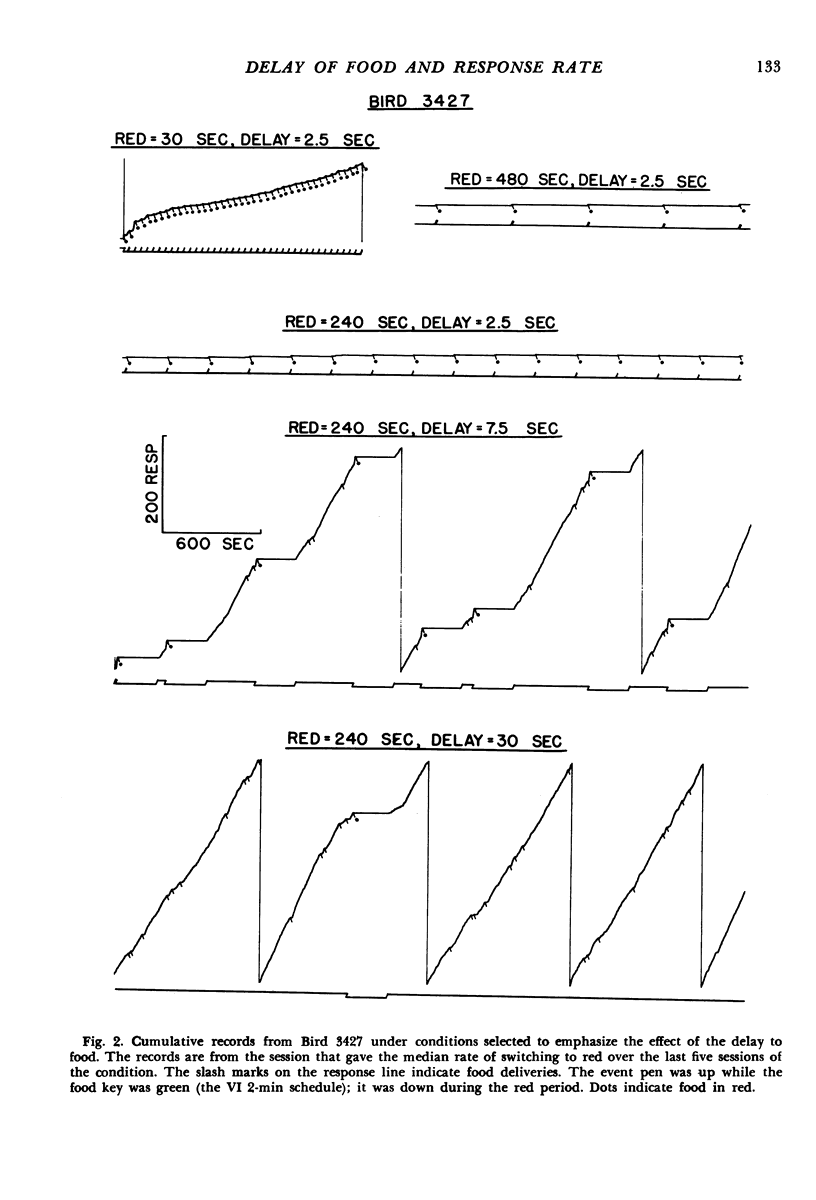
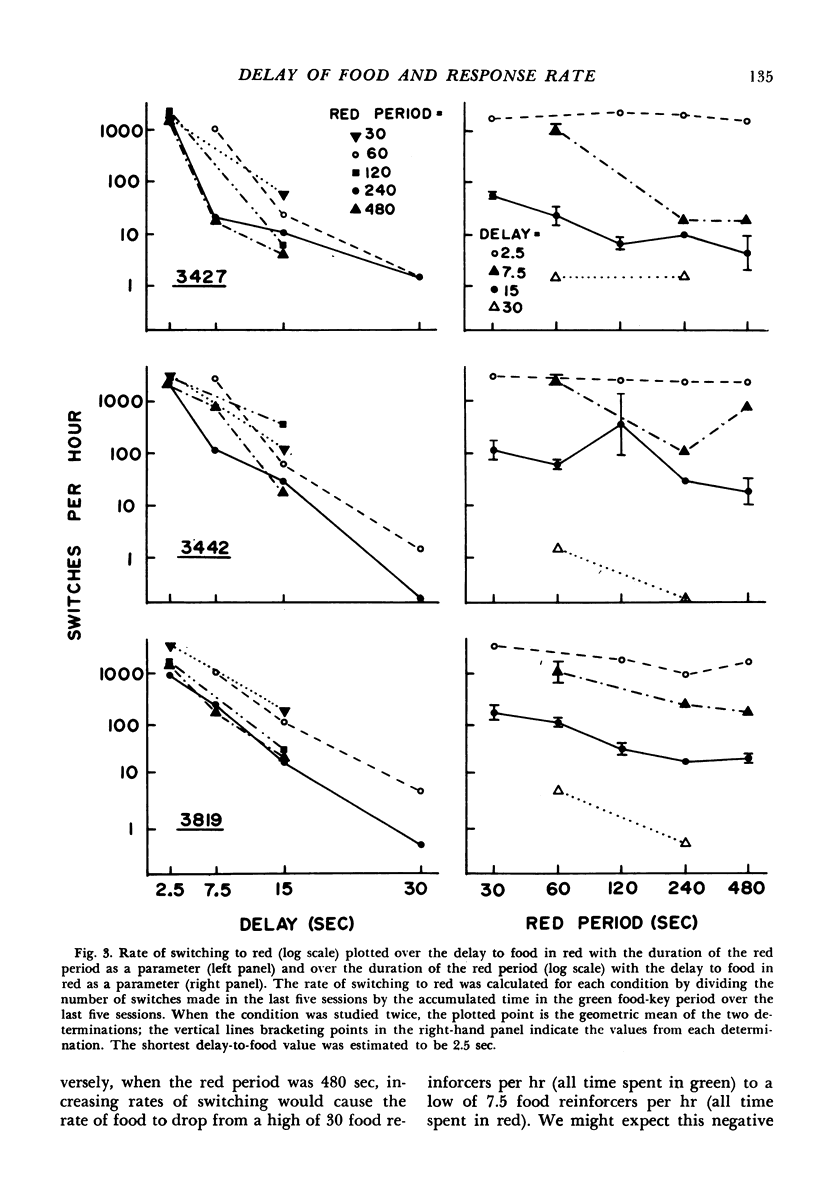
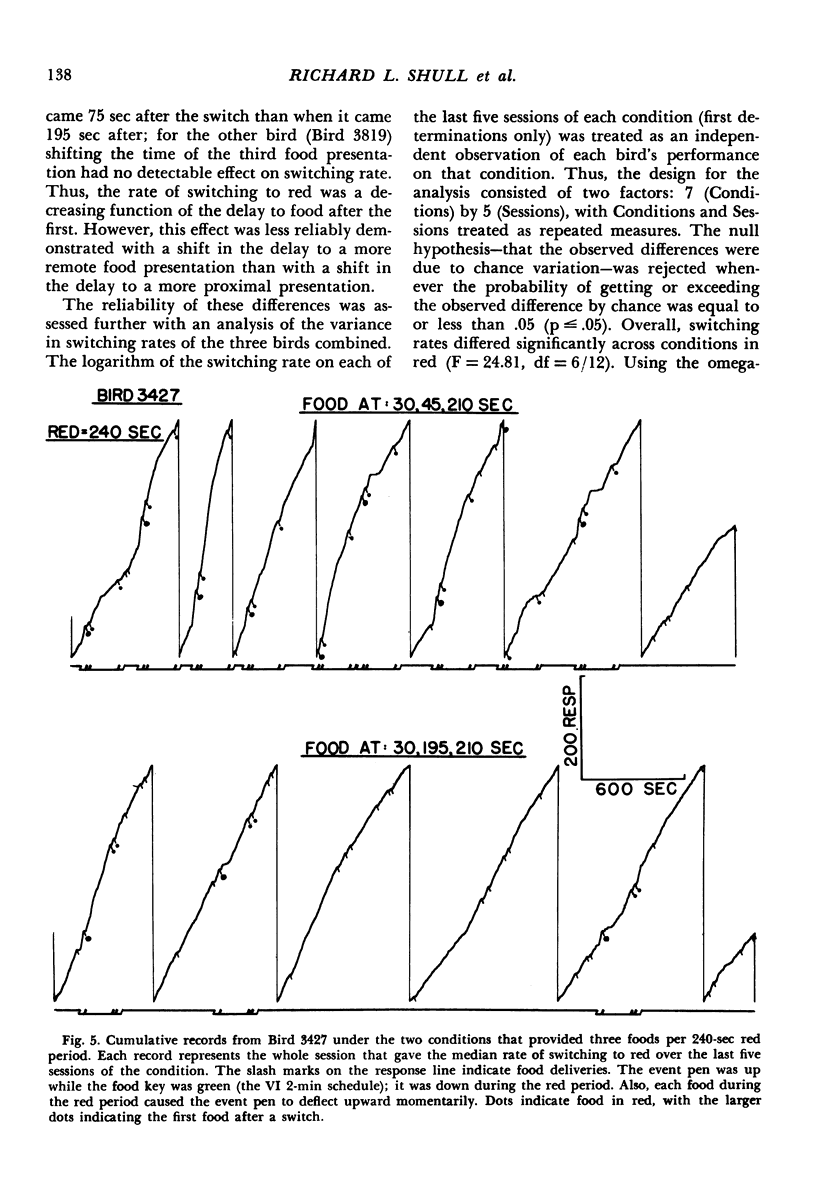
Pigeons were confronted with two keys: a green food key and a white changeover key. Food became available for a peck to the green key after variable intervals of time (mean = 113 seconds). A single peck on the changeover key changed the color of the food key to red for a fixed period of time during which the timing of the variable-interval schedule in green was suspended and the switching option eliminated and after which the conditions associated with green were reinstated. In Experiment 1 a single food presentation was obtainable during each red-key period after a minimum delay timed from the switch. This delay and the duration of the red-key period were held constant during a condition but varied between conditions (delay = 2.5, 7.5, 15, or 30 seconds; red-period duration = 30, 60, 120, 240, or 480 seconds). In Experiment 2 additional food presentations were scheduled during a 240-second red-key period with the delay to the first food delivery held constant at 30 seconds, and the delays to later food deliveries varied over conditions. Considering the data from both experiments, the rate of switching to red was a decreasing function of the delay to the first food, the delay to the second food, and perhaps the delay to the third food after a switch. There was no clear evidence that the rate of food in the red-key period made an independent contribution. The ordering of response rates among conditions was consistent with the view that each food presentation after a response adds an incremental effect to the rate of the response and that each food presentation's contribution is a decreasing function of its delay timed from the response.
Keywords: delay of reinforcement, rate of reinforcement, changeover delay, response rate, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainslie G. Specious reward: a behavioral theory of impulsiveness and impulse control. Psychol Bull. 1975 Jul;82(4):463–496. doi: 10.1037/h0076860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M., Rachlin H. C. Choice as time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):861–874. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. The correlation-based law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jul;20(1):137–153. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C. Reinforcement schedules: the role of responses preceding the one that produces the reinforcer. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 May;15(3):271–287. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. H., Herrnstein R. J. Choice and delay of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):67–74. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWS P. B. The effect of multiple S delta periods on responding on a fixed-interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jul;5:369–374. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner E. T., Lewis P. Parameters affecting the maintenance of negatively reinforced key pecking. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Sep;28(2):117–131. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.28-117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. Method and theory in the study of avoidance. Psychol Rev. 1969 Jan;76(1):49–69. doi: 10.1037/h0026786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursh S. R., Fantino E. Relative delay of reinforcement and choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 May;19(3):437–450. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall S. B. Some effects of fixed-interval duration on response rate in a two-component chain schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jul;10(4):341–347. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. On the measurement of reinforcement frequency in the study of preference. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3):263–269. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P., Gardner E. T., Hutton L. Integrated delays to shock as negative reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Nov;26(3):379–386. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MISCHEL W., METZNER R. Preference for delayed reward as a function of age, intelligence, and length of delay interval. J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1962 Jun;64:425–431. doi: 10.1037/h0045046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macewen D. The effects of terminal-link fixed-interval and variable-interval schedules on responding under concurrent chained schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Sep;18(2):253–261. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. Choice and number of reinforcers. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Jul;32(1):51–63. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.32-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENNER K. E. DELAYED OF REINFORCEMENT: A HISTORICAL REVIEW. Psychol Bull. 1964 May;61:341–361. doi: 10.1037/h0048335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H. A molar theory of reinforcement schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Nov;30(3):345–360. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H., Green L. Commitment, choice and self-control. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jan;17(1):15–22. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


