Abstract
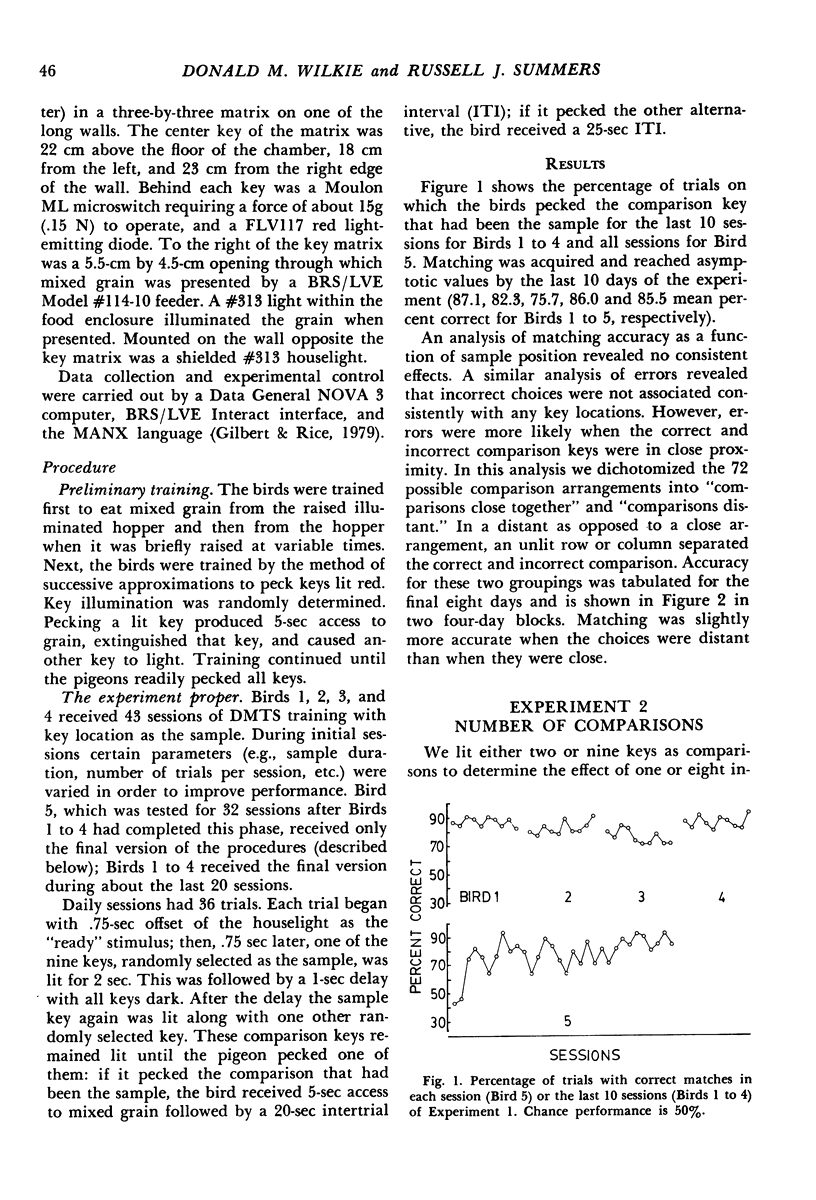
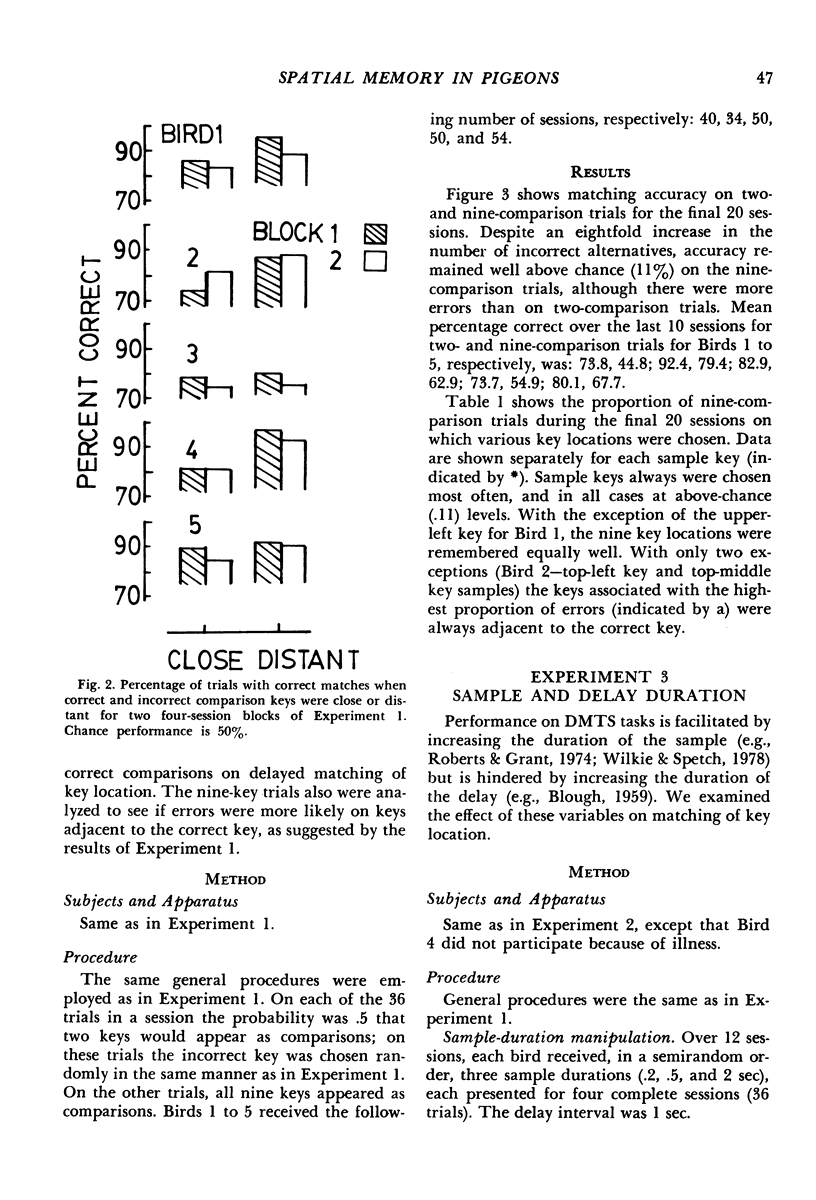
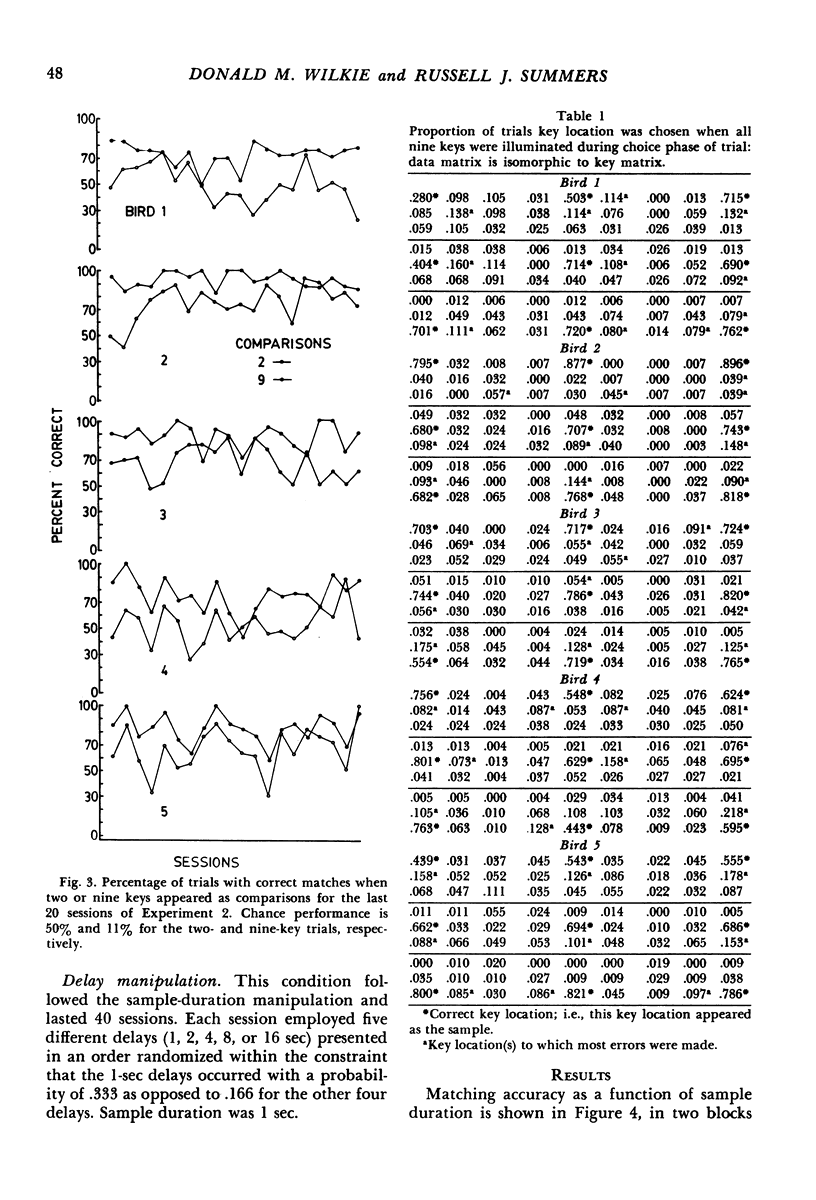
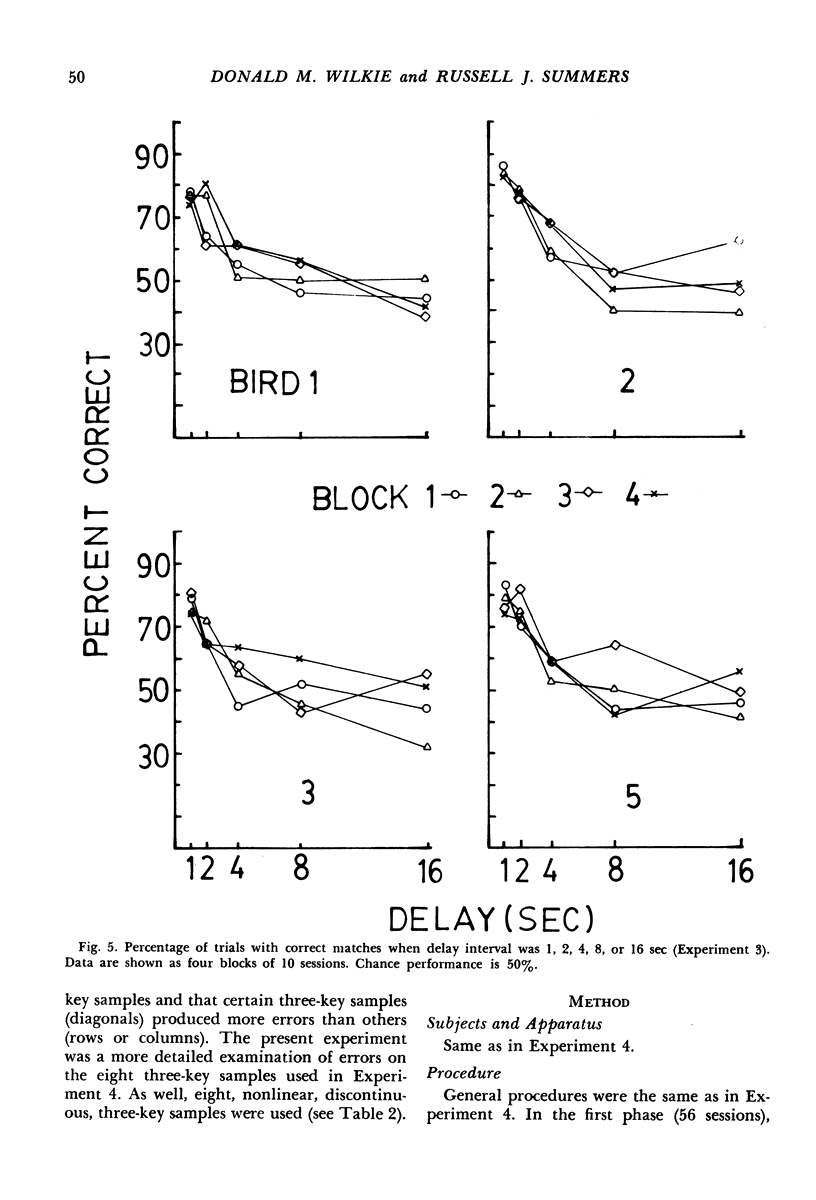
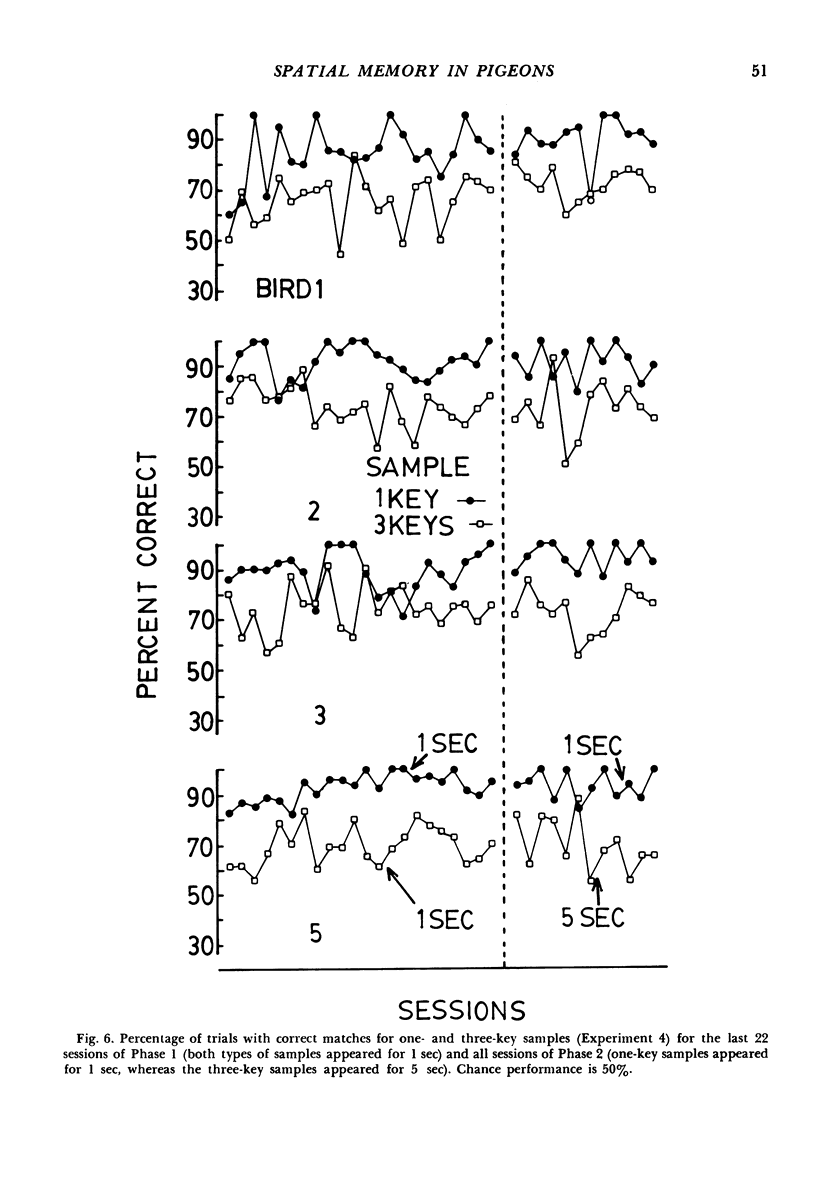
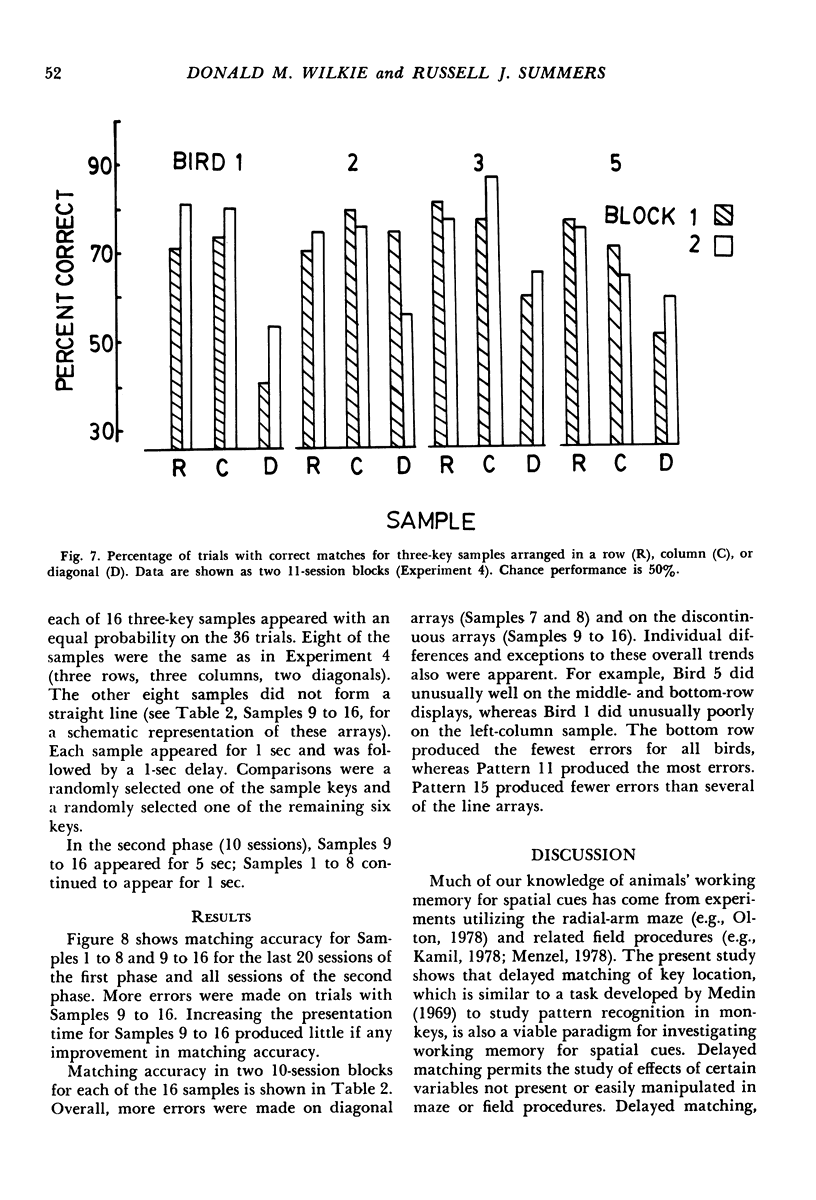
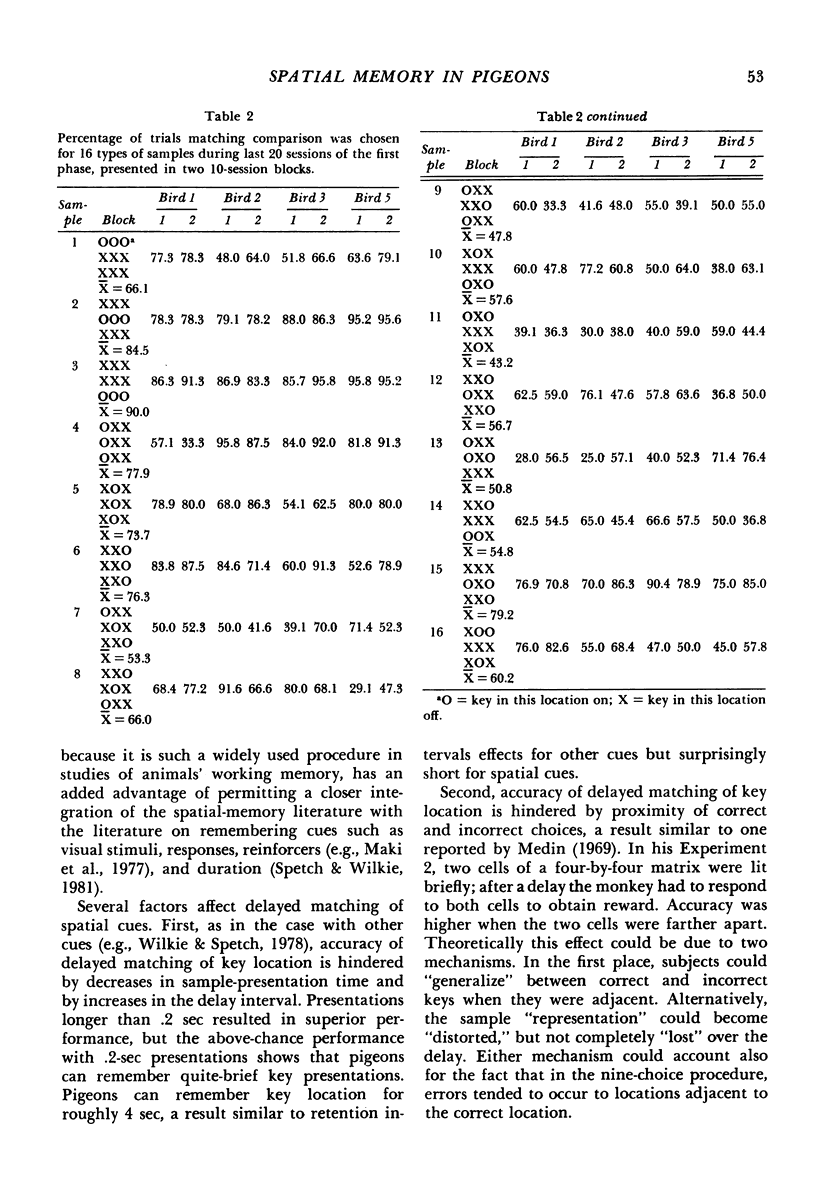
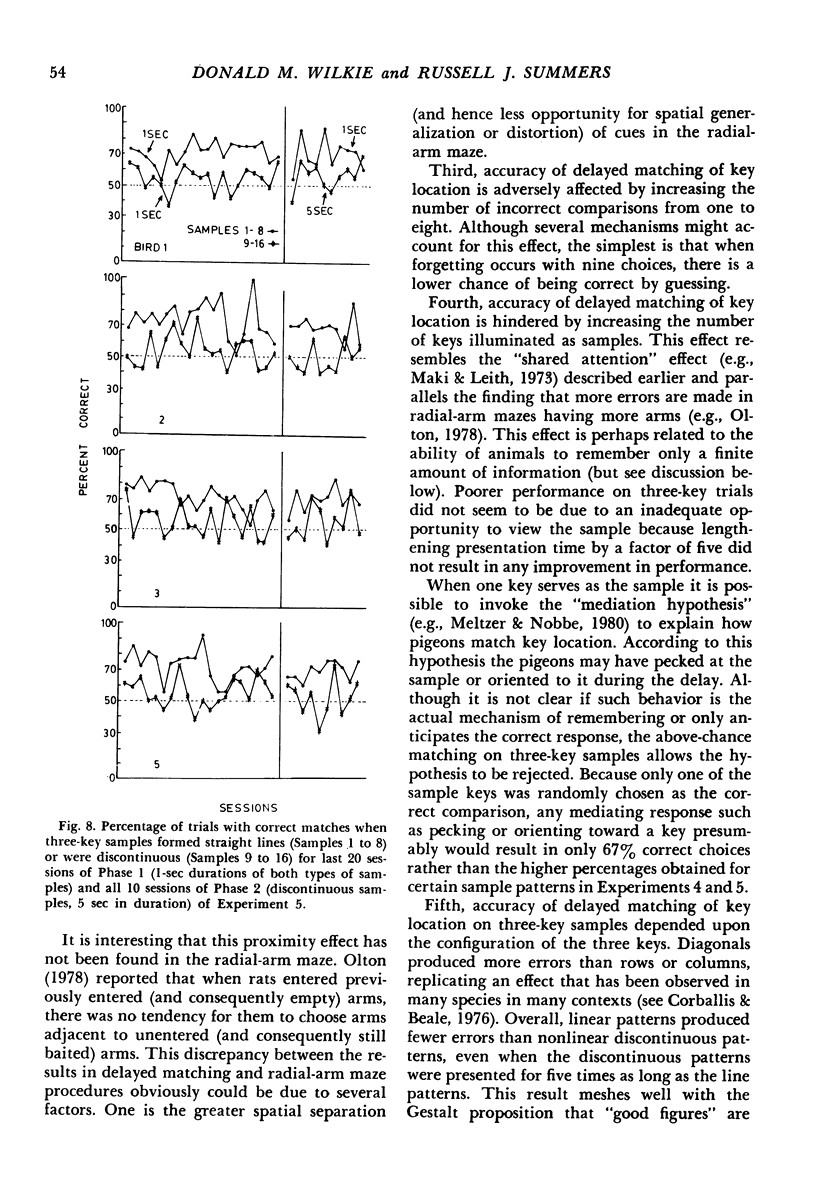
The delayed-matching-to-sample procedure was modified to study pigeons' spatial memory. Nine pecking keys, arranged as a three-by-three matrix, served as the spatial cues. Trials began with a brief "ready" stimulus (dimming of the houselight). Then a randomly chosen key was lit briefly as a sample. After a short delay the sample key was lit again along with one of the other eight keys. A peck at the key that had served as the sample produced grain reinforcement, where as a peck to the other key produced only the intertrial interval. After delayed matching of key location was learned, the effects of sample and delay duration, number of keys illuminated as sample and comparisons, and organization of three-key samples were studied. Matching accuracy decreased as sample duration decreased, delay increased, the number of locations serving as samples increased, the number and proximity of comparisons increased, and when the three-key samples were "discontinuous" rather than "lines".
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOUGH D. S. Delayed matching in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Apr;2:151–160. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. E., Eckerman D. A. Symbolic matching by pigeons: rate of learning complex discriminations predicted from simple discriminations. Science. 1975 Feb 21;187(4177):662–664. doi: 10.1126/science.1114318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medin D. L. Form perception and pattern reproduction by monkeys. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1969 Jul;68(3):412–419. doi: 10.1037/h0027519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


