Abstract
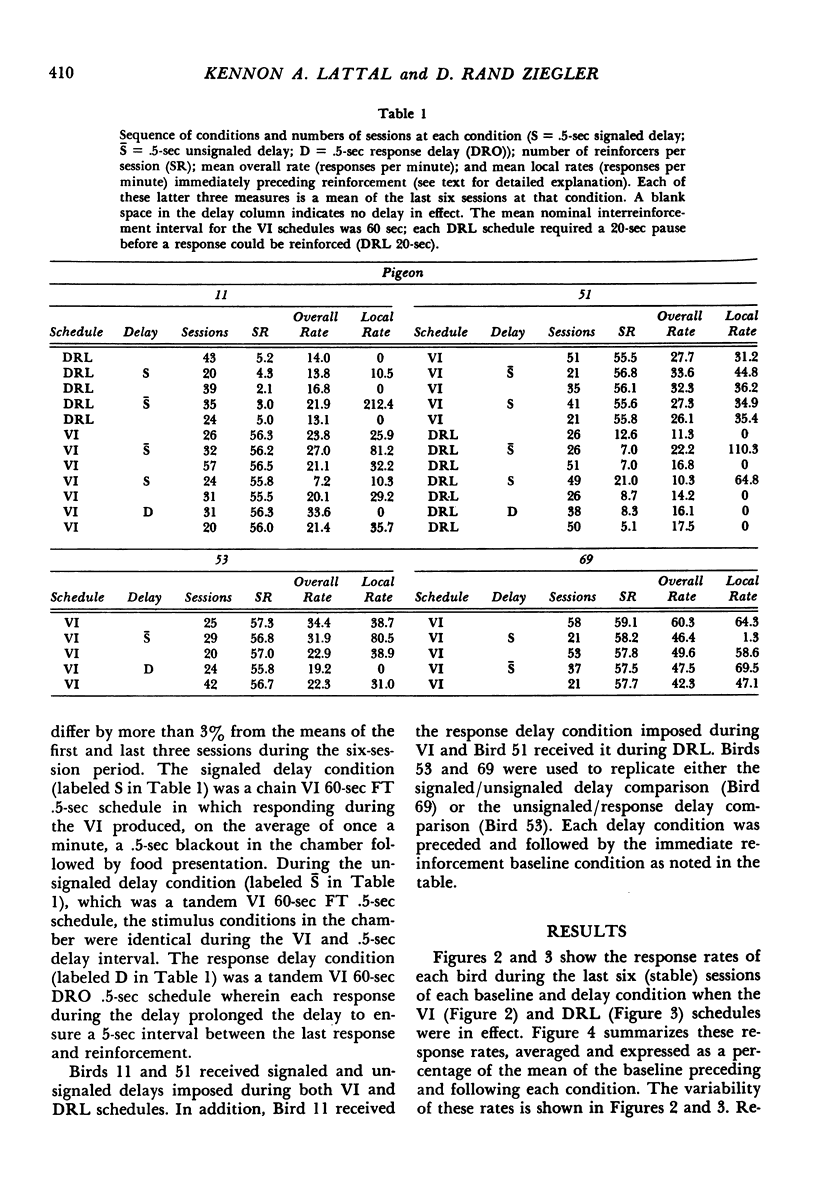
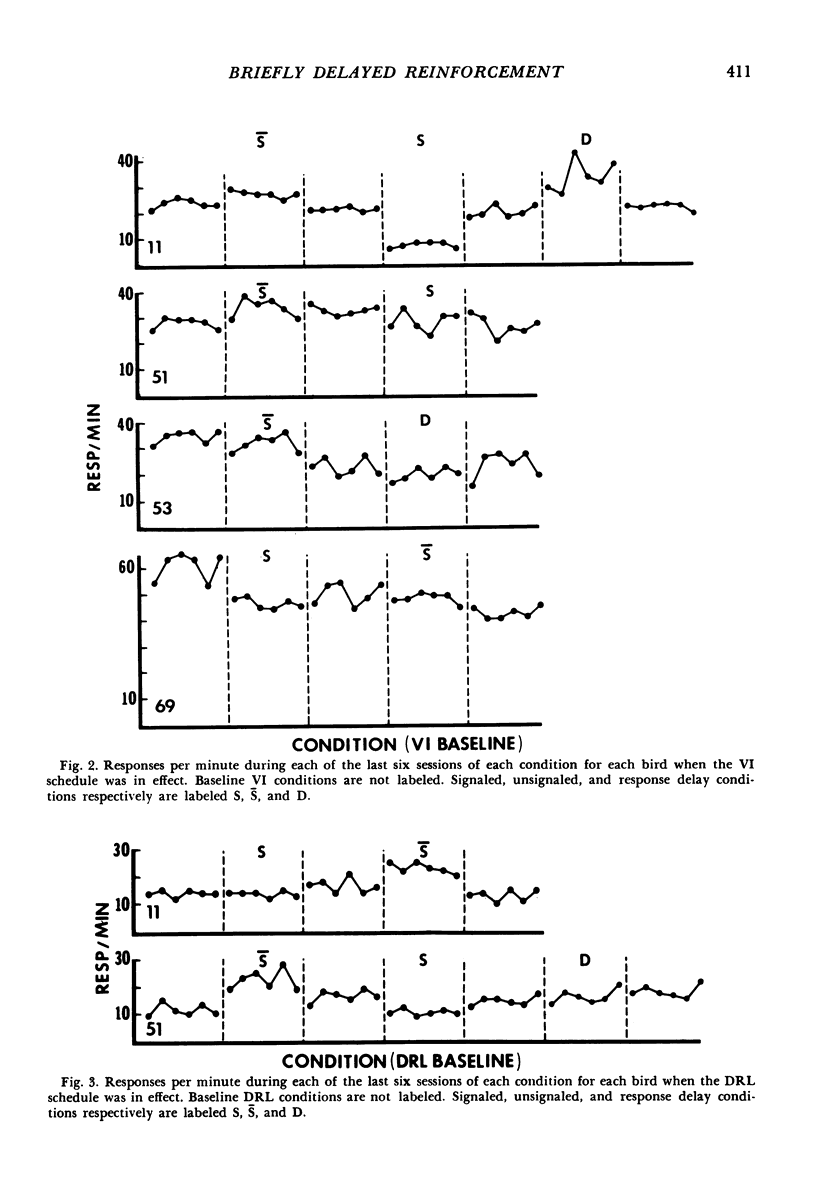
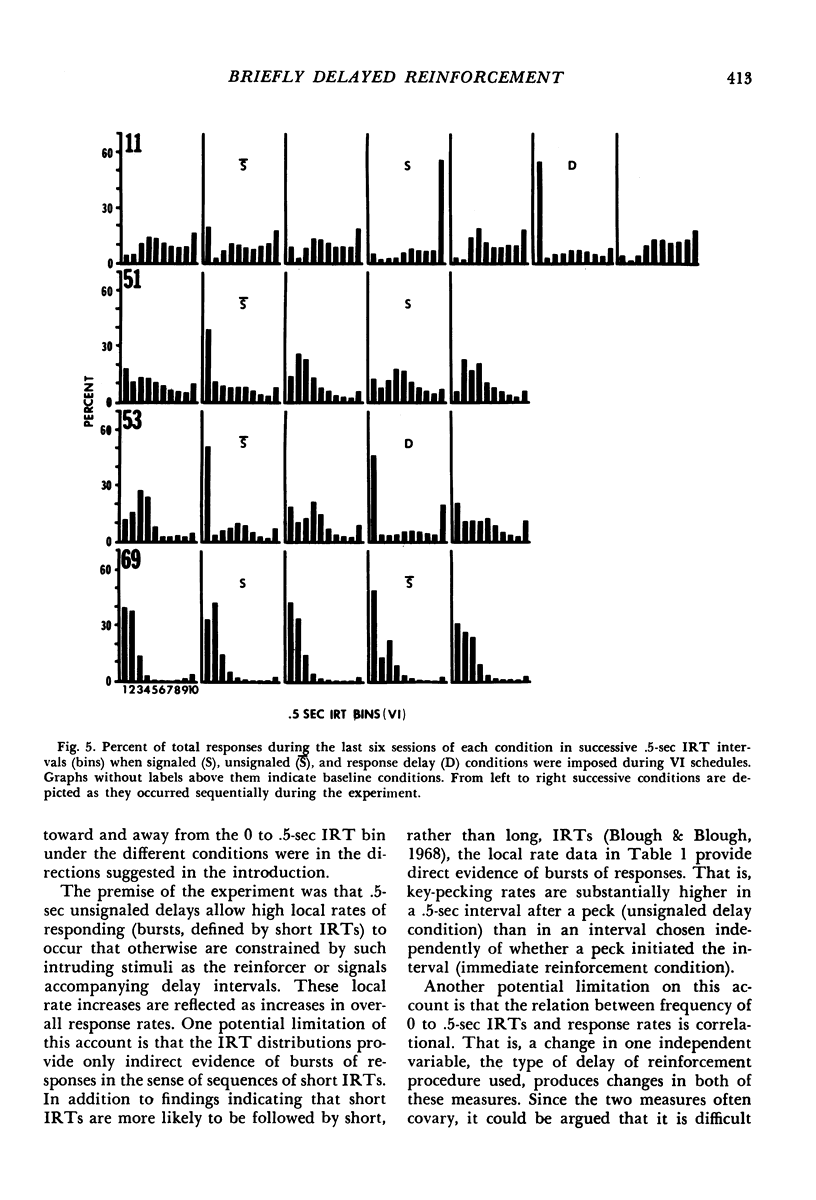
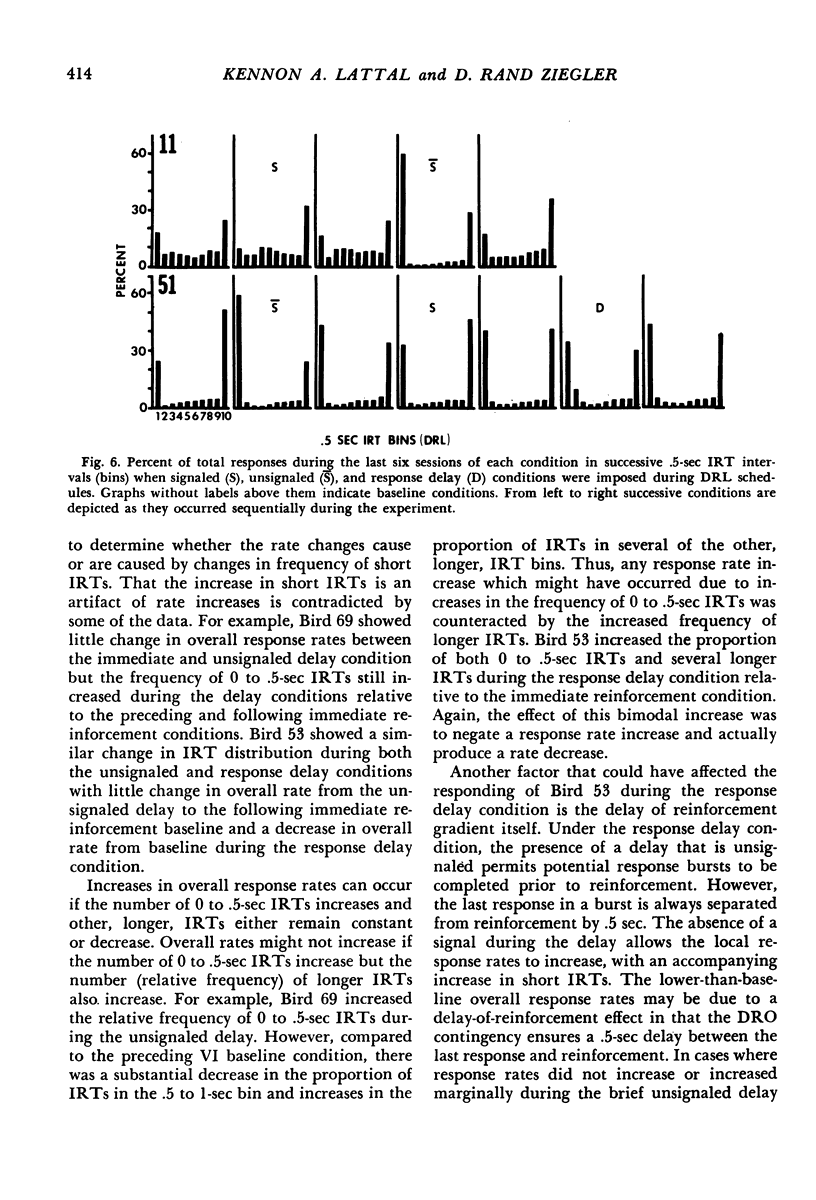
Key-peck responding of pigeons was compared under VI or DRL schedules arranging immediate reinforcement and briefly (.5 sec) delayed reinforcement. Delays were either signaled by a blackout in the chamber, unsignaled, or unsignaled with an additional requirement that responding not occur during the .5 sec interval immediately preceding reinforcement (response delay). Relative to the immediate reinforcement condition, response rates increased during the unsignaled delay, decreased during the signaled delay, and were inconsistent during the response delay condition. An analysis of interresponse times (IRTs) under the different conditions revealed a substantial increase in the frequency of short (0 to .5 sec) IRTs during the unsignaled condition and generally during the response delay conditions compared to that during the immediate reinforcement baseline. Signaled delays decreased the frequency of short (0 to .5 sec) IRTs relative to the immediate reinforcement condition. The results suggest that brief unsignaled delays and, in many instances, response delays increase the frequency of short IRTs by eliminating constraints on responding.
Keywords: signaled delay, unsignaled delay, response delay, DRL, VI, interresponse time, pigeons
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGER D. The dependence of interresponse times upon the relative reinforcement of different interresponse times. J Exp Psychol. 1956 Sep;52(3):145–161. doi: 10.1037/h0041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZZI R., FIX D. S., KELLER F. S., ROCHAESILVA M. I. EXTEROCEPTIVE CONTROL OF RESPONSE UNDER DELAYED REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Mar;7:159–162. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough P. M., Blough D. S. The distribution of interresponse times in the pigeon during variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jan;11(1):23–27. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C. Reinforcement schedules: the role of responses preceding the one that produces the reinforcer. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 May;15(3):271–287. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dews P. B. Studies on responding under fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement: the effects on the pattern of responding of changes in requirements at reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Mar;12(2):191–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERSTER C. B. Sustained behavior under delayed reinforcement. J Exp Psychol. 1953 Apr;45(4):218–224. doi: 10.1037/h0062158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Newlin R. J. Effects of a delay-reinforcement procedure on performance under IRT>t schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Sep;26(2):221–235. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. H., Hanford P. V., Zimmerman J. Effects of different delay of reinforcement procedures on variable-interval responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):141–146. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. W. A comparison of signaled and unsignaled delay of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Mar;35(2):145–152. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sizemore O. J., Lattal K. A. Unsignalled delay of reinforcement in variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Sep;30(2):169–175. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


