Abstract
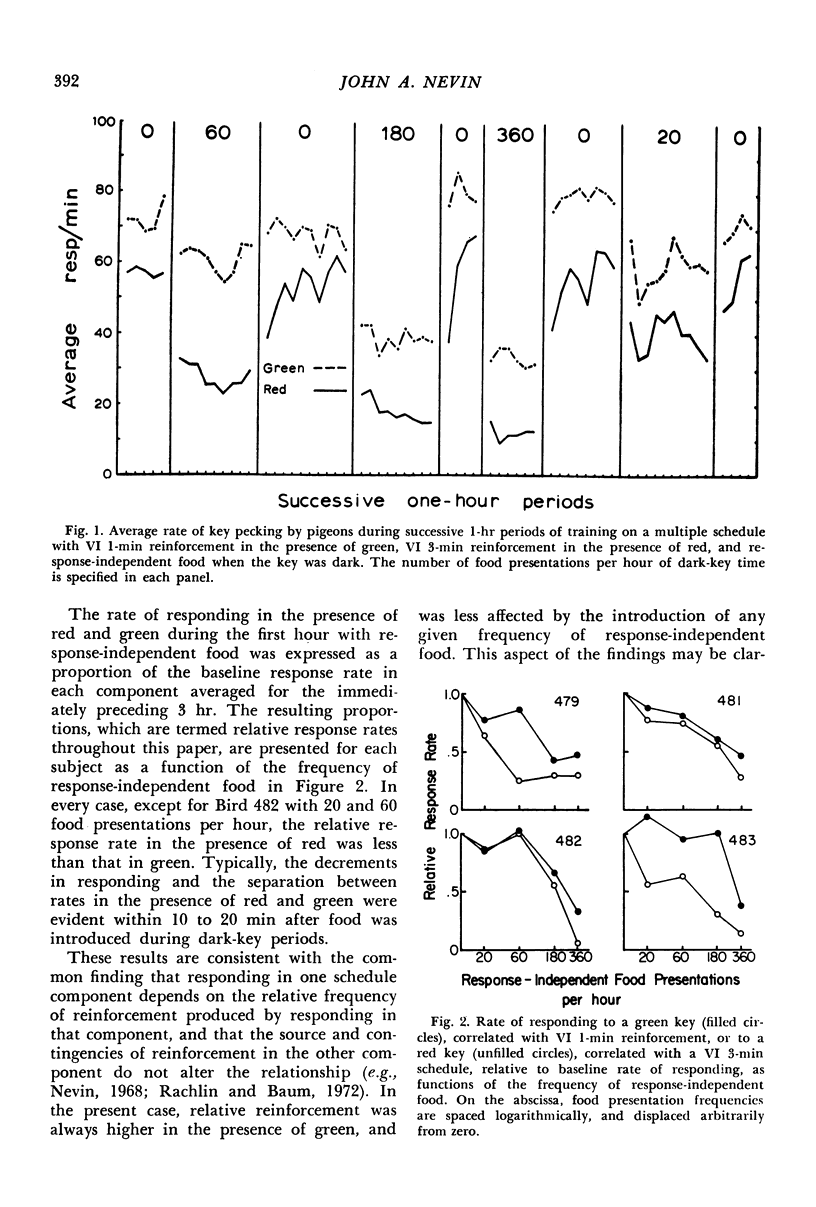
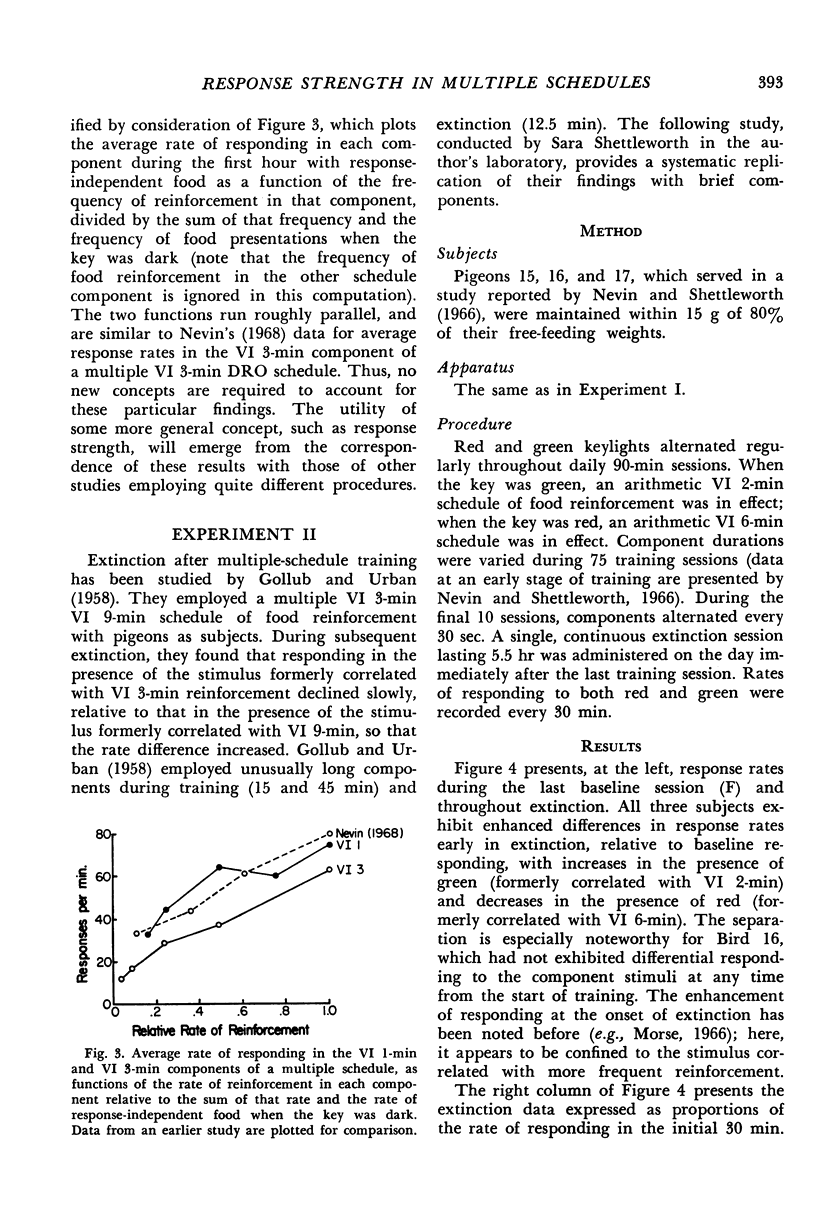
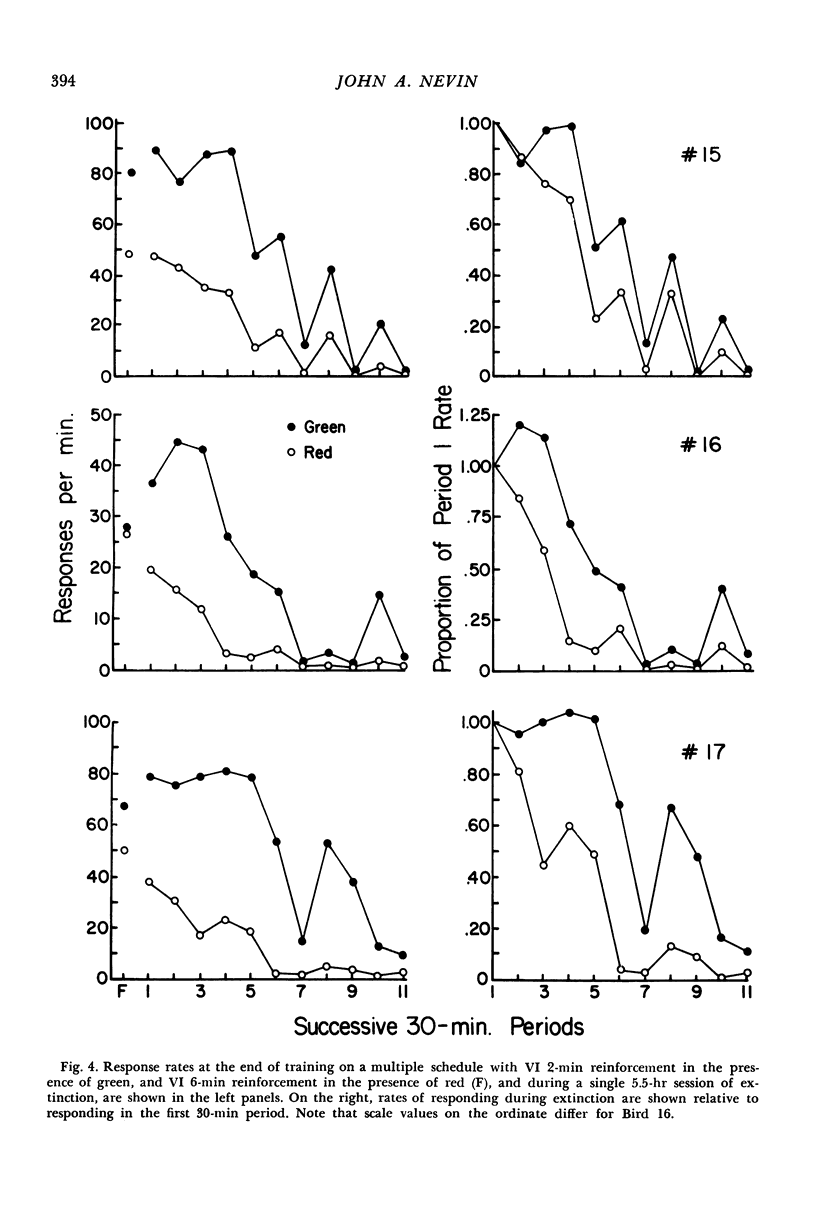
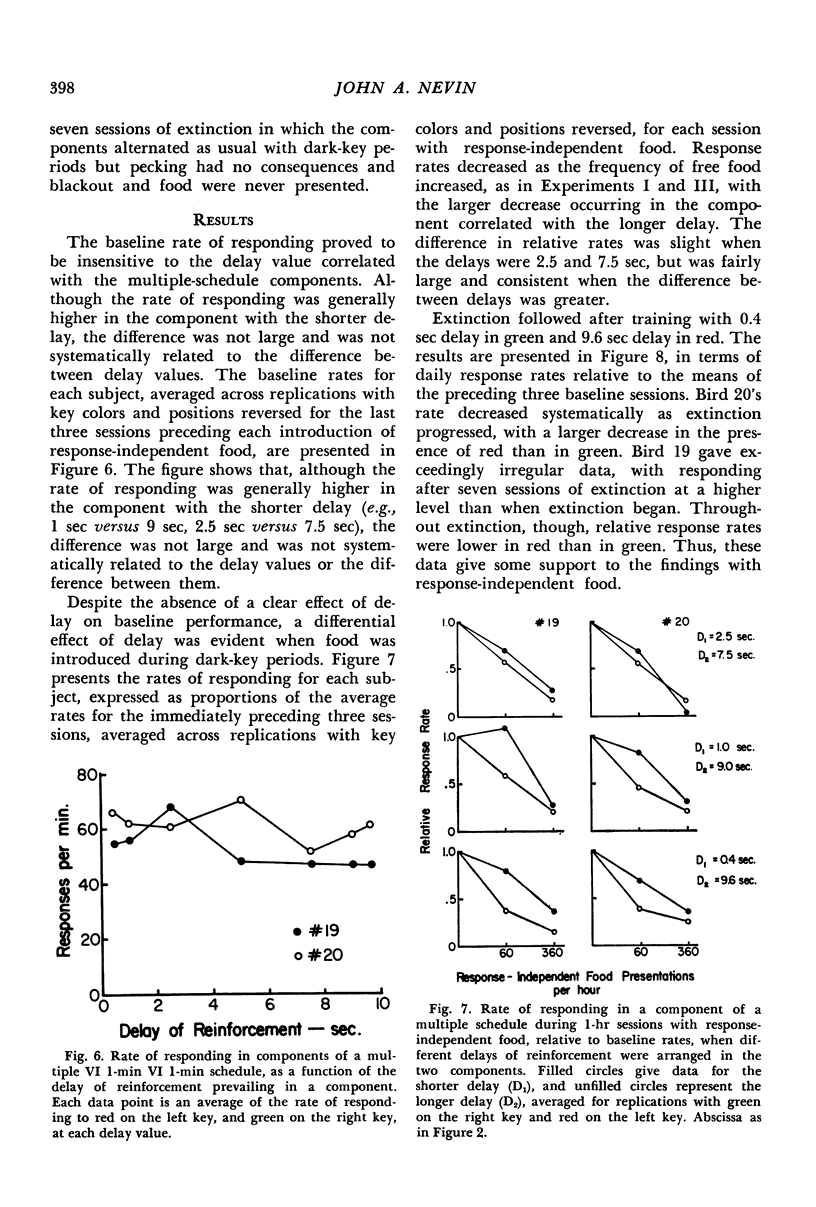
In several different experiments, pigeons were trained with one schedule or condition of food reinforcement for pecking in the presence of one key color, and a different schedule or condition in the presence of a second key color. After responding in both of these multiple schedule components stabilized, response-independent food was presented during dark-key periods between components, and the rates of pecking in both schedule components decreased. The decrease in responding relative to baseline depended on the frequency, magnitude, delay, or response-rate contingencies of reinforcement prevailing in that component. When reinforcement was terminated, decreases in responding relative to baseline rates were ordered in the same way as with response-independent food. The relations between component response rates were power functions. Internal consistencies in the data, in conjunction with parallel findings in the literature, suggest that the concept of response strength summarizes the effects of diverse procedures, where response strength is identified with relative resistance to change. The exponent of the power function relating response rates may provide the basis for scaling response strength.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackman D. Conditioned suppression or facilitation as a function of the behavioral baseline. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jan;11(1):53–61. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman D. Response rate, reinforcement frequency, and conditioned suppression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):503–516. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLTON P. L. The interacting effects of deprivation and reinforcement schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Oct;4:379–381. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: reinforcement interaction and response independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:253–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Silverman P. J., Stubbs D. A. Concurrent performances: stimulus-control gradients during schedules of signalled and unsignalled concurrent reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jan;21(1):99–107. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. H., Herrnstein R. J. Choice and delay of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):67–74. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer K., Fantino E. The dissociation of discriminative and conditioned reinforcing functions of stimuli with changes in deprivation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):703–710. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollub L. R., Urban J. T. The accentuation of a rate difference during extinction. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Oct;1(4):365–369. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARST E. Resistance-to-extinction functions in the single organism. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:133–144. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. SECONDARY REINFORCEMENT AND RATE OF PRIMARY REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearst E. Stimulus intensity dynamism and auditory generalization for approach and auditory generalization for approach and avoidance behavior in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1969 May;68(1):111–117. doi: 10.1037/h0027680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., GOLLUB L. R. A review of positive conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:543–597. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-s543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON D. O. Frequency of reinforcement as a parameter of conditioned suppression. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:95–98. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on choice and rate of responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):417–424. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. Differential reinforcement and stimulus control of not responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):715–726. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A., Shettleworth S. J. An analysis of contrast effects in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jul;9(4):305–315. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Some limitations on behavioral contrast and induction during successive discrimination. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:131–139. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H., Baum W. M. Effects of alternative reinforcement: does the source matter? J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Sep;18(2):231–241. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H., Baum W. M. Response rate as a function of amount of reinforcement for a signalled concurrent response. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jan;12(1):11–16. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. W. Reinforcement delay: some effects on behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 May;17(3):381–394. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHETTLEWORTH S., NEVIN J. A. RELATIVE RATE OF RESPONSE AND RELATIVE MAGNITUDE OF REINFORCEMENT IN MULTIPLE SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jul;8:199–202. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrace H. S. Behavioral contrast and the peak shift: effects of extended discrimination training. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Nov;9(6):613–617. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON M. P. Periodic reinforcement interval and number of periodic reinforcements as parameters of response strength. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1954 Feb;47(1):51–56. doi: 10.1037/h0057224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYCKOFF L. B. Toward a quantitative theory of secondary reinforcement. Psychol Rev. 1959 Jan;66(1):68–78. doi: 10.1037/h0046882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


