Abstract
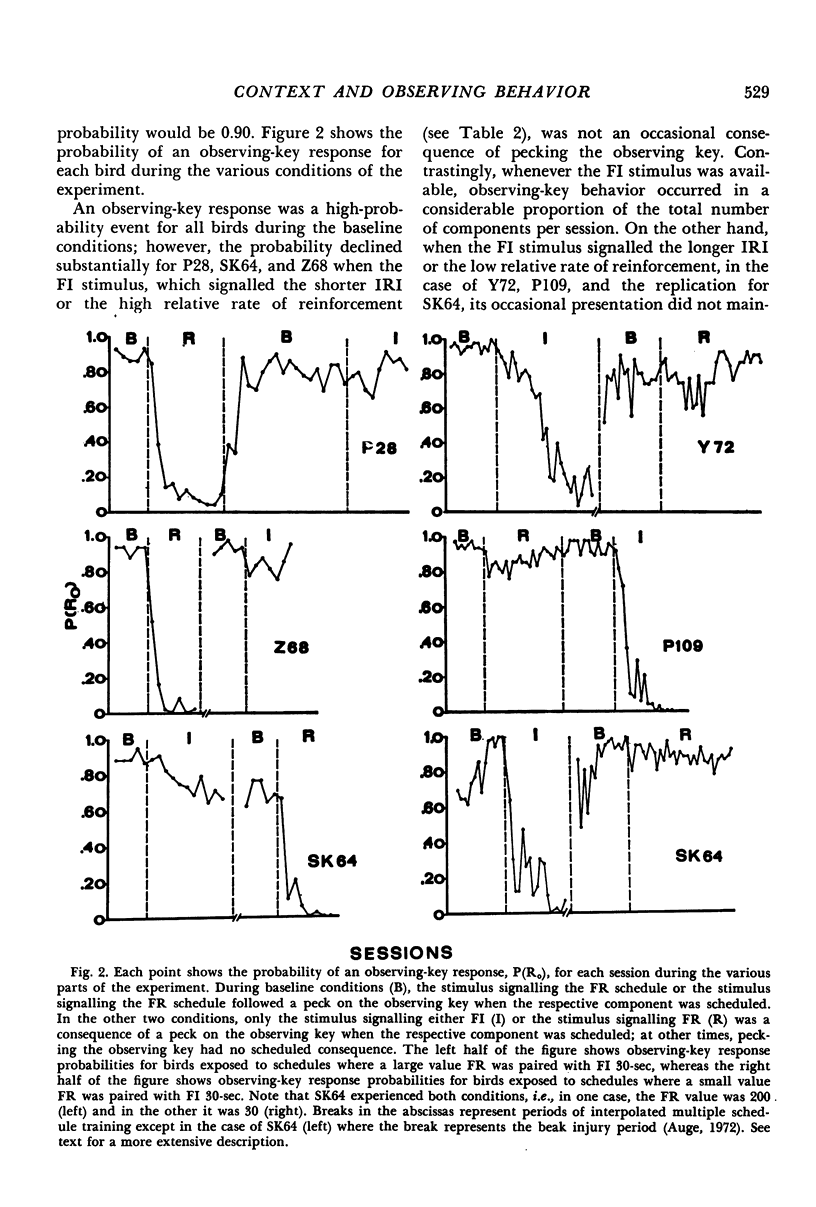
Pigeons made observing responses for stimuli signalling either a fixed-interval 30-sec schedule or a fixed-ratio x schedule, where x was either 20, 30, 100, 140, or 200 and the schedules alternated at random after reinforcement. If observing responses did not occur, food-producing responses occurred to a stimulus common to both reinforcement schedules. When the fixed-interval schedule was paired with a low-value fixed ratio, i.e., 20 or 30, the presentation of the stimulus reliably signalling the fixed-ratio schedule reinforced observing behavior, but the presentation of the stimulus reliably signalling the fixed-interval schedule did not. The converse was the case when the fixed-interval schedule was paired with a large-valued fixed ratio, i.e., 100, 140, or 200. The results demonstrated that the occasional presentation of the stimulus signalling the shorter interreinforcement interval was necessary for the maintenance of observing behavior. The reinforcement relationship was a function of the schedule context and was reversed by changing the context. Taken together, the results show that the establishment and measurement of conditioned reinforcement is dependent upon the context or environment in which stimuli reliably correlated with differential events occur.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auge R. J. Effects of stimulus duration on observing behavior maintained by differential reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):429–438. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M., Rachlin H. C. Choice as time allocation. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):861–874. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. The correlation-based law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jul;20(1):137–153. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan W. The contextual basis of behavior. Am Psychol. 1968 Oct;23(10):701–714. doi: 10.1037/h0026697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bower G., McLean J., Meacham J. Value of knowing when reinforcement is due. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1966 Oct;62(2):184–192. doi: 10.1037/h0023682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. L., Jenkins H. M. Auto-shaping of the pigeon's key-peck. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jan;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmoor J. A., Browne M. P., Lawrence C. E. A test of the negative discriminative stimulus as a reinforcer of observing. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):79–85. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins H. M., Boakes R. A. Observing stimulus sources that signal food or no food. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Sep;20(2):197–207. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., GOLLUB L. R. A review of positive conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:543–597. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-s543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall S. B. Effects of two procedures for varying information transmission on observing responses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jul;20(1):73–83. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall S. B. Some effects of response-dependent clock stimuli in a fixed-interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Mar;17(2):161–168. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvaney D. E., Dinsmoor J. A., Jwaideh A. R., Hughes L. H. Punishment of observing by the negative discriminative stimulus. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jan;21(1):37–44. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREMACK D. Reversibility of the reinforcement relation. Science. 1962 Apr 20;136(3512):255–257. doi: 10.1126/science.136.3512.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires N., Fantino E. A model for choice in simple concurrent and concurrent-chains schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jan;15(1):27–38. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A. Second-order schedules and the problem of conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):289–313. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYCKOFF L. B., Jr The role of observing responses in discrimination learning. Psychol Rev. 1952 Nov;59(6):431–442. doi: 10.1037/h0053932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton R. N., Clements R. O. Observing responses and informative stimuli. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Mar;15(2):199–204. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton R. N., Clements R. O. The role of information in the emission of observing responses: a test of two hypotheses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Sep;16(2):161–166. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


