Abstract
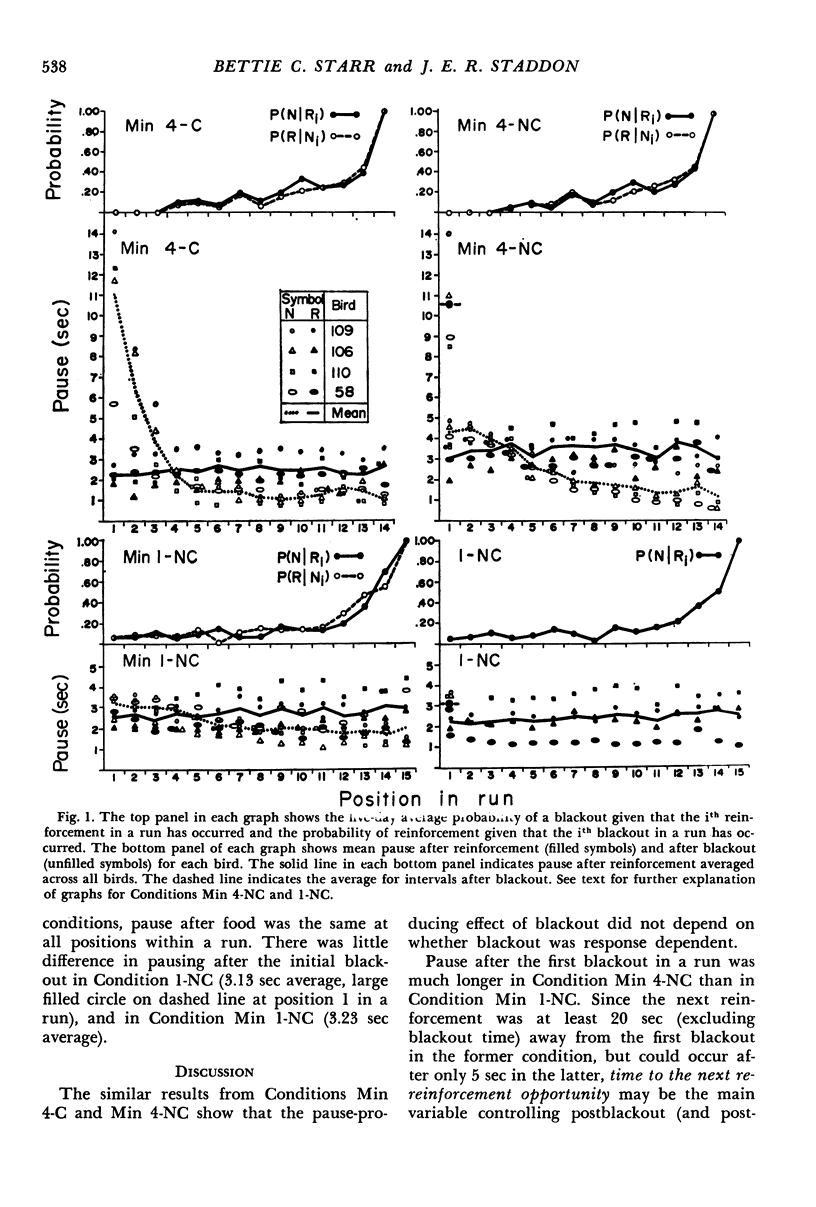
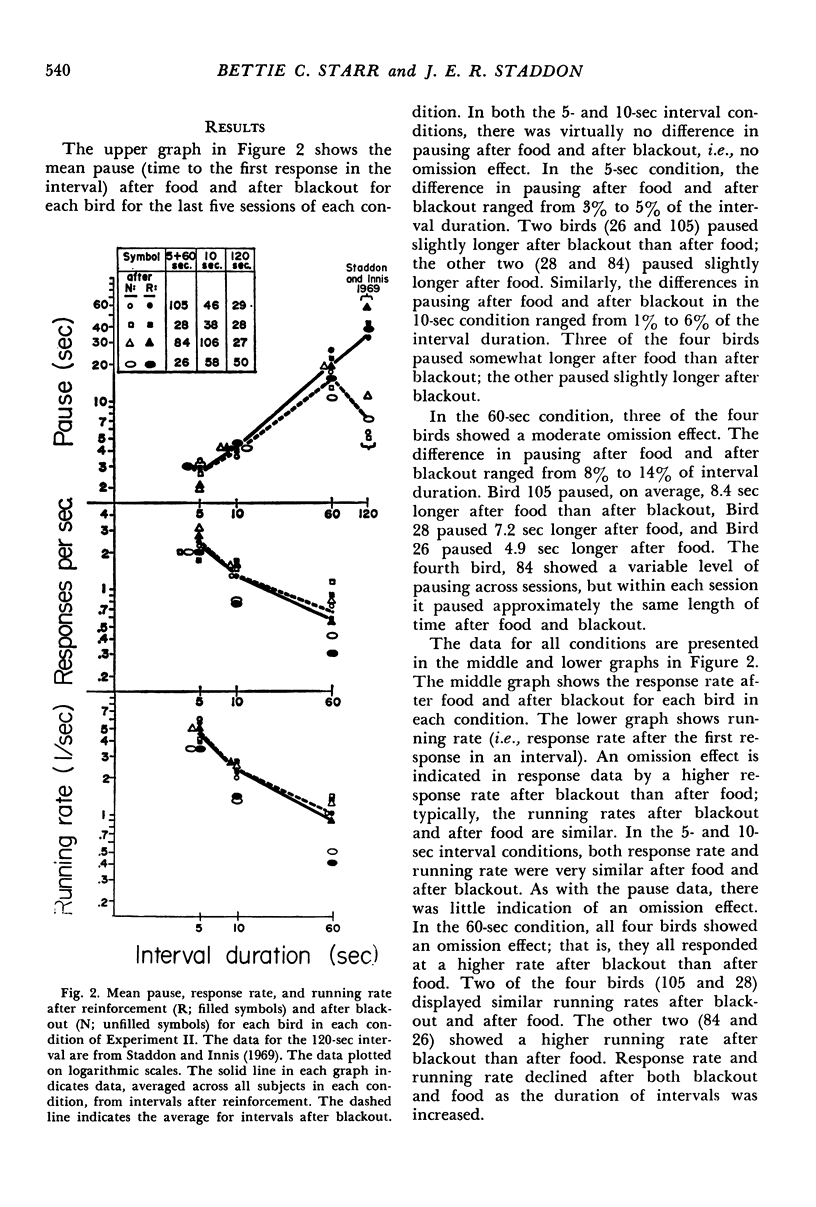
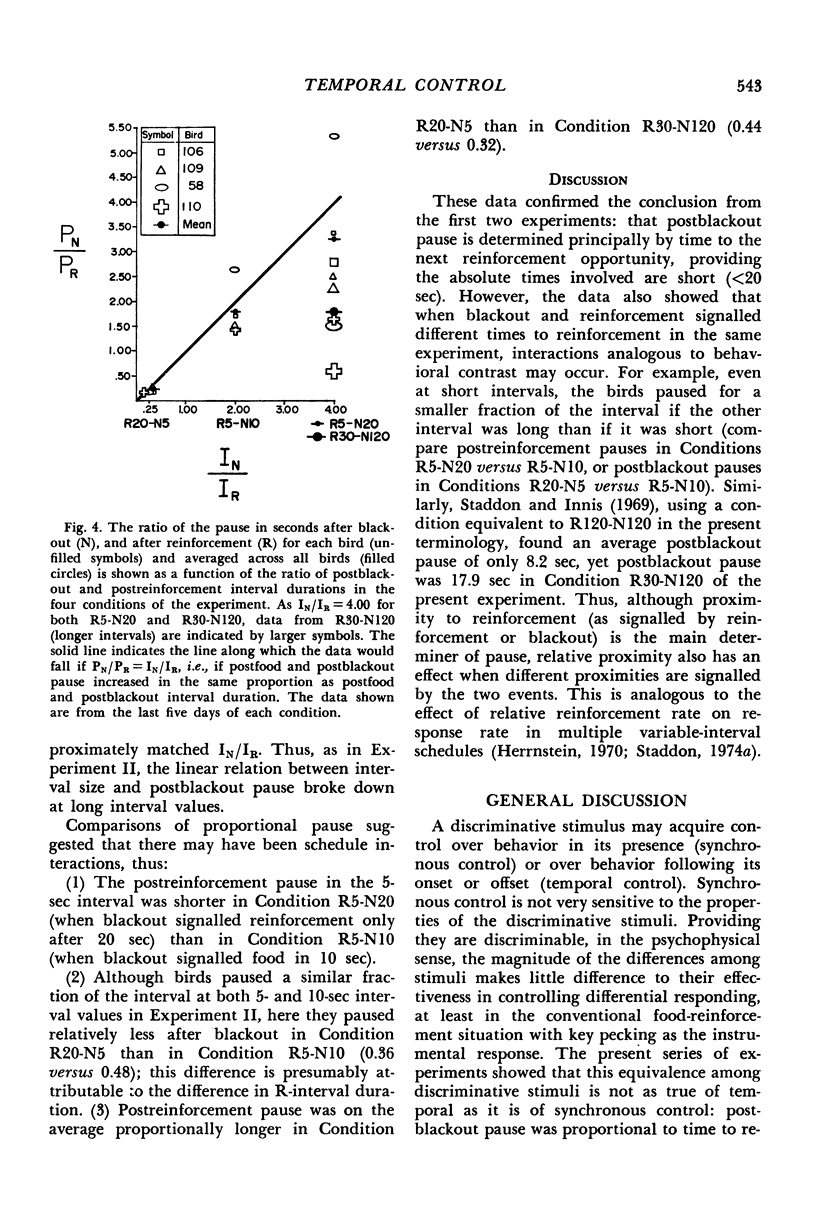
Pigeons were exposed to periodic food-reinforcement schedules in which intervals ended with equal probability in either reinforcement or brief blackout. The effects on the pattern of key pecking of sequential probability of reinforcement, interval duration, and time to reinforcement opportunity were investigated in three experiments. The major results were: (1) at short absolute interval durations, time to reinforcement opportunity determined both postreinforcement and postblackout pause (time to first key peck within an interval); (2) at long intervals, postblackout pause was consistently shorter than postreinforcement pause, even if both events signalled the same time to the next reinforcement opportunity (omission effect); (3) when reinforcement and blackout signalled different times to the next reinforcement opportunity, within the same experiment, there was some evidence for interactions analogous to behavioral contrast.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMSEL A., ROUSSEL J. Motivational properties of frustration. I. Effect on a running response of the addition of frustration to the motivational complex. J Exp Psychol. 1952 May;43(5):363–366. doi: 10.1037/h0059393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd L. D., Marr M. J. Relations between patterns of responding and the presentation of stimuli under second-order schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):713–722. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lorge J. Fixed-interval behavior maintained by conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 May;10(3):271–276. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lorge J. The effects of brief stimuli presented under a multiple schedule of second-order schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jan;15(1):19–25. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis N. K., Staddon J. E. Temporal tracking on cyclic-interval reinforcement schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):411–423. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr M. J., Zeiler M. D. Schedules of response-independent conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):433–444. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan J. C. Percentage reinforcement of fixed-ratio and variable-interval performances. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 May;15(3):297–302. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J., Chung S. H. Quasi-reinforcement: control of responding by a percentage-reinforcement schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):45–54. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. A. A two-state analysis of fixed-interval responding in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):677–687. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scull J., Davies K., Amsel A. Behavioral contrast and frustration effect in multiple and mixed fixed-interval schedules in ther rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1970 Jun;71(3):478–483. doi: 10.1037/h0029160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E., Innis N. K. Reinforcement omission on fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):689–700. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A., Cohen S. L. Second-order schedules: comparison of different procedures for scheduling paired and nonpaired brief stimuli. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Nov;18(3):403–413. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A. Second-order schedules and the problem of conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Nov;16(3):289–313. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler M. D. Fixed-interval behavior: effects of percentage reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Mar;17(2):177–189. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


